USING TRANSACTIONAL STRATEGIES INSTRUCTION IN TEACHING
READING DESCRIPTIVE TEXT OF SMAN 1 SEGEDONG
Hesti Oktari, Zainal Arifin, Eusabinus Bunau
English Language Education Study Program, Languages and Arts Education Department, Teacher Training and Education Faculty, Tanjungpura University
Email: [email protected]
Abstract: The purposes of this research are to find out whether Transactional Strategies Instruction is effective or not in teaching reading comprehension of descriptive text and to find out the effectiveness of using Transactional Strategies Instruction in teaching reading comprehension of descriptive text. The research applies pre-experimental study with one group of pre-test and post-test. The population of this research is tenth grade students of SMAN 1 Segedong. The sample are 30 students of class XC. Based on the research findings, the t-test is 13.6 where the degree of freedom is 2.045. It can be seen that the t-test is higher than the t-table. Therefore, the null hypothesis (Ho) is rejected and the alternative hypothesis (Ha) is accepted. The effect size (ES) of treatment is 2.31. Based on the category, the Effect Size (ES) is higher than the category (2.31>1.00) and categorized as strong effect. Therefore, it can be concluded that using Transactional Strategies Instruction in teaching reading comprehension of descriptive text to the tenth grade students of SMAN 1 Segedong in academic year 2016/2017 is effective and strong effect.
Key Word : Reading Comprehension, Transactional Strategies Instruction, Descriptive Text
T
here are two purposes of doing reading namely reading for information and reading for a pleasure. In the academic environment, reading for information become one of the main purpose that should be done by the students. Thus, reading comprehension is needed to achieve the purpose of reading. Reading comprehension is the process of constructing meaning from text that involves the process of decoding the writer’s word and prior knowledge to reach clear understanding of text. Martin (1991,p.7) stated that reading comprehension requires motivation, mental framework for holding ideas, concentration and good study technique.” It means that in order to success in reading comprehension, the reader needs to motivate him/herself to be more concentrate in reading, try to form mental frame works for holding ideas, and the reader must have a good technique in reading.According to Brown (2003, p.206) they are five aspects that should be mastered by the students in comprehending the text : (a)
Main idea is important information that tells about overall idea of a text. Main idea is directly related to both the topic and the supporting details in the paragraph. Main idea may take place in the beginning of the paragraph, the end of the paragraph, or combination between the beginning and the end of the paragraph; (b) Supporting details are additional details that explain main idea by giving definitions, examples, facts or kinds of evidence; (c) Inference is conclusion drawn based on the passage by combining information in the text with prior knowledge; (d) References are words that refer back to a previous word or phrase without repeating it. (e) Vocabulary is set of words which known by individual.
text the students are lead to comprehend stating the object that is the focus explanation of the text’s content. The second is the
description which describes parts of physical features, qualities, characteristic or habits of the person/something to be described.
Unfortunately, many students got difficulty to comprehend the content of descriptive well. According to pre-observation, this phenomenon happened in SMAN 1 Segedong. In teaching learning process, the teacher only explained about generic structure and social function of descriptive text and then let the students translated the text word by word without any guidance how to cover five aspects of reading comprehension. As a result, they faced difficulty in covering comprehensive questions given.
According to Linse and Nunan (2005,p.71) teaching reading comprehension is teaching students how to derive meaning as well as analyze synthesize what they have read. Thus, it can be defined that teaching reading comprehension is a complex activity to make the students comprehend and deepen understanding from what they read on the text, where the teacher has the important role in order to help students to be a good reader.
In teaching reading comprehension, the teacher cannot directly just teach reading to the students by giving texts and asks them to understand it. There are some principles which have to be considered by the teacher. As it is proposed by Harmer (1998, p.70-71), there are some principles in teaching reading: (a) Reading is not Passive Skill. Reading is an active skill, to do reading successfully. As an active skill, reading should be taught in creative ways to make the students comprehend entire the text and be able to respond the text by giving the argument based on the text after they read the text. Reading is not only read the text word by word but about the topic, and the purpose of reading so the student will be interested in the text, and eager to read the text; (c) Predicting is a major factor in reading. A reader involved in making predictions is focused on the text ,constantly thinking ahead and also refining, revising, and verifying his or her predictions. When the students read the text they frequently have a good idea of content, book covers give them a hunt of what article are about, and the brain start up to predict what are going to read and the article process of reading is ready to begin; (d) The teacher should match the task to the boring and appropriate questions.
Transactional Strategies Instruction is one of the appropriate reading strategy that can be used to help students comprehend the text well. Transactional Strategies Instruction is comprehensive strategy to teach reading comprehension by modeling six steps (predicting, responding to the text based on prior knowledge, seeking clarification, visualizing, questioning and answering, summarizing).
