THE QUALITY OF ENGLISH LANGUAGE TESTING
IMPLEMENTED IN KBRI SCHOOL, SEKOLAH INDONESIA
KUALA LUMPUR, MALAYSIA
THESIS
Submitted in Partial Fulfilment of The Requirement for The Degree of Sarjana Pendidikan (S.Pd) in English Teaching
By
NUR KHOLILAH
D35209027
ENGLISH TEACHER EDUCATION DEPARTEMENT
FACULTY OF EDUCATION AND TEACHER TRAINING
STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY SUNAN AMPEL
SURABAYA
ABSTRACT
Kholilah, Nur (2015) The Quality of English Language Testing Implemented in KBRI School, Sekolah Indonesia Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia A thesis English Education Department Faculty of Tarbiyah and Teacher’s training State Islamic University of Sunan Ampel Surabaya.
ix
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Cover Page
Title Page ... i
Approval Sheet ... ii
Examiners Approval Sheet... iii
Dedication Sheet ... iv
Motto ... v
Abstract... vi
Acknowledgement ... vii
Table of Contents ... ix
List of Table ... xii
List of Appendices ... xiii
CHAPTER I: INTRODUCTION A. Background of The Study... 1
B. Statements of The Problem ... 8
C. Objective of The Study... 9
D. Significance of The Study ... 9
E. Scope and Limit of The Study... 9
x
CHAPTER II: REVIEW OF THE RELATED LITERATURE
A. Testing ... 11
1. Definition of Test... 11
2. Testing and Teaching... 12
3. The Effects of Testing on Teaching and Learning ... 13
4. Focus on Assesment, not on Test ... 13
5. Standards in Testing ... 15
6. The Purpose of Test... ... 16
B. Types and Kind of The Test ... 18
1. Types of The Test... .... 18
2. Kind of The Test... . 20
C. Form the Test... 22
D. Characteristic of A Good Test... 27
E. Previous study ... 36
CHAPTER III: RESEARCH METHODOLOGY A. Research Design ... 38
B. Research Subject... 40
C. Setting of the Study ... 40
D. Data Collection Technique & Instruments ... 41
E. Data Analysis Procedure ... 41
CHAPTER IV: RESEARCH FINDING AND DISCUSSION A. Descrition of English Test ... 50
B. The Result of the Final Test ... 51
C. Research Finding ... 53
xi
CHAPTER V: CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION
A. Conclusion ... 68 B. Suggestion ... 69
Bibliography
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
A. Background of Study
English learning aimed in junior high school is oriented to reach functional level. It means that the students should be able to communicate oral and written in their daily life activity. While, English learning in senior high school is expected to reach informational level, because they have been prepared to continue their study in university.1So, English subject in senior high school is important subject for students have been prepared for their study in university afterward. Senior high school students expected to master English subject well before they going to university.
Testing is revealing a person’s capabilities by putting them under strain; challenging.2In learning process testing is important point to know and measure the students’ skills in a subject. Testing has assumed a prominent role in recent effort to improve the quality in education. Viewing standardized tests as a significant, positive and cost-effective reform tool, educational
1
Depdiknas, Standard Kompetensi Mata Pelajaran Bahasa Inggris SMP dan Madrasah Tsanawiyah, (Depdiknas: Jakarta, 2004) page 3
2
2
policymaker has been using them at an increasing rate.3
Test is used to provide information concerning not only with the individual students performance, but also with the effectiveness of teaching learning activities. And test is one type of measurement is used to measure student's behavior goal of instructions. For teachers, a test is used to measure the effectiveness of teaching learning activities.4
Language teachers are often faced with the responsibility of selecting or developing language tests for their classrooms and programs. However, deciding which testing alternatives are the most appropriate for a particular language education context can be daunting, especially given the increasing variety of instruments, procedures, and practices available for language testing. Such alternatives include not only test types with long traditions of use—such as multiple choice, matching, true-false, and fill-in-the-blank tests; cloze and dictation procedures; essay exams; and oral interviews—but also tests differing in scope and structure from these well-known options. For ex-ample, technological developments have led to a number of new language testing formats, including computer-based and computer-adaptive tests (Brown 1997; Dunkel 1999; Yao and Ning 1998), audiotape-based oral
3
Joan Herman, Jean Dreyfus and Sharin Golan, The Effect of Testing on Teaching Learning, (UCLA C enter of Research on Evaluation, Standards, And Student Testing, 1990). Pg 1
4
3
proficiency interviews (Norris 1997; Stansfield and Kenyon 1992), and web-based testing (Roever 1998).5
In teaching learning activities, testing has an important role. The results of teaching without testing will be useless, because testing helps to show the achievement of the objectives of education. From the result of the test it can be seen whether the teaching learning process is successful or not. Both testing and teaching are so closely interrelated that it is virtually impossible to work in either field without being constantly concerned with other.6 It was cleared that relation between testing and teaching can’t be ignored. Teachers, students, and school want to know their effort to achieve the educational objectives are successfull or not. They will be satisfied if their effort are succeccfull. But if heir effort unsuccessful so they will change their ways.7
According to Norris,
“Language tests are simply instruments or procedures for gathering particular kinds of information, typically information having to do with students’ language abilities. Tests may have a variety of formats, lengths, item types, scoring criteria, and media. We may differentiate among language test types according to such characteristics and the information provided by each. For example, a 20-item cloze test, which asks the examinee to write single-word responses to complete a reading passage, provides a very different kind of information than does a 20-item multiple choices reading comprehension
5
John M Norris”Purposeful Language Assesment: Selecting The right Alternative Test”. Vol 38, No 2, 2000
6
J.B. Heaton, Writing English Language Test, (New York: Longman),1988. Pg 5
7
4
test, in which the examinee has only to choose the correct responses.”8
Chittenden said that the purpose of testing are “keeping track, checking-up, finding-out, and summing up”. Keeping track is collecting the data about student progress in learning process in the school. Checking-up is checking the students’ skill in learning process and to know weakness of the student in learning process. Finding-out is searching, finding, and detecting the weakness and mistakes from the students in learning process. Summing up
is concluding the students’ learning progress which appropriate with standard competency in that school.9
Thus, as one tool of evaluation test is needed to be employed in teaching activities. Moreover it has lot of benefits in order to support the success of teaching learning process, such as: (1) To measure language proficiency. (2) To diagnose student’s strengths and weakness, to identify what they know and what they do not know. (3) To discover how successful student have been in achieving the objectives a course of study. (4) To assist placement of student by identifying the stage or part of a teaching program most appropriate to their ability10
From the achievements term, English test divided by; final
8
John M. Norris, Purposeful Language Assessment: Selecting the Right Alternative Test, Vol 38, No. 1 2000, pg 1
9
Drs. Zainal Arifin,M.Pd, Evaluasi Pembelajaran, (Bandung: PT Remaja Rosdakarya), 2012. Pg 15
10
5
achievement test and progress achievement.11 In this research, the researcher focuses on final achievement test.
