i
IMPROVING STUDENTS’ VOCABULARY RETENTION IN OI 743 PETRA CHILDREN DEVELOPMENT CENTER
A THESIS
Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements to Obtain the Sarjana Pendidikan Degree
in English Language Education
By Dudy Virnandi
Student Number: 031214084
ENGLISH LANGUAGE EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAM DEPARTMENT OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDUCATION FACULTY OF TEACHERS TRAINING AND EDUCATION
SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY YOGYAKARTA
iv
LEMBAR PERNYATAAN PERSETUJUAN
PUBLIKASI KARYA ILMIAH UNTUK KEPENTINGAN AKADEMIS
Yang bertanda tangan di bawah ini, saya mahasiswa Universitas Sanata Dharma : Nama : Dudy Virnandi
Nomor Mahasiswa : 031214084
Demi pengembangan ilmu pengetahuan, saya memberikan kepada Perpustakaan Universitas Sanata Dharma karya ilmiah saya yang berjudul :
IMPROVING STUDENTS’ VOCABULARY RETENTION IN OI 743 PETRA CHILDREN DEVELOPMENT CENTER
beserta perangkat yang diperlukan (bila ada). Dengan demikian saya memberikan kepada Perpustakaan Universitas Sanata Dharma hak untuk menyimpan, mengalihkan dalam bentuk media lain, mengelolanya di Internet atau media lain untuk kepentingan akademis tanpa perlu meminta ijin dari saya maupaun memberikan royalty kepada saya selamA tetap mencantumkan nama saya sebagai penulis.
Demikian pernyatan ini yang saya buat dengan sebenarnya. Dibuat di Yogyakarta
Pada tanggal : 10 March 2008 Yang menyatakan
v
STATEMENT OF WORK’S ORIGINALITY
I honestly declare that the the sis I wrote does not contain the works or parts of the works of other people, except those cited in the quotations and the bibliography, as a scientific paper should.
Yogyakarta, 15 February 2008 The Writer
vi
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
I am so grateful to my dearest Lord Jesus for His blessing. His gracious love shines on me through many people around me by whom I have been given care, encouragement, assistance, and accompaniment. I would like to say my very best thanks to these beloved people.
My biggest gratitude goes to my major sponsor, F.X. Ouda Teda Ena, S.Pd., M.Pd., for his advice and guidance through the process of writing of this thesis, for endowing me his time to read and to correct it, and for his fatherhood in sharing his knowledge with me. Undeniably, I have received so much from him. His patience, friendliness, and care have comforted me in improving my writing through every thesis consultation I had with him.
I would also like to thank to my co-sponsor, Made Frida Yulia, S.Pd., M.Pd., for patiently furnishing my thesis with her precious suggestions and for encouraging me through the writing process of this thesis. Her interest in details has improved my thesis and has changed it into a better one. I have learned many things related to grammar and the mechanics of formal writing from her.
My thankfulness goes to my beloved father, mother, brothers, and sister. They have become my motivation in accomplishing this thesis. I would like to thank them for their concern, encourage ment, prayer, and accompaniment.
vii
accomplishment of my thesis. It is my prayer to my gracious Lord to bless all who have so kindly supported and fostered me through all this time.
viii 1.2 Proble m Formulation ……….………
1.3 Problem Limitation ……… 1.4 Research Objective ……… 1.5 Research Benefits ……… 1.6 Definition of Terms ………
CHAPTER II. REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
ix
2.1.2.5 Techniques of Vocabulary Teaching ……… 2.1.2.6 Pictures in Vocabulary Teaching .. ……….
2.1.2.7 Vocabulary Selection ……… 2.1.3 Children Language and Learning ………. 2.1.3.1 Children as Active Processors ………... 2.1.3.2 The Principle of Children Language Learning ……….. 2.1.3.3 The Principle for Teaching English to Children ……….… 2.1.4 Elementary School Students ……… 2.1.4.1 Fifth Grade Students ………. 2.1.4.2 The Students’ Characteristics in Learning ……… 2.2 Theoretical Framework……… 3.4 Data Gathering Techniques ………. 3.5 Data Analysis Technique ……… 3.6 Research Procedure ……….
CHAPTER IV. RESEARCH RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS
4.1 Research Findings ……… 4.1.1 The Implementation of the Chosen Strategy …….
x
4.2.2.1 Implementing Action and Collecting Data ……… 4.2.2.2 Reflecting and Planning Informed Action ……… 4.3 Discussions ……… 4.4 Other Findings ………
CHAPTER V. CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS
5.1 Conclusions ……… 5.2 Suggestions ….………...
BIBLIOGRAPHY.……….….
