i
2016/2017, Thesis Advisor (I) Adieli Laoli, S.Pd., M.Pd, and Thesis Advisor (II) Yasminar Amaerita Telaumbanua, S.Pd., M.Pd.
Key Words: Students’ Ability in Mastering Vocabulary, Taxonomy Strategy
Mastery vocabulary is the skill or ability to use words in the daily life interaction. Meanwhile, vocabulary itself is defined as the body words used in a particular language or in a particular activity. Besides, vocabulary is also one of the important aspects of language teaching and learning because it is a key for understanding toward what has been read or listened. Building vocabulary is foundational at any skill of English because through this, the students know more words
and these words give to the students’ mind more ways to think about things and more tools to plan or figure out about something.
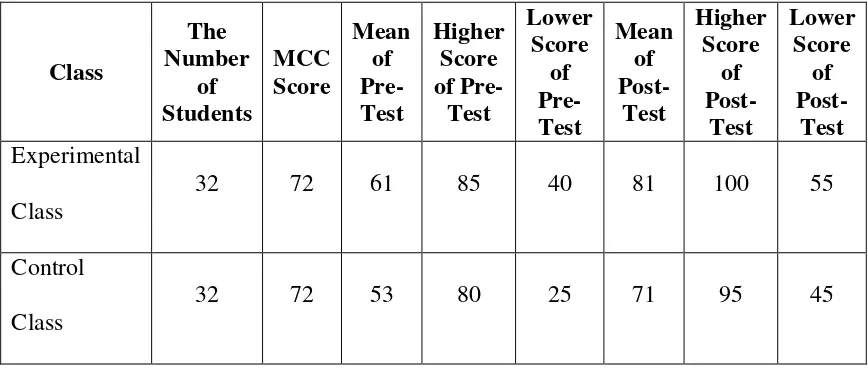
The purpose of the research is to know the significant effect of Taxonomy Strategy on the students’ ability in mastering vocabulary at the eighth grade of SMP Negeri 3 Lolofitu Moi 2016/2017. In conducting the research, the researcher used quasi-experimental design. The instrument test used in the research was multiple choice test that was validated externally in SMP Negeri 2 Lolofitu Moi. The population of the research was the eighth grade students of SMP Negeri 3 Lolofitu Moi that consisted of 92 students. The total number of sample was 64 students that consists of two classes and has been selected through cluster sampling. The sample of the research was VIII-1 class as experimental class and VIII-2 class as control class. Each class consisted of 32 students.
ii
iii
entitled: “The Effect of Taxonomy Strategy on the Students’ Ability in Mastering
Vocabulary at the Eighth Grade of SMP Negeri 3 Lolofitu Moi in 2016/2017.” Thisthesis is presented to fulfill one of the requirements for Scholar Degree (S-1) in
IKIP Gunungsitoli, Faculty of Education of Languages and Arts, English Education Study Program.
However, the researcher realizes that she cannot finish arranging this thesis by herself withoutsome people who help, support, and suggest a lot of significant things for her. Here, the researcher wants to express her sincere appreciation and thanks to:
1. Mr. Drs. HenokiWaruwu, M.Pd., as the Rector of Institute of Teacher Training of Education of Gunungsitoli, for his best service to the students of IKIP
Gunungsitoli.
2. Mr. AdieliLaoli, S.Pd., M.Pd., as the Dean of Faculty of Education ofLanguages and Arts, and also as the first advisor who always help, suggest and motivate the
researcher in finishing this thesis.
3. Miss. YasminarAmaeritaTelaumbanua, M.Pd, as the chair of the
EnglishEducation Study Program andalso as the second advisor who really care and help the researcher in finishing this thesis.
4. Mr. Drs. Ellyanus, M.Pd as the second assistant of the Rector of Institute of
iv
Study Program and also the examiner of study who always support and motivate the researcher in finishing this thesis.
6. Mrs. Dra. NursayaniMaru’ao, M.Pd., as the chief of research bureau of IKIP Gunungsitoli and also as the examiner of education who helps the researcher in fulfilling the administration when the researcher conducted the research and also
the lecturer who suggest the researcher for some great idea for finishing this thesis.
7. Mrs. Dra. MondangMunthe, M.M., as the chief of the library of IKIP Gunungsitoli who allows the researcher to use many books as the learning sources and the reference for finalizing this thesis.
8. All of the lecturers of IKIP Gunungsitoli especially in English Education Study Program who ever taught the researcher when studying since from the first semester until finalizing this the study.
9. Mr. Mar’IwanWaruwu,S.Pd., as the headmaster of SMP Negeri3 LolofituMoi who allows the researcher to conduct the researcher in the school.
10. Mr. DerianusWaruwu, S.Pd., as the English teacher who help and advice the researcher when conducting the research in the field.
11. The students of the eighth grade of SMP Negeri3 LolofituMoi especially VIII-1
v
Waruwu)
13. Her close friends (Jernih Putri Hartati Waruwu, Muliani Haeli, Ratnawati Halawa, Cherry Gea, Midar Telaumbanua, Adventy Zebua, Ernida Zai,
Krisdayanti Gulo, Seven Gulo, Netty Hia, Binari Hia, Henny Rita waruwu, Mei Warni Waruwu , Serius Harefa, Periman Bate’e, Herry Debi Anugerah Laoli,); for accompanying and supporting each other until finishing this thesis.
Finally, thank you too much for all of suggestions, advices, supports,
motivation and praying. Actually, the researcher is aware that this thesis is far from being perfect. Therefore, the researcher expects the constructive suggestions and criticisms so this thesis can be better in the future.
