i
A STUDY OF COGNITIVE STRATEGIES IN LEARNING SPEAKING USED BY THE SECOND SEMESTER STUDENTS OF ENGLISH EDUCATION DEPARTMENT AT ALAUDDIN STATE ISLAMIC
UNIVERSITY
A Thesis
Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Sarjana Penididikan in English Education Department of
Tarbiyah and Teaching Science Faculty of UIN Alauddin Makassar
By : A. NUR ALANG Reg. Number: 20400113096
ENGLISH EDUCATION DEPARTMENT
TARBIYAH AND TEACHING SCIENCE FACULTY ALAUDDIN STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY OF MAKASSAR
ii
iv
v
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Alhamdulillahi Rabbil Alamin, all praises and gratitude to the Almighty God Allah SWT for all blessing and mercies that the researcher has had in life. This undergraduate thesis entitled A Study of Cognitive Strategies in Learning Speaking Used by The Second Semester Students of English Education
Department at Alauddin State Islamic University is submitted as the final requirement in accomplishing undergraduate degree at English Education Department of Tarbiyah and Teaching Science Faculty, UIN Alauddin Makassar.
In arranging this thesis, a lot of people have provided motivation, advice, and support for the researcher. In this valuable chance, the researcher intended to express her gratitude and appreciation to all of them.
The special thanks present to her parents, A.Usman and Kartini for their sincere prayers, love, advice, and sacrifices for her success.The researcher presents her sincere appreciation goes to:
1. Prof. Dr. Musafir Pababbari, M.Si. as the Rector of UIN Alauddin Makassar.
2. Dr. Muhammad Amri Lc., M. Ag. as the Dean of Tarbiyah and Teaching Science Faculty of UIN Alauddin Makassar.
3. Dr. Kamsinah, M.Pd.I, as the Head and the Secretary of English Education Department of Tarbiyah and Teaching Science Faculty of UIN Alauddin
vi
vi
4. Also this thesis would not have been possible without the help, support and patience of my first advisor, Dra. St. Azisah, M.Ed.St.,Ph.D for her supervision, advice, and guidance from the very early stage of this research as well as giving me extraordinary experiences throughout the past few years. Then to my second advisor Andi Asmawati, S.Pd.,M.Pd who has helped researcher patiently finishing this undergraduate thesis by giving suggestion, guidance, and correction until the completion of this thesis.
5. Special thanks to English Education Department students in second semester who sincerely helped the researcher in this study by being subject of this research.
6. Also to the entire brothers and sisters of English Education Department group 5 and 6 who cannot be mentioned here one by one.
7. Finally, the writer would like to thank everybody who was important to the successful realization of this undergraduate thesis.
This undergraduate thesis is far from perfect, but it is expected that it will be useful not only for the researcher, but also for the readers. For this reason, constructive thoughtfull suggestion and critics are welcomed.
The last, may all our efforts are blessed by Allah SWT. Amiin.
Samata-Gowa, 28 Agustus 2017 The Researcher
viii
viii
CHAPTER III : RESEARCH METHOD ... 20
A. Research Method ... 20
B. Research Subject and Location ... 20
C. Research Instruments... 21
D. Data Collection Procedure ... 21
E. Data Analysis Technique ... 22
CHAPTER IV : FINDINGS AND DISCUSSION ... 25
A. Findings ... 25
1. Kinds of Students‟ Cognitive Strategy in Learning Speaking ... 25
2. The Impact of Cognitive Strategy Toward Students‟ Speaking Performance ... 31
B. Discussion ... 35
CHAPTER V : CONCLUSSION AND SUGGESTION ... 38
A. Conclussions ... 38
B. Suggestions ... 39
BIBLIOGRAPHY ... 41
ix
LIST OF TABLE
Table 3.1 : The Score Criteria of Speaking Accuracy ... 26
Table 3.2 : The Score Criteria of Speaking Fluency ... 27
Table 3.3 : The Score Criteria of Speaking Comprehensibility ... 28
x
x
LIST OF FIGURE
Figure 2.1: Theoretical framework of cognitive strategies in learning
xi
LIST OF APPENDIXES
Appendix I : Interview question Appendix II : Interview transcription
xii
A Study of Cognitive Strategies in Learning Speaking Used by The Second Semester Students of English Education Department at Alauddin State Islamic University
Consultant I: Dra. Hj. St. Azisah, M.Ed.St.,Ph.D Concultant I: Andi Asmawati, S.Pd.,M.Pd.
This study was about the cognitive strategy of the second semester students in learning English speaking at English Education Department at Alauddin Islamic State University of Makassar. There were two research problems that formulated in this reseasrch they were (1) what are the kinds of cognitive strategies used in English speaking class, and (2) what is the impact of cognitive strategies toward students‟ speaking performance. The aim of this research are (1) to find out the kinds of cognitive strategies used in English speaking class, (2) to find out the impact of cognitive strategies toward students‟ speaking performance.
The study was designed in the form of descriptive qualitative method. Interview and observation were committed by the researcher to help her in arranging the data. Subject in this research were 90 students in the second semester majoring English Education Department of Tarbiyah and Teaching Science Faculty at Alauddin State Islamic University. Furthermore, there were four students who were interviewed and those 90 students were observed while they were in speaking class learning. The data were analyzed trough four procedures models from Miles and Huberman (1994) that are data collection, data reduction, data display and data verification.
1 CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION
This chapter consists of background explanation, research problem, research objective, research significant, research scope and operational definition of term that is explained as follow.
A.Background
Nowadays, English becomes an international language of United Nation. All countries that come to be the part of United Nation use English language to communicate in both oral and written language. It can be seen when a president or a diplomat of a country speech, he/ she uses English language in international meeting and conference of United Nation.
Indonesia is a member of United Nation. As the part of United Nation, Indonesian people use English language in both international and national events such as international conference and seminar. Not only that, English has been used in everyday life. To operate Phone and Computer it needs English language. Person who wants to send message has to know the meaning of some words like message, inbox, receive, number and many more.
2
Speaking is part of productive skills and it also one of skill that should be increased by students because to know the progress of students‟ learning is by seeing their speaking skills. Speaking is the way where students express themselves, their ideas or information to share with others. By speaking, people can explore what in their mind, like information or asking help, easily and quickly. Among the four language skills speaking is viewed to be at the heart of second language learning (Egan, 1999).