Final achievement test is the test that is held at the end of the class. Final exam decides whether the students can go up to the next grade or not. For the teacher, final exam is the complete test that must be built. The teacher must combine all skills and measure all skills in one test. Testing has a technique how to make and do a test. In creating testing, the teacher must understand every technique that must be used in construct the testing to the students for example in testing writing, the teacher must give the test that represent writing skill of the student like write the essay, narrative, etc. English subject also has many skills that must be evaluated.
Regarding to the case above, it is very important to have tests or some kind another, are valid, well designed and formulated. Hughes mentioned in his book that test is said to be valid if it is measure accurately what it should be measured. Nurkanca and Sumartana also pointed out that a qualified test should be reliable, valid and having degrees of difficulty-index and discriminating power.12
Language testers are sometimes asked to say what is ‘the best tests’ or ‘the best testing technique’. Such question reveals a misunderstanding of what
11
Arthur hughes, Testing for Language Teachers. Pg 13
12
6
is involved in the practice of language testing. A test that proves ideal for one purpose maybe quite useless for another; a technique that may work very well in one situation can entirely inappropriate in another. Equally, two teaching institutions may require different test, depending on objectives of their courses, the purpose of the tests, and the resources available.13 From that point, the teacher must recognize which test that is appropriate to measure the student skills. The teacher must create the test that is suitable with the student ability too.
The following standards, English as used by native speakers and English as used by L2 students, are built of a large number of components, including (but not limited to) the following: 1).Vocabulary - number and quality of items known; ability to use items correctly and appropriately. 2). Grammar - knowledge of morphology and syntax; ability to apply knowledge correctly and appropriately. 3). Oral production - the ability to create utterances comprehensible to native speakers. 4). Listening comprehension -the ability to comprehend utterances produced by native speakers. 5).Written production - the ability to manipulate symbols (letters, characters) and produce language structures comprehensible in a visual context, and to express feelings, concepts and ideas in writing. 6). Reading comprehension -the ability to comprehend language symbols and structures in a visual or
13
7
tactile context, and to understand feelings, concepts, and ideas expressed in writing14
In this research, the researcher will focus on language testing technique that other the teachers do in schools. The researcher wants to identify how the teacher built the test to the students: what technique that is used by the teachers and how the test can measure the skills of the students and whether the test is suitable with the students or not.
Indonesia has embassy in every country that have relation with Indonesia that called by Embassy of The Republic Indonesia or KBRI
(Kedutaan Besar Republik Indonesia). KBRI build school in those countries like Singapore, Malaysia, Thailand etc. which still under KBRI control. One of the examples is Sekolah Indonesia Kuala Lumpur.
Sekolah Indonesia Kuala Lumpur is KBRI’s School that is located in Lorong (street) Tun Ismail no.1 50480 Kuala Lumpur Malaysia. Sekolah Indonesia Kuala Lumpur is under control supervision of Indonesians’ embassy, it means that the curriculum and the rules of the school are based on Indonesian curriculum.
Like Indonesian school, Sekolah Indonesia Kuala Lumpurs’ curriculum is based on Education National Standard or BSNP (Badan Standar
14
8
Nasional Pendidikan) in Indonesia. From the method term, the teacher use CTL (Contextual Teaching Learning) in English subject. This method aims to help the student to know and use the language in a real situation of the target language. For the textbook of English subject in Senior High School, the teacher uses Indonesian books from Dinas Pendidikan Indonesia or
Indonesian Education Agency and Singaporean books. From the method CTL that they use, means they use KTSP or School Based Curriculum. From the competency standards of this school is Standar Kompetensi 2006 as same as in Indonesia. 15
The reason of the researcher to do this research is, the researcher wants to identify the validity of the test in that school. Also are the culture of Malaysia influenced the teacher on the way they teach the subject and build the test of the students?. From those points above, the researcher wants to know how the teachers do a testing for the student in that school and what technique that the teacher use to do a test.
B. Statement of Research Problem
This study will try to find out the answers to the following questions:
1. How the quality of English Language testing in KBRI school, Sekolah Indonesia Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia?
15
9
C. Objective of The Study
Based on the statements of the problem above, the objective of the study is describe:
1. Explain the quality of English language testing that be used by the teacher in Sekolah Indonesia Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
D. Significance of the Study
This study is conducted and hopefully the result would give some advantages as follow:
1. New English teacher to know the technique of language testing 2. For the students to know their skill from the test that they do
3. Serving as reference for the reader about language testing technique
E. Scope and Limitation
10
F. Definition of Key Terms
The researcher wrote down the definition of key terms to support the readers understanding this study easily and have same interpretation:
1. Language Testing technique is the technique that be used by the teacher to know the student skill with giving assessment to the student.
2. Quality of test is the aspect which can determine the test acceptable or not. The aspect of the quality of test are;
a. Validity of test, the test is valid if the test can measure accurate the student progress, skill and ability of the subject.
b. Item analysis is identifying the items of test which is acceptable or not to measure students’ skill. Item analysis divided into three points, there are;
Index difficulty, the test is good if the items test not too easy and not too difficult for the students
Index discrimination, is indicates which items discriminate the students
The distracters, the test is good if the objection item work properly to the students.
CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
This chapter explains some literature which is related to the questions of this research. This literature will focus on: theoretical foundation and previous and review study.