APPENDICES ……….
49 50 50 52
54 55
xi
LIST OF FIGURES
Figure Page
xii
LIST OF TABLES
Table Page
xiii
LIST OF APPENDICES
Page
Appendices Cover ……….. 59
Appendix 1. Triangulation Matrix: Three ACR Questions ……… 60
Appendix 2. Triangulation Matrix Data ………..………... 61
Appendix 3. Learning Designs …..………... 68
Appendix 4. Weekly Quizzes ..……….…….. 74
xiv ABSTRACT
Virnandi, Dud y. 2008. Improving Students’ Vocabulary Retention in OI 743 Petra Children Development Center. Yogyakarta: English Language Education Study Program, Sanata Dharma University.
English learning is very essential in this modern era. One of the important factors for the improvement of English mastery is vocabulary mastery. In this research, the fifth grade students of elementary school in PPA OI-743 Petra
Yogyakarta could not memorize English words optimally. The problem occurred when they were only able to memorize below 10 out of 15 English words. Considering the phenomenon, the writer tried to search for an effective strategy to teach English words toward the fifth grade students of elementary school in PPA OI-743 Petra as it is formulated in the research question. What is the teaching strategy that is appropriate to improve the vocabulary learning achievement of the fifth grade students in OI 743 Petra Children Development Center?
The writer applied Classroom Action Research (CAR) method in this research. The method allowed the writer to apply any strategy which was considered effective to teach English words. In order to evaluate the strategy used in the research, the writer used Triangulation Matrix and weekly quizzes as data gathering techniques.
xv ABSTRAK
Virnandi, Dudy. 2008. Improving Students’ Vocabulary Retention in OI 743 Petra Children Development Center. Yogyakarta: English Language Education Study Program, Sanata Dharma University.
Pembelajaran bahasa Inggris sangat penting di zaman modern ini. Salah satu faktor penting dalam peningkatan penguasaan bahasa Inggris adalah penguasaan kosa kata. Didalam penelitian ini, siswa kelas lima sekolah dasar di PPA OI-743 Petra Yogyakarta tidak mampu mengingat kosa kata bahasa Inggris secara maksimal. Permasalahan muncul ketika mereka hanya mampu mengingat dibawah 10 dari 15 kosa kata bahasa Inggris. Dengan mempertimbangkan hal ini, penulis mencoba untuk mencari sebuah strategi yang efektif untuk mengajar kosa kata bahasa Inggris ke anak-anak kelas lima sekolah dasar di PPA OI-743 Petra seperti yang sudah dirumuskan di pertanyaan penelitian ini. Apa strategi pengajaran yang efektif untuk meningkatkan pencapaian pembelajaran kosa kata anak-anak kelas lima sekolah dasar di PPA OI-743 Petra?
Penulis menerapkan metode Classroom Action Research (CAR) di penelitian ini. Metode ini memberikan kesempatan kepada penulis untuk menerapkan strategi yang dianggap efektif untuk mengajar kosa kata bahasa Inggris. Untuk mengevaluasi strategi yang digunakan didalam penelitian ini, penulis menggunakan Triangulation Matrix dan kuis mingguan sebagai teknik pengumpulan data.
1 CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
This research is conducted in order to investigate a strategy to improve students’ retent ion in their vocabulary mastery. To achieve the goal of the research, there are some important points which will be discussed in this chapter. They are background of this research, problem limitation, problem formulation, research objective, benefits, and definition of terms.
1.1 Background
After the researcher ha ve been teaching in this foundation for about one year, the researcher find that students are weak in their vocabulary mastery.. Based on the researcher’s observation, the students face difficulty in memorizing the vocabulary of the previous meeting. Only one third of students of the fifth grade are able to memorize some of the words but two third of the students are not able to memorize English words they learn. Moreover, students are not accustomed to memorizing the written form effectively, so even though they are able to memorize the sound of the words, it is sometimes difficult for the m to write the written form of the vocabulary.