Since the successful of learners‟ language learning is measured by
observing their performance or oral ability many learners want to be good in speaking. They try to develop their oral ability by applying some strategies. Strategy is very helpful tool for people to do their job, especially for learners it makes their learning process easily and quickly because they know what will they do.
competence indicates the ability to us e techniques or strategies in order to overcome limitations in the language or to get the message across.
The use of appropriate strategies will help students in solving and clearing their problems and difficulties in learning speaking. Not only that, students will also be more creative and attractive in comprehending of some materials and upgrading their speaking skills.
One of learning strategies that students‟ use is cognitive strategy. According to some research, cognitive strategies have some particular strategies that are effective on different kinds of tasks. It examines strategies that have proven to be effective in comprehending, writing, solving problem, reasoning, and discussing several affective domain-general strategies for general self-regulation.
4
B.Research Problems
In terms of cognitive strategies in learning speaking, the research problems of the research are:
1. What are the kinds of cognitive strategies used in English speaking class? 2. What is the impact of cognitive strategies toward students‟ speaking
performance?
C.Research Objectives
Related to the research problems above, the objectives of the research are: 1. To find out the kinds of cognitive strategies used in English speaking class. 2. To find out the impact of cognitive strategies toward students‟ speaking
performance.
D. Research Significance
The results of this study are expected to have positive contribution for the development of second or foreign language teaching and learning.
1. Theoretical Significance
This study is expected to be useful information for teacher, students and government. This study will improve their knowledge about language learning strategy which has a big value to improve the education system particularly in teaching and learning speaking. Especially for teacher and students this can help them to understand well what cognitive strategies are and its contribution in upgrading speaking competence.
a. For teacher
From this study, researcher hopes it can give the value contribution especially for English teachers to interact with their students while they teach in the classroom especially in teaching speaking skill.
b. For students
By knowing these strategies, researcher expects students will be more attractive in learning speaking, they can apply cognitive strategies to enhance their speaking learning process.
c. For teaching and learning process
From this study, the researcher assumes that it can give contribution for the English Language Teaching mainly in speaking. Hopely, it brings the positive effect in speaking teaching and learning process, so it will be running well.
d. For government
For the government, it is expected to be useful information as well that they will realize the importance of the language learning strategies particularly cognitive strategies in increasing students‟ speaking ability to be well understood by the teachers and students, therefore, they will support and provide a chance for activities that can help the teachers and students to more comprehend about cognitive strategies as one of kinds in language learning strategies.
e. For other researchers
6
E.Research Scope
From all the language learning strategies (LLSs) in EFL classroom and skills which are in English language teaching, the area of this study focused on the cognitive strategies they are practicing, receiving and sending messages, analyzing and reasoning, creating structure for input and output in speaking skill. This study discuss about those kinds of cognitive strategies used in English speaking class since researcher analyzed the cognitive strategies provided by Rebecca L. Oxford.
F. Operational Definition of Terms
This part explains more about the speaking skill and cognitive strategies. 1. Speaking
Speaking, according to the researcher, is the ability to perform the linguistic knowledge in the actual communication by using sound and symbol produced by the speaker to communicate with the listener to share the meaning. Speaking ability is indicated by the use of speaker utterances found in the conversational exchanges which is restricted in the components of speaking accuracy that covers acceptable pronunciation, appropriate vocabulary, and correct grammar, speaking fluency that covers an effort with a fairly wide range of expression, and speaking comprehensibility that covers easy for listener to understand the speakers‟
and sharing meaning through the use of verbal and non-verbal symbols in variety of contexts.
From the description above, it can be concluded that speaking skill is the way of someone delivering information to others which aims to interact with them.
2. Cognitive Strategies
Cognitive strategies are useful tools in assisting students with learning problems. The term "cognitive strategies" in its simplest form is the use of the mind (cognition) to solve a problem or complete a task. This is in line with O‟Malley and Chamot (1987), cognitive strategies, in which the learners interact
8 CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
This part consists of some related research findings, some pertinent ideas, and theoretical framework.
A. Related Research Findings
Some recently researchers have shown that cognitive strategies are very helpful tool to improve students learning process. In this part, researcher gives some research findings to support this study.
The first is from Strakova (2013), studied at Presov University of Slovakia, undertaken a research untitled Developing Cognitive Strategies in Foreign Language Education with research object 22 students at the fourth year in one of Elementary school in Slovakia. The research finding was training of cognitive learning strategies can help students to approach reading in a foreign language.
Third, Khezrlou (2012), students of Tehran University, in his research with title The Relationship between Cognitive and Metacognitive Strategies, Age, and Level of Education stated that that there was a moderate, positive, and significant relationship between cognitive strategies and students‟ reading performances of the adult learners in the TOFL test and also for the young learners.
The last is the presented research by Phakiti (2006) who has done a study with title Modeling Cognitive and Metacognitive Strategies and Their Relationship to EFL Reading Test Performance with research participants the students of Thai University consisted of 358 students. The researcher found that the degree of relationship between strategies varied depending on the function of cognitive processing. The nature of cognitive and metacognitive strategies and their relation to a given foreign language reading test performance could, however, be far more complex than has been detected in this study due to the number of interactions among the constructs, other unmeasured constructs (e.g., automaticity) and the context in which strategy and language use occurred.
To sum up, this study totally differs from those kinds of research in the form of cognitive strategies. Theirs are talking about cognitive strategies in reading while this focused on cognitive strategies in speaking. For that reason, this study was held.
B. Some Pertinent Ideas
10
The term of speaking accuracy in this research is same with Brown (2001) argues that accuracy is achieved to some extent by allowing learners to focus on the element of phonology, grammar, and discourse in their spoken output. By having these three elements of speaking accuracy students will be easier in utterance what in their minds are. Furthermore, in teaching English speaking, the teacher has to explain to the learners to speak accurately (clear, articulate, grammatically, and phonologically correct) language and fluent (flowing and natural) language.