A. Testing
1. Definition of Test
Test is set techniques, procedures, and items that constitute an instrument of some sort that require performance or activity on the part of the test taker (and sometimes on the part of the tester as well).1Test is procedures designed to elicit certain behavior from which one can make inferences about certain characteristics of an individual.2
In line of that, test as quoted from Webster’s Collegiate by Daryanto, is any series of questions or exercise or other means of measuring the skill, knowledge, intelligence, capacities of aptitudes or an individual or group.3
1
Brown, H. Douglas, Teaching by Principles: An Interactive Approach to Language Pedagogy, Second Edition.(San Francisco: Longman Inc.) 2001. Pg 334
2
Bachman, Lyle F. Fundamental Considerations in Language Testing. (USA: Oxford University Press) 1990. Pg20
3
12
In the other word, Kubizyn and Borich stated in their book, that test is just as tools that can contribute importantly to the process of evaluating pupils, the curriculum, and the teaching method.4
2. Testing and Teaching
The effect of testing on teaching learning is known as backwash, and can be harmful or beneficial. If a test is regarded as important, if the stakes are high, preparation for it can come to dominate all teaching and learning activities. And if the test content and testing techniques are at variance with the objective of the course, there is likely to be harmful backwash. An instance of this would be where students are following an English course that is meant to train them in language skills (including writing) necessary for university study in an English speaking country, but where the language test that they have to take in order to be admitted to a university does not test those skills directly. If the skill of the writing, for the example, is tested by multiple choice items, then there is great pressure to practice such items rather that practice the skills of writing itself. This is clearly undesirable.5
4
Tom Kubiszyn and Gary Borich, Educational Testing and Measurement(Singapore, John Wiley & Sons, INC, 2003), Pg 1
5
13
3. The Effects of Testing on Teaching and Learning
Testing has assumed a prominent role in recent efforts to improve the quality of education. Viewing standardized tests as a significant, positive and cost-effective reform tool, educational policymaker has been using them at an increasing rate. The testing process now costs hundreds of millions of dollars and thousands of hours of administrative, teacher and student time.
The reasons for the increased use of testing are many. Following advice from testing advocates, policymakers believe that testing sets meaningful standards to which school systems, schools, teachers, and students can aspire; that test data can help shape instruction; that is serves important accountability purposes; and that coupled with effective incentives or sanctions, testing is powerful engine of change. As an evidence of the matter, proponents point with pride to rising test scores.6
4. Focus on assessment, not on tests
But deciding which of these test types is better or more appropriate is not easy. Knowing that each uses a unique format to provide different kinds of information does not bring us much closer to selecting one or the other alter-native. Indeed, attempting to select the most appropriate among available testing alternatives on the basis of their characteristics alone would be like
6
14
trying to choose between a hammer, a shovel, or a screwdriver based entirely on what these tools look like. Obviously, to select the appropriate tool, we first need to have an idea about the job to be accomplished. Alone, language tests tell us little about the jobs to be accomplished in language programs and classrooms. We cannot distinguish between good or bad, appropriate or inappropriate, reliable or not reliable, valid or not valid tests based solely on characteristics of the test instruments and procedures. Rather, we must focus instead on language assessment.
Language assessment is the process of using language tests to accomplish particular jobs in language classrooms and programs. In language assessment, we first gather information in a systematic way with the help of language testing tools. For example, we may use an oral interview to gather information about students’ speaking abilities, then make interpretations based on that information. Or, we may make interpretations about students’ abilities to perform a range of real-world speaking tasks based on how well students perform in the oral interview. Finally, based on these interpretations, we make a decision or take action within the classroom or program. We may decide that our students need more work on oral fluency and that we should therefore devote more class time to fluency-oriented activities.7
7
15
5. Standards in testing
One area of increasing concern in language testing has been that of standards. The word 'standards' has various meanings in the literature, as the Task Force on Language Testing Standards set up by ILTA discovered One common meaning used by respondents to the ILTA survey was that of procedures for ensuring quality, standards to be upheld or adhered to, as in codes of practice. A second meaning was that of levels of proficiency - what standard have you reached?. A related, third meaning was that contained in the phrase 'standardized test', which typically means a test whose difficulty level is known, which has been adequately piloted and analyzed, the results of which can be compared with those of a worming population: standardized tests are typically norm referenced tests. In the latter context 'standards' is equivalent to 'norms'.
16
the early 1990s) practice was wanting. Practice and procedures among boards varied greatly, yet (unpublished) information was available which could have attested to the quality of examinations. Exam boards appeared not to feel obliged to follow or indeed to understand accepted procedures, nor did they appear to be accountable to the public for the quality of the tests they produced. Fulcher and Bamford (1996) argue that testing bodies in the USA conduct and report reliability and validity studies partly because of a legal requirement to ensure that all tests meet technical standards. They conclude that British examination boards should be subject to similar pressures of litigation on the grounds that their tests are unreliable, invalid or biased. In the German context, Kieweg (1999) makes a plea for common standards in examining EFL, claiming that within schools there is litde or no discussion of appropriate methods of testing or of procedures for ensuring the quality of language tests.8
6. The purpose of test
Test is used to measure students’ mastering with the subject given9. Some experts mention the other purpose of test. According to Nurkanca and Sumartana, a test has many purposes. First, is to know how far the result of a programmer applied whether it has reached its goal or not. Second, is to see
8
J Charles Alderson and Jayanti Banerjee, Language testing and assessment (Part I),(United Kingdom: Cambridge University), 2001. Pg 218-219
9
17
whether the materials should be re-taught or not. Third, is to get some information about the students’ weakness and difficulties in learning about the given materials. Fourth, is to determine the students’ achievement and to allow them going through to the grade. Fifth, is to select and group students based on their achievement.
David conducted six objectives of language testing:10 1. To determine readiness for instructional programs.
2. To classify or place individuals in appropriate language classes.
3. To diagnose the individual’s specific strengths and weaknesses.
4. To measure aptitude for learning.
5. To measure the extent of student achievement of the instructional goals.
6. To evaluate the effectiveness of instruction.
10
18
B. Type & Kind of Test 1. Types of The Test
a. Based on the Number of test-taker
Based on the number of the test taker, test is divided into:11
Individual test: refers to a test where the tester tests only one testee, while
Group test: refers to a test where the taster faces more than one testee.
b. Based on the test maker
Test could be determined into teacher-made test and standard test. Although both are have the same purpose to measure the progress of teaching learning process, however they differ each other.
Teacher-made Test
Teacher made test is the test that is made the teacher of that classroom/or course itself. This test purposes to know measure how far the students achieve the instructional aim of particular lesson or course that are taught in the classroom.
11
19
Teacher made tests are designed based on the particular aim and description of the lesson that are taught in that class. Generally, this kind of test is not tried out before and even revised after. Thus, the validity of teacher made test often considered poor.12
Standardize Test
Standard test is a test constructed by test construction specialist, usually with the assistance of curriculum experts, teachers, and school administrators.13 index of discrimination should be replace.14
12
Burhan Nurgiyantoro, Penilaian dalam Pengajaran Bahasa dan Sastra, (Yogyakarta, BPFE-Yogyakarta, 2001), Pg 60
13
Tom Kubiszyn and Gary Borich, Educational Testing and Measurement (Singapore, John Wiley & Sons, INC, 2003), Pg 343
14
20
In addition, standard test is administered and scored according to specific and uniform. Thus it can be used in all and different school even it can used many times.15In the other word, a standard test administered and scored in Surabaya, would be administered and score in exactly the same manner in Malang, Sidoarjo, or anywhere in Indonesia. 2. Kinds of tests
Acording Arthur hughes, there are four types of test. Such as : profeciency test, achievment test, diagnostic test, and placement tests16.
a. Proficiency tests
Proficiency tests are designed to measure people’s ability in language, regardless any training they may have in that language17. The content of a proficiency test was not based on the content of the objectives of language courses. It’s based on a specification of what candidates have to be able to do in the language in order to be considered proficient. b. Achievment test
The content of the course in achievement tests are directly related to language course.The purpose is being able to establish how
15
Tom Kubiszyn and Gary Borich, Educational Testing and Measurement, pg 343
16
Arthur hughes, Testing for Language teachers, pg. 11
17
21
successful individual students, group of students and the course in achieving the objectives.
