THE USE OF METHAPOR IN SLOGAN ADVERTISEMENT: A CASE
STUDY OF ASEAN TOURISM DESTINATION
THESIS
Submitted as Partial Fulfillment as the Requirements for the SarjanaDegreeof English Department Faculty of Letters and Humanities UIN Sunan Ampel Surabaya
By:
Reni Ariyanti Reg. Number A73213124
ENGLISH DEPARTMENT
FACULTY OF ARTS AND HUMANITIES
THE STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY OF SUNAN AMPEL
SURABAYA
ABSTRACT
Ariyanti. R. 2017.The Use of Metaphor In Slogan Advertisement: A Case Study of ASEAN Tourism Destination. English Department, Faculty of Arts and Humanities. The State Islamic University of Sunan Ampel Surabaya.
The advisor: Dr. Mohammad Kurjum, M. A.g
Key words: Metaphor, Type of metaphor, coherence discourse, advertisement
Metaphor gets much attention especially in advertisement, which metaphor can influence the customer to interest with goods promote in advertisement. This thesis examines metaphor through slogan tourism in ASEAN which is concentrated in the content of slogan. Content of slogan is included about text and picture. In addition, type of metaphor in advertisement is investigated in research. And language uses in slogans tourism are also evaluated with discourse aspect, which the text is become the primary subject.
Forceville’s theory of type of metaphor in advertisement is applied. Forceville (2008) are explained that there are three type metaphors in advertisement. Besides, Lakoff and Johnson (1980) and Kovecses (2010)’s theory of coherence discourse in metaphor are also used to analyze the text of slogan tourism in ASEAN. Qualitative content analysis and descriptive research are chosen to investigate slogan tourism in ASEAN which consist of the text and the picture. The researcher herself becomes the only instrument or human instrument. Reading and selecting the entire text and picture of slogan tourism and video promotion tourism in ASEAN becomes the steps of data collection. Then, the procedures of data analysis contain identifying, classifying, and describing the data. The conclusion is also drawing in the last step to make understanding.
INTISARI
Ariyanti. R. 2017.The Use of Metaphor In Slogan Advertisement: A Case Study of ASEAN Tourism Destination. Sastra Inggris, Fakultas Adab dan Humaniora. Universitas Islam Negeri Sunan Ampel Surabaya.
Pembimbing: Dr. Mohammad Kurjum, M. A.g
Kata kunci: metafora, tipe metafora, wacana koheren, iklan
Metafora mendapat banyak perhatian terutama dalam hal iklan, yang mana metafora dapat mempengaruhi minat pelanggan terhadap barang yang dipromosikan dalam iklan. Tesis ini mengkaji metafora melalui slogan pariwisata di ASEAN yang terkonsentrasi pada isi slogan. Isi slogan terdapat tentang teks dan gambar. Selain itu, tipe metafora dalam iklan juga termasuk dalam penelitian. Dan penggunaan bahasa dalam slogan pariwisata juga dievaluasi dengan aspek wacana, yang teksnya menjadi subjek utama.
Teori Forceville tentang jenis metafora di iklan diterapkan dalam penelitian ini. .Forceville (2008) menjelaskan bahwa ada tiga jenis metafora dalam iklan. Selain itu, teori wacana yang koheren Lakoff dan Johnson (1980) dan Kovecses (2010) dalam metafora juga digunakan untuk menganalisis teks slogan pariwisata di ASEAN. Analisis ini kualitatif dan termasuk penelitian deskriptif yang dipilih untuk menganalisa slogan pariwisata di ASEAN yang terdiri dari teks dan gambar. Peneliti sendiri menjadi satu-satunya instrumen atau sebagai instrumen manusia. Membaca dan memilih keseluruhan teks dan gambar di promosi slogan pariwisata di ASEAN menjadi langkah pengambilan data. Kemudian, prosedur analisis data berisi identifikasi, klasifikasi, dan penggambaran data. Kesimpulannya juga menggambar pada langkah terakhir untuk membuat pemahaman.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Inside Cover Page………i
Inside Title Page………..ii
Declaration Page……….iii
Motto………...………...…………...iv
Dedication Page………....………..v
Thesis Advisor’s Approval Page………...vi
Thesis Examiners’Approval Page………vii
Acknowledgement………...viii
Table of Contents…………..………...x
List of Appendices………...………….………..xiii
Abstract………..……….xiv
Intisari………...………...xv
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION 1.1Background of the Study……….1
1.2Research Problems………...7
1.3Research Objectives………...7
1.4Significance of the Study………...8
1.5Scope and Limitations………..…9
CHAPTER II REVIEW OF LITERATURE
2.1 Theories of Metaphor………....11
2.2 Conceptual of Metaphor………...13
2.2.1 The Systematic of Metaphorical Concept……….…14
2.2.2 Conceptual Metaphor as a Set of Mapping……….………..16
2.2.3 Source Domain and Target Domain in Metaphor……….………....19
2.2.3.1 Source Domain……….…19
2.2.3.2 Target Domain………..23
2.3 Metaphor Coherence in Discourse………....25
2.4 Metaphors in Advertisement………....28
2.4.1 Types of Metaphors in Advertisement……….28
2.5 Slogan………...29
2.6 Tourism destination management ………29
CHAPTER III RESEARCH METHOD 3.1Research Design………...30
3.2Subject of The Study………...…....30
3.3 Data and Data Sources………...32
3.4Research Instruments………...33
3.5Techniques of Data Collection………....39
CHAPTER IV FINDINGS AND DISCUSSION
4.1 Findings……….………....41
4.1.1 Type of metaphor in Advertisement...………...41
4.1.1.1 Pictorial Metaphor………...45
4.1.1.2 Verbal Metaphor………...………...45
4.1.1.3Verbo-Pictorial Metaphor……….……...49
4.1.2 The coherence text of slogan in advertisement………...60
4.1.2.1 Intertextual………...62
4.1.2.2 Intratextual………...68
4.2 Discussion……….…...82
CHAPTER V CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION 5.1 Conclusion……….…...83
5.2 Suggestion…….………...86
REFERENCES
1
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
1.1 Background of Study
Metaphor is a figure of speech that consists of name or descriptive word is
concerned to an object or action (Oxford English Dictionary, 2007). The basic of
metaphor is contained a matter of language, which is described about certain
pre-existing similarities two things in the world (Rios, 2007). Metaphor is a class of
linguistic expressions that is called metaphorical linguistic expressions, which is
about linguistic words and expression that are from the terminology of the
conceptual metaphor. The conceptual metaphor has related with metaphorical
linguistic expression, which in conceptual metaphors, one domain of experience is
used to understand another domain of experience and the metaphorical linguistic
expression are explained particular conceptual metaphors. Metaphor is one aspects
of language where becomes the basic of the cognitive linguistic in conceptual
metaphor. The texts of metaphorical structure in the cognitive linguistic view
metaphor have two domains in conceptual metaphor. They are called source
domain and target domain. Metaphors are sets of mappings between a more
concrete or physical source domain and a more abstract target domain (Kovecses,
2002). To make understand this definition for purposes of the research, metaphor
is a powerful linguistic device because it extends knowledge about human
cognitive. Through linguistic metaphors, human can deliver the idea from the
2
The word Metaphor is commonly used by many researchers to analyze a kind
of language in the linguistic or literature field. Some researchers had already
analyzed metaphor in magazine, newspaper, advertisement, etc. It can be found in
the form of analysis, journal research (Rossa, 2009; Rios, 2007; Yu, 2009; Czerpa,
2006), undergraduate thesis (Yalcinkaya, 2012; Anderson, 1998) and dissertation
(Famelart, 2010) but in other case, the writer informs that some other researchers
had metaphors in literary works like poetry, novel (Freeman, 2007; Semino and
Steen, 2008; Hogan, 2003). Dealing with this, the writer knows some information
about metaphor and gets idea from those previous researches. The writer found
idea that metaphor has feature in analysis of text, especially in the advertisement.