1. Pronunciation
Talking about oral language, which is used in conversational exchanges, pronunciation influences all words used within it. Good pronunciation will guide everyone to communicate well therefore “good language learners do not neglect pronunciation” (Griffiths, 2008). Pronunciation involves far more than individual
sounds. Pronunciation involves too many complexities for learners to strive for a complete elimination of accent, but improving pronunciation will boost self-esteem, facilitate communication, and possibly lead to a better job or a least most respect in the workplace. Effective communication is the greatest importance, so choose first to work on problems that significantly hinder communication.
a) Native pronunciation. Native pronunciation is the way in expressing words by native speaker. The style of his pronunciation is a typical one that is difficult to non-native to do the same thing.
b) Native like pronunciation. Native like pronunciation is the way expressing words by non-native but sounds like a native one, the style of his pronunciation usually found in the countries where English is taught and learned as a second language.
c) Non-native like pronunciation. Non-native like pronunciation is all English learners in countries where English is used as a foreign language. The learners of the language find that it is very difficult to use a non-native like pronunciation. They use the non-native pronunciation means they use their own ability to pronounce the words as it are. It also happens in some countries in Asia.
12
people the goal of native speaker pronunciation was not important but to communicative efficiency. It emphasizes the importance of listening as way to acquiring pronunciation.
Pronunciation is one of the existent elements in English class that should be paid attention by the teacher. During the late 1960‟s and the 1970‟s questions were asked about the role of pronunciation in the EFL curriculum whether the focus of the program and the instructional methods were effective or not. Pronunciation programs until then were viewed as a meaningless no communicative drill-and-exercise gambits.
Regarding with the explanations above, it can be said that pronunciation refers to the way of person pronounces all the words in speaking.
2. Vocabulary
One of the important things that should be mastered in learning language is vocabulary. Because it brings the learners to be able to communicate with others toward their ideas, thoughts, feelings or imagination whether it is in a spoken or in a written way. Vocabulary is word that can be seen, heard, have meaning but someone cannot use a single word to communicate with others, it have to put together with some words to make useful meaning.
Regarding with the statement above, it can be concluded that vocabulary is all the words in the broadest senses used in the language skills (listening, reading, writing, and speaking). It has meaning based on the contest and it is as the stock of words used by the language users.
3. Grammar
Grammar is one of the major language components. Furthermore, Ur (1996) confirmed that grammar is the way words are put together to make correct sentences. It pertains to sentence and word. It figures the categories such as noun subject, imperative clause, and so on. Grammar is a field of linguistic that involves all the various things that make up the rules of language.
Many people often presuppose that speaking communicatively does not require grammar, one only needs to have much vocabulary. However, it sometimes do not realize that by ignoring grammar speakers/listeners can misunderstand which may not be bad in a relax conversation, but it can really have serious effects on a formal conversation.
In addition, in Oxford dictionary, grammar is rules for forming words and making sentences. The word, sentences and even phrases put together by these rules are grammatical in the language concerned. In a slightly wider sense, the grammars of language include the system of connection between grammatical expressions and their meaning and uses.
14
complete meaning that makes easier an understanding not only in written language but also in spoken language.
b. Speaking fluency
In term of fluency, Longman dictionary defines fluency as “mode expressing thought in a language, whether oral or written, especially such use of a language in the expression of thought as exhibits the spirit and faculty of an artist, choice or arrangement of words in discourse, rhetorical expression”.
In addition, Oxford and Burry-Stock (1995) said that fluency is the quality or condition of being fluent. Besides, pronunciation, grammar, vocabulary, the other things that someone uses in processing information are an idea, the conventional relation between idea and words, the connecting moving way of articulation and words and the functional articulation. The four factors above have to exist, if they are not, the strangers of language will happen.
Further, fluency as a part of speaking indicates how well or how smooth a speaker expresses ideas in terms of sentences. Fluency in speaking is the quality of being fluent and it needs the intensity or practices, talent, habit and proper speech.
for a while to find the other words to continue the whole explanation to get the information clear.
In short, fluency shows how good the students speaking while they express their idea that can be known by seeing their expression and how often they stop. c. Speaking Comprehensibility
Comprehensibility is the power of understanding an exercised aimed at improving or testing ones understanding of a language in written or spoken (Hornby, 1984). Moreover, it defines as the ability to understand completely and be aware of understanding whatever said by speaker or toward the topics that are discussed during having conversation.
Comprehension is one of many components that should be paid attention to increase learners‟ speaking ability in order to speak better. There are
pronunciation, structure, vocabulary and fluency. Yet, speaking means making up a language in ordinary way that involving those components.
Basically, there is a number of different ways of getting learners to speak, ranging from asking learners a set of questions to request them to give a detailed presentation. This way aims to get the learners to speak in order to improve his or her comprehension.
In conclusion, comprehension shows students‟ understanding about language and what other people say.
2. Cognitive Strategies
16
step or operation that learners use to process both linguistic and sociolinguistic content, for example retaining what someone had understood, practicing what someone had learned and practicing someone‟s language skills.
In addition, Stern (1992) gave definition about cognitive strategies that it refers to procedures and activities which learners apply to improve their ability to learn or remember the materials, and solve the problems, especially those actions which learners use with specific classroom tasks.
Furthermore, Williams and Burden (1997) stated that cognitive strategies are seen as mental processes directly concerned with the processing of information in order to learn, that is for obtaining, storage, retrieval or use of information.
Moreover, Brown (2007) stated that cognitive strategies are more limited to specific learning tasks and they involve more direct manipulation of the learning material itself. Repetition, resourcing, translation, grouping, note taking, deduction, recombination, imagery, auditory representation, key word, contextualization, elaboration, transfer, and inferencing are among the most important cognitive strategies.
conscious control and we may be at least partly able to verbalize them, so that we can analyze the strategies followed in solving the problem.
In conclusion, cognitive strategies, are mental routines or procedures for accomplishing cognitive goals like solving a problem, studying for a test, or understanding what is being read.
Cognitive strategies are essential in learning a new language. Such strategies are a varied lot, ranging from repeating to analyzing expressions to summarizing (Oxford, 1990). With all their variety, cognitive strategies are unified by a common function: manipulation or transformation of the target language by the learner. Cognitive strategies are typically found to be the most popular strategies with language learners because cognitive strategies were significantly related to the second language proficiency in studies (Ehrman & Oxford, 1995) andPark (1994), among others.