There are two kinds of achievement tests18:
a. Final achievement test b. Progress achievement test
The content of a final achievement test should be based directly on a detailed course syllabus or on the books and other materials used. This has been referred to as the syllabus-content approach. If Progress achievement tests, as their name suggests, are intended to measure the progress that students are making. They contribute to formative assessment. Since progress is towards the achievement of course objectives, these tests, too, should relate to objectives.
c. Diagnotice test
Diagnostic test concerns with the student’s persistent learning Difficulties that are left unsolved by the standard corrective prescriptions of Formative test. In other word we can say that diagnostic test was a test of student learning difficulties during instruction. The primary aim of Diagnostic test was to determine the
18
22
causes of learning problems and to formulate a plan for remedial action19.
d. Placement test
It’s intended to provide information that will help to place students at the stage of the teaching programme most appropriate to their abilities. Typically it’s used to assign students to classes at different level. One possible exception is placement tests designed for use by language schools, where the similarity of popular text books used in them means that the schools' teaching programmers also tend to resemble each other20.
C. Forms of Test
There are two kinds of form of test: objective and subjective test. The distinction between both tests is concern on method of scoring, and nothing else.21The following explanation will clarify enough about them.
1. Objective Test
Sudijono claimed that objective test is one type of test that is created using items tests, then what the entire test taker has to do is just answering the question by choosing one among several probably answers
19
Athur Hughes, Testing for Language Teachers, pg 16
20
Athur Hughes, Testing for Language Teachers, pg 17
21
23
available in each items or writing sentences or particular symbols in place provided in each item test.22
In line of that, objectives test as cited from Lado is:
“Objectives test are those that are scored rather than mechanically without need to evaluate complex performance on scale”23
a. Types of an objectives test
Sudijono also added that there are five types of objectives test including: true or false test, matching test, completion test, fill in test and also multiple choices. However in this thesis only will clarify the last one.
Multiple choices as stated by Sudijono are a test which is created likely incomplete sentences and the testee should complete the sentence in order to answer the question.24Before going to design multiple choice test, the test maker or in this case is teacher should know primarily several terms used in multiple choices. First is stem
which refers to initial part of each multiple choice items. Second is option/responses/alternatives, refers to the options which are available
22
Prof. Drs. Anas Sudijono, Pengantar Evaluasi Pendidikan, (Jakarta: PT. Rayagrafindo Pustaka, 1990), pg 106
23
Robert Lado, Language Testing, (London: Longman Group, 1961), Pg 28
24
24
for student to select their answer. One option among them is called the correct answerand the other is distractors25
The illustration from the explanation above as follows:26 Stay here until Mr. Short………..you to come. = stem
A. Told
B. will tell = options/response/alternatives = distractors
C. is telling
D. tells = correct answer
b. The Benefits and Weakness of Objective Tests 1. The Benefits of Objective Test
When objective test of language are properly made, they have important values. Arikunto mentioned several goodness of objective test:27
Represent more all objective materials that are being tested
They can test in short time
They can be scored with speed and ease
They use careful objective score in evaluating the test.
25
, J. B. Heaton, Writing English Language Tests(New York: Longman Group, 1988). Page 28
26
J. B. Heaton, Writing English Language Tests, pg 28
27
25
They able to be scored not only by teacher or test maker.
2. The weakness of Objective Test
The usual objections to objective test are mentioned by Lado as follows:28
They are too simple
They do not require real thinking but simply memory
They do not test the ability of the students to organize his thoughts.
Beside the three previous objective test’s weakness, Arikunto also added the rest objections29:
Objective test enable student being speculative in responding the question in a test
Open widely possibilities for students to cheating each other in doing a test
It is more difficult to construct the objectives test than subjective test because it contains a lot of item tests.
28
Robert Lado, Language Testing, (London: Longman Group, 1961), Page 35
29
26
2. Subjective Test
As quoted from Lado, subjective test is:
“Tests that require an opinion and a judgment on the part of the examiner”30.
In the other word, Nurgiyantoro have said that subjective test is a test that require student to answer in essay using their word.31
a. Scoring an essay test
Scoring an essay test generally based on the weight of each item test, the level of difficulty, and the amount of the element contained by the answer which is considered as the rightes answer.
For example, there are 5 items test in essay test. The tester had determined that all items have the same level of difficulty, and the elements in each item had made in the same amount. Based on that, tester decided that testee who could answer with the rightest answer or which the answer provides the entire element that required by the tester within the item test, will get 10 marks. When the testee answer almost perfectly or the answer provide mostly the element that required by the test taker, will get 9 mark, and so on.32
30
Robert Lado, Language Testing, (London: Longman Group, 1961), Pg 28
31
Burhan Nurgiyantoro, Penilaian dalam Pengajaran Bahasa dan Sastra, (Yogyakarta, BPFE Yogyakarta, 2001), Pg 71
32
27
b. The Benefit and the weakness of subjective test
The characteristics of subjective can be seen from its benefits and weakness as follow
a) The Benefit
Subjective test can create easily and fast
Avoid students being speculative in answering the items test The test taker is able to know how far students understand the material
Motivate student to organize their thoughts b) The weakness
Less able to represent all materials
It is difficult to score the subjective test. It because the answer of each item might be varieties and wide. Thus, it needs a lot of time, and thoughts to score it.
Enable test taker to score subjectively
Validity and reliability of subjective test is poor.
D. Characteristic of a Good Test
28
it has criteria for testing a test. According to Arikunto, there are some criteria of good test; validity, reliability,objectivity, practicality, economy33.
a. Validity
A test was classified to be valid if it measures accuracy what it is intended to measure. According to Heaton, validity of a test is the extent to which it measure what it is supposed to measure and nothing else. There are four types of validty ; face validity, content validity, contruct validity, and emperical validity34.