The reason for being interested in the lexical dimension of language is the fact that most people language is largely a matter of words. Stubbs (1986: 99) puts it as quoted in Exploring the Second Language Mental Lexicon written by David Singleton, “When people think of language, they think almost invariably of words.” It has been the concern of the researcher to be able to teach the students effectively, especially in their learning of vocabulary because as it is quoted in Singleton (1999: 9) “without grammar very little can be conveyed, without vocabulary nothing can be conveyed” (Wilkins, 1972: 111).
their mind is still developing, their brain is still functioning maximally and they are motiva ted to study. In spite of the difficulties which might appear in the class, the researcher believe that by choosing or even constructing an effective strategy, students will be able to learn English words effectively.
Since there is no curriculum of English available in OI 743 Petra Children Development Center, the researcher hover the chance to choose and to apply any useful strategy for the learning of the students. This opportunity brings the researcher to adopt and to do a research in the researcher’s class without being afraid of any inconvenience or objection from the chairman of the foundation. This foundation is considered as Non-Government Organization; hence, it gives freedom to the researcher to set his learning as the researcher desired.
In this research, the researcher tries to investigate any beneficial strategy for the improvement of students’ retention in their vocabulary mastery. The track of finding or even constructing a strategy which is appropriate with students’ characteristics is considered from the previous actions taken by the researcher. The researcher is aware that some strategies do not function for the students of OI 743 Petra Children Development Center. The researcher hopes that this research will establish an appropriate strategy to teach English words toward the students who face difficulties in memorizing English words they learn.
1.2 Problem Formulation
What is the teaching strategy that is appropriate to improve the vocabulary learning achievement of the fifth grade students in OI 743 Petra Children Development Center?
1.3 Problem Limitation
It is the responsibility of a language teacher to understand the difficulties faced by the students in their achievement in English vocabulary learning. Moreover, students in the age of Elementary school level are considered capable to obtain good memorization of English words. Based on critical period theory, young learners learn language better than adult s.
As it is mentioned that students tend to forget the English words they learn previously, the critical period theory has influenced the researcher to search for a strategy which is effective to teach English words to the fifth grade students in OI 743 Petra Children Development Center. The concern of this research is how to improve students’ retention in their English vocabulary learning. Therefore a strategy is looked for the teaching of English words in OI 743 Petra Children Development Center.
1.4 Research Objective
1.5 Research Benefits
This research is expected to bring beneficial effects toward both the teacher and the fifth grade students of Elementary school level in OI 743 Petra
Children Development Center. The benefits of this research are first, it is aimed to give a good view related to the process of retention that occurs in English vocabulary learning in OI 743 Petra Children Development Center.
Second, the result is expected to help the fifth grade students of Elementary school level in OI 743 Petra Children Development Center in their English learning. By providing an effective strategy, it is expected that they are able to increase their achievement in their English words learning.
Third, it will ease the ir formal English teacher in their formal study. The students of the fifth grade of Elementary school level in OI 743 Petra Children Development Center have been educated effectively in their vocabulary learning. They are expected to do better in their English formal study.
1.6 Definition of Terms
In order to support the reading of this report, some definitions are provided to help the reader to comprehend some difficult terms.
1. Vocabulary
language. They can stand-alone or together. They may be different in meaning from each other.
2. Learning strategies
Wenden and Rubin (1987: 71) define learning strategies as techniques, approaches, or deliberate actions that students take in order to facilitate the learning and to recall of both linguistic and content area information. In this research, the researcher bases the success of the research on the learning strategy which is used to teach English words. They participate as the main factor to solve the problem formulation of this research.
3. Cognitive
As it is quoted in Wenden and Rubin (1987: 72), in Brown and Paliscar’s point of view, cognitive strategies are directly related to a specific task and learning objective and may not be applicable to different types of learning task. The researcher uses cognitive strategies hence they are suitable with the research
4. Retention
Bauman (1980: 35) explains retention as an active process requiring learning. In this study, retention is focused on the active process of memorizing the English words. It uses required learning which is effective to improve students’ achievement in learning English vocabulary.
5. Triangulation Matrix: ACR Three Questions
In order to collect the data in this research, the researcher records the teaching using Triangulation Matrix: Three ACR Questions. The form of
his book entitled The Action Research Guide Book. Sagor explains The Triangulation Matrix as a tool designed to recount the data which occur in the teaching and learning process. It is like a journal. It records written data from the research.
6. Children Development Center OI 743 Petra
8
CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
This research is conducted to investigate the appropriate strategy to improve the achievement of the fifth grade students in their English vocabulary learning in OI 743 Petra Children Development Center. Thus, the researcher bases the research on theories in language teaching and learning. The theories are used to search for an appropriate strategy in teaching English vocabulary toward students of the fifth grade of elementary school in OI 743 Petra Children Development Center in their English vocabulary learning.