Oxford (1990) said that four sets of cognitive strategies were practicing, strategies for receiving and sending messages, analyzing and reasoning strategies, and creating structure for input and output. First, practicing is the most significant strategy in context of cognitive but many learners sometimes do not recognize the essential of this. Some ways in doing practicing are repeating, formally practicing with sounds and writing systems, recognizing and using formulas and patterns, recombining, and practicing naturalistically.
18
using skimming or scanning technique. Learners may also using resources for receiving and sending messages to make their learning more attractive.
Third, analyzing and reasoning strategies are commonly used by language learners. Many learners, especially adults tend to “reason out” the new language,
they construct a formal model in their minds based on analysis and comparison, create general rules, and revise those rules when new information is available (Oxford, 1990). Some strategies included are reasoning deductively, analyzing expression, analyzing contrastively (across language), translating, and transferring the idea.
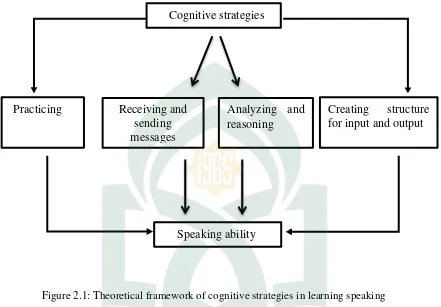
C. Theoretical Framework
Figure 2.1: Theoretical framework of cognitive strategies in learning speaking
Based on the theoretical framework above, this study focused on cognitive strategies. There four kinds of cognitive strategies they are practicing, receiving and sending messages, analyzing and reasoning, and creating structure for input and output. The researcher analyzed more about those kinds of cognitive strategies to know which kinds that the students use in speaking class and to know the effect of those strategies to the speaking ability of the students of English Education Department at Islamic State University of Alauddin Makassar.
Speaking ability Practicing Receiving and
sending messages
Analyzing and reasoning
20 CHAPTER III RESEARCH METHOD
This chapter consist research method, research subject, research instrument, data collection procedure, and data analysis technique. The following are those descriptions.
A. Research Method
In this study, researcher used descriptive qualitative research method to describe what kinds of cognitive strategies used by the students in the speaking class and what the impact of those strategies since these strategies would be clear and applicable to be explained in descriptively rather than numerically.
B. Research Subject and Location
C.Research Instrument
It had been known that the main instrument of qualitative research is the researcher herself. But, to finish this study, researcher needed a helpful tool in acquiring information and data effectively. Hence, the secondary instruments used were interview text and observation. In this study the researcher used structured interview. Structured interviewed had a specified a set of questions that elicit specific information from participants. It allows the qualitative researcher to ask all of the participants the same series of questions (Gay, Mills & Airasian, 2006). Interview was used to gather information about cognitive strategies that learners use and observation is used to help researcher to find out information more valid. In term of observation, the researcher took nonparticipant observation (external observation) where the observer is not directly involved in the situation being observed. The researcher only observed and recorded behaviors but did not interact or participate in the life of the setting being studied (Gay, Mills & Airasian, 2006). Further, video recorder or audio recorder needed to record the students while interview held and running the observation.
D.Data Collection Procedure
The data of this research was collected by observation and interview. The first step of this research was observing the students classroom activities. Whilst researcher observed the students‟ activity, she also made a note. The observation
took place in the class of PBI group 1 and group 2 and it started at 08.00 until 09.40 o‟clock in the morning on 22nd
22
class. The researcher was also observing the use of cognitive strategy in their learning process.
Subsequently, the interview was held directly after the observation process. The researcher chose four students to be interviewed. The researcher interviewed the students one by one on 23rd to 24th March, 2017. The interview took two places that were at students‟ boarding house and at university area with
duration about 10 minutes each student. There were eleven number of question that asked to the students. Kind of the interview was structured interview and it was also functioned as speaking test for students. It was done to know the impact of cognitive strategy toward their speaking. The questions in interview text asked to the students deal with the cognitive strategies used in EFL classroom. While the observation and interview were held, the researcher also recorded all the process to be transcribed and analyzed.
E. Data Analysis Technique
1. Data Collection
As mention in the sentence previously, the activity of data collection is a cyclical and interactive process. Thus, during the data collection the researcher circulated among these four steps continually in order to grasp all of the information needed in the next steps of data analysis. Accordingly, in this step, the researcher tried to find out the unripe data that would be reduced, displayed, and concluded in the next step.
2. Data Reduction
According to Milles and Huberman (1994), “data reduction refers to the process of selecting, focusing, simplifying, abstracting, and transforming the data that appear in written-up field notes or transcriptions”. They further point out the data reduction or data condensation process was varied in several ways, such as through selection, summary or paraphrase and being subsume in larger pattern. Simply in this step, in analyzing students‟ cognitive strategies, researcher classified and organized data after transcription process.
3. Data Display
24
4. Conclusion drawing and Verification
25 CHAPTER IV
FINDINGS AND DISCUSSION
This chapter presented the findings of research and its discussion. The findings and discussion presented the kinds of cognitive strategy and the impact of cognitive strategy toward students‟ performance.
A.Findings
1. Kinds of Students’ Cognitive Strategy in Learning Speaking
As stated earlier, the subject of this research was the second semester students of English major at State Islamic University of Makassar. To know the kinds of cognitive strategies in learning speaking, researcher conducted an observation in the classroom and chose four students to be interviewed. Based on the observation and interview the researcher collected the data which referred to the answer of research problem of this research that was about cognitive learning strategies in speaking which deals with Oxford that were practicing, receiving and sending messages, analyzing and reasoning, creating structure for input and output.
26
After the researcher conducted observation and interview, the researcher transcribed the data for categorizing the cognitive strategies in speaking used by the second semester students of State Islamic University of Makassar.
Cognitive strategies were more limited to specific learning tasks and they involve more direct manipulation of the learning material itself. Cognitive strategy was one of learning strategy that applied by the second semester students of English major at State Islamic University to gain their objective in learning that was increasing their speaking ability. It was proven with their answers when interview process, cognitive strategy is learning strategy about using our mind in increasing English specially speaking (Sakura, interviewed on 24th March, 2017).
Based on observation and interview result, the strategies worked by all of the actions or activities done by students. Strategies described the learning action employed by the students in order to comprehend the information or material by engaging friends, teacher, or whenever could help her.
