Personal Selling,
Sales Management, &
Chapter Objectives
• role of personal selling
within the promotion mix
• steps in personal selling process
• role of the sales manager
Personal Selling
• when a company representative
• interacts directly
• with a (prospective) customer
• to communicate
Personal Selling
• Personal touch” is more effective
than mass-media appeal.
• Selling/sales management • jobs provide high mobility,
especially for college grads
The Role of Personal Selling
• Personal selling is more important:
--when firm uses push strategy.
--in B2B contexts.
--with inexperienced consumers
• who need hands-on assistance.
Technology and Personal Selling
• Customer relationship management
(CRM) software
• partner relationship management
(PRM)
• Teleconferencing,
• Video-conferencing,
• Improved corporate Web sites
• Voice-over Internet protocol
Types
of Sales Jobs
• Order taker
• Technical specialist
• Missionary salesperson
(stimulate clients to buy)
• New-business salesperson
Cold calls, breaking in new territory
Approaches to Personal Selling
• Transactional selling: Putting on the hard sell
High-pressure process
focuses on immediate sales
no concern for developing long-term customer
Approaches to Personal Selling (cont’d)
• Relationship selling
Process of building long-term customers
by developing mutually satisfying,
Creative selling Process
• Makes positive transactions happen
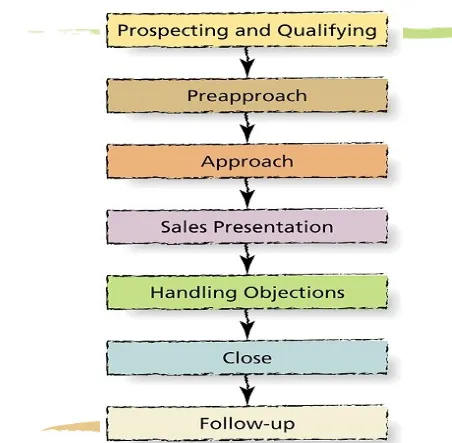
The Creative Selling Process
• Step 1: Prospecting and qualifying
--Prospecting:
• developing a list of potential customers
--Qualifying:
The Creative Selling Process (cont’d)
• Step 2: Pre-approach
Compiling prospective customers’
• background information
The Creative Selling Process (cont’d)
• Step 2: Pre-approach
Purchase history,
current needs,
customer’s interests
From
• informal sources, • CRM system,
• customers’ Web sites,
The Creative Selling Process (cont’d)
• Step 3: Approach
Contacting the prospect
Learning prospect’s needs, create a good impression, build rapport
The Creative Selling Process (cont’d)
•
Step 4:
Sales presentation
benefits & added value • of product/firm
advantages over competition
Step 5:
Handling
Objections
• Anticipating why
prospect is reluctant to make a commitment
• Welcoming objections
• Handling objections
successfully
Step 6:
Closing
the Sale
• Gaining the customer’s commitment
• in the decision stage
--Last-objection close --Assumptive close
--minor-points close
Step 7:
Follow-Up
•
Arranging for delivery,
Ensuring sure customer received delivery and is satisfied
•
Payment
Credit, factors, etc.
•
purchase terms
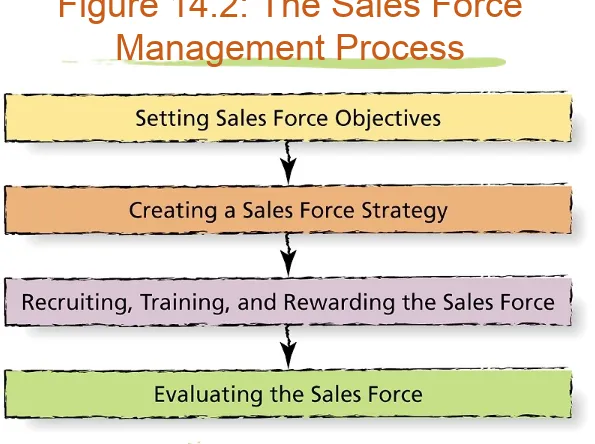
Sales Management:
Sales force objectives
• What sales force is expected to
accomplish and when
Customer Satisfaction
Loyalty
Retention / turnover
New customer
New product suggestions
Training
Reporting on competition
Creating a Sales Force
Strategy
• Establishing structure and size
of a firm’s sales force
• Sales territory: a set group of customers
Geographic sales force structure
Product-class sales territories
Recruiting
, Training, & Rewarding
• Recruiting
the right people
Good listening and follow-up skills
adaptive style
• from situation to situation Tenacity
Recruiting,
Training
, & Rewarding
•
Sales training
:• teaches salespeople about firm,
• its products,
• how to develop skills,
• knowledge, and
Recruiting, Training, and
Rewarding
• Paying
salespeople well to
motivate them
Straight commission plan
Recruiting, Training, and
Rewarding
• Running sales contests
for short-term sales boost
• Call reports:
Evaluating
the Sales Force
• Is sales force meeting its objectives? • What are possible causes of failure?