Gunungsitoli, , 2016 The Researcher
NeriyanaWaruwu
Page
TABLE OF CONTENTS ... i
ABSTRACT ... i
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS ... ii
TABLE OF CONTENTS ... v
LIST OF FIGURE ... ix
LIST OF TABLES ... x
LIST OF APPENDICES ... xii
CHAPTER I : INTRODUCTION……….. 1
A. The Background of the Problem ... 1
B. The Identification of the Problems... 4
C. The Limitations of the Problems ... 5
D. The Formulation of the Problems ... 5
E. The Purpose of the Research ... 5
F. The Hypotheses of the Research ... 6
G. The Significances of the Research ... 6
H. The Assumptions of the Research ... 7
I. The Limitations of the Research ... 7
J. The Key Terms Definitions of the Research ... 8
CHAPTER II : REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE ... 9
a. Definition of Taxonomy Strategy ... 9
b. Procedures of Taxonomy Strategy ... 10
c. Purpose of Taxonomy Strategy... ... 12
d. Advantages and Disadvantages of Taxonomy Strategy ... 13
2. Conventional Method ... 14
a. Definition of Conventional Method ... 14
b. Procedure of Conventional Teaching Method ... 15
c. Advantagesand Disadvantages of Conventional Teaching Method ... 16
3. Vocabulary ... 16
a. The Definition of Vocabulary ... 16
b. The Importance of Vocabulary ... 18
c. Types of Vocabulary ... 19
d. Teaching Vocabulary ... 20
e. Relationship between Vocabulary and Reading ... 21
f. Mastering Vocabulary based on Syllabus of SMP Negeri 3 Lolofitu Moi in 2015/2016 ... 22
g. The Assessment of Vocabulary ... 25
h. Relationship between Taxonomy Strategy and Vocabulary ... 28
B. Latest Related Research ... 28
CHAPTER III : RESEARCH METHOD ... 32
A. The Design of the Research ... 32
B. The Variables of the Research ... 33
C. The Population and Sample ... 34
1. Population ... 34
2. Sample ... 35
D. The Kind of Data and Research Instrument ... 37
E. The Procedure of Collecting the Data ... 38
F. The Techniques of analyzing the data... 39
1. Trying Out the Instrument... ... 39
a. Validity ... 39
b. Reliability ... 40
2. The Data Analysis ……… 41
a. The Students’ Ability in Vocabulary... 41
b. The Mean Score and Standard Derivation... 42
c. Examining the Normality... 43
d. Examining the Homogeneity... 44
e. Examining the Hypothesis (t test)... 45
CHAPTER IV: RESEARCH FINDINGS AND DISCUSSIONS………. 47
A. Research Findings ... 47
a. Validity of the Instrument ... 48
b. Reliability of the Instrument ... 49
3. The Data Analysis ... 49
a. Mean ... 50
b. Degree of Mastery ... 51
c. Standard Deviations ... 54
d. Variance ... 54
e. Normality ... 55
f. Homogeneity ... 56
g. Hypotheses Testing ... 57
B. The Discussions of the Research Findings ... 59
1. The Common Response of the Research Problems ... 59
2. The Analysis and Interpretation of the Research Findings ... 60
3. The Research Findings versus the Latest Related Research ... 62
4. The Research Findings Implications ... 63
5. The Research Findings versus Theory ... 64
6. The Analysis of Research Findings Limitations ... 65
CHAPTER V : CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS A. Conclusions ... 66
x
2. The Population of the Eighth Grade Students of SMP Negeri 3 Lolofitu
Moi ... 35
3. The Work Table for Liliefors Formula ... 44 4. The Mean of Pre Test and Post Test Scores of Control Group and
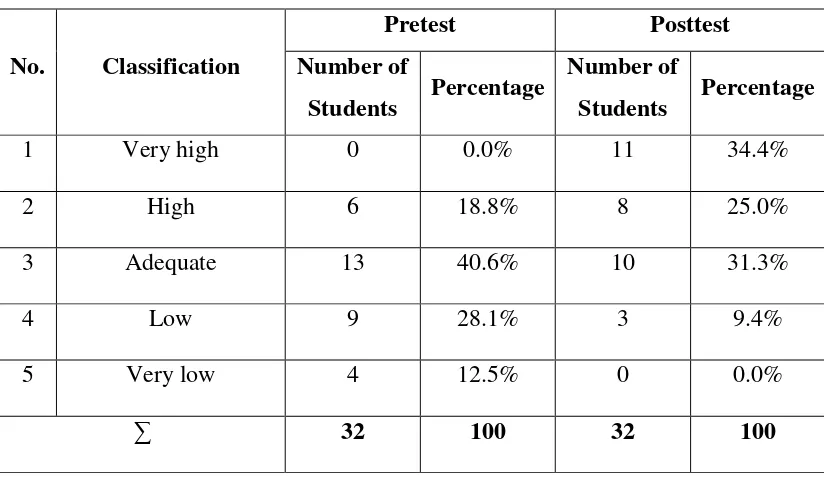
Experimental Group ... 51 5. The Table of The percentage degree of students mastery of pretest
and posttest of mastering vocabulary through taxonomy strategy
of experimental class ... 52 6. The Table of The percentage degree of students mastery of pretest
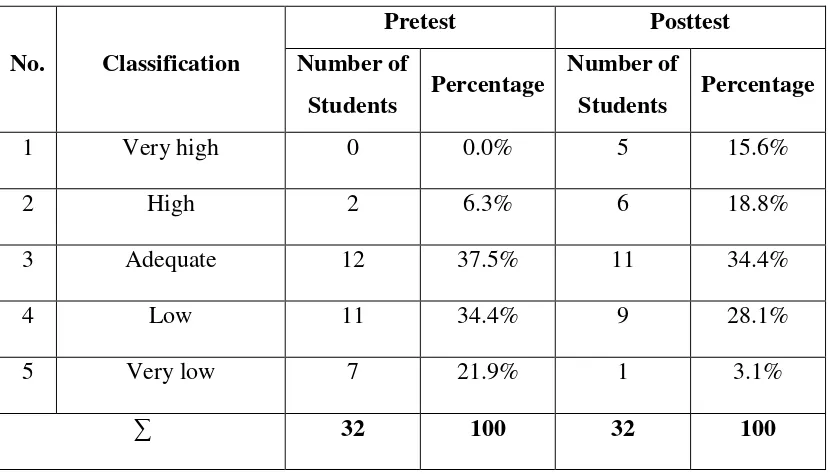
and posttest of mastering vocabulary through conventional
teaching of control ... 53
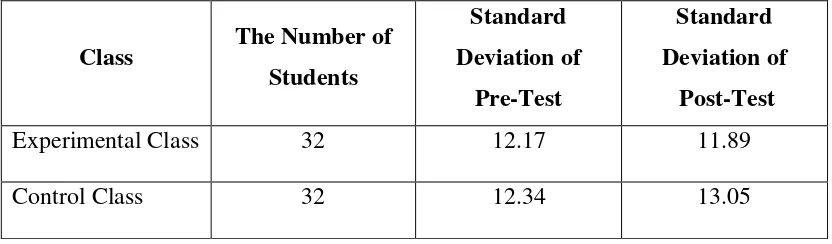
7. The standard deviation of pre-test and post-test score of
experimental class and control class ... 54
8. The Variance of pre-test and post-test score of
experimental class and control class ... 55
9. The Normality of pre-test and post-test score of
experimental class and control class ... 56
10. The Homogeneity of pre-test and post-test score of
experimental class and control class ... 57
11. The hypothesis testing of the research ... 58
12. The calculation for seeking validity of the research instrument
for pre-test ... 120
13. The calculation for seeking reliability of the research instrument
for pre-test the item number ... 161
14. The students’ ability of experimental class in mastering
xi
vocabulary through taxonomy strategy (post-test) ... 210
17. The students’ ability of control class in mastering
vocabulary through conventional teaching (post-test) ... 211 18. The classifications students’ ability of experimental class in mastering
vocabulary through taxonomy strategy (pre-test) ... 212 19. The classifications students’ ability of control class in mastering
vocabulary through conventional teaching (pre-test)... 213
20. The classifications students’ ability of experimental class in mastering
vocabulary through taxonomy strategy (post-test) ... 214
21. The classifications students’ ability of control class in mastering
vocabulary through conventional teaching (post-test) ... 215
22. The percentage degree of the students ability of experimental
class in mastering vocabulary through taxonomy strategy (pre-test) ... 216
23. The percentage degree of the students ability of control
class in mastering vocabulary through conventional teaching (pre-test) ... 217
24. The percentage degree of the students ability of experimental
class in mastering vocabulary through taxonomy strategy (post-test) ... 218 25. The percentage degree of the students ability of control
class in mastering vocabulary through conventional teaching (post-test) ... 219
26. Mean, standard deviation and variance of the students mark of experimental class in mastering vocabulary through taxonomy strategy (pre-test) ... 220
27. Mean, standard deviation and variance of the students mark of control
class in mastering vocabulary through conventional teaching (pre-test) ... 221
xii
31. Lilifor’s formula for the normality of pre-test data of
control class in mastering vocabulary... 225
32. Lilifor’s formula for the normality of post-test data of
experimental class in mastering vocabulary... 226
33. Lilifor’s formula for the normality of post-test data of
control class in mastering vocabulary... 227 34. The calculation process to seek the homogeneity of the sample (pre-test)...228 35. The calculation process to seek the homogeneity of the sample
xiii
2. a. Lesson Plan of Control Class ... 75