1) Face validity
Face validity refers to researchers’ subjective assessments of the presentation and relevance of the measuring instrument as to whether the items in the instrument appear to be relevant, reasonable, unambiguous and clear.35Hughes states: a test was said to have face validity if it looks as if it measures what it is supposed to measure. Face validity is not scientific notion and is not seen as providing evidence for construct validity, yet it can be very important.36
The test has face validity if the test looks right to other tester, teachers, and moderator and test- takers. It means that face validity measured by subjective judgment.
33
H. Douglas Brown., language Assessment: principles and classroom practices, (New York: Pearson Education, 2004), pg.3
34
J. B. Heaton. Writing English Language Test.(New York: Logman, 1975). pg. 159
35
Ayodele James, Oluwatayo, Validity and Reliability Issues in Educational Research (Vol 2),(Nigeria: Institute of Education,Ekiti State University, 2012) pg. 392
36
29
Face validity will be high if the students or test takers encounter some or the entire characteristic of good face validity, as follow:
a. The test well-constructed and familiar format task, b. The test is doable within the allotted time limit, c. The items are clear
d. The test have clear directions, e. The test related to the course work,
f. A difficulty level that presents a reasonable challenge37. 2) Content validity
Content validity is defined as any attempt to show that the content of the test is a representative sample from the domain that is to be tested38.
Hughes states that a test is said to have content validity if its content constitutes a representative sample of the language skills, structures, etc39.
b. Reliability
One of the necessary characteristic of good test is reliability. The test was said to be reliable if it is consistent in the measurements. It means that the students must have same mark if the test marked by two or more
37
H. Douglas Brown, language Assessment: principles and classroom practices, pg. 27
38
Glenn Fulcher,Language testing and assesment.(New York: Routledge, 2007) ,pg. 6
39
30
examiners. Moreover, the reliability of the test was considered a number of factors that may contribute to the unreliability of the test. According to Heaton, the factors affecting the reliability are:
1) The extent of the material selected for testing. Reliability is concerned with the size of the test; it is not too long and not too short. 2) The administration of the test40.
The students or test-takers must have same condition and time limit. 3) The instruction. The clarity of the instruction will affect the students’
comprehension to answer the test.
4) Personal factors, such as motivation and illness.
5) Scoring the test. It means that the objective test is more reliable than the subjective test.
There are some methods to estimate reliability. such as test – retest method, split half, equivalent method, and internal consistency method. Here, the reseacher uses split half method to get reliability because the
31
After that the result above to corelation with sperman Brown pattern, this formula is :
This is Criteri reliable
0.00-0.20 Not reliable
0.20-0.40 Less Reliable
0.40-0.60 Reliable enough
0.60-0.80 Reliable
0.80-1.00 Very Reliable
c. Objectivitas
According to arikunto the test is called objective if it is free from subjective factors which influence the test41. Objectivity of a test can be increased by using more objective types test items and the answers are scored according to model answers provided. Arikunto adds that there are
41
32
two factors that influence the objectivity of a test they are the form of a test and the test scorer.
d. Practicality
A test is called as practical test if it is easy to do and does not require many equipments and give freedom to the students to do the easier part, easy to score, is completed with clear instructions42. Arikunto stated that practicality of a test deals with a level of difficulties in admintering the test it self.
e. Economy
According to Arikunto the economices in a test related with the amount money, time and energy that a test taker spends to take a test43. it means that the test doesn’t need expensive fee, a long time and extra energy to finish the test.
f. Item Analysis
The purpose of items analysis was to identified the test items whether
it is good or not. To know the answer, all items should be identified from
the index of difficulty and index discrimination.
a) Index of difficulty
The good test items are not too easy and not too difficult. According to Heaton, index of difficulty was used to know how easy
42
Suharsimi arikunto, dasar – dasar evaluasi pendidikan, pg. 61
43
33
or difficult particular items in the test are. It is generally expressed as fraction or percentage of the students who answered the item correctly. To calculate the index of difficulty, Heaton uses the following formula44.
FV = index of difficulty
R = number of students whose correct answer N = number of students
It means that a good test to be given the students is the test with the criterion index of difficulty between o,30 – o, 70. Meanwhile, the index of difficulty which shows 0,00 – 0,30 and 0,70 – 1,00 was not good to be given to the students because the test is either too difficult or too easy for them.
b) Index of discrimination
Index of discrimination indicates the extent to which the items discriminate between the students. It is to discriminate the students who have high ability on the test and the students who have low ability on the test45. Heaton’s formula to calculate inex of discrimination is:
44
J. B. Heaton. Writing English Language Test p. 178
45
34
D = index of discrimination
Correct U = the number of students in upper group who answer the item correctly
Correct L = the number of students in lower group who answer the item correctly
N = number of candidate of one group
Arikunto classifies the criteria of index of discrimination as follows.46
D: 0,00-0,20 = poor D: 0,20- 0,40 = satisfactory D: 0,40- 0,70 = good D: 0,70- 1,00 = excellent
The range index of discrimination according to heaton as follows. +1= an item which discrimination perfectly
0 = an ite which does not discrimination in any way at all -1 = an item which discrimination in entirely the wrong way. c) The distractors
Analyzing the distractors aimed not only to know which items that cannot work properly, but also to check why particular test taker
46
35
failed to answer certain items correctly. Distractors can function well if these are chosen by students from the lower level. Arikunto state the distractor is chosen at least by 5% students who taking the test is called good test.
No item Option Upper lower comment
1 A*
B C D 0
When we want to analyze a test, we should know about the criteria of a good test itself. Based on arikunto, the criteria a good test, there are five criteria good a test: validity, reliability, objectivity, practically, and economy. Because My research concern on the test of multiple choice, I only use two criteria . Those are validity and items analysis include index difficulty, index discrimination, and distractors.
E. Previous Study
36
teacher made English try out test for national examination 2010-2011 for the third graders of MAN Sidoarjo. The research analyzed content validity, the index of difficulty, and the index of discrimination of the teacher made English try-out test in national examination 2010 – 2011 for the third graders of MAN Sidoarjo. The result shows that the content validity of the teacher-made English try-out test of MAN Sidoarjo has good content validity since 52% items test covered the indicators of Standard of Graduates Competencies. The test has acceptable index of difficulty because the Science class have 60% items which are adequate items and Social class have 68% items which are adequate items. And the index of discrimination of the test was different between both of class. The result of Science class shows that 44% items can be used. It means that the test is unacceptable for the Science class. And the Social class has acceptable index of discrimination since 60% items has satisfactory and good criteria47.