Measuring performance
Monitoring expense accounts
Direct Marketing
• Any
direct communication
to a consumer or business recipient
Direct Marketing
• Response:
• in the form of an
order,
request for further information, a visit to a store
• other place of business
• for purchase of a product
Direct Marketing: MAIL ORDER
• Catalogs:
collection of products • offered for sale
described in book form,
Direct Marketing: MAIL ORDER
• Direct mail:
brochure/pamphlet
Direct Marketing:
telemarketing
• conducted over the telephone
More profitable for business • than consumer markets
In 2003, FTC established:
Direct Marketing (cont’d)
• Direct-response advertising: • allows consumer to respond
• by contacting the provider
Direct Marketing (cont’d)
•
Direct-response TV (DRTV):
• short commercials,
• 30-minute+ infomercials, • home shopping networks
–HSN –QVC
Direct Marketing (cont’d)
• M-Commerce:
Direct Marketing (cont’d)
•
M-Commerce:
(SMS)
• Short-messaging system marketing
Spim:
• instant-messaging version of spam
Adware:
Marketing Plan Exercise
• In developing her marketing plan, Esther Ferre at IBM must use marketing communication mix elements (1) in an integrated way that (2) best invests her promotional dollars.
• --Should personal selling be a high priority in Esther’s marketing plan? Why or why not?
Marketing in Action Case:
You Make the Call
• What is the decision facing Eli Lilly? • What factors are important in
understanding this decision situation? • What are the alternatives?
• What decision(s) do you recommend? • What are some ways to implement your
Keeping It Real: Fast-Forward to Next
Class, Decision Time at Darden Restaurants
• Meet Jim Lawrence, Vice President, Supply Management & Purchasing.
• Volatility in the supply chain threatened food supplies to restaurants.
Real People, Real Choices
• IBM (Esther Ferre)
• IBM must prioritize investment of resources to achieve revenue and profit targets.
Option 1: reduce sales and support resources for a specific customer or business segment.
Option 2: maintain current level
of resources.
Option 3: evaluate lower-cost
ways to provide sales and
Real People, Real Choices
• IBM (Esther Ferre)
• Esther chose option 3: evaluate lower-cost ways to provide sales and support
resources.
Minimized impact to customer and improved cost structure of sales team.
Discussion
• Professional selling
has evolved from hard-sell to relationship
selling.
--Is hard-sell still used? If so, in what types of organizations? --Can hard-sell still succeed –is
transactional
Group Activity
• Your group are field
salespeople for a firm that markets university
textbooks.
Individual Activity
• What are the pros and cons of personal
selling as a career choice for you?
Discussion
• Will sales training and development needs
vary based on how long salespeople have been in the business? Why or why not?
• Is it possible (and feasible) to offer
different training programs for salespeople at different career stages? Why or why
Discussion
• Based on the compensation figures in the
chapter, do you think professional
salespeople are appropriately paid? Why or why not?
• What do salespeople do that warrants the
Discussion
• What is a sales manager’s best approach
for determining the appropriate rewards program?
• What issues are important in developing
Discussion
• Some experts think consumer catalog shopping has
increased because of poor service in retail stores.
Evaluate the quality of most retail salespeople you meet.
How can retailers can improve the quality of their sales associates?
Discussion
• M-commerce allows marketers to pinpoint
where consumers are and send them messages about a local store.
--Do you think consumers will respond positively to m-commerce?