2.1 Theoretical Description
2.1.1 Teaching English as a Foreign Language
As the rapid growth of advanced communication system, world seems to be shrinking very rapidly. It happens as the international barriers break down and people can more easily come into contact with other cultures and languages through travel, communication or new technology. Brewster et al. (2002: 1) state this so-called globalization of the world is a modern and sometimes controversial trend which looks as though it may be here to stay, at least for the time being.
language skill will benefit their children greatly by giving them more opportunities to gain economic, cultural or educational advantages. As it is explained by Brewster et al. (2002: 1) that
Governments and private schools all over the world have decided to introduce English at primary level, because there is a strong “folk” belief, a sort of ‘act of faith’, that young children learn language better and more easily than older children. This means there is a wide spread belief that there are definite advantages to introducing language learning early in life which outweigh the disadvantages.
Therefore, English teachers might ask their selves whose language they teach, for what purpose and what their relationship with English, do they consider it to be foreign, second or native language. The term “foreign” is also used to distinguish the teaching of English in an area where there is an exposure toward English with an area where the access to English is almost impossible. Indonesian students are foreign language learners in which exposure toward native speaker of English is almost impossible to be daily meeting exposure. On the contrary, students face non-native English speakers in their English learning. It is why, the need of a very qualified strategy of teaching is necessarily required to help students learning.
2.1.2 Vocabulary
2.1.2.1 The Meaning of Vocabulary
language. They can stand-alone or together. They may be different in meaning from each other.
According to Nation (1990: 31), “Learner’s vocabulary is divided into two groups, active and passive.” Active vocabulary is the vocabulary that the learner should use in speaking and writing. While passive vocabulary is words the learner needs to recognize in listening and reading. Speaking vocabulary is words used to communicate someone’s thoughts, feelings, and ideas to others. Writing vocabulary is words that the children use to express their thoughts on paper. As Nation (2002: 6) proposes
All words are created equal. Some occur much more frequently than others and are thus more useful for learners. This knowledge is very important pre-requisite for planning a vocabulary program, and for making day-to-day decisions about how to treat particular words.
Nation (2002: 6) divides vocabulary into four major groups. They are 1) High frequency words, 2) Academic words, 3) Technical words, and 4) Low frequency words. In this research, the researcher is going to use the high frequency words as the vocabularies which are frequently used in the English vocabulary teaching. This selection will help students to expose themselves with daily English words and to give them more exposure toward their needs of certain words related to their daily life.
2.1.2.2 The Importance of Vocabulary
communication. It records the thoughts or ideas and drives them into others’ mind. Taylor (1990: 1) states:
In order to live the world, we must name it proposes another evidence of the importance of word. Names are essential for the construction of reality for without a name it is difficult to accept the existence of an object, an event, a feeling. Naming is the means whereby we attempt to order and structure the chaos and flux of existence, which would otherwise be an undifferentiated mass. By assigning names, we impose a pattern and meaning which allow us to manipulate the world.
She (1990: 1) mentions in foreign language teaching, vocabulary has for a long time been a neglected area. It happens because pride of place has been given to “structures” or latterly “function”. Course books have provided little guidance other than word list, so that apart from turning to the specialized supplementary material, such as dictionary workbooks, teachers have been hard to satisfy their students’ demand for “words”. Happily, this situation has changed in the opposite direction. Nowadays many of newer course books include word study section. Nation (1990: 2) argues
The fact that simply increase learners’ vocabulary without giving attention to putting this knowledge to use may not be effective, but getting learners to do language task when their vocabulary is inadequate for the task is a frustrating experience.
2.1.2.3 Vocabularies Proposed in the Curriculum
The goals of Indonesian government in teaching English to the fifth grade of elementary school are able to listen, to read, to pronounce, and to write some English words; the students have functional skill in sentences and English utterances dealing with student’s environment and student’s school (GBPP, 1994: 6). Those goals are related to English vocabulary teaching. The Indonesian government lists English in its curriculum and inside of it; there are English words for the fifth grade students.
2.1.2.4 Approaches to Vocabulary Learning
Vocabulary teaching can fit into a language learning course in any of four ways. Nation (1990: 4) explains those four ways from the most indirect to the most direct as follows.
1) Material is prepared with vocabula ry learning as a consideration. The most common examples of this are the preparation of simplified material and the careful grading of the first lessons of learning English.