Second research was conducted by Milatul Islamiyah. This research analyzed the content validity and item analysis of English final test at last semester for tenth grade students of SMAN 3 Sidoarjo by. She finds that SMAN 3 Sidoarjo has good content validity of the test and acceptable index
47
37
difficulty of the test. Her research design is descriptive research and quantitative approach to collect numerical calculation data.48
Iffah Mursyidah Mayangsari conducted the research in 2009. The research analyzed teacher-made formative English test in SMA 2 Muhammadiyah Sidoarjo. The research focused on the content validity, reliability, item difficulty and item discrimination. This research used descriptive research as design in the study. The result of the analysis concluded that the test has high content validity, adequate reliability, acceptable item difficulty and acceptable item discrimination49.
From those previous studies above, the researcher prove that this research was different with previous study that showed above, the researcher do this research in KBRI school that located in Kuala Lumpur Malaysia, and the researcher focus on what the language testing technique that used in KBRI school and how the quality of the English testing that school. The researcher still do not know what exactly technique of testing that used by KBRI school Malaysia in this case Sekolah Indonesia Kuala Lumpur
48
Millatul Islamiyah, Content Validity and Item Analysis of Semester II English Final Test for Tenth Gr ade Students of SMAN 3 Sidoarjo, Thesis (Surabaya: Perpustakaan IAIN Sunan Ampel Surabaya, 20 10).
49
CHAPTER III
METHODOLOGY
A. Research Design
Based on the problem statements of this study, the goal of this research is to explain the answer about the language testing technique that used by Sekolah Indonesia Kuala Lumpur and explain how the test valid with the student, so this research use qualitative descriptive study.
Mardalis categorized four types of research method which are often used; they are Historical research, explorative research, descriptive research and explanatory research.1Descriptive research is used to obtain information concerning the current status of the phenomena to describe "what exists" with respect to variables or conditions in a situation. The methods involved range from the survey which describes the status quo, the correlation study which investigates the relationship between variables, to developmental studies which seek to determine changes over time.2
This study the writer will use descriptive methodology. This descriptive study is designed to obtain information concerning particular issues and then describe them. Arikunto states that descriptive research is not
1
Drs. Mardalis, Metode Penelitian, (Jakarta: Bumi Aksara,1995). Page 25
2
39
meant to test a certain hypothesis, but it only describes the phenomena, situation and condition that occur during the study3.
Best moreover divide descriptive research into four parts: document or content analysis study, case study, ethnographic study, and explanatory observation study. Document or content analysis study is the study which is concern with the explanation of the status of phenomenon at particular time. Case study is the way of organizing social data for the purpose of viewing social reality. Ethnographic study is the process of collecting data on many variables on an extended period of time, in naturalistic setting. Explanatory observation study is the study which seeks to find answers to question through the analysis of variable relationship.4
From the statements above, it can be concluded that the study is categorized as document or content analysis study since this study concern about the answer of what the language testing technique that use in Sekolah Indonesia Kuala Lumpur and also this research is concurrent embedded method because it is combine between qualitative approach and quantitative approach to get and analyze that data.
3
Suharsimi arikunto, dasar – dasar evaluasi, (jakarta, 1986), p.212
4
40
B. Research Subject
The subject of this study is the teacher of Sekolah Indonesia Kuala Lumpur Malaysia which uses the language testing technique in their learning.
In this study, researcher focuses on the English language testing technique that use in this school. In this case, researcher seeks to find what the technique that teacher use to measure student skill in Sekolah Indonesia Kuala Lumpur and how the technique can refers the student skill in English Language.
The subject of research in this case is the entire English teacher that teaches in second grades. The researcher chooses the teacher that teaches second grade of high school because in this grades, the teacher prepare the students well to make the student ready to deal with the Final Exam that they will do in the end of third grade of senior high school.
The researcher also takes sample test of second grades in high school in Sekolah Indonesia Kuala Lumpur. The researcher take the English final test from two classes to be analyzed.
C. Setting of The Study
41
the teacher themselves, but the teacher rarely analyzes their own test. So, it still questioned whether the test has a good quality or not.
D. Data Collection Technique and Instrument
In this research, the researcher use study document technique to answer the questions. The teacher made English test, the answer key and Standard of Graduates Competence academic year 2012-2013 are used to answer the validity of the test. The students’ answers sheet and the students’ scores of the teacher-made English test are used to answer realibility, the index of difficulty and index of discrimination, distractors of the English test. Those instruments are to prove the answer for all questions.
E. Data Analysis Procedure
In this study, researcher use interview technique because from the researcher point this technique is appropriate to collect the data and this technique is easiest one to know the answer of researcher question. The researcher conduct step in analyzing the data, as follows:
1. Explain the document (English final exam test) in second grades of Sekolah Indonesia Kuala Lumpur.
42
a. Analyzing face validity
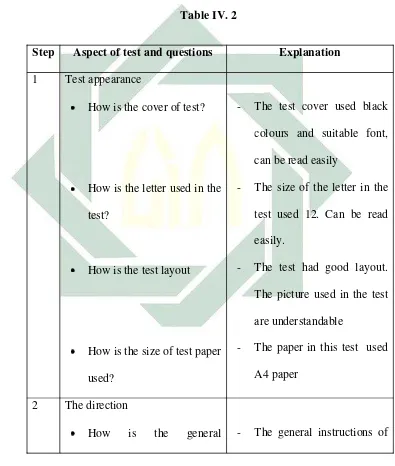
Face validity will be high if the students or test takers encounter some or the entire characteristic of good face validity, as follow:
Step Aspect of test and questions Explanation 1 Test appearance
How is the cover of test? How is the letter used in the test?
How is the test layout
How is the size of test paper used?
2 The direction
How is the general instruction of the test? How is the specific instrument of the test? How is the instruction for going on to text section in the next page?
3 Test items types
43
have been chosen?
How are the test presented?
b. Analyze the Validity content
In analyzing the content validity, the researcher want to know accuracy of English test with the idicators of curricullum or Standard Competencies. The researcher collect the data through the following steps:
i. Making a list of the standard competencies, basic competencies, indicators, and learning experience for the tenth grade students of senior high school and the indicators of basic competencies given by Sekolah Indonesia Kuala Lumpur high school for second grade student.
ii. Placing each of the test items in the appropriate place with the standard competencies and basic competencies to identify whether or not the standard competencies and basic competencies covered by the final test.