According to Apel et al (2007, p.551) the term transactional is used to emphasize that the students are engage to find out the text meaning through transaction between group member rather than being found by individual. Second, to find out the text meaning through transaction between teacher instruction and student use strategies together to read and comprehend the text and the last help students link their prior knowledge to a text through discussion.
goals and plan for reading; (b) Use prior knowledge and text cues to construct meaning during reading; (c) Monitoring comprehension; (d) Solve problems encountered during reading; (e) Evaluate progress. Transactional Strategies Instruction is an instructional reading strategy used to guide students through a text. The students begin by predicting the topic or title using the clues in the text. The clues in the text allowing them to predict the title or topic of the text. It also help the students to find main idea because main idea relates with topic of the text. Then, in responding to the text based on prior knowledge the students make connections between the text and their prior knowledge and use that knowledge to help them understand what they are reading. Prior knowledge is the knowledge that the students already known about the topic including word identification or word meaning. Brown (2008, p.539) states prior knowledge help the students better understand what they are reading. Furthermore, prior knowledge also helps the students in making inference. In line with Roit (2005, p.4) making inferences involves creating a meaning that is not explicitly stated by the author. Readers use clues in the text and prior knowledge to make meaning of the text.
In seeking clarification, involves discerning when there is a breakdown in comprehension and taking steps to restore meaning. This strategy assures that the passage will make sense to the reader. To learn this strategy, students are instructed to be alert to occasions when they are not understanding the meaning of text, and when this occurs to process the text again. For instance, if a word did not make sense to the student, he or she would be instructed to try to define the word by reading the sentences that precede and follow it. Students are taught to attend to words such as or, which may signal the meaning of an unfamiliar word, and to be certain they know to what referents such as her, his, it, and they refer to. This strategy helps students learn to be actively involved and monitor their comprehension as they read
.
In visualizing involves the ability of the students to think about words that visualize thecontent of a text. This ability can be an indication that the student understands a text. Then in questioning and answering, the students make their own questions about the text, students may generate questions about key points from the text. By generating questions, students become aware of whether they can answer the questions and if they understand what they are reading. In answering the questions help the students to think actively as they read and encourage students to monitor their comprehension. Here, students need to identify the question– answer relationships. Armbuster et al (2003, p.43) states that question-answer instruction encourages the students to actively engage with the text because it requires an understanding of information stated in or implied in the text. This strategy is the process of identifying the important information and ideas within the text, to condense this information, and to put it into their own words. Summarizing may be based on the single paragraph, a section of text or an entire passage. Teaching students to summarize what they read is other way to identify or generate main idea, connect the main or central idea, eliminate redundant and unnecessary information and also remember what they read (Duke and Pearson, 2002, p.220).
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
In accordance with the problem, the method to be used in this research is pre-experimental design which has no control group. According to Cohen et al (2007, p.282), the design of pre-experimental as follow :
Table 1. The Procedure of Pre-experimental
O1
X
O2
can see the influence of treatment. The population of this research is tenth grade students of SMAN 1 Segedong in academic year 2016/2017 which consists of six classes. In this research the researcher takes the sample from XC which consists of 30 students. The technique of data collection in this research is measurement technique which consist of pre-test and post-pre-test. The tool of data collecting is objective test items in form of 30 multiple choices.
The researcher also provides the table of classification which provide with evidence that a test has content validity. Muijs (2004, p. 65) refers, “content validity” to “whether or not the content of the manifest variables (e.g. items of a test or questions of a questionnaire) is right to measure the latest concept (self-esteem, achievement, attitudes) that we are trying to measure.” In other words content validity refers to the match between the test items and the content that was taught. A table of specification is made to measure students’ reading comprehension mastery.