As stated earlier that there were four kinds of cognitive strategy including practicing, receiving and sending message, analyzing and reasoning, and creating structure for input and output. Those strategies were not only employed in the classroom, but also when they returned to the home and whenever they needed it to find and to comprehend knowledge. After the researcher analyzed all the phenomena that she found during the research in previous part, it was found that there were several kinds of cognitive strategy performance by students. Those strategies were explained as follows:
The first strategy in cognitive was practicing. There were some ways to train students‟ speaking skill that were repeating (the students repeat the sentences/
expression), formally practicing with sound and writing system (the students more focus on pronunciation), recognizing (the students talks by applying the grammatical structure), recombining (the students use the combination into different focus on meaning), and practicing naturalistically (the students have become accustomed with the utterances). In practicing students tried to have good utterances by repeating the material that they learnt or heard. As a foreigner language learner, practice the previous knowledge was very crucial.
Based on the interview and observation result, researcher found that not all of the strategy in practicing was used by the students. They only applied some of them like repeating. The four students tried to imitate the utterances of the native speaker when they hear or watch movie, I learn speaking by listening and watching the native speaker in the movie and imitating them (Sakura, interviewed on 24th March, 2017). Imitating occurred when the students repeated what the speaker said, I repeat the actor voice (Jasmine, interviewed on 24th March, 2017). For that, in this case imitating speaker was same with repeating the speaker utterances. Repeating helped students to improve speed in acquire and understanding something new. This not only occurred just in formal class but also in non formal class.
28
rules was also sometimes applied by the students, sometimes I use repeating, recognizing (Orchid, interviewed on 23rd March, 2017).
From four students that had been interviewed, the data showed that all of the students used repeating. Then, two of them sometimes combined both of repeating, formally practicing with sound and writing system, and recognizing to have good performance in speaking.
2) Receiving and sending message
The second strategy in learning speaking that applied by the students were receiving and sending message. This strategies divided into two branches that were getting the idea quickly means after talking, the students response it quickly and gives their idea about what is asked, and using resources for receiving and sending message means that the students had to think for a while before answering the question.
All of the respondent showed that cognitive strategy particularly receiving and sending message also had contribution in helping them to learn speaking.
3) Analyzing and reasoning
The third strategy in term of cognitive was analyzing and reasoning. This strategy was divided into five branches they were reasoning deductively means the students explained or declared the reason from the common one to the specific one. Analyzing expression means the students try to make other people understand what they are really explaining, analyzing contrastively means the students use two or more languages, they give additional explanation to make sure what they said was understood by different language, and translating means the students pay more attention to translate everything, and transferring means the students directly applying knowledge of words, concepts or structures from one language to another in order to understand or produce an expression in the new language.
In addition, another strategy that could help students in learning speaking was analyzing and reasoning. Based on the interview and observation, researcher found that the students tried to analyze the expression of the speaker while he or she talked, I‟m ... try analyzing the expression or the material that I hear (Orchid, interviewed on 23rd March, 2017).
30
make their friends understand when they talked, I usually use two language, in example I use English and Indonesian language (Orchid, interviewed on 23rd March, 2017).
4) Creating structure for input and output
This was the last strategy in cognitive strategy. The following were three ways to create structure which necessary for both comprehension and production in the new language, taking notes, summarizing and highlighting. Taking notes allowed the students to write down the main idea or specific points. Then, in summarizing, students only made a summary or abstract of a longer passage or what they learnt. The last in highlighting students just needed to underlining, starring or using code to focus on important information of a passage. The following were the students‟ ways in making structure of the material or what they
learnt.
When the research was conducted, researcher found that learners were not applying these three strategies. There were only two ways that the students used that were made summary and took a note. Students created a summary for helping them easier to understand what they heard or learnt, it was related with their answer when interview, applying my cognitive strategy… make a note (Orchid, interviewed on 23rd March, 2017).
2. The Impact of Cognitive Strategy Toward Students’ Speaking Performance
After analyzing the kinds of cognitive strategy used by the students in learning speaking, the researcher also want to know the impact of those strategies toward students speaking performance. For that, the researcher needed to see the students speak up. In order to show the students‟ speaking performance it could be seen based on interview and observation result. The researcher found from the data that used cognitive strategy influenced the students‟ speaking performance.
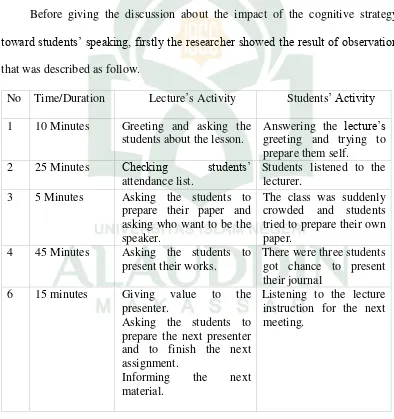
Before giving the discussion about the impact of the cognitive strategy toward students‟ speaking, firstly the researcher showed the result of observation
that was described as follow.
No Time/Duration Lecture‟s Activity Students‟ Activity 1 10 Minutes Greeting and asking the
32
The researcher took a note during the observation in the class and sat in the back of the classroom without disturbing the lecturer and the students. The researcher focused on collecting data on students through nonparticipant observation. The researcher described the phenomenon above, according to the table of observation.
The lecturer started by greeting and asking about students felt of previous lessons, and the students gave feedback by answering the lecture greeting in the classroom. Next, the lecturer asked the students about their preparation about the presentation.
The researcher saw the students‟ activity in the classroom during the observation, there was a common reaction from the students when the lecture asked about presentation. The lecturer informed some students to prepare them self to present their task in front of class, but some of students did not have preparation to present the material in front of class. Some students were worry about their task and asked to change the time with their friend that was ready to present their task. Also there were some students relax and did not give a comment.
After prepare the presentation, students came to the front of class one by one to show and describe their task. There were three students that wanted to do the presentation. The presenter was given about ten minutes to explain their topic by using English. The three students presented their task fluently and good without feel anxiety. After presenting the material the lecture and students gave question related to the material and the presenters could answer the question given by their lecture and their friends.
The observation description above was also related to the impact of cognitive strategy toward students‟ performance. As stated earlier that there were
several kinds of cognitive strategy used by the students in learning speaking. The researcher analyzed the impact of learning strategy that students‟ utterance in speaking. Based on the interview and observation result, researcher found that practicing, receiving and sending message, analyzing and reasoning, and creating structure for input and output had a good or positive impact for students‟ speaking
performance.