44
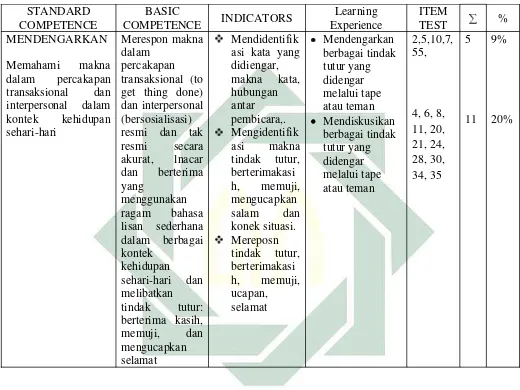
Table III. 1. The example of analyzing Content Validity5
STANDARD
45
c. Item analysis
1. Index of Difficulty
The Index of difficulty of an item simply shows how easy or difficult the particular item proved in the test.6To analyze the index of difficulty of test items, the researcher takes the following steps:
i. Arranging the students’ score from the highest score to the lowest one.
ii. Finding the top and the bottom of the students’ score, as upper and lower groups. Dividing the scripts in rank order of total score into two groups of equal size, the top half as the upper level and the bottom half as the lower group.
iii. Computing the item difficulty by using the formula of by Heaton below:7
Where:
FV = Index of difficulty
R = the number of students who answer correctly
6
J. B Heaton, Writing English Language Test, (New York: Longman Group, 1988). P 178
7
Suharsimi Arikunto, Dasar-dasar Evaluasi Pendidikan, (Jakarta, Bumi Aksara, 1993), Page 210
46
N = the number of students who taking the test
iv. Classify the result based on the criteria of Arikunto, as follow:8 Test items with 0,00 – 0,30 Difficult value
Test items with 0,31 - 0,70 Moderate value
Test items with 0,71- 1,00 Easy value
2. Analyzing the Index of Discrimination
The Index of Discrimination indicates the extent to which the item discriminates between the testees, separating the more able testees from the less able.9To analyze the Index of Discrimination here use the same steps using in analyze Index of difficulty. Those steps are:
i. Arranging the students’ score from the highest score to the lowest one.
ii. Finding the top and the bottom of the students’ score, as upper and lower groups. Dividing the scripts in rank order of total score into two groups of equal size, the top half as the upper level and the bottom half as the lower group.
8
Suharsimi Arikunto, Dasar-dasar Evaluasi Pendidikan, Page 225
9
47
D = Correct U – Correct L N
iii. Calculate the index of discrimination, the researcher used the formula below:10
Where
D : The Index of Discrimination
Correct U : The number of students in upper group who
answered the items correctly
Correct L : The number of students in lower group who
answer the items correctly
N : The number of students taking the test in one
group.
iv. Classify the result based on the criteria of Arikunto, as follow:11
Test items with 0,00 – 0,20 is Poor
Test items with 0,21 - 0,40 is Satisfactory
Test items with 0,41- 0,70 is Good
Test items with 0,71 – 1,00 is Excellent
10
J. B Heaton, Writing English Language Test, Page 180
11
48
3. Analyzing the Effectiveness of Distractor
Besides calculating index of difficulty and discrimination, it also important to analyze the items in very detail, moreover on those which cannot perform as expected. Analyzing the distractor aimed not only to know which items that cannot work properly but also to check why particular test taker failed to answer certain items correctly.
Distractors shave functioned well if these chosen mostly by students from lower level. According to Arikunto, the distractor which is chosen at least by 5% students from is called good distractor.12
In addition, to conduct the effectiveness of distractor the researcher should determine the amount of students from upper and lower level who chosen each options in each item. The researcher also determines the amount of students who do not chose the options at all (omit). However, to ease the analyzing, the researcher used a table as follow:
12
49
Table III.2. The example of analyzing the Effectiveness of Distractors13
Layinatul Cholbi, The Final English Test for the fourth grade students of SDN Pucang III Sidoarjo,
CHAPTER IV
RESEARCH FINDING & DISSCUSSION
This chapter is to explain about the result of the research. The researcher analyzed English language testing that had been constructed by an English teacher of second grade in Sekolah Indonesia Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia based on characteristic of a good test, validity, and item analysis which include index of difficulty, index of discrimination and distracters.
Furthermore, all data that helped the researcher to analyze were conducted from documents such as, the English teacher interview result, the item test, and the answer keys.
A. Description of the English Final Test
51
objective test that consisted of forty multiple choice questions and had five multiple choice objections.
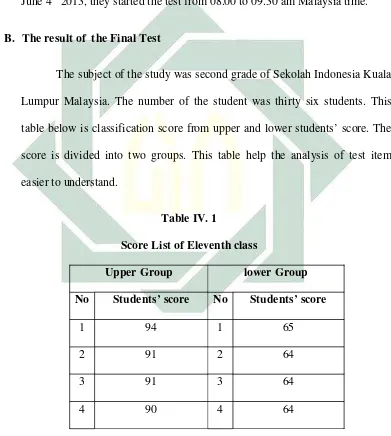
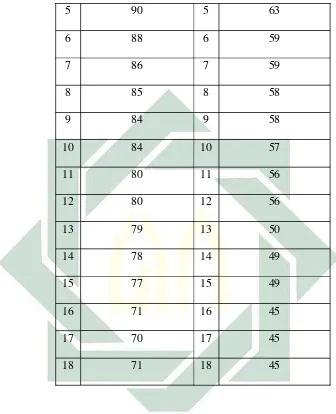
The content of the test is reading test. The English test was held on June 4th2013, they started the test from 08.00 to 09.30 am Malaysia time.1
B. The result of the Final Test
The subject of the study was second grade of Sekolah Indonesia Kuala Lumpur Malaysia. The number of the student was thirty six students. This table below is classification score from upper and lower students’ score. The score is divided into two groups. This table help the analysis of test item easier to understand.
Table IV. 1
Score List of Eleventh class
Upper Group lower Group
No Students’ score No Students’ score
1 94 1 65
2 91 2 64
3 91 3 64
4 90 4 64
1
52
5 90 5 63
6 88 6 59
7 86 7 59
8 85 8 58
9 84 9 58
10 84 10 57
11 80 11 56
12 80 12 56
13 79 13 50
14 78 14 49
15 77 15 49
16 71 16 45
17 70 17 45
18 71 18 45
53
C. Research findings
After classifying the students to the upper and the lower group, the next step is analysing the validity and item analysis. The researcher takes two kinds of validity; include face validity and content validity. Item analysis includes index of difficulty, index of discrimination and distracters.
1. Face validity
To show the result of face validity of English Test for second grade in Sekolah Indonesia Kuala Lumpur, the researcher took two steps. First step was classifying the matter of the test. Second step was analysing test based on criteria in the table below.
54
Second, analyzed the test based on the table below.