Metaphor has great impact in text because metaphor makes art and unique in every
text. So, the writer is chosen metaphor for taking focus in her research.
American linguists, Lakoff and Johnson, has found theory of metaphor that
becomes a major pillar of cognitive linguistic paradigm, which relates linguistic
metaphors and human cognitive. Cognitive linguistic have knowledge about the
nature of human cognitive in various aspects of language structure and use. Lakoff
and Johnson’s theory of metaphor is commonly used by researchers to study in the term metaphor (Anderson, 1998; Maalej, 2005; Yu, 2009; Hong Bo and Wen-Juan,
2010; Wittink, 2010; Reichert and Morgan, 1999; Rosa, 2009; Famelart, 2010;
Pitcher, 2013). In the case, the writer found research from dissertation in Faculty
of English Philology I by Famelart (2010) who is done to analyze a trilingual
comparative study of the use of multimodal metaphor in Spanish and French bank
3
Dealing with previous research, the writer is interest to use theory of Lakoff and
Johnson with different object advertisement in the further research.
Metaphor has coherence in discourse. Through discourse, the metaphors find
a major function to know the meaning of metaphor usage in text. The coherence of
metaphors can be either intertextual or intratextual (Kovecses, 2002). Most
researchers who studies on metaphor in real discourse are agree that a major
function of the metaphors is provided coherence to discourse (e.g., Hong Bo and
Wen-Juan, 2010; Maalej, 2005; Wittink, 2010; Musolff, 2006; Herrmann, 2013;
Shen and Balaban, 1999). In addition, most of the research is done analysis about
the opportunities that arise from using the linguistic insight in identifying metaphor
in discourse. In this matter, the writer found analysis from the publication on
International journal by UV University of Amsterdam researcher is written by
Wittink (2010) who investigated identify of metaphor in discourse. In the analysis,
he put data from text of organizational research with focused aspect de-contextual
and contextual approaches in discourse. In the research, researcher also identified
locally specific uses and meanings of metaphors and the interaction with other
elements of discourse. Meanwhile, another analysis from Maalej (2005) is done
analysis about critical discourse with the contemporary theory of metaphor. In the
research, researcher used critical model of metaphoric discourse, the stage of
interpretation is the product complementary fashion of a critical mind, pursuing
the result of the description offered by discourse and following conceptual
metaphor. It is the real socio-cultural contexts, which is used to make sense
4
Therefore, by this study, the researcher has a space of the study for analyzing about
metaphor coherence in discourse with byidentifying metaphor in context-induced
across intertextual or intratextual approaches in discourse. This present study aims
to fulfill in these gaps by analyzing the metaphor with discourse coherence of the
text in slogan to investigate the study.
Metaphor are concerned with language (Written text), visual image (photo,
computer drawn images, or digital animations), and the combination of the
language with visual image in advertisement. In the study of metaphors, metaphors
have been classified to distinguish in differences usage in advertisement. The kinds
are pictorial or visual metaphor, verbal metaphor or verbo-pictorial metaphor.
Metaphors are also classified to divide between monomodal and multimodal
metaphors. The former are metaphors whose target and source are conveyed in the
same mode. Monomodal is typically a metaphor that is both target and source are
introduced in one mode. Multimodal is typically a metaphor that is target and
source are introduced entirely in two different modes (Forceville, 2008). Many
researchers are publishing in International journal and thesis that take types of
metaphors as their focus of study, but most of the study only focuses to analyze
one type of metaphors (Anderson, 1998; Kadry, 2015; Indurkhya and Ojha, 2008;
Yu, 2009; Rosa, 2009; Czerpa, 2006; Yalcinkaya, 2012; Oritonang and Ownie,
2011; Famelart, 2010; Xu, 2009). In addition, most researchers are done analysis
about the type of visual metaphors in advertisement. The research from the
publication on Thesis by Kristianstad University College researcher is written by
5
Researcher analyzed in one of slogan of McDonald’s, “Mac your day (McDonald’s, 2000)”. The point from the analysis that day is conceptualized as food or the Big Mac hamburger in the slogan. The kinds of slogan are from McDonald’s, Cola-Cola, Burger King, and the others. Meanwhile, in the difference analysis of type in
metaphor from Kadry (2015) is done investigated about type of visual metaphor in
The Persuasive effect of using Visual Metaphors in Advertising Design.
Researcher is analyzed the persuasive role of visual metaphors as one technique in
advertising communication. It explored through the various types of visual
metaphors where the visual metaphor was the hero image in design and how the
effect image in the persuasive design is. Therefore, by this study, the researcher
intends to take analysis in kinds of metaphors for further research. The writer is
not only focused in one kind of metaphor, but also all kinds of metaphor in the
analysis. The kinds are verbal metaphors, the pictorial metaphors, and
verbo-pictorial metaphors.
Metaphors has implications for advertising as active audiences are highly
interpret the advertising message in a more meaningful and personal way.
Metaphor is used for people to understand an abstract concept in media industry,
advertising, as one of the most efficient ways of publicizing products. The selling
power of the advertisements largely depends on a well chosen the conceptual
metaphors like pictures or words used in them (Anderson, 1998; Yu, 2009). The
use of metaphor is an attractive and efficient way for advertisement to make
positive claims for the product, brands, or service. The metaphor is focused almost
6
(Forceville, 2008). The use of metaphors in advertisement is becomes special
interest as it comes to provide any linguistic researchers with accessible of thesis,
international journal, and dissertation (Yu, 2009; Czerpa, 2006; Indurkhya and
Ojha, 2008; Chorianopoulus and Spinellis, 2003; Aritonang and Ownie, 2011;
Famelart., 2010; Sacristan, 2009; Rios, 2007; Rosa, 2009).