First, practicing help them to be good at utterance a word or sentences. They utterance the sentences smoothly, then they enjoy the class without feel anxious. Also they were being accustomed with the word or sentences that they pronounce.
The second, the researcher found that receiving and sending message strategy also had contribution for students‟ speaking skill. Even this strategy not really worked in students‟ performance but it worked when students tried to
34
The third, analyzing and reasoning strategy was also run by the students in learning speaking. Those strategies helped students to be easier in understanding a material that they learned. It was related to the second strategy. The students needed to analyze the material like translated it, I tried my self to translate what the speaker said so I understand what they really want to ask for me (Jasmine, interviewed on 24th March, 2017). This strategy also helped students in learning speaking.
The last, the researcher found that strategy for creating structure for input and output was also working in helping the students learning process. Making a summary helped the students to be easy in learning English speaking.
Based on description above, interview and observation result showed the students‟ classification or criteria in speaking. The first, the researcher classified the accuracy was “very good”. It showed from the pronunciation is still
moderately influenced by the mother tongue but not series phonetically errors. A few grammatical and lexical were errors but only one or two major errors causing confusion.
The second, the researcher classified the fluency was “good”. It showed that although she has to make an effort and search for words, there are not too many unnatural pauses. Fairly smooth delivery.
From the description above, the researcher concluded that the application of cognitive strategy in learning speaking had a positive impact toward students‟
speaking performance.
B.Discussion
This section, the researcher focused in discussing the data found that related to theories and previous findings which on the focused of the research. There were four kinds of cognitive strategies that used by the students in learning speaking that were practicing, strategies for receiving and sending messages, analyzing and reasoning strategies, and creating structure for input and output. All this strategies were very helpful tool for students to upgrade their speaking learning process.
In practicing term, there were some way that students used to practice their learning process that were repeating, formally practicing with sounds and writing systems, recognizing and using formulas and patterns. Further, the most favorite strategy was repeating. Repeating was the action that students performance in order to understand and comprehend the material. Repeatition had effect on the ways people make meaning. In this respect, Johnstone in Eka (2013) argued that repeatation created a cognitive effect.
Repeatation help students to improve speed in acquire and understanding
36
The second strategy was receiving and sending messages. In this strategy there were some students that had to think a moment before gave idea. It meant that they needed some times to understand what other said.
The other strategy that students used was analyzing and reasoning. There were three kinds of this strategy that students applied in learning speaking that were analyzing expression, analyzing contrastively, and translating. Analyzing expression means to understand something spoken in the new language, it is often helpful to break down a new word, phrase, sentence, or even paragraph into its component parts (Oxford, 1990).
Furthermore, analyzing contrastively is a fairly easy one that most learners used naturally. It involved analyzing elements of the new language to determine likenesses and differences in comparison with one‟s own native language. Addition, translating was one of strategy applied by the students in learning speaking. According to Oxford (1990) that translating can be helpful strategy early in language learning, as long as it is used with care. It allowed learners to use their own language as the basis for understanding what they heard in the new language.
the students listening to material of speaking. Depending on the purpose, note taking can be in the target language or the students own language (Oxford, 1990).
In addition, summarizing teaches the students how to reduce the text or what they herd to the key ideas. Learners need to decide what the most important information in the text is and which ideas can be omitted. This is not an easy task for young learners, since, for them, everything seems to be important. It is more suitable for them to start with summarizing paragraphs or shorter passages than to ask young learners to summarize longer text or the story (Strakova, 2013)
38 CHAPTER V
CONCLUSSION AND SUGESSTION
This chapter consisted of the conclusion of finding and discussion and presented some suggestion.
A. Conclusion
1. Kinds of Cognitive Strategy
Based on the explanation above, the researcher found that the students of English Education Department at State Islamic University of Makassar were very potential in learning English especially speaking. They made some effort to upgrade their ability. One of effort that appeared while this research running was applying strategy.
According to the analysis of the research findings and the discussion, the researcher concluded that the students applied almost all of the cognitive strategies which proposed by Oxford theory including practicing, receiving and sending message, analyzing and reasoning, and creating structure for input in helping their speaking learning process. Even the learners used same learning strategies, but they had different activities in using the strategies.
analyze contrastively. Then, in creating structure for input students took a note and made summary of the material.
2. The Impact of Cognitive Strategy Toward Students’ Performance
Although the use of that strategy was different, the application of those strategies was helping the learners in upgrading their speaking skill. They were being more active and confidence in speaking. They showed good performance while speaking because they had the criteria of good speaker that were good at accuracy, good at fluency and good at comprehensibility.
B. Sugesstion
1. Since the successful learners in speaking at this semester employed strategy, it is suggested to the learners to raise awareness to apply language learning strategies especially cognitive strategy into correct ways in order to increase speaking English.
2. It is suggested to the others researchers do same research with larger respondents by modifying certain strategy where necessary in order to cover strategies that the students might use but not just language learning strategy proposed by Oxford but the other experts can be used.
40
41 Bibliography
Abbas. A. 2013. An Investigation of students’ language learning strategie in mastering speaking skill at English and literature department of UIN Alauddin Makassar.Unublished thesis. State University of Makassar. Brown, D. H. 2001. Teaching by Principles: an Interactive approach to Language
Pedagogy. New York: Longman.
Brown, D. H. 2007. Principles of language learning & teaching. Pearson: Longman.
Chamot, A. U. 1987. The Learning Strategies of ELS students. London: Prentice Hall.
Channey, A. L. and Burk.T.L.1998. Teaching Oral Communication in Grades K.8. Boston.
Egan, K. 1999. Speaking. A Critical skill and challenge. Calico Journal. Vol. 16, No: 3.
Ehrman, M. E. and Oxford, R. L. 1995. Cognition Plus: correlates of language learning success. Modern Language Journal. Vol. 79. No. 1.
Gay, L. R., Mills, G. E. and Airasian, P. 2006. Educational Research: Competences for Analysis and Application. New Jersey: Pearson Education.
Ghaith, G. and Rihan, S. H. 2012. An Investigation of the Relationship of Learning and Communication Strategies, Gender, and Reading Proficiency in English as a Foreign Language. IJGE: International Journal of Global Education. Vol. 1. No. 4.