b. Lesson Plan of Experimental Class ... 85
3. Material ... 97
4. Table of specification ... 99
5. a. Text for pre test (try-out/control/experimental group) ... 101
b. The Pre-Test Items ... 101
c. The Answer Key of Pre-Test Items ... 105
6. a. Text for post test (try-out/control/experimental group) ... 106
b. The Post-Test Items ... 106
c. The Answer Key of Post-Test Items ... 112
7. a. The Test Instrument Validity (Validator I) ... 114
b. The Test Instrument Validity (Validator II) ... 116
c. The Test Instrument Validity (Validator III) ... 118
8. a. The Table of The Students’ Alternative Answers Distribution in Try Out (Pre –Test) ... b. The Table of The Students’ Alternative Answers Distribution in Try Out (Post –Test) ... 103
9. a. The Result Validity Test (Pre-Test) ... 120
b. The Result Validity Test (Post-Test) ... 121
10.a. The Result of Reliability (Pre-Test) ... 161
xiv
12.a. The List of Students’ Marks in Control Group Pre Test ... 115 b. The List of Students’ Marks in Control Group Post Test ... 117
13.a. The List of Students’ Marks in Experimental Group Pre Test ... 119 b. The List of Students’ Marks in Experimental Group Post Test ... 121
14.a. The Result of Mean, Standard Deviation, and Variance of Control
Group (Pre-Test) ... 123
b. The Result of Mean, Standard Deviation, and Variance of Control
Group (Post-Test) ... 124
15.a. The Result of Mean, Standard Deviation, and Variance of Experimental Group (Pre-Test) ... 125 b. The Result of Mean, Standard Deviation, and Variance of Experimental
Group (Post-Test) ... 126 16.a. The Result of Students’ Test Normality in Control Group (Pre-Test) .... 127 b. The Result of Students’ Test Normality in Control Group (Post-Test) ... 128
17.a. The Result of Students’ Test Normality in Experimental Group
(Pre-Test) ... 129
b. The Result of Students’ Test Normality in Experimental Group
(Post-Test) ... 130
18.a. The Homogeneity of the Samples in Pre-Test ... 131 b. The Homogeneity of the Samples in Post-Test ... 133
19.Testing Hyphotesis ... 135 20. The Students Presence List in Conducting Try Out Research Instrument
xv
23.r Product Moment Values ... 143 24.Critical Values for t-Students Distribution ... 144 25.The Width under the Normal Standard from 0 to Z ... 146
26.Critical Values for Liliefor’s Test ... 147 27.a. The Documentation at the Eighth Grade of SMP Negeri 3 Lolofitu Moi
in 2016/2017 ... 148 b. The Documentation of the Research Did Try-Out at the Eighth Grade
1 A.The Background of the Problem
Learning a language is not something new for people who have been interested in it since a long time ago. It is caused by the main function of language that is for communication. In the learning process, one of the important parts in
creating and understanding the language is vocabulary mastery. People can not express their opinion and ideas in English without knowing their vocabulary. Low
vocabulary mastery also makes them unable to express the opinion properly. English teaching involves four language skills, they are listening, speaking, reading and writing. In teaching and learning a language, there are four
aspects that support four language skills above such as: grammar, vocabulary, spelling and pronunciation that are also taught in English teaching and learning
process.Vocabulary is more than a list of words, and although the size of one’s vocabulary matters, it is knowing how to use it which matters most.The elements cover vocabulary is so useful in communication. Thus, in order that it is successful
for the students during involving in the communicative process they have to master vocabulary. Therefore, vocabulary component should be involved during
However, vocabulary is not put directly in the Junior High Schools syllabus, especially in English subject. The students learn vocabulary in the
school, because vocabulary has a close relation with reading skill. Regarding to the relation between reading and vocabulary, Davis (2000:2) says that vocabulary
knowledge is highly correlated with overall reading achivement. In addition to affecting reading performance, vocabulary knowledge affects a student’s ability to participate fully in both social and academic classroom routines.
In addition, vocabulary is one of important aspects in teaching language, as stated by Edward (1997:149), “Vocabulary is one of the important factors in all
language teaching, student must continually be learning words as they learn”. It is vocabulary as the key for the students to understand what they hear and read, and communicate successfully with other people. For the reason, it is very important to
quickly build up a large store of the words. Related to that, Richards and Renandya (2002:255) affirm that vocabulary is “a core component of language proficiency
and provides much of the basis how well learners speak, listen, read and write”. In other words, vocabulary is very important, not only to build up the students’ words but also support the four skills in a language especially in reading skill.
Biemiller DCSF (2008:5) states “Vocabulary is a strong indicator of
reading success.” It is if the students do not understand the meaning of individual
The syllabus of KTSP (2006) of SMP Negeri 3 Lolofitu Moi at the Eighth Grade, the competence standard expects the students to had ability to express the
meaning of the written text to make interaction with the environs. Also, the basic competence states that the students should be able to respond the meaning of the
written text to make interaction with environs in descriptive text. The students have ability to know the word meaning from the text when the students’ have passed on the minimum competence standard (72) in their school.
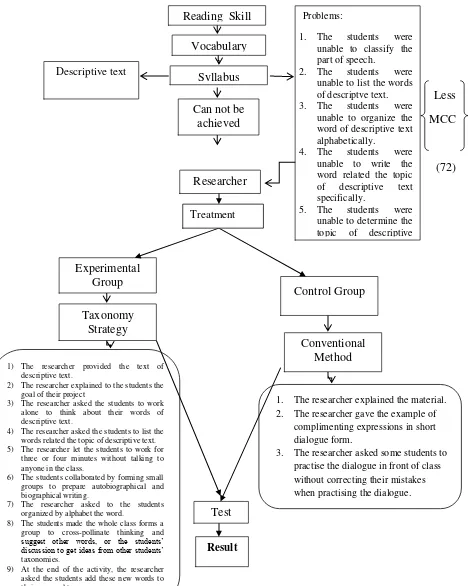
Based on the preliminary observation at the eighth grade students of SMP Negeri 3 Lolofitu Moi, the researcher found some problems faced by the students
when teaching vocabulary, there were : The students were unable to classify the part of speech, the students were unable to list the words of descriptive text, the students were unable to organize the word of descriptive text alphabetically, the
students were unable to write the word related the topic of descriptive text specifically, and the students were unable to determine the topic of descriptive
text. As the impact of those root of problems, the students can not achieve the Minimum Competence Criterion (72) in their school. The problems were caused by some factors. The first, the students had low motivation in studying vocabulary.