Part of the research is done to analyze about advertisement in product, Yu
(2009) conducted a research on the use metaphors in food advertising, while
Czerpa (2006) observed metaphors in cosmetic advertising. And also magazine
advertising is becomes subject for researcher (Aritonang and Ownie, 2011; Rosa,
2009). Unlike the previous researchers, the writer takes different focuses in slogans
of ASEAN tourism destination advertisement. The reason of the writer choice of
ASEAN tourism destination advertisement is because tourism has a tractive power
that is very interesting for people in the world.
Nowadays, travelling becomes famous in world. Most of people are interested
in travelling. Slogan of ASEAN tourism destination is one of the important things
to become information for every people, especially for people who are interested
in travelling. But some people seem to do not care with slogan of ASEAN tourism
destination, although it is the only slogan in this country. Sometimes, the slogan of
ASEAN tourism destination advertisement is puzzling. There is an implicit
message hidden inside it. Thus, the writer wants to reveal what exactly the meaning
is behind. Therefore, the writer has a goal to know what kind of metaphors used in
slogan of ASEAN tourism destination advertisement and the coherence of
7
1.2 Research Problem
This research is analyzed to answer the problems formulated in the
following questions:
1. What is the most common type of metaphors used in slogan of ASEAN
tourism destination advertisement?
2. How is the coherence text of metaphors usage in slogan of ASEAN tourism
destination advertisement?
1.3 Research Objectives
Based on the problems described above, the objectives of the study are
pointed:
1. To show the most common type of metaphors used in slogan of ASEAN
tourism destination advertisement.
2. To describe how the coherence text of metaphors usage in slogan of ASEAN
tourism destination advertisement is.
1.4 Significances of the Research
There are many kinds of advertisement, which has different interest for the
people. They are many kinds of advertisement likes food, cosmetic, cigarette,
fashion, magazine, and other advertisement. The writer of recent study takes
tourism destination advertisement, especially in slogan. Tourism destination
8
had been already done in analyzing advertisement by using metaphor aspect in
research. Therefore, the writer focuses metaphor aspect to analyze the slogan of
ASEAN tourism destination advertisement. Thus the recent study is for readers,
especially for the people who love travelling.
For the specific aim, the writer hopes the research can show the reader about
analyzing metaphor by using the conceptual metaphor, which consists of human
cognitive and linguistic metaphor from the slogan of ASEAN tourism destination
advertisement. In addition, the reader can understand the type of advertisement
likes verbal metaphors, pictorial or visual metaphors, and verbo-pictorial
metaphors in slogan ASEAN tourism destination advertisement. Also, the reader
can know the coherence text of slogan. Sometimes people still do not know the
coherence meaning in slogan of ASEAN tourism destination, thus in here, the
reader can be guided to understand how the coherence text of meaning metaphor
in slogan is through interpretation in this research.
Hopefully, the research about metaphor with slogan of ASEAN tourism
destination can be the reference for the readers so they can get advantage and
knowledge from this recent study.
1.5Scope and Limitations
This research is conducted in two major analyses, types of metaphor in slogan
tourism advertisement and metaphor coherence discourse in text of slogan tourism
advertisement. The Researcher also creates two different focuses. Firstly, types of
9
countries in ASEAN. They are investigated by using Forceville’s theory, which are
explained types of metaphors in advertisement. Secondly, for metaphor coherence
discourse, the researcher is focused the term of intertextual or intratextual in
analysis. The research focuses on language (written text), visual image (photo, hand
or computer drawn image, or digital animation) and both of them, which is
contained in the slogan. In addition, the video promotion tourism is also taken as
the data to support the analysis. The data is taken from slogan tourism in ASEAN,
which are only 10 countries that have slogan tourism.
1.6Definition of Key Term
The researcher gives the definition of key term which is related to the title of
the research and to make clear the discussion of research.
1. Metaphor is a figure of speech that consists of name or descriptive word
is concerned to an object or action, whether metaphor is a class of
linguistic expressions that called metaphorical linguistic expressions,
which is about linguistic words and expression in the conceptual
metaphor. (Oxford English Dictionary, 2007; Kovecses, 2002)
2. Slogan is a long-term headline that becomes a memorable phrase or a
motto, which is a key element in advertising strategies. (Ferris, 2014;
Krcmarova, 2008)
3. Advertisement is a form of communication used to persuade an audience
like viewers, readers or listeners to take some action with respect to
10
message such as words or images in a more meaningful in product.
(Anderson, 1998; Aritonang and Ownie, 2011; Krcmarova, 2008)
4. ASEAN is the largest continents and the most populated continent,
located primarily in the Eastern and Northern hemispheres.
(http://www.thefreedictionary.com/ASEAN)
5. Tourism destination is the place visited that is central to decision to take
11
CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
In the previous chapter, the researcher has mentioned some researchers who
studied metaphor. The purpose of this chapter is to introduce the reader about the
study of metaphor. The researcher will take a brief history of metaphor in linguistic
from different philosophical perspectives. This framework comprises some
required the theories to the analysis. The researcher investigated slogan of Asia
tourism destination advertisement. This present study combines some theories in
order to draw a great result of the analysis.
2.1 Theories of Metaphor
Metaphor is a figure of speech which implies comparison between two
differences entities, as distinguished from simile, an explicit comparison model by
the words “like” or “as”. There are most common definitions of metaphor in the study. Firstly, metaphor is a property of words in linguistic aspect. Secondly,
metaphor is useful for artistic purpose, for example in poem. Lastly, metaphor is a
figure of speech which is used for special effect and part of everyday human
communication. The definition of metaphor has been stated by some experts, such
as Kovecses (2010: 3-4) who defined that metaphor is large part of the way to speak
naturally for everyday purposes. Metaphor is also the abstract and explicit concept
of life. In the theory, he emphasized that metaphor is nature of language, which
words or other linguistic expressions come from the more concrete conceptual
12
explanation for understanding metaphor in the research. The theory still can not be
specific reference in metaphor. It is because metaphor is not only about nature of
language or word linguistic expression in speaking but also about the important part
that has relation with human thought.
In addition to Kovecses’s theory, Black (1955: 276-277) also has another theory about metaphor. Black asserts that metaphor is a loose word, which is as a
term properly applicable to certain expression without attention to anything likes
the thoughts, acts, feelings, and intentions of speakers on which the expression is
used. He suggests that metaphor only focuses in the frame. The main focus of the
metaphors is remained of the sentence in which that word. It would be good
understanding to know about the meaning of metaphor with translated word.
Through the black’s theory, it still can not be a good reference in understanding
metaphor because in metaphor we can not just focus in the sentence or word to
understand meaning from metaphor. There are other aspects which are important to
make sure about the meaning of metaphor likes though, feelings, and art.