Griffiths, C. 2008. Language teaching Library: Lessons from good language learners, Cambridge University Press, New York.
Hornby, A. S. 1995. Oxford advanced learner’s dictionary of current English. New York. Oxford University Press.
Khezrlou, S. 2012. The Relationship between Cognitive and Metacognitive Strategies, Age, and Level of Education. The Reading Matrix. Vol. 12. No. 1.
42
O‟Malley, J. M., & Chamot, A. U. 1987. The cognitive academic language learning approach: A bridge to the mainstream. TESOL Quarterly. Vol. 21. No. 2 strategies worldwide with the ESL/EFL version of the strategy inventory for language learning (SILL). System Vol. 23, No.1.
Park, G. 1994. Language Learning Strategies: Why Do Adults Need Them? Unpublished manuscript, University of Texas, Austin.
Phakiti, A. 2006. Modeling Cognitive and Metacognitive Strategies and Their Relationships to EFL reading Test Performance. Melbourne Papers in Language Testing. Australia.
Rosmiaty, 2012. The Contributing Factors Toward the Improvement of the
Participants’ Speaking Ability at Pioneer English meeting Conversation
Club (PEMCC) Fort Rotterdam Makassar. Thesis. Makassar State University.
Stern, H. H. 1992. Issues and Options in Language Teaching. Oxford: OUP. Strakova, Z. 2013. Developing Cognitive Strategies in Foreign Language
Education. Journal of Language and Cultural Education. Vol. 1. No. 1. Ur, Penny. 1996. Grammar Practice Activities: Practical Guide for Teachers.
Cambridge University Press. New York.
Van Dijk, T. A., and Kintsch, W. 1983. Strategies for discourse comprehension. Orlando, FL: Academic Press.
Wenden, A. 1991. Learner Strategies for Learner Autonomy, Planning and Implementing Learner Trainings for Language Learner. New York: Prentice Hall.
A
P
P
E
N
D
I
X
E
44 APPENDIX I INTERVIEW QUESTION
1. Tell me about your personality!
2. Tell me about your educational background! 3. What do you think about English?
4. How do you learn the skills of English especially speaking? 5. What do you know about cognitive strategies?
6. How do you use cognitive strategies in learning speaking?
7. How do you use cognitive strategies to give your idea in speaking? 8. How do you use cognitive strategies to response an idea in speaking? 9. What do you do to understand the material?
10.How do you use cognitive strategy to have good comprehension and production?
45
APPENDIX II
INTERVIEW TRANSCRIPTION
1. Respondent 1 (Orchid)
Interviewer: Tell me about your personality!
Respondent: My name is Wulandari Noor rasyid and I am 19 years old. Interviewer: Tell me about your educational background!
Respondent: I was graduated from TK Aisyiyah Bustanul Athfal…. Then, I was graduated from Elementary School of Tetebatu 1. … … (look above) And then I continue my study at Junior High School of 1 Pallangga. I continue again my study at … Senior High School of 1 Sungguminasa. For now, I am studying at State Islamic University of Alauddin Makassar.
Interviewer: What do you think about English?
Respondent: English is … an International language that … … we … we can use to … to communicate with people around the world (look around). Interviewer: How do you learn the skills of English especially Speaking?
Respondent: I always memorize vocabulary as … my preparation for speaking … and then I use some technique to learn.
Interviewer: What do you know about cognitive strategies?
Respondent: Cognitive strategies are … our way to learn, which … involve thinking process (look above).
Interviewer: How do you use cognitive strategies in learning speaking?
Respondent: I use cognitive strategy … … … in learning speaking … by repeating
sentences or … … expression and recognizing the subject.
Interviewer: How do you use cognitive strategies to give your idea in speaking? Respondent: I use cognitive strategy to give …. … … my idea in speaking I am
used to thinking… … before giving my idea.
Interviewer: How do you use cognitive strategies to response an idea in speaking?
46
idea … before I response it.
Interviewer: What do you do to understand the material?
Respondent: I just giving attention to the material. … I try analyzing the expression… … or the material that I hear …. … … And to make other people understand… … what I say, I usually use… … two language, in example I use English and Indonesian language.
Interviewer: How do you use cognitive strategy to have good comprehension and production?
Respondent: To be good at comprehension and production… … I Applying my cognitive strategy like … practicing and then make a note or… … summarizing the learning material (look around).
Interviewer: What kind of cognitive strategies do you use more of time? Respondent: … … I use repeating strategies or practicing.
2. Respondent 2 (Rose)
Interviewer: Tell me about your personality!
Respondent: my name is Denny Sriuli and I am 20 years old. Interviewer: Tell me about your educational background!
Respondent: My educational background … as started at Elementary School of 245 Batutompo. … … And then I continued to Madrasah Tsanawiyah YPPI in Bulukumba. … I continued again … … my study at Madrasah Aliyah YPPI Bulukumba. And now… …, I am studying at State … Islamic University of Alauddin Makassar.
Interviewer: What do you think about English?
Respondent: I think English is a … … special language. Because we can communicate … … with many people from around … the world.
Interviewer: How do you learn the skills of English especially Speaking?
Respondent: when I learning speaking, … I always practice (look above)… … with my friends and sometimes I … practice with myself in a mirror (look above).
Respondent: Cognitive strategy is … … a lesson discuss about how … we improve our English skills.
Interviewer: How do you use cognitive strategies in learning speaking?
Respondent: I use cognitive strategy … like repeating, … (look above) formally practicing with sound … and writing system.
Interviewer: How do you use cognitive strategies to give your idea in speaking? Respondent: I use cognitive strategy to give … my idea by thinking a while then
… giving my idea.
Interviewer: How do you use cognitive strategies to response an idea in speaking? Respondent: Of course … when I want to response an idea in speaking, first … I
… … must understand the idea.
Interviewer: What do you do to understand the material?
Respondent: To understand the material, I … I …(look above) reading the material, analysis or … giving attention to the material.
Interviewer: How do you use cognitive strategy to have good comprehension and production?
Respondent: I use cognitive strategy to be … to be … good in comprehending and production (look above)… like I always practicing and … I also making summary. I … also take a note to be easy … to remember what I learnt (look above).