The second was the students did not have preliminary of knowledge about descriptive text. The third was the students lack of prior knowledge in part of
Therefore the reseacher solved the problem in order to find out the way out of these problems by teaching vocabulary to the students through Taxonomy
Strategy. Taxonomy Strategy is a list of words related to a specific topic or subject matter area. Work alone and think of as many words, enter each word next to its
initial letter, collaborate by forming small groups and share their words, adding new words to they personal taxonomies, have the whole class form a group to cross-pollinate thinking and suggest other words, or do a gallery walk to get ideas
from the other students’ taxonomies, have all the students add new words to their personal taxonomy. It is supported by Xhafery (2008) “Schmitt's taxonomy is
considered most appropriate taxonomy developed so far for learning words in English.”
Based on the statement, the researcher conducted a research entitled “The
Effect of Taxonomy Strategy on the Students’ Ability in Mastering Vocabulary at
the Eighth Grade of SMP Negeri 3 Lolofitu Moi in 2016/2017.
B. The Identification of the Problems
There were some problems of the English classroom that the researcher
found in the classroom, as follows.
1. The students were unable to classify the part of speech.
2. The students were unable to list the words of descriptive text.
4. The students were unable to write the word related the topic of descriptive text specifically.
5. The students were unable to determine the topic of descriptive text.
C. The Limitation of the Problems
In conducting the research, the researcher limited the problem namely; the effect of Taxonomy Strategy on the students’ ability in mastering vocabulary
especially in descriptive text material at the eighth grade of SMP Negeri 3 Lolofitu Moi in 2016/2017.
D. The Formulation of the Problem
Based on the limitation of the problem above, the researcher formulated
the problem as follows, “Is there any significant effect of Taxonomy Strategy on
the students’ ability in mastering vocabulary especially in simple present tense at
the eighth grade of SMP Negeri 3 Lolofitu Moi in 2016/2017?”
E. The Purpose of the Research
Purpose of the research is to find out whether there is a significant effect of Taxonomy Strategy on the students’ ability in mastering vocabulary especially
F. The Hypotheses of the Research
In the research, there are two hypotheses as follows.
Ha : There is a significant effect of Taxonomy Strategy on the students’ ability in mastering vocabulary at the eighth grade of SMP Negeri 3 Lolofitu Moi in
2016/2017.
Ho : There is no any significant effect of Taxonomy Strategy on the students’ ability in mastering vocabulary at the eighth grade of SMP Negeri 3 Lolofitu
Moi in 2016/2017.
G. The Significances of the Research
The findings of the research can be signified for.
1. The researcher, as experience and practice to teach vocabulary in her teaching
activity through Taxonomy Strategy.
2. The readers, as the information about the effect of Taxonomy Strategy on the
students’ ability in mastering vocabulary.
3. The English teacher, as an input to them to use the appropriate strategy to implement in teaching-learning process especially in mastering vocabulary.
H. The Assumptions of the Research
In doing the research, the researcher has some assumptions as follows.
1. Taxonomy Strategy is a strategy that can be used in teaching vocabulary. 2. Taxonomy Strategy is a very useful for making the students successful in
mastering vocabulary
I. The Limitations of the Research
The limitations of the research are made as follows.
1. Population of the research was the eighth grade of SMP Negeri 3 Lolofitu Moi
in 2016/2017.
2. Sample of the research was the eighth grade of SMP Negeri 3 Lolofitu Moi,
and it was selected through cluster sampling.
3. In the research, the researcher conducted quantitative research as the research method.
4. The searched aspect was the students’ ability in mastering vocabulary only. 5. In the research, the researcher implemented Taxonomy Strategy.
6. The researcher chose the descriptive text about describing animal as the
J. The Key Terms Definition of the Research
To avoid misunderstanding during the research, the researcher gave
explanations that concern to the definitions of the research title.
1. Vocabulary is the way of a word or language is usually uttered by the
students. And also vocabulary is a total number of the words of a language that should be obtained by the students.
2. Taxonomy Strategy is a list of some word especially about the topic or subject
the students will going to learn. And the strategy has the purpose to help the students to increase vocabulary-and especially vocabulary they may need to
write about a given topic-and also to encourage the students to work together to share knowledge. So the researcher role is to guide the students to do the research.
3. Descriptive text is a type of spoken or written text that tells a story of one character or more who faces certain problematic situation, description of
9 A. Theoretical Framework
1. Taxonomy Strategy
a. The Definition of Taxonomy Strategy
Taxonomy Strategy is one effective strategy that can be applied by the teacher in teaching English because by using this strategy teachers can increase the
students’ vocabulary. The strategy is easy to understand about the relation word in
vocabulary. According to Clayton County Public Schools (2008:18),
To increase vocabulary and especially vocabulary they may need to read about a given topic-and also to encourage students to work together to share knowledge.
Regarding to the NAF (2009:35) also support the definition above. They
state taxonomies become each student’s personal thesaurus. As the students build
taxonomies across the curriculum, they begin to build personal thesaurusses. In
order to keep track of their taxonomies, the students can create a table of contents for their notebook.
In addition, Bass and Gezim (2008:34) say,
Oxford's model was taken as model for developing a vocabulary learning taxonomy that has been used for the purpose of this study. Taxonomy have developed a vocabulary learning questionnaire containing a considerable number of strategies, divided into the following major categories: beliefs about vocabulary learning, metacognitive regulation, guessing strategies, dictionary strategies, note-taking strategies, memory strategies (rehearsal and encoding), and activation strategies. Schmitt's taxonomy is probably the most extensive but the Oxford model is more suitable for the participants of this study.
Kohl explains the model supports the need to differentiate the curriculum so all students are able to participate in the same content area during a
lesson. The structure allows the teacher to accommodate a variety of students’ needs by applying the appropriate questions and activities for children so that they may equally participate in the lesson.
Regarding to all theories above, it can be concluded that Taxonomy Strategy solved the students’ problem in mastering vocabulary. Moreover, it is believable strategy in teaching vocabulary which is very fit to build the ability of
the students in mastering vocabulary especially in descriptive text.
b. The Procedures of Taxonomy Strategy
There are some procedures of Taxonomy Strategy according to experts.
According to Clayton County Public Schools (2008:18), the steps are as follows. 1) Students work alone and think of as many words as they can that
relate to the topic being studied.
2) Students work for three or four minutes without talking to anyone in the class.
words, adding new words to their personal taxonomies.
4) Have the whole class form a group to cross-pollinate thinking and suggest other words, or the students do a gallery walk to get ideas
from other students’ taxonomies.
While, Bass, et al, (2013:33), state some flows of the strategy, namely.
Work alone and think of as many words as they can relate to the topic being studied, enter each word next to its initial letter, collaborate by forming small groups and share their words, adding new words to their personal taxonomies, have the whole class form a group to cross-pollinate thinking and suggest other words, or the students do a gallery walk to get ideas from
other students’ taxonomies, have all the students add these new words to
their personal taxonomy.
In addition, there are some steps to implement Taxonomy Strategy according
to NAF (2009:36), as follows.
1) Students work alone and think of as many words as they can that relate to the topic being studied.
2) Students enter each word next to its initial letter.
3) Students work for three or four minutes without talking to anyone in the class.
4) Students then collaborate by forming small groups and share their words, adding new words to their personal taxonomies.
5) Have the whole class form a group to cross-pollinate thinking and suggest other words, or the students do a gallery walk to get ideas from
other students’ taxonomies.
6) Have all the students add these new words to their personal taxonomy.