Lakoff and Johnson (1980: 124) view metaphor as a concept of human
thought. Metaphor is human conceptual system, the way we think, what we
experience, and what we do every day is very much a matter of metaphor. The basic
of linguistic aspect, human has found the most ordinary conceptual system as
metaphorical in nature. Also, metaphors are that structure how we perceive, how
we think, and what we do. The theory is known as “cognitive linguistic view of
13
Lakoff and Johnson showed that theory of metaphor is included both in
though and in everyday language. Lakoff and Johnson (1980: 134) also emphasized
that metaphor is one of our most important tools for exploring to understand what
can not be understood totally as our feelings, aesthetic expression, moral practice,
and spiritual awareness. The function of metaphor is to better understand certain
concept, and not just some artistic or esthetic purpose.
Based on the three theories of linguist above, the researcher concludes that
the appropriate theory for conducting the research is from Lakoff and Jonhson
linguist (1980), and also Kovecses (2010) who is book writer the second edition
from book title “what we live by” by Lakoff and Johnson 1980 about metaphor to support this research. Metaphor is human though that is abstract concept of life,
which the part is used to speak naturally for everyday purposes.
2.2 Conceptual Metaphor
A conceptual metaphor consists of two conceptual domains, in which one
of conceptual domains is understanding another conceptual domain. Conceptual
metaphor contained metaphorical linguistic expression, which comes from the
language of the more concrete conceptual domain. There are two special names of
domains in conceptual metaphor. They are source domain and target domain
(kovecess, 2010: 4). The metaphorical linguistic expression is used to study the
nature of metaphorical concept and to get understanding of the metaphorical nature
14
the people use to talk about aspect of the concept is systematic (Lakoff and Johnson,
1980: 456)
2.2.1 The Systematic of Metaphorical Concept
According to Lakoff and Johnson (1980: 124-125), conceptual metaphor
becomes the basic of linguistic evidence, which most of our ordinary conceptual
system is metaphorical in nature. Conceptual system plays a central role in everyday
realities, then the way of thinking, what human experience, and what human activity
every day is very much a matter of metaphor. There are examples to give some idea
of what it means for a concept system to be metaphorical and a concept to structure
an everyday activity, the variety example of expression:
The example uses the concept ARGUMENT and the conceptual metaphor
ARGUMENT IS WAR.
ARGUMENT IS WAR Your claims are indefensible.
He attacked every weak point in my argument. His criticisms were right on target.
I demolished his argument.
I’ve never won an argument with him. You disagree? Okay, shoot!
If you use that strategy, he’II wipe you out. He shot down all of my argument.
From the example, it is not just talk about arguments in terms of war.
Many of the things we do in arguing are partially structured by the concept
of war. There are a verbal battle and structure of an argument as attack,
defense, counterattack, etc, which reflect this. The ARGUMENT IS WAR
15
in arguing. Imagining a culture, argument is viewed as a dance, the
participants are seen as performers, and the goal is to perform in a balanced
and aesthetically pleasing way. In such culture, people would view
argument in different perspective. This is an example of what it calls a
metaphorical concept, namely ARGUMENT IS WAR, to structure is what
we do and how we understand about it, so we argue. The essence of
metaphor is understanding and experiencing one kind of thing in terms of
another. Argument and war are different kind of things, which it is verbal
discourse and armed conflict. ARGUMENT is partially structured,
understood, performed, and talked about terms of WAR. So, the concept,
the activity, the language are metaphorically structured. This is the ordinary
way of talking about use the words in attacked position. The metaphor is not
always about the words we use but it is also in our concept of an argument.
2.2.2 Conceptual Metaphor as a Set of Mapping
Kovecses (2010: 7-11) argues that conceptual metaphor as set mapping is
about the systematic correspondences between the source and the target in the sense
that the conceptual elements of B correspond to constituent element of A. However,
technically, the conceptual correspondences are often referred to as mappings.
Process of metaphorical understanding is the word “understand” as being
synonymous in the definition of metaphor to the words construe or conceive, which
it enters us to the real-time, online aspect understanding and can be more easily
16
construe a more abstract through a more physical domain in long-term memory or
as a result of a historical-cultural process. The word construe in the discussion
makes that conceptual metaphor coherent with grammatical construction that it is
used in cognitive linguistics, in grammatical contraction also has function as ways
construing aspects of experience in the more general sense.
There are examples to give some cases where elements of the source domain
are mapped into elements of the target domain, the example variety of expression:
LOVE IS JOURNEY
This sentence gives three constituent elements of journeys as the travelers, the travel
or the journey as such, and the destination. When everyone sees the sentence, he/she
will interpret about love, and thinks that the speaker of the sentence has mind
lovers, not real as travelers, not only physical journey but also the events in a love
relationship, and not only physical destination but also the goal of the love
relationship. To give interpretation about sentence, we must map between
constituent elements of the source and the target.
Source: JOURNEY Target: LOVE
The traveler the lovers
The vehicle the love relationship itself
The journey events in the relationship
The distance covered the progress made
The obstacles encountered the difficulties experienced Decisions about which way to go choices about what to do The destination of the journey the goal(s) of the relationship
This is the systematic set of mappings that characterize the LOVE IS
17
systematic mapped with elements of conceptual domain B. From this discussion,
the domain of love did not have these elements before it was structured by the
domain of journey. Another thing of evidence for the target of love is not structured
independently of any source domains is the following. In the present example, we
talk about the goals associated with love, but this is just a slightly “disguised” way of talking about destinations given in the source. And the word goal has an
additional literal use, which it is not just a metaphorical one. This example showed
that many elements of target concepts come from source domains and they are not
preexisting.
Another example shows how correspondences or mapping make up a conceptual
metaphor:
SOCIAL ORGANIZATIONS ARE PLANTS
Its means of more interpretation:
He works for the local branch of the bank Our company is growing
They had to prune the work force.
The organization was rooted in the old church.
There is now a flourishing black market in software there.
His business blossomed when the railways put his establishment within reach of the big city.
Employers reaped enormous benefits from cheap foreign labour.
The characterization by the following set of mapping:
Source: PLANT Target: SOCIAL ORGANIZATION
(a) The whole plant the entire organization
18
(e) The root of the plants the origin of the organization (f) The flowering the best stage, the most successful stage (e) The fruits or crops the beneficial consequences
In the case, constituent elements of plants correspond systematically to
constituent elements of social organizations, such as companies, and the word the
words about plants that are employed systematically in connection with
organization. This correspondence can show in all the mapping, and the matching
expression that make them indicate in the plants metaphor are (b) branch, (c) is
growing, (d) prune, (e) root, (f) blossom, flower (g) fruits.