Interviewer: What kind of cognitive strategies do you use more of time? Respondent: I always … use practicing especially repeating.
3. Respondent 3 (Sakura)
Interviewer: Tell me about your personality!
Respondent: my name is Nur Hilalia. I am 19 years old. Interviewer: Tell me about your educational background!
48
School of Barru. And now, … I am studying at … State Islamic University of Alauddin Makassar.
Interviewer: What do you think about English?
Respondent: English is … an useful language. Through English … we can communicate with many people … from around the world. While studying English is fun … and enjoyable.
Interviewer: How do you learn the skills of English especially speaking?
Respondent: I learn English speaking by … listening and watching … the native speaker … in the movie and imitating them.
Interviewer: What do you know about cognitive strategies?
Respondent: cognitive strategy is a … kind of strategy which can … be used to improve our skill in English.
Interviewer: How do you use cognitive strategies in learning speaking?
Respondent: I usually use cognitive strategy … in learning speaking by repeating, … … recognizing and practicing with… sound and writing system.
Interviewer: How do you use cognitive strategies to give your idea in speaking? Respondent: I give my idea in speaking by … thinking for a while then giving
idea.
Interviewer: How do you use cognitive strategies to response an idea in speaking? Respondent: I used cognitive strategy to response an idea by … … understanding
the question first …, then I response or giving answer (look around). Interviewer: What do you do to understand the material?
Respondent: to understand the material that I learned …, I have to reading the material …, listening the explanation … about the material, and asking … about something that I do not know about the material.
Interviewer: How do you use cognitive strategy to have good comprehension and production?
Respondent: I only repeating and then … make summary about what I hear … or I have learned.
Interviewer: What kind of cognitive strategies do you use more of time?
4. Respondent 4 (Jasmine)
Interviewer: Tell me about your personality!
Respondent: My name is Nurqalbi Rustan, I am from Palopo and I am 17 years old. And now I live at Monumen Emysaelan street at Makassar.
Interviewer: Tell me about your educational background!
Respondent: Well, when I was a kid … I was graduated at SDN Surutama Palopo and I continued my study at … Junior High school number 1 in palopo, and then I continued my study again in Senior High School number 3 in Palopo. And now, … I continue my study again at Makasar in Islamic State University of Alauddin Makassar.
Interviewer: What do you think about English?
Respondent: I think English is fun to study and it…. Actually English is depend on every one, … because if you like English … it will make your life more easy to learn about it.… And if you think English is difficult,… may be it hard to you to … solve anything which include English, I think.
Interviewer: How do you learn the skills of English especially Speaking?
Respondent: I learn … …, actually I learnt it from watching movies … especially Hollywood, not bad Hollywood … but like animation, I repeat the actor voice … and I then practice my speaking, like that.
Interviewer: What do you know about cognitive strategies?
Respondent: What I know about cognitive strategy … cognitive strategy is learning strategy about using our mind and … … …. in cognitive strategy there are some strategy that we can use. … … First is practicing. I really like practicing because it is easy way … and then there also receiving and sending message, and then I forgot.
Interviewer: How do you use cognitive strategies in learning speaking?
Respondent: I apply, I apply cognitive strategy in learning English especially speaking is … when I use practicing strategy. … This is one of my favorite. Because just like I said before that … it is easy and practicing is like when … … I repeat the sentence, it makes my mind work. Like … I memorize some vocabulary from that … and maybe practicing makes me more confidents … because by practicing we can repeat every sentence that we want to say.
50
Respondent: I use cognitive strategy … to give my idea in speaking is … first I think what I‟m going to say …, what should I say or what will I say. It depends on … what topic that going to discuss.
Interviewer: How do you use cognitive strategies to response an idea in speaking? Respondent: Well, I„m responding a speaker, … sometimes I have to think for a
while, … but sometime I response them like what they want to … hear from me. Actually it depends on the speaker.
Interviewer: What do you do to understand the material?
Respondent: I usually focus on listening to them … and after focus on listening to them…. I tried my self to translate what … the speaker said so I understand … what they really want to ask for me.
Interviewer: How do you use cognitive strategy to have good comprehension and production?
Respondent: Sometimes I … summarize the material that I learn … after hear the material and also I make like notes. Just it.
Interviewer: What kind of cognitive strategies do you use more of time?
51
APPENDIX III
TRANSCRIPTION OF STUDENTS PRESENTATION
1. First Students’ Presentation Assalamu alaikum wr. Wb.
Thanks for the chance that given to me…… my name is Nurhilal, Now I
would like to present my material with the title “nomophobia”. Nomophobia come
from term no-mobile-phone-phobia. It is the fear of being without your smartphone or more simply is called as a smartphone addiction …… the sign of
this addiction is you …… will be happy if you get your smartphone and in
contras…… in contras you will be worry if you did not with your
smartphone……a… you will use your…… smartphone whenever and wherever.
…… the disadvantages of nomophobia is wasting time and disturbing other
activities, you are not sleeping well, and post phone other activities……. But you
can overcome this problem…… you…you can turn of…our cell phone at least one hour before bad. Set certain hour to check your smartphone.……. And be a
smart user. That‟s all from me. Thank you for your attention.
52
2. The Second Students’ Presentation
Assalamualaikum wr. Wb.
First of all let say thanks to Allah SWT who has given us mercy and blessing so that we can attend in this lovely class. Next I don‟t forget to send
shalawat and salam to our prophet Muhammad SAW. who has guided us from the darkness to the brightness. The last I don‟t forget to say thanks to our lecturer Mr.Muis who have given me a chance. So today I want to present my material about narcisme.
Do you know what is narcisme? Narcisme is…… is the nature of a person
who likes to boast about himself …… himself over and over with what he owns. …… ... narcisme come from…… Come from Greek myth of a man named
Narsisus that love his own shadow. ……. narcissist nature exist in human from
birth……narcisme has a healthy role …… people who have this…….think that he
or she smartest, greatest and cannot be criticized. Then… mmmm…. Factor that cause this is their parents are less responsive and underestimate…… excessive
childhood praise……. And learning manipulative behavior of parents.
…… this condition have negative impact like…….. like disturbing people around him or her. And the….. and then not being able to respect other…..
causing… causing self-abnormalities and… and… damaging the heart. Ok thank you for your attention. I think that‟s all from me.