Based on the theories above the researcher modified the steps of
implementation of Taxonomy Strategy in teaching vocabulary as follows. 1) The researcher provided the text of descriptive text.
3) The researcher asked the students to work alone to think about their words of descriptive text.
4) The researcher asked the students to list the words related the topic of descriptive text.
5) The researcher let the students to work for three or four minutes without talking to anyone in the class.
6) The students collaborated by forming small groups to prepare autobiographical
and biographical writing.
7) The researcher asked to the students organized by alphabet the words.
8) The students made the whole class forms a group to cross-pollinate thinking and
suggest other words, or the students’ discussion to get ideas from other students’
taxonomies.
9) At the end of the activity, the researcher asked the students add these new words to their personal taxonomy.
c. The Purpose of Taxonomy Strategy
As written by Bass, et al, (2013:33), that the purpose of Taxonomy
Strategy is to have students build the personal taxonomy to prepare for both authobiographical and biographical vocabulary.
need to write about a given topic-and also to encourage the students to work together to share knowledge.
Regarding to the theories above, the researcher concludes that the purposes of Taxonomy Strategy are to motivate and to activate the students’
knowledge related to the text they read by noting some items in the text that they think familiar. So the students felt easy to comprehend the text, at least that they know what the general meaning of the text.
d. The Advantages and Disadvantages of Taxonomy Strategy
According to NAF (2009:35), building a taxonomy addresses these skills.
1) Organizing prior, ongoing, and new knowledge 2) Focusing on a topic
3) Taking notes
4) Expanding vocabulary
5) Developing cooperative learning experiences.
Wright (1988:40) says that the advantages of Taxonomy Strategy, as follows.
1) To support the teaching of important general principals about word and how they work.
2) To foster reading and writing
3) To promote independence on the part of young students as they work with words in writing and reading.
4) To develop a growing core of words that become part of reading and writing vocabulary.
5) To provide reference to children during their reading and writing. 6) To improve the students vocabulary.
7) To make the students enjoy and not bored with the materials.
However, Wright (1988:3) says that a disadvantage of Taxonomy Strategy is very broad there is no clear division between memory and cognitive
strategies.
In summary, the researcher noticed the advantages of Taxonomy Strategy
to the students’ learning outcome. The implementation of the strategy gave the
positive effect toward the students’ ability in acquiring vocabulary. After learning
vocabulary through the strategy, the students had progression in mastering
vocabulary and they were also able to comprehend the descriptive text easily.
2. Conventional Teaching Method
a. Definition of Conventional Teaching Method
According to Otomi (2008:75), “Metode ceramah disebut juga metode
tradisional (konvensional) dalam kegiatan pembelajaran”. It is Conventional Method is one of the traditional or conventional methods in teaching learning
process. The Conventional Teaching Method is still the most frequently used method of instruction. However, presenting a Conventional Teaching Method without pausing for interaction with students can be ineffective regardless of your
skill as a speaker. The use of pauses during the conventional for direct oral questioning creates interaction between teacher and students. Unfortunately, when
Furthermore, Conventional Teaching Method is defined as the method of instruction in which the teacher has full responsibility for presenting facts and
principles orally. The lecture may be conducted in either a formal or an informal manner. The informal lecture includes active student participation. The primary
consideration in Conventional Method is the achievement of desired learning outcomes. Learning is best achieved if the students participate actively in a friendly and relaxed atmosphere. Therefore, the use of the informal lecture is
encouraged. At the same time, it must be realized that a formal lecture is still to be preferred on some subjects and occasions, such as lecture introducing new subject
matter. The instructor can achieve active student participation in the informal lecture through the use of question. In this way, the students are encouraged to
make contributions that support the lecture. However, it is the instructor’s
responsibility to plan, organize, develop and present the major portion of a lesson.
b. The Procedure of Implementing Conventional Method
According to Wiley (2006:76) there are some steps in Conventional Method, they are:
1) Having the student’s attention and establishing the objective and desired out comes.
2) Introducing the course’ outline in orally or writing.
3) Relating the course that will you teach with the students’ previous knowledge and experience.
4) Beginning to teach from the general to the specific one. 5) Organizing the material.
In summary, Conventional Teaching Method is one of the conventional methods which has the traditional teaching-learning process and more centered to
the teacher. By doing Conventional Method, the students are not motivated to learn and it makes the students unable to create something related to the material.
In the research, the researcher applied Taxonomy Strategy to teach the students in mastering vocabulary to get any significant effect to their ability, while the students of control class were taught through Conventional Teaching Method.
c. The Advantages and Disadvantages of Conventional Method
Agata (1999: 23) says “Conventional Method provides for the effective
use of time which the instructor can present many ideas to a large group in short
period of time”. While the disadvantages of Conventional Method limits the
amount of student participation. A conventional is inadequate for teaching skills
and it is not an effective method for maintaining the students’ interest.
3. Vocabulary
a. The Definition of Vocabulary
Studying language cannot be separated from studying vocabulary because
it is an essential component of language. Vocabulary is one of components of language beside grammar and pronunciation. The students who want to learn a
Building vocabulary is foundational at any English skill. It is much more than grammar because is the key to communicate successfully with other
people. Knowing more words gives our mind more ways to think about things and more tools to plan or figure out about something. McCarten (2007:18) says,
Vocabulary is a challenge for learners, partly because of the size of the task, and partly because of the variety of vocabulary types to be learned, including single words, phrases, collocations, and strategic vocabulary, as well as grammatical patterning, idioms, and fixed expressions.
It is supported by Lado (1979:115) asserting, “The vocabularies of language are collected in dictionaries, of which there are many kinds.” In addition to, Lado
(1979:115),
No one all the words of any of the major languages of the world. All of the speakers of a given language, however, it is function words, which role is chiefly grammatical. All of them likewise know a core of content of words which have wide currency in the speech community.
Hatch and Brown (1995) define vocabulary as a list of words with their meanings, especially one that accompanies a textbook in a foreign language.
While according to Ur (1996), vocabulary refers to words that are taught in foreign language. Those words do not come from the students’ native language. They come from foreign language being learned, in the case
English. So the researcher concludes that vocabulary is a list or set of words with their meanings for certain foreign language which is being taught and
In other words, vocabulary is words in a language which is by the students to get the four skills in a language; they are listening, speaking, reading
and writing. By mastering vocabulary, the students can expose their idea, feeling, and opinion to other persons orally and writtenly. So in the research,
the students acquired vocabulary easily because of the very appropriate strategy that was used in teaching vocabulary itself.
b. The Importance of Vocabulary
Vocabulary is obviously a very important element within a language. In
learning a foreign language, vocabulary plays an important role. In order to communicate well in foreign language, the students should acquire an adequate number of words and should know how to use them accurately.
According to Widdowson in Praira Journal (1989) that vocabulary knowledge is the heart of a language comprehension and use. In addition to by
Nation (2015:22) describing the relationship between vocabulary knowledge and language use as a complementary: knowledge of vocabulary enables language use and conversely, language use leads to increase vocabulary.
As Maximo (2000:23) that many reasons for devoting to vocabulary. 1) First, a large vocabulary is of course for mastery language.
In conclusion that mastering vocabulary is the ability to get or to receive a lot of words. A good vocabulary and ability to use words correctly and
effectively can help the students to listen, speak, read, and write.
c. Types of vocabulary
There are four types of vocabulary according to Chester (2008:13), namely.