In the conclusion, we know that a conceptual metaphor is used in the
linguistic expressions that reflect it in such way that we do not violate the mappings
that are conventionally fixed for the linguistic community. In other means, there is
not any element of B which can be mapped into any element of A. The linguistic
expressions used metaphorically must be adaptable established mappings, between
the source and the target.
2.2.3 Source Domain and Target Domain in Metaphor
Source domain and target domain are included in conceptual metaphors,
which are as a set mapping to make understanding about metaphor. The source
domain is typically more concrete and more clearly described concepts, whereas
the target domain is natural abstract and less described concept. Kovecses (2010: )
defines about the direction of conceptual metaphor and also gives explanation to
allow us to understand more in one basic aspect of the cognitive linguistic view of
19
2.2.3.1 Source Domain
The most common source domains, there is the list of sources to briefly
mention in metaphor research especially in the most frequent sources:
a) The Human Body
The human body is included the source domain because it is clearly
delineated. The aspects which are used in metaphorical comprehension
involve various part in the body likes the head, face, hands, legs, heart,
and etc.
For example: The heart of the problem
b) Health and Illness
Both of health and illness frequently constitute metaphorical source
domains.
For example: She hurt my feelings
c) Animals
The animals are productive as source domain in metaphor. The body
parts of animals are also commonly used in the metaphorical
conceptualized of abstract domains. The metaphorical use of animal
terms is not limited to human beings.
For example: It will be a bitch to pull this boat out of the water.
d) Plants
Plants become the variety of purposes and different things in the concept
20
growth in relation to plants. One of the cases is that people cultivate
plants for eating, for pleasure, for making things, and so on.
For example: Exports flourished last year and He cultivated his
friendship with her.
e) Buildings and Constructional
Both the static object and the act of building are served as common
metaphoric source domain.
For example: A towering genius
f) Machines and Tools
Both the machines and tools are the activities related as metaphorical
expression. People use machines and tool to work, play, or for pleasure.
For example: The machine of democracy
g) Games and Sport
Games and sport are characterized by certain properties that are used for
metaphorical purpose. People play and do activities to entertain
themselves.
For example: To toy with the idea
h) Money and Economic Transactions
People living in human society have relation in economic transactions
of various kinds. The understanding of various abstract things is based
on the example:
Spends your time wisely
21
Cooking is included a complex process of several elements likes recipe,
ingredients, action, and also product. The activity and product are served
as a source domain.
For example: what your recipe for success?
j) Heat and Cold
Heat and cold are basic human experiences. It is the result of the
temperature. We often use the temperature domain metaphorically to
talk about attitude people and things. For example: in the heat of passion
k) Light and Darkness
Light and darkness are also human experience. The properties of light
and darkness often appear as condition when people speak and think
metaphorically.
For example: a dark mood
l) Forces
Kinds of forces are gravitational, magnetic, electric, etc. And also the
forces take many shapes in the physical words like waves, wind, storm,
etc. There are many different effects as there are different forces. For
example: Don’t push me m) Movement and Direction
Movement can involve a change of location. It has connection with
direction like forward and backward and up and down. The various
kinds are conceptualized metaphorically as movement that involves a
22
For example: she solved the problem step by step
In the discussion, common source domain includes the various properties of
object and substances, such as their shape, color, size, hardness, sharpness, and so
on. The representative of the source domain lists gives sense of the most common
source domains and the kind of world that our most common metaphor portrays.
The objects and substances from the list of source domain are the simple nature of
the world that enable people to make use of parts in creating more complex abstract
as metaphor.
2.2.3.2 Target Domain
The targets have several sources as the source domains applied to several
targets in metaphorical conceptualization. There are the most common target
domains:
a) Emotion
The domain of emotion is superior in target domain. Emotion concepts
such as fear, love, sadness, and so on are understood by means of
conceptual metaphors. For example: He was bursting with joy
b) Desire
Desire is similar with emotion in metaphorical conceptualization. For
example: she is hungry for knowledge.
c) Morality
Moral is such as good and bad, which are understood by means of more
23
d) Thought
Rational thought is understood in terms of perception. Human tries to
understand the mind by resorting to metaphors in various kinds. For
example: she is grinding out new ideas.
e) Society / Nation
The concepts of society and nation are complex or calls for
metaphorical understanding. For example: neighboring countries
f) Politics
Politic has power in the exercise. Political power is conceptualized as
physical force. Politic has many variety aspects of further source
domains such as games, sport, business, and war. For example: The
president plays hardball
g) Human relationship
Human relationships include concepts as friendship, love, and
marriage. For example: Their friendship is in full flower.
h) Communication
Human communication involves a speaker and a hearer. It is viewed in
linguistic expression to transfer the message from the speaker to the
hearer. For example: That is a dense paragraph.
i) Time
Time is difficult concept to understand in the major of metaphor. Time
24
j) Life and Death
Life and death are included in every language of the metaphorical
concept. For example: The baby will arrive soon.
k) Religion
Religion has key aspect in relationship to God. Other aspects of
religious experience involve the conceptualization of such nations, life
and death, which are necessarily metaphorical.
l) Events and Actions
Events and actions are concepts that comprise a variety of different
kinds of events and actions. The aspects of events and actions are
understood as movement and force. For example: You are driving me
nuts.
It can be seen in the discussion that the common target domains are
classified as psychological, social groups, personal experience, and so on. The
several different sources of information are not permanent to concern in the most
common source and target domain. Hence, the conclusion of the conceptual
metaphors is unidirectional. It works from concrete to abstract domains. The most
common source domains are concrete while the most common targets are abstract
concepts.
2.3 Metaphor Coherence in Discourse
Lakoff and Johnson (1980: 124-125) argue that metaphorical coherence is
25
while the systematic natural is related to the idea with underlying conceptual
structure. It means that the concept, the activity, and the language are
metaphorically structured. The essence of metaphor is understanding and
experiencing one kind of thing in terms of another. Whereas, Kovecses (2010:
285-289) also argues that metaphor has creativity that appears in discourse. Through
conceptual domain of metaphor, the human is creative in language and it is though.
One of the aspects of discourse in coherence metaphors is the intertextual or
intratextual. Metaphors can either make several different texts coherence with each
other or coherence to a single part of discourse.
a) Intertextual Coherence
Intertextual coherence occurs through inheriting and using
conceptual metaphor at different historical period. This type of
intertextuality is about many other domains within the same
historical period. Therefore, metaphor can give coherence across a
variety of discourse both historically and simultaneously.
For example: the prayer of bible in bookmark Durham cathedral
Who called your servent Cuthbert From keeping sheep to follow your son And to be shepherd of your people
The basic conceptual metaphor in the shepherd is Jesus. Source is
the shepherd and target is Jesus. Later, this metaphor God called a
simple man, called Cuthbert, and become “shepherd of people”.