Table 2. Table of Spesification of the Test Item
Reading Comprehension Item Number Main Idea 1,11,21,22,30 Supporting details
Identification 3,5,9,12,16,23,24
Description 4,8,13,14,15,17,28 Inference 2,7,18,26
Pronoun Reference 10,19,27 Vocabulary 6,20,25,29
Regarding to the research purpose that formulated to find out the effectiveness of the treatment, the researcher calculated the data in several ways. The very beginning is analyze the student’s individual pre-test ad post test using the following formula :
A = 𝑅
𝑁 X 100 ……….. (1)
Where :
A = students individual score R = the right answers
N = the number of items
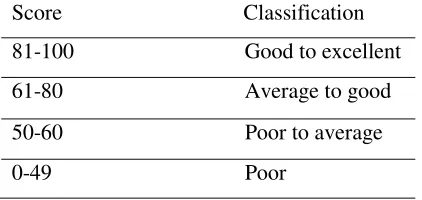
Table 3. The Specification of Student’ Pre -test and Post--test
Score Classification
81-100 Good to excellent
61-80 Average to good
50-60 Poor to average
0-49 Poor
After that, analyze the students’ interval score of pre-test and post-test using the substraction formula :
D = X2 – X1 ……… (2) Where :
D = The interval score of pre-test and post-test
X1 = The students’ mean score of pre-test X2 = The students’ mean score of post-test
The third step the researcher calculate the t-test in order to determine whether or not Transactional Strategies Instruction effective in teaching reading comprehension of descriptive text.The calculation of t-test by using this formula :
𝑡 = 𝐷
√∑D2 –(∑𝐷)𝑁2 𝑁 (𝑁−1)
……… (3)
Where :
𝐷 = The interval score of pre-test and post-test
∑𝐷 = The sum of difference students’ score between pre-test and post-test
∑𝐷2 = The sum of difference students’ score
between pre-test and post-test N = The number of the students
The last step is analysis of the effect size of treatment
𝐸𝑠 = 𝑡 √𝑁1 ……… (4)
Where :
Es = effect size of treatment t = t-test score
FINDING AND DISCUSSION Finding
After analyzing the data, the researcher wants to describe about research finding in order to answer the research problem The students’ score from pre-test and post-test can be seen the following chart (based on the computation) :
Chart 1. The Students’ Score of Pre-test and Post-test
The minimum score of pre-test was 30 while the maximum was 76.6. The total score of achievement was 1489.2. The mean score achievement in pre-test was 49.5 and considered as poor category.
The minimum score of post-test was 50 while the maximum was 93.3. The total score of achievement was 2105.9 . The mean score is 70 and considered as average to good category. So, there is improvement between the students’ mean score of pre-test and post-test result.
Besides, the researcher also analyzed the students’ ability in five aspect of reading comprehension. The students’ ability in answering the questions of main idea in pre-test was 53% while in the post-pre-test was 71%.The students’ ability in answering the questions of supporting details in pre-test was 56.4% and in the post-test was 71.6%. The students’ ability in answering the questions of inference in pre-test was 30% while in the post-test was 67%. The students’ ability in answering the questions of referent in pre-test was 49.4% while in the post-test was 72.8%, the students’ ability in answering the questions of vocabulary was 37.5% and in the post-test was 68%. It indicates that there is significant improvement of the students’ ability in answering 5 aspects of reading comprehension from pre-test to post-test.
Chart 2. The Percentage Of Student’ Ability in Five Aspect of Reading Comprehension in Pre-test and Post-test
30
50 76.6
93.3
49.5
70
0 20 40 60 80 100
Pre-test Post-test
Minimum
Maximum
Average
53%
71%
56.4%
71.6%
30%
67%
49.4%
72.8%
37.5%
68%
0% 10% 20% 30% 40% 50% 60% 70% 80%
Pre-test post-test
Main idea
Supporting details
inference
Referent
Discussion
In this research, the researcher applied Transactional Strategies Instruction in teaching reading comprehension of descriptive text to the tenth grade students of SMAN 1 Segedong in academic year 2016/2017. Transactional Strategies Instruction is a strategy to teach reading through six steps namely predicting, responding to the text based on prior knowledge, seeking clarification, visualizing, questioning and answering, summarizing. Transactional Strategies Instruction is a flexible strategy which the teacher can change every step based on the teacher’ needs.
The researcher chose one class as an experimental group. In the process of collecting data, in experimental group was given pre-test and post-test in the form of 30 multiple choice questions. Previously, the researcher conducted pre-test in order to measure the students’ reading ability of descriptive text. In pre-test, there were 3 students fulfilled the KKM (KKM is 70) while 27 students failed and categorized as poor. Then, the researcher calculated the mean score of test by dividing the total score of pre-test with the whole number of research sample that is 30 students. The mean score of pre-test was 49.5 which considered as poor classification.
After giving the pre-test, the researcher conducted the treatment to the research sample. In the research, the researcher conducted three meeting that focused on teaching reading comprehension of descriptive text by using Transactional Strategies Instruction. In the treatment, the researcher taught about descriptive text and five aspects of reading such as main idea, supporting idea, inference, referent and vocabulary. Then, the researcher divided the students into small group which consisted of 3 students for each group.
In the first treatment the researcher gave 2 texts such as National Monument and Eiffel Tower. In predicting, the students were guided to predict the topic by using the clues
from context. In responding to the text based on prior knowledge, they wrote down some informations related with the topic or words from the text which they had known. In this step, the students were taught about how to covered inference from the text. In seeking clarification, the students were guided to find the meaning of unfamiliar words and referent from the text using context clues. Then in visualization, the students were guided to make a list some words which visualize the content of the text. In questioning and answering, they were guided how to covered supporting ideas from the text by generate some questions using WH questions or yes/no questions and answered them based on the information from the text. In summarizing, the students were guided to covered main idea by making a summary using the 5WH. After that, the researcher gave text about Eiffel Tower and asked them to do the tasks in group and discussed together. Then, the students answered individual task consisted of 5 essay questions. During the first treatment, some groups still did not pay attention well during the learning process. They got confused in each step because this strategy has not been applied by the teacher yet. So they were not active enough.