1) Listening vocabulary
A person’s listening vocabulary is all the words he or she can recognize when
listening a speech. This vocabulary is aided in size by context and tone of voice. 2) Reading vocabulary
A person’s reading vocabulary is all the words he or she can recognize successfully when a text or passage read.
3) Writing vocabulary
A person’s writing vocabulary is all the words he or she can write in a paper
correctly.
4) Speaking vocabulary
A person’s speaking vocabulary is all the words he or she can use in speech to express his or her idea, feeling, and opinion.
So, in summary that there are four types of vocabulary, namely listening vocabulary, reading vocabulary, writing vocabulary and speaking vocabulary. However, in the research, the researcher focused on reading
d. Teaching vocabulary
Teaching vocabulary is a complex task because it includes the meaning of
the words. A good teacher should use appropriate techniques and enough practice for certain words, so that the objectives will be achieved. Concerning the
appropriate techniques, a teacher must choose suitable method to teach vocabulary. The teacher has to teach not only the meaning of the words but also has to use appropriate method for each other aspect of language. Vocabulary is one
of the most obvious components of language and one of the first things applied linguists turned their attention to. Learning language must be given special
attention in order to get the goal of language learning.
According to the Blachowicz, et al, (2005:6), there is some teaching specific vocabulary.
1) Teach the suggested words prior to the reading selection from the basal.
2) Brainstorm synonyms for the word said as part of a mini-lesson in writing.
3) List word families as part of spelling instruction
4) Teach the meaning of quadrant for word problems in math.
5) Have the Mexican-American and Korean-American students in her class teach the rest of the students the Spanish and Korean words for plains, rivers, clouds, mountains, rain as part of Social Studies on the Great Plains.
6) Develop a semantic web for the Great Plains, including words learned so far in the unit.
7) Talk about honesty in relation to one student having “borrowed” a marker from another student without permission.
So, as the conclusion, in teaching vocabulary, the researcher taught not only the meaning of the words but also how to use appropriate methods for other aspect
of language, because vocabulary is one component of the language which is applied for the students to make them master vocabulary.
e. The Relationship between Vocabulary and Reading Skill
The relationship between reading and vocabulary is typically one of
mutual improvement and growth. It is because as students read more, her or his vocabulary typically expands and grows and then her or his is able to read a
wider range of works. While there are some exceptions to this idea, in general, a person is likely to develop a stronger vocabulary by reading and reading a wide range of materials. In order for reading and vocabulary to have the mutually
beneficial relationship, however, a reader must be sure to actually try to improve his or her vocabulary while reading by learning new words.
Davis (2000), says “Vocabulary knowledge is related to and effects comprehension. The relationship between word knowledge and comprehension is
unequivocal”. It is supported by McKeown and Beck’s (1988) asserting “Word
knowledge is not an all or nothing proposition. Word may be known at different
levels.”
needed to produce vocabulary grow this not more vocabulary instruction, but more
reading.”
Based on the theories above, the researcher drawn a conclusion that vocabulary has a close relation with reading since vocabulary is the most
powerful predictors of reading and the students can master vocabulary through reading.
f. Mastering Vocabulary based on the Syllabus of SMP Negeri 3 Lolofitu Moi in 2016/2017
In the English syllabus of SMP Negeri 3 Lolofitu Moi at the eighth grade, there are four skills that should be mastered by the students. Especially in reading
skill, the things should be mastered by the students stated in competence standard of reading that the students process, present, and think about concrete domains
(using, analyzing, combining, modifying, and making) and abstract domains (writing, reading, accounting, drawing, and composing) as learned in the school and the other sources in the same point of view/theory. While the basic
competence is applying the text structure and language feature to conduct the function of social descriptive text by explaining and asking the students to describe
So, there are two types of text that should be comprehended by the students, as follows.
1) Descriptive text
According to Wardiman (2008:16) that descriptive text is a text that
describes the features of someone, something or certain place. There are two structures of descriptive texts, namely identification and description. In the identification step, the writer identifies or introduces phenomenon to be described.
In the description step, the writer describes the characteristics of animal.
My cat zedva
Zedva is my beautiful gray Persian cat. He walks with pride and grace, performing a dance of disdain as he slowly lifts and lowers each paw with the delicacy of a ballet dancer. His pride, however, does not extend to his
appearance, for he spends most of his time indoors watching television and growing fat.
He enjoys movie in Television, especially chanel those for vichanel and cinemas 24. almost every day of my cat zedva Always watch television, after the feed and Sometimes he ate while watching television.
Zedva is as finicky about visitors as he is about what he eats, befriending some and repelling others. He may snuggle up against your ankle, begging to be petted, or he may imitate a skunk and stain your favorite trousers. Zedva does not do this to establish his territory, as many cat experts think, but to humiliate me because he is jealous of my friends.
After my guests have fled, I look at the old fleabag snoozing and smiling to himself in front of the television set, and I have to forgive him for his
obnoxious, but endearing, habits.
2). Recount text
Recount text is a kind of the texts that tells about the past event. According to Anderson (2000), a recount text is a type of text that tells about something that
has happened or retells past events activities and has a purpose to give detail information about what and when of that events. The main elements of recount
text are orientation, list of events, and reorientation. In the orientation step the writer mentions people and things that are involved, time of the vent, the place, and the situation. In the list of events, the writer tells the events happen
chronologically. In the reorientation, the writer concludes the story by giving the comments.
The example of recount text:
(Source: Scaffolding, 2008)
However, in the research, the researcher chose descriptive text as the material used in applying Taxonomy Strategy to know whether there is a
significant effect of using Taxonomy Strategy on the students’ ability in mastering vocabulary at the eighth grade of SMP Negeri 3 Lolofitu moi in 2016/2017.
A Bomb in Plane
g. The Assessment of Vocabulary
Assessment is important to evaluate the students’ ability. It is important after
teaching-learning process because without assessment there is no reliable means of knowing how effective a teaching sequence has been. Assessment provides a form
of feedback, both for students and teacher. According to Sudijono (2009:16), there are two general purposes of assessment.
1) To accumulate the data as a source to know the students’ ability after following the teaching-learning process.
2) To know and measure the effectiveness of teaching method that teachers use during the teaching-learning process.
According to Nation (2001:344), there are some tests to assess vocabulary that commonly said as language testing.
1) True/false test
Write T if a sentence is true. Write N if it is not true. Write X if you do not understand the sentence.
a. We cut time into minutes, hours and days. b. Some children call their mother Mama. c. The entire world is under water.
d. When you keep asking, you ask once.
2) A vocabulary depth test
3) A matching test
Choose one word from the list on the right to complete the sentence. Do not use the same word twice.
a. A journey straight to a place is faint
Circle the choice that best gives the meaning of the underlined word. Chronic means: a. lasting for a long time
Translate the underlined words into your first language. a. You can see how the town has developed.
b. I cannot say much about his character. c. Her idea is a very good one.
In the research, the researcher chose the multiple-choice to test the students’
ability in vocabulary, because multiple-choice might be easier than the other tests. It was supported by Djiwandono (2008:37) that there were nine kinds of
evaluating vocabulary, such as objective test, matching test, true-false test, multiple-choice test, subjective test, essay test, questioning test, question-answer short test and completion test. In the evaluation the researcher used
multiple-choice test. In the case, the researcher prepared some questions with four possible answers in their evaluation sheet and the students crossed which one correct
answer was not appropriate with the key of answers so they did not get the score but when the students answered correctly so they got score.