26
particular values of the metaphor in the text always chance with the
appropriate of historical period.
b) Intratextual Coherence
Intratextual coherence is the same conceptual metaphor that can give
coherence to a single word. The metaphor that structures the
discourse not only focuses on conventional conceptual metaphor but
also can call a Metaphorical Analogy. Clearly, the metaphor is a
common rhetorical function which is assigned to perform in
discourse. Conceptual metaphors or metaphorical analogies have the
effect of taking over what the people say or think about a subject
matter. In addition, conceptual metaphors or metaphorical analogies
can become rule of the entire discourse.
For example: The newspaper article
Performance targets are identical to the puissance at
the Horse of the Year Show. You know the one-the
high-jump competition, where the poor, dumb horse
is brought into the ring,…….”
In this case, puissance horses are compared “to people”, this shows that the elaboration of the metaphorical analogy provides a great deal of
structure for the text. Most of the structure of the text is given in the part of
metaphor to suggest what the analogy is about. Therefore, metaphorical
analogies appear in text in order to get the effect of taking over what
27
2.4 Metaphors in Advertisement
Forceville (2008: 272-310) states that metaphor is the attractive and the
efficient way to make costumers interested in the product. It also makes positive
impact for the products, brands, or service in advertisement. Metaphor studies not
only about language but also the pictorial or visual metaphor which is developed in
the advertisement, particularly in the field of print advertising and billboards.
Conceptual metaphor as source domain and target domain is included to play role
in the identification and interpretation of the metaphor meaning in advertisement.
2.4.1 Types of Metaphors in Advertisement
According to Forceville (2008: 272-310), he suggests that there are three
types in the analysis of pictorial metaphor in the printed advertisement and
billboards:
a) Verbal metaphors are textual written language used to convey meaning
of the first subject. It means that the word is completely textual and has
no contained image to accompany of any kind.
b) Pictorial metaphors use image for the first element, without words or
any text accompanying the visual image. The concept of pictorial
metaphor is usually used in the printed advertisement and billboards.
c) Verbo-pictorial metaphors is a combination of images and words as the
primary subject in presentation. Moreover, the combination of the verbal
and visual elements can make the meaning of metaphors clear. Nothing
28
2.5 Slogan
According to Foster (2010: 2-23), the main function of the slogan is to
convey the key brand message in the mind of the target and to give the message that
the company pretends to transmit for the target of audience. Slogan is usually a brief
and an easy to memorable statement that is connected with the product. The ability
of slogan, as well relevant to communicate the function, leads us to consider it as
strategic elements. Slogans are used as part of marketing activity to describe
consumer attention, communicate a brand premise and enhance consumer memory
of the brand. In addition, there are some characteristics of the slogans in
advertisement:
• It should be memorable
• It should recall the brand name
• It should include a key benefit
• It should impart positive feelings for the brand
• It should reflect the brand's personality
• It should be strategic
• It should be competitive
• It should be simple
2.6 Tourism destination management
The benefit of tourism can help for sending peace and prosperity to develop
countries by providing jobs, generating income, diversifying the economy,
29
tourism becomes the important thing in the global economy (Honey and Gilpin,
2009).
Everyone in the world also has interest in travelling in the tourism
destination. There are various reasons about why people travel. The variety of
reasons is to escape, to explore, to understand, and to participate. In fact, the main
point of why people choose the destination to get experience of the place is because
it becomes something interesting for the traveler to keep it forever and share with
others. This helps the destinations to be put in the strategic place and programs that
will be an invitation for visitors as the purpose of their journey. Destination
management organizations (DMO) are the only thing recommend for a holistic
tourism industry in a place. Moreover, DMO becomes the best serve to facilitate
dialogue among the private sector, public sector, and other sector for destination’s
long tourism. DMO also proves invaluable for supporting tourism development,
especially in developing destination where tourism is an important economic driver
30
CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
The purpose of this chapter is to present the methodology of the research
study about metaphor in slogan of ASEAN tourism destination advertisement. This
part of the methodology of the research consist of research design, research
instrument, subject of the research, data and data source, data collection, and data
analysis. Determination of the sample will also be explained. Methods examined
will be those for coding, collection, and analysis of the data through the research
study.
3.1Research Design
The researcher used qualitative content analysis in her study. Krippendorff
(1989: 403-404) defines that content analysis is research techniques for making the
data to their context. And the data of content analysis are texts, which meaning is
conventionally likes verbal discourse and written documents. The text can be found
in newspaper, magazine, advertisement, books, television programming, and etc.
Qualitative content analysis is made researcher to get deeply investigate the data in
advertisement. The researcher analyzed about the context of type metaphor in
slogan of ASEAN tourism destination advertisement and also analyzed about the
coherence discourse of the text in slogan of ASEAN tourism destination
advertisement through the metaphor.
Moreover, the researcher also used descriptive research design in analyzing the
31
of different kinds, and has purpose to describe of the state of affairs as exist at
present. Researcher has no control over about the variable, which it can only report
what is happening or what has happened.
3.2Subject of The Study
The subject for this present study is slogan tourism advertisement of ASEAN
countries. Slogan is become brand in advertisement, especially for every country in
ASEAN has slogan to support the quality of tourism. Slogan is also become the
selling power to promote special quality tourism in every country. In the world of
tourism, slogan has great impact for performance economic advancement, which is
slogan purposed to attractive tourist for visiting tourism destination in every
country.
Therefore, the researcher has reason to pick slogan tourism advertisement as the
subject in this thesis is contained metaphor elements. Slogan in the advertisement
described that slogan has implicit meaning of the text, which it can be understood
if the reader knows about the whole context of slogan itself. The characteristic of
text in slogan tourism interested the researcher to conduct research about slogan in
case of metaphor. The researcher completed the analysis with some theories to
support this research. Conceptual metaphor is the appropriate theory in slogan
tourism and linguistic features like discourse are also required to support the
32
3.3Data and Data Source
The research is used the primary data. Kothari (1990: 95) argue that the primary
data is collected by someone in a fresh and for the first time. The data source of the
research was taken from content of advertisement – the picture of slogan and videos advertisement. The slogan tourism of ASEAN is contained 10 pictures, which only
10 countries of 11 countries have slogans tourism in the official tourism destination.
The countries are Indonesia, Malaysia, Singapore, Vietnam, Thailand, Myanmar,
Cambodia, Laos, Philippine, and Brunei Darussalam.
The researcher downloaded the picture of slogan and videos from the source
from www.sportourism.id/tourism/logo.com and www.youtube.com on February
15, 2017. Therefore, this research used the whole text and image of picture in the
slogan tourism to be the data. And also the researcher used transcript of videos to
support the analysis.