Table below shows the result of the analysis of the face validity of the test.2
Table IV. 2
56
There are seventh columns in that table. The first column contains of standard competence, second column contains of basic competencies, the third column contains of indicators, the forth column contains of learning experience, the fifth column contains of item test that is appropriate with the basic competencies, the next column contains of the number of items test ( ) and the last column contains of the percentage of total numbers of particular items represent the elated basic competence.
According to J.B Heaton, the test can be said had a good content validity if it covers all the contents as stated in the curriculum. Based on the result of analysing content validity in appendix 3, this test just covers two criteria, the percentage of every aspect of learning content is concluded as follows:
1. There are 45% 0r 18 items for reading which focused on narrative, hortatory exposition, and spoof.
2. There are 40% or 16 items for linguistics which focused on simple past, past tense, and adverbs.
3. There are 15 % or 6 items unsuitable because it focused on descriptive and present future tense.
57
according to Bloom if the agreement of the test is 50% or more, it can be concluded that the test had high content validity3.
Moreover, there are 6 items or 15% of the test did not cover the materials, they are the items test number 7, 8, 9,10,30,35. Those item are unsuitable with the indicator of standard and basic competencies and were not taught in this semester.
3. Analysing of item test
a. Analysing index of difficulty
To get the data of index of difficulty, the researcher divided the class into 2 groups (see table IV.1). The first group was upper group, who were students who get a good score. The second is lower group, who were student who get the bad score.
After the researcher got the data, she did the analysis using formula as follows:
Note : FV : index of difficulty
R : the number of correct answer N : the number of students taking test
There are eight columns in the table. First column contained the number of English test items. The second, it was contained the
3
58
score of the upper group which answer correctly of each English test items. The third contained the score of the lower group who answer correctly of each English test items. The fourth column contained total of upper group and lower group who answer correctly of each items. The fifth column contained the value of index of difficulty. The sixth column contained upper group minus lower group who answer correctly of each items. The seventh column contained the value of index of discrimination. The eight columns contained comment for each item of index difficulty and index discrimination. See appendix 4.
59
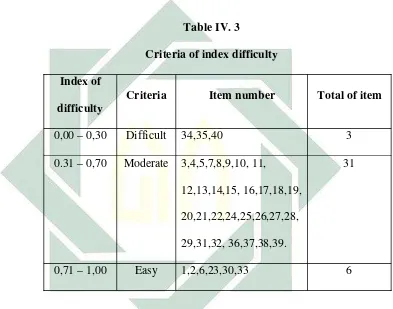
After analysing the index of difficulty, the next step is machining the result with the criteria of index of difficulty according to Arikunto. The analysis is organized in the following table.
Table IV. 3
Criteria of index difficulty Index of
difficulty
Criteria Item number Total of item
0,00 – 0,30 Difficult 34,35,40 3
0.31 – 0,70 Moderate 3,4,5,7,8,9,10, 11, 12,13,14,15, 16,17,18,19, 20,21,22,24,25,26,27,28, 29,31,32, 36,37,38,39.
31
0,71 – 1,00 Easy 1,2,6,23,30,33 6
60
b. Index discrimination
Index discrimination is tools to differentiate between students who are in the upper group (achieved well) and the lower group (who did not achieve well). To analyze index discrimination, the researcher arranged student in the upper group and the lower group, same as analysing the index difficulty. After arranging the upper and the lower group then the researcher computed data of the index of discrimination.
61
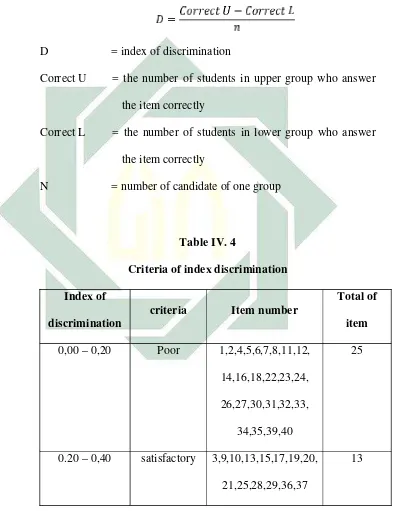
To calculate the index discrimination for each item number, the formula used:
D = index of discrimination
Correct U = the number of students in upper group who answer the item correctly
Correct L = the number of students in lower group who answer the item correctly
N = number of candidate of one group
Table IV. 4
Criteria of index discrimination Index of
discrimination
criteria Item number
Total of item 0,00 – 0,20 Poor 1,2,4,5,6,7,8,11,12,
14,16,18,22,23,24, 26,27,30,31,32,33,
34,35,39,40
25
0.20 – 0,40 satisfactory 3,9,10,13,15,17,19,20, 21,25,28,29,36,37
62
0,40 – 7,00 Good 38 1
0,70 – 1, 00 Excellent -
--0 Wrong -
-Based on the table, the result of index of discrimination shows that there are 25 items had poor index of discrimination, there are 13 items had satisfactory, and there are 1 items had good index of discrimination. Almost students index of discrimination are poor. It means that those items are categorized poor. It means that the English test must be revised.
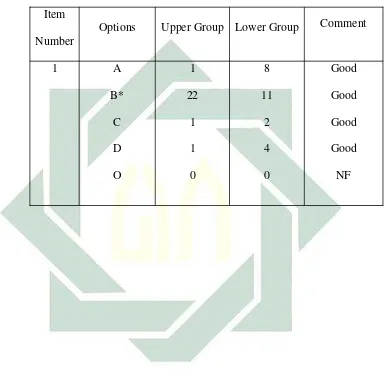
c. Analyzing the Effectiveness of Distracters
Item distractors are the incorrect options in the multiple choices which district the testee from the correct answer. A good distractor will attract more students from the lower group than the upper students. Thus, if there are more able students chosen the distracters, it means that the item does not function as expected in it must be revised.
63
Third column is the total correct answer from the lower group. The last column is the comment of the distracter. See appendix 5.
According to Arikunto, if the distracter was chosen at least by 5% of student who take the test, it is called a good test. (5% from testee = 5% x 60 students = 3 students)4. In this case 5% of the total student is 2 students (5% x 36 students).
The result of distracters shows that most of all distractors had good criteria because the distracters have been chosen by more the lower group than the upper group. So the English test had good distracters.
D. Discussion
1. Face Validity
The result of face validity above shows that the test had the criteria of good test. From the cover of the test, it had clear font and colour. The test also had fine letter size to be read. In addition, the test had the acceptable paper size, the test used A4 paper. From the instructions, the instructions are simple and clearly understandable. The first instruction contains date of the test, time to do the test, and how the test must be done. The instruction of each section used unclear instructions. The instruction
4