In the second treatment, the researcher discussed about Borobudur temple and Prambanan temple. The researcher taught about main idea, supporting idea, inference, referent, and vocabulary through those steps in Transactional Strategies Instruction. Then, the students answered individual tasks which consisted of 5 multiple choice questions. During the second treatment, most of the students were enthusiastic because they started to understand in applying those steps in Transactional Strategies Instruction.
listed some words which visualize the content of the text and generate some questions using WH questions or yes/no questions and answer the questions based on the text. The students restated main idea through 5WH. Finally, the researcher asked the students to do individual tasks which consisted of 5 multiple choice questions. During the third meeting, all of them were active in learning process and each step run well.
After that, the researcher conducted the post-test. It was used to identify the students’ ability after the treatment. In post-test, there were 4 students categorized as good to excellent classification, 19 students were categorized as average to good classification and 7 students were categorized as poor to average. Then, the researcher calculated the mean score of post-test by dividing the total score of post-test with the whole number of research sample that is 30 students. The mean score of post-test was 70 and considered as average to good classification. It indicated that there was improvement of students score in reading comprehension.
Then, the result obtained from the t-test calculation was (13.6) the degree of freedom of this research (df) = N-1 (30-1) and the t-critical at 0.05. Hence, it can be known that the t-table of freedom 29 is 2.045. this meant that the test score was higher than t-table (13.6 > 2.045). Therefore, the null hypothessis (Ho) of tis research is rejected and the alternative hypothesis (Ha) is accepted. It meant that Transactional Strategies Instruction is effective in teaching reading comprehension of descriptive text.
Furthermore, the researcher computed the effect size of treatment using formula of effect size. The effect size (2.31) was greater than 1.00 and it was categorized as strong effect. Thus, the hypothesis which stated “The effectiveness of using Transactional Strategies Instruction in teaching reading comprehension of descriptive text is strong if effect size is > 1.00” is accepted. The other statistical hypotheses are rejected.
CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION Conclusion
The finding showed that Transactional Strategies Instruction contributed significant change of the students’ ability, especially how to find main idea, supporting idea, inference, referent and vocabulary. Besides, Transactional Strategies Instruction is an effective strategy and has strong effect in teaching reading comprehension of descriptive text to the tenth grade students of SMAN 1 Segedong in academic year 2016/2017. Suggestion
Based on the results of the research, the writer gives some suggestions : (a) The teacher can use Transactional Strategies Instruction as an alternative strategy in teaching reading comprehension of descriptive text because it is flexible. The flexible means the teacher is allowed to plan and create the activities of Transactional Strategies Instruction based on the situation that the teacher faces; (b) In applying this strategy, the teacher should ask each member of group to be active and think together in each step; (c) The teacher can use this strategy in different kinds of text at other grade level and to be more effective, it is better to make the students in small group discussion; (d) The teacher should manage the class as effective as possible so that they can focus on the lesson and control the students if they make some noise in teaching learning process.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
Apel, K., Ehren, B. J., Silliman, E. R., & Stone, C. A. (2007). Handbook Of Language And Literacy. New York: The Guilford Press.
Armbuster, B. B., Lehr, F., & Osborn, J. (2003). Put Reading First; The Research Building Blocks Of Reading Instruction. Washington D.C: National Institute For Literacy.
Ary, D., Jacobs, L. C., & Sorensen, C. (2010).
Introduction To Research In Education.
Canada: Wadsworth Cengage Learning.
Brown, H. D. (2003). Language Assessment Principles And Classroom Practice.
Brown, R., & Coy Ogan, L. (1993). The Evolution Of Transactional Strategies Instruction (TSI) In One Teacher's Classroom. The Elementary School Journal , 221-233.
Cohen, L., Lawrence, M., & Morrinson, K. (2007). Research Method In Education.
USA: Routledge.
Duke, N. K., & Pearson, P. D. (2002).
Effective Practices For Developing Reading Comprehension: What Research Has To Say About Reading Comprehension. International Reading Association , 205-242.
Gerrot, L., & Wignell, P. (1995). Making Sense of Functional Grammar . Sydney: Antepodean Education Enterprises.
Harmer, J. (1998). How To Teach English.
England: Longman.
Linse, C. T., & Nunan, D. (2005). Practical English Language Teaching: Young Learners. New York: The Mcgraw-Hill Company. Inc.
Muijs, D. (2004). Doing Quantitative Research In Education. London: Sage Publications