The researcher formulated the students’ score for each number of items, as follows.
True answer = 1
False answer = 0
Then, the researcher counted the students’ mark by using the formula from Djiwandono (2008:68) as follows.
Obtained Score
Value = × 100
Maximum Score
The criteria of the students’ ability as follows. 86 - 100 = Very high
71 - 85 = High
56 - 70 = Adequate
41 - 55 = Low
<40 = Very low
h. Relationship Between Taxonomy Strategy and Vocabulary
In order to construct the meaning, the material supposed to contain
vocabularies arranged accordingly. That is why reading cannot be separated from vocabulary mastery. Then, can be seen from syllabus of reading at the eighth grade
students of SMP Negeri 3 Lolofitu Moi as follows, “Communicating in English
based on the elementary level” and the basic competence is “Responding the
meaning of short functional text in simple essay accurately, clearly, and acceptable
in daily life context to accesses the science in narrative, descriptive, and analytical
exposition”. It is the basic competence expects the students to be able to get the
meaning from the descriptive text. In descriptive text, the students found the new vocabulary that as their new vocabulary to increase their vocabulary mastery. The researcher gave the new topic to the students about reading text especially
descriptive text, and then students work alone and think of as many words as they can that relate to the topic being studied. From it, the researcher trainned them how
to get the vocabulary as much as possible by using Taxonomy Strategy.
B. The Latest Related Research
In the students’ ability in vocabulary through Taxonomy Strategy, Firian
(2010) had searched about “Increasing the Students’ Ability in Mastering
Vocabulary by Using Taxonomy Strategy at the seventh Grade of SMP Negeri 1 Pariaman.” In doing her research, Firian used Classroom Action Research (CAR)
subject of her research, she chose the students of seventh grade (VII-3) that
consisted of 25 students in SMP Negeri 1 Pariaman in 2010. On Firian’s research,
the teaching learning process was divided into two cycles where each cycle consisted of two sessions. In collecting the data, Firian used some instruments to
collect qualitative data and quantitative data. The qualitative data was taken from
students’ activities by using observation sheet and field notes. While, the
quantitative data was taken from the students’ score in multiple choice test.
Regarded to Firian’s research, it can be said that Taxonomy Strategy gives a
positive impact to the students’ ability in mastering vocabulary. In the research,
the researcher used the same teaching vocabulary strategy in solving the problems as were found by the reseracher in the field. Through Taxonomy Strategy, the researcher searched its effect on the students’ ability in mastering vocabulary at
the eighth grade of SMP level after all, whether there was an improvement, as the
result of Firian’s research, or the reverse or there was no any significant effect at
C. Conceptual Framework
To comprehend the problem in the research, the researcher described what
she conducted in the field since the research was conducted and also what is the problem that she solved. In the case, there were things which should be
considered: the researcher, material, students and method. Taxonomy Strategy that is used to teach vocabulary to the students.
Before applying the Taxonomy Strategy, the researcher did pretest to the
students of the both class. After that, the researcher treated the students in the experimental group by using Taxonomy Strategy whereby in the control group,
the researcher applied a Conventional Teaching Method which was commonly used by the English teacher in the classroom. Then, the researcher performed the posttest to the students to investigate the effect of using Taxonomy Strategy to
the students’ ability in mastering vocabulary.
To make it easier to be understood, the researcher makes a framework on the
Less unable to list the words of descriptve text. topic of descriptive
Conventional
2) The researcher explained to the students the goal of their project
3) The researcher asked the students to work alone to think about their words of descriptive text.
4) The researcher asked the students to list the words related the topic of descriptive text. 5) The researcher let the students to work for
three or four minutes without talking to anyone in the class.
6) The students collaborated by forming small groups to prepare autobiographical and biographical writing.
7) The researcher asked to the students organized by alphabet the word.
8) The students made the whole class forms a group to cross-pollinate thinking and
suggest other words, or the students’ discussion to get ideas from other students’
taxonomies.
9) At the end of the activity, the researcher asked the students add these new words to their personal taxonomy.
1. The researcher explained the material. 2. The researcher gave the example of
complimenting expressions in short dialogue form.
3. The researcher asked some students to practise the dialogue in front of class without correcting their mistakes when practising the dialogue.
Figure 1 : Conceptual Framework of the Research Can not be
achieved
32
In the research, the researcher conducted Quantitative Research and the type
was Experimental research which quasi experimental design. So, the research design is very suitable and useful in teaching-learning process. Anderson
(1998:146) states,
Quasi Experimental is a form research that examines differences between research groups based on some natural characteristics using treatments or interventions but not randomization. It is also known as ex-post facto or causal comparative research.
Furthermore the researcher adds that quasi experimental design being much more flexible and has been used for years in evaluation projects. So, the researcher
concluded that quasi experimental method is one of research methods that does not require individuals be randomly assigned to programs and it is easier to apply.
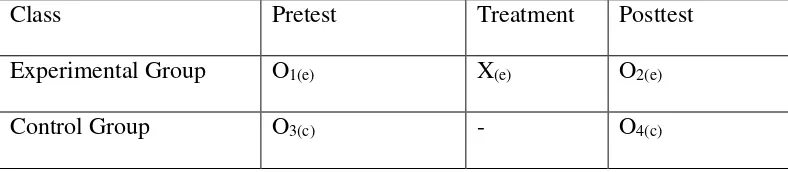
Regarding to the statement above, the researcher conducted Quasi
Experimental Design by using pre test and post test with comparison group design. The group consisted of two, they were experimental group and control group.
However, the researcher administered a pre test for both of the group. It was done before treatment. While after treatment, the researcher administered post test to
know the result of the treatment.
Table 1
RESEARCH DESIGN
Class Pretest Treatment Posttest
Experimental Group O1(e) X(e) O2(e)
Control Group O3(c) - O4(c)
Where:
O1 (e) = Pretest in experimental group
O3 (c) = Pretest in control group
X (e) = Teaching by Taxonomy Strategy
- = Teaching by using treatment conventional method
O2 (e) = Posttest in experimental group
O4 (c) = Posttest in control group
B. The Variables of the Research
There are two variables in the research. The variables are Taxonomy Strategy
as independent variable (X), and the students’ ability in mastering vocabulary as
dependent variable (Y). In the case, the researcher used the two variables to know the
effect of Taxonomy Strategy on the students’ ability in mastering vocabulary at the eighth grade of SMP Negeri 3 Lolofitu Moi.
Taxonomy Strategy The students’ ability in mastering vocabulary
Notes :
X : Taxonomy Strategy (The independent variable)
Y : The students’ ability in mastering vocabulary (The dependent variable)
Based on the graphic above, it was noted that in conducting the research, the researcher applied Taxonomy Strategy as independent variable by holding the
teaching-learning activity in the classroom. As the result, automatically, Taxonomy
Strategy affected to the students’ ability in mastering vocabulary. The more skillful
students in mastering vocabulary was affected of the successfulness of
implementation of Taxonomy Strategy in teaching-learning process.