3.4Research Instrument
The instrument of this research was the researcher herself. It means that the
research instrument of research called as human instrument. Denzin and Lincoln as
cited in Simon (2011: 1) argue that a qualitative study is used human as instrument
rather than questionnaires or machines. Kothari (1990: 3-4) noticed that qualitative
studies is concerned with qualitative phenomenon, which it closed with the human
behavior. It means that to find how the people feel or what they are think about a
33
Human instrument was applied in the research because the collecting and
identification of content of slogan tourism of ASEAN were found by researcher
herself. The types of metaphor and the coherence metaphor of text in slogan tourism
of ASEAN advertisement were collected and identified by the researcher herself.
The researcher collecting the data after read the whole content of slogan.
3.5Techniques of Data Collection
The data collected from the content of advertising slogan of ASEAN tourism
destination. The data are the language (written text) and image of metaphor.
a. Downloading advertising slogan of ASEAN tourism destination.
The beginning analysis of doing research is obtaining the data source.
In the case, the data source is contained text and image of the slogan.
Thus, the researcher collected the data research by browsing the jpg
version of slogan of ASEAN tourism destination. Therefore, the
researcher also downloaded video promotion tourism and transcript to
support the analysis. The researcher downloaded the picture of slogan
and videos from the source from:
www.sportourism.id/tourism/logo.com and www.youtube.com on
February 15, 2017.
b. Comprehension the data
The researcher read slogan advertisement to get understanding the
content of every advertising slogan in ASEAN. And also watch video
34
totally understand the slogan well. Furthermore, the researcher also
found great idea about what the slogan mean is.
c. Coding the data of the advertisement slogan
The researcher proper coding the data source had to be defined for
analyzing about the type of metaphor, the researcher making easy to
code the data source in the research. The types of metaphor are pictorial
metaphor, verbal metaphor and verbo-pictorial metaphor. The three
highest classifications of metaphor are pictorial, verbal, and
verbo-pictorial metaphors, denoted by P, V, and VP. Furthermore, the
researcher also will code for analyzing about text in the coherence
metaphor in discourse through the intertextual or intratextual. It
[image:44.595.138.547.196.596.2]denoted with type 1 as intertextual and type 2 as intratextual.
Figure 3.1 Example of coding data in advertisement slogan
d. Collecting Data
The researcher collected the data in one points to answer two research
questions in the research. Collecting the data for types of metaphor in
35
collected the whole content of slogan without exceptional, which it is
contained about text and image in slogan. After collecting the data for
types of metaphor in advertisement, the research automatically gets the
data for analyzing about the coherence text of slogan in advertisement.
Researcher is only taken the text for the data. The data collected was
described as the example below.
Figure 3.2 Example of Collecting Data for type of metaphor in
advertisement and the coherence text of slogan in advertisement
The example of collecting data was processed in the next procedure
that is data analysis.
3.6Techniques of Data Analysis
Data analysis was separated into two concerns in the research. The first
focus is type of metaphor in advertisement. Furthermore, the second focus is the
coherence text of slogan in advertisement, which the second focus is become the
final result of this research. The procedures were explained in the detail below.
[image:45.595.140.504.243.548.2]
36
a. Identifying the data
- Type of metaphor in advertisement
In the analysis, the collected data was identified by highlighting content
in slogan. Highlighting was appeared in two colors in the analysis. Each
color has different meaning related to identify the type of metaphor in
advertisement. The data identification was highlighted as the example.
Figure 3.4 Example of identifying the collected data for type of
metaphor in advertisement
The content of slogan is represented with different color, which is
divided for analyzing type of metaphor in advertisement. It presented
in the table below.
Slogan Content of Slogan
Picture text
Indonesia ✓ ✓
Table 3.1 The Rule of identifying type metaphor in slogan 1/ picture
[image:46.595.187.500.593.684.2]
37
- The coherence text of slogan in advertisement
After collecting and identifying the data for type of metaphor in
advertisement, the researcher go to the second case, it is about the
coherence text of slogan in advertisement. In the second case,
researcher only needs text from the slogan. The coherence of text has
two kinds in metaphor related discourse. The kind is intertextual or
intratextual. This below example explained how the researcher
identification the data.
“Wonderful Indonesia”
Figure 3.5 Example of Identifying the Collected Data for the
Coherence Text of Slogan in Advertisement
The texts were divided by underscoring in two different colors as
illustrated in the table below.
Types of underlines
Kind of coherence discourse
in metaphor based on text
Intertextual (Type 1)
[image:47.595.135.514.265.685.2]Intratextual (Type 2)
Table 3.2 The Rule of identifying the coherence of text in
38
b. Classifying the data
- Type of metaphor in advertisement
After collecting and identifying data for type of metaphor in
advertisement which came from label of content slogan, researcher
needed to describe the data to know the meaning of each data in slogan.
And the data also explains to know clearly classification in the table.
Data:
The advertising slogan of Indonesia is used “VP”. The slogan contained
the picture is mythical bird, which is became symbol of Indonesia
country and the slogan also cointained the text “Wonderful Indonesia”.
Figure 3.6 Example of Describing Type of Metaphor in
Advertisement
1/ image
[image:48.595.138.514.204.554.2][image:49.595.125.513.115.532.2]
39
Table 3.3 Example of Classifying the Data for Type of Metaphor
Then, the data was charted to compare the percentage between types of
metaphor. The chart consist three types, which are pictorial metaphor,
verbal metaphor, and verbo-pictorial metaphor. The researcher wants to
compare the common type of metaphor in advertisement.
- The coherence text of slogan in advertisement
In this case, researcher needed to describe the data in order that to know
about the coherence text of each other in slogan. The researcher also
needed to show the classification the data in the table.
No. Slogan P V VP
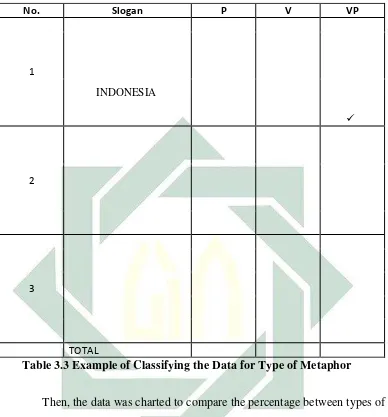
1
INDONESIA
✓
2
3
40
Data:
“Wonderful Indonesia”
[image:50.595.138.511.265.557.2]The coherence text: “Wonderful” is compared with the world cultural heritage humanity. (1:44)
Figure 3.7 Example of Describing the Coherence Text
After that, the researcher categorized the data with the table below.
Table 3.4 Example of Classifying the Data for Type of Metaphor
In the analysis, Researcher was used the chart to show the
percentage between type 1 and type 2 labels. The chart was helped
researcher to choose about the result of the common type in the
coherence text in slogan.