C. The Population and Sample 1. Population
According to Ary (2007:53), “Population is all members of well defined class
of people, events, or object”. The researcher has to determine the population from
people, events, or object based on the research.
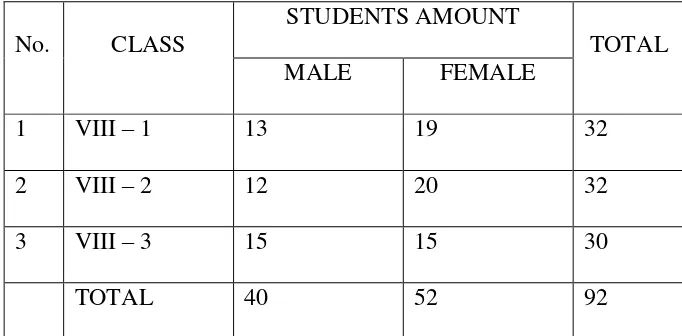
The population of the research was the eighth grade of SMP Negeri 3 Lolofitu
Moi that consists of 92 students. The number of population can be seen at the next page.
Table 2
THE POPULATION CONDITION of the EIGHTH GRADE of SMP NEGERI 3 LOLOFITU MOI in 2015/2016
No. CLASS
STUDENTS AMOUNT
TOTAL
MALE FEMALE
1 VIII – 1 13 19 32
2 VIII – 2 12 20 32
3 VIII – 3 15 15 30
TOTAL 40 52 92
Source: Office Administration of SMP Negeri 3 Lolofitu Moi
2. Sample
Sample is a part of all population that will be searched. Fox in Singh (206:82)
says,
In the social sciences, it is not possible to collect data from every respondent relevant to our study but only from some fractional part of the respondents. The process of selecting the fractional part is called sampling.
Based on the assumption, the researcher is going to take some of the students as the sample of the research. In deciding the sample the researcher used cluster
sampling. As Gay (2000:129) says, “Cluster sampling randomly selects groups,
not individuals. All the members of selected groups have similar characteristics.”
According to Gay (2000:130), there are some steps to select the research sample in cluster sampling as follows.
a. Identify and define the population. b. Determine the desired sample size.
c. Identify and define a logical cluster.
d. List the entire cluster (or obtain list) that make up the population of clusters. e. Estimate the average number of the population members per clusters.
f. Determine the number of cluster needed by dividing the sample size by the estimated size of a cluster.
g. Randomly the select the needed number of cluster.
The steps that will be done by the researcher as follows.
a. The researcher made the lottery as many as the classroom.
b. The researcher asked the representations from each classroom to take the lottery.
One representation takes one lottery.
c. The researcher made three lottery again to choose where is a class of experimental and control group.
d. The researcher decided what the number that will be the research sample is. For instance, the researcher chose the number 1 as Experimental Group and number 2
D. The Kind of Data and Research Instruments
Kinds of data that was looked for by the researcher is quantitative data. And
the type of data is primary data. As Azwar (2007: 91) says that primary data is the data that is obtained directly from the research subject by using instrument or
data measurer directly to the research subject as the source of intended information. So, the researcher used primary data is obtained by using instrument and in this case, the sources were taken from the students at the eighth grade of
SMP Negeri 3 Lolofitu Moi that consists of 62 students.
The instruments that was used by the researcher in conducting the research
especially to get data is evaluation sheet, to know the students’ ability in mastering vocabulary especially descriptive text. It is very important for the researcher to get the data from the students especially by giving test to the
students. In the research, there two types of test, they are pretest and posttest. Pretest was given to the students before they get any treatment to examine the
E. The Procedure of Collecting the Data
The procedure which the researcher applies in the research, they are.
1. Finding the location. The location of the research was the SMP Negeri 3 Lolofitu Moi.
2. Selecting the population. The population of the research was the 8th grade students of SMP Negeri 3 Lolofitu Moi.
3. Selecting sample. The samples of the research were taken through Cluster
Sampling.
4. Administering the pretest in the experimental group and the control group to
examine the normality of the data and the homogeneity of the sample. The purpose of normality of the data in pretest is to examine whether the samples can represent all the population and the purpose of examining the
homogeneity of the sample in pretest is to know whether the samples has the same ability in vocabulary.
5. Holding the tried out of the instruments, that was external validation in SMP Negeri 1 Lolofitu Moi.
6. Correcting the students’ worksheet and examining the normality of the data
and the homogeneity of the sample. After that, the researcher decided which formulas are going to be used, whether parametric or non-parametric formula.
F. The Techniques of Analyzing the Data 1. Trying Out the Instrument
a. Validity
The instrument on the research is a tool for collecting the data or
information. Sudjana (2001:12) affirms that to know the real result and process of
the students’ learning accurately depend on the quality of instrument beyond the
procedures. Meanwhile the quality of instrument itself refers to the validity
scores. So, an instrument is valid or contains a very high validity only if it can measure what it should be measure.
So, before conducting the research, the researcher tried out the instrument externally in in SMP Negeri 2 Lolofitu Moi with purpose to validate the instrument of the research. In validation, the researcher tried out 20 items of multiple
choice in SMP Negeri 2 Lolofitu Moi. To seek the validity of the test, the obtained scores of the tryout were calculated by using the Product Moment Formula as
suggested by Arikunto (2013:213):
r
xy=
𝑁∑𝑋𝑌−(∑𝑋)(∑𝑌)√{𝑁𝑋2−(∑𝑋2) {𝑁∑𝑌2−(∑𝑌2)}
which:
rxy = the coefficient correlation
N = the number of sample (respondent)
Y = the total score of Y variable
It is valid if the rcount ≥ rtable.
b. Reliability
According to Anggoro, et al., (2011:5.31), reliability means the accuratenes
of the instrument for measuring. As Sudjana (2001:16) says that if the instrument has constancy to measure what it should measure, of course it is reliable. The constancy
itself is the situation wherein the instrument gives the same result even the instrument itself is used many times in different occasion.
To seek the reliability of the instrument, the researcher used the split-half
method as suggested by Arikunto (2013:223) as follows.
r11 =
2 x r1/2 1/2
(1 + r1/2 1/2 )
Which:
r11 = the reliability of instrument
r 1/2 1/2 = the correlation between the score every split-half method
Then, the result of the calculation is confirmed to the following criteria as suggested by Sutomo (1985:146) namely.
2. The Data Analysis
a. The Students’ Ability in Vocabulary
To know the students’ ability in mastering vocabulary, the researcher used the formula from Arikunto (1984:175).
Note :
S = Score
R = Right Answer
Then, the researcher calculated all the scores in percentage by using the formula
from Sudjana (2001:88).
Note:
TP = the degree of mastery B = the student’s right answer N = Total score
S=R
Then, the researcher confirmed it to the criteria of Taylor (1988:263).
0% - 54 = very low
55% - 64% = low
65% - 79% = adequate
80% - 89% = high
90% - 100% = very high
b. The Mean Score and Standard Deviation
In getting the Mean Score, Standard Deviation, and Variance of the students’
test result even in experimental class and control class.
Through manual computation, the researcher used the formula from
Djiwandono (2008:212) to get the mean score,
𝑋̅ =∑ 𝑋𝑁
Which :
X = The mean for the data
∑X = The sum of all of scores
N = Number of sample
To get the standard deviation, the researcher used the formula from Djiwandono (2008:215).