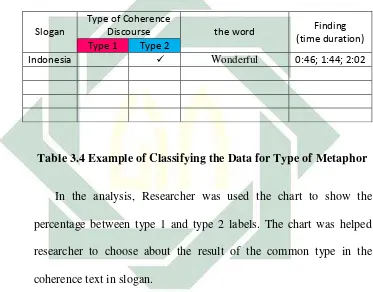
Slogan
Type of Coherence
Discourse the word Finding (time duration) Type 1 Type 2
Indonesia ✓ Wonderful 0:46; 1:44; 2:02
41
CHAPTER IV
FINDINGS AND DISCUSSION
This chapter will present the findings of the performed research analysis as
discussed in chapter methodology. The result from the two-research question will
be examined and compared in detail. Research findings will be discussed in general
term.
4.1 Findings
This present study creates several results of the data analysis. Type of
metaphor in advertisement as the first finding that have three types in analysis. They
are pictorial metaphor, verbal metaphor, and verbo-pictorial metaphor. In addition,
the coherence text of slogan ASEAN tourism is presented the second findings as
coherence metaphor in discourse, which has intratextual and intertextual types.
4.1.1 Type of Metaphor in Advertisement
Type of metaphor in advertisement is the first data analyzed in this study.
The researcher collects all slogan tourisms contain as image and text to produce the
result in study. Eventually, there are 10 slogans which contain some promotion as
image and text. This below chart presents type of metaphor in advertisement used
[image:52.595.116.512.104.558.2]
42
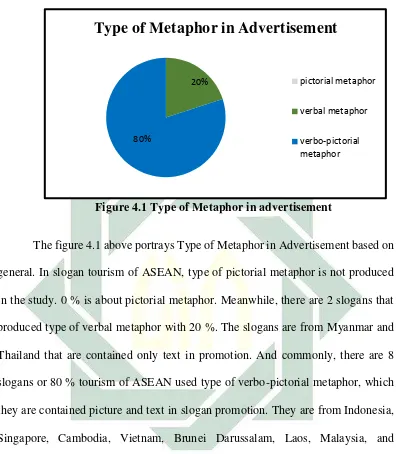
Figure 4.1 Type of Metaphor in advertisement
The figure 4.1 above portrays Type of Metaphor in Advertisement based on
general. In slogan tourism of ASEAN, type of pictorial metaphor is not produced
in the study. 0 % is about pictorial metaphor. Meanwhile, there are 2 slogans that
produced type of verbal metaphor with 20 %. The slogans are from Myanmar and
Thailand that are contained only text in promotion. And commonly, there are 8
slogans or 80 % tourism of ASEAN used type of verbo-pictorial metaphor, which
they are contained picture and text in slogan promotion. They are from Indonesia,
Singapore, Cambodia, Vietnam, Brunei Darussalam, Laos, Malaysia, and
Philippines. The content of each slogan are explained in table 4.1 below. 20%
80%
Type of Metaphor in Advertisement
pictorial metaphor
verbal metaphor
[image:53.595.117.506.110.530.2]
43
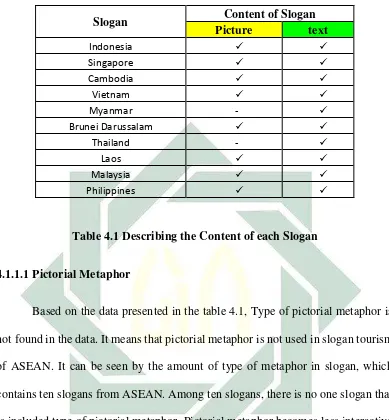
Table 4.1 Describing the Content of each Slogan
4.1.1.1 Pictorial Metaphor
Based on the data presented in the table 4.1, Type of pictorial metaphor is
not found in the data. It means that pictorial metaphor is not used in slogan tourism
of ASEAN. It can be seen by the amount of type of metaphor in slogan, which
contains ten slogans from ASEAN. Among ten slogans, there is no one slogan that
is included type of pictorial metaphor. Pictorial metaphor becomes less interactive
type for promoting as slogan tourism because the type is only focus about picture
to promote anything in advertisement.
4.1.1.2 Verbal Metaphor
Verbal metaphor becomes the minority type in the data. Based on the data
presented in the figure 4.1 and the table 4.1, verbal metaphor is only contained in
one slogan. Among ten slogans tourism from ASEAN, there is one slogan that is
type of verbal metaphor. Verbal metaphor is only focus about text, which is not
Slogan Content of Slogan
Picture text
Indonesia ✓ ✓
Singapore ✓ ✓
Cambodia ✓ ✓
Vietnam ✓ ✓
Myanmar - ✓
Brunei Darussalam ✓ ✓
Thailand - ✓
Laos ✓ ✓
Malaysia ✓ ✓
44
included picture to support promotion in advertisement. According to Forceville
(2008: 272-310), Verbal metaphors are textual written language used to convey
meaning of the first subject. It means that the word is completely textual and has no
contained image to accompany of any kind. This type seldom is used for promoting
slogan because the type is little interest to use in advertisement. Furthermore, type
of verbal metaphor found in the data is slogan from Myanmar. Besides, the others
slogan are not found in this type. It is obviously elaborated below.
1) Myanmar
Myanmar’s slogan is included type of verbal metaphor in slogan
tourism of ASEAN. Myanmar is become one of slogan which contain
text in advertisement. It is equal to 10 % from 20 % the amount of verbal
metaphor percentage in the entire data of slogan tourism in ASEAN.
Based on the data analyzed, the researcher found “text” in slogan from
Myanmar. It is illustrated in Data 1 as followed.
Data 1
The text “Myanmar let the journey begin” which is sign with
highlighted by yellow color in slogan of Data 1 is classified as one of
text
45
the type of V. Specifically, this slogan is categorized as V because it
contain only text in slogan tourism promotion. Yu (2009: 24) clarifies
that since advertising slogans carry the property of context, there is
possible interpretation the slogan of a single focus.
The existence of V in slogan of Myanmar is contained the text
““Myanmar let the journey begin” to promote about tourism destination
from the country. The slogan is only used one subject to convey meaning
about the feature of tourism in advertisement. The subject of the slogan
is text “Myanmar let the journey begin”, which has meaning about
Myanmar become the first country to start journey in the world. When
the people read the slogan, every people have different meaning from the
slogan. But the point is “Myanmar let the journey begin”.
It can be concluded that Data 1 is generally represent as V. The
slogan of Myanmar is only contained with text to convey meaning to the
reader. The use of V is generally focused about textual as word, which is
no picture to support this slogan.
2) Thailand
There is slogan of Thailand which is categorized as V. Thailand’s
slogan is included V because there is only contained the text in slogan.
This slogan supports 10 % of 20 % the amount of V in percentage the
46
Data 2
The above of Data 2 is slogan from Thailand which is represents
type of Vin slogan. The Thailand’s slogan tells that Slogan consist one
subject to promote about tourism in advertisement. Therefore, Thailand
is given only one focus of the text in the slogan to promote tourism