2) Words are dealt with as they happen to occur. This means that if an unknown word appears in a reading passage, the teacher gives some attention to it at the moment it causes a problem.
3) Vocabulary is taught in connection with other language activities. For example, the vocabulary of reading passage is dealt with before the learners read the passage.
4) Time is spent either in class or out of school on the study of vocabulary without an immediate connection with some other language activities. For example, time is spent on learning spelling rules or on activities like dictionary use, guessing words, the use of word parts or list learning.
2.1.2.5 Techniques of Vocabulary Teaching
There are two general techniques in foreign vocabulary learning, namely “receptive and productive learning” (Wallace, 1991: 21). Receptive learning makes the students able to recall the translation of foreign word when the foreign word has been seen or heard. For example, the teacher says the word ‘red’, the students hear the word and are able to remember the meaning in their first language.
Productive learning supports the students to produce the foreign word by speaking and writing. It requires more time than receptive learning. For productive learning, “saying the words aloud brings faster learning with better retention” (Wallace, 1991: 29). For instance, the teacher shows a picture of an elephant and asks the student to word in English. It can be concluded that based on the techniques, the research deals with receptive and productive learning. First, students need to be able to recall translation of the word and second, the students are required to speak the word in oral way and to write the word in script form.
2.1.2.6 Pictures in Vocabulary Teaching
(1987: 72), Brown and Paliscar (1982) classify general learning strategies as metacognitive or cognitive. Their point of view, metacognitive strategies involve thinking about the learning process, planning for learning, monitoring for learning while it is taking place and self-evaluation of learning after the learning activity. Metacognitive strategies can be applied virtually all types of learning task whereas cognitive strategies are more directly related to a specific task and learning objective and may not be applicable to different types of learning task.
Based on the above explanation, the researcher proposes the cognitive strategies, thus, they involve manipulation or transformation of material to be learned; in other words, learners interact directly with what is to be learned (Wenden and Rubin, 1987: 72). Cognitive strategies can vary in the amount of leaners’ interaction or transformations involved; greater involvement is thought to result in increased learning.
Quoted in Wenden and Rubin (1987), Brown and Paliscar (1982) divide cognitive strategies into several kinds. They are repetition, resourcing, directed physical response, translation, grouping, note taking, deduction, recombination, imagery, auditory representation, key word, contextualization, elaboration, transfer, and differencing.
The other way is through verbal explanations. They are (1) analytical definition, (2) putting the new word in defining context, and (3) translating into another language
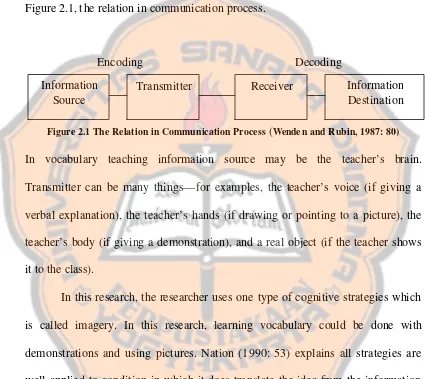
Nation (1990: 52) draws the relation in communication process as in Figure 2.1, the relation in communication process.
Encoding Decoding
Figure 2.1 The Relation in Communication Process (Wende n and Rubin, 1987: 80)
In vocabulary teaching information source may be the teacher’s brain. Transmitter can be many things—for examples, the teacher’s voice (if giving a verbal explanation), the teacher’s hands (if drawing or pointing to a picture), the teacher’s body (if giving a demonstration), and a real object (if the teacher shows it to the class).
In this research, the researcher uses one type of cognitive strategies which is called imagery. In this research, learning vocabulary could be done with demonstrations and using pictures. Nation (1990: 53) explains all strategies are well applied to condition in which it does translate the idea from the information source. He also suggests that English language teachers could help their learners to grasp the concept by varying the situation in which it is demonstrated and by giving verbal definition as well as nonverbal one. In this case, Wenden and Rubin (1987: 77) state that imagery is used by relating new information to visual concepts in memory via familiar easily retrievable visualizations, phrases or
locations. Those visual concepts are suitable and helpful for students’ strategy in memorization of English words.
2.1.2.7 Vocabulary Selection
It is important to decide the kind of vocabulary and the amount of English words which are going to be used for vocabulary teaching. This information should be provided in the curriculum. In the local 1994 content curriculum, there is no syllabus for the 2nd and 3rd grades of Elementary School level. In the research the researcher selects the English words, determines number of the words to teach and makes lesson plans for English words teaching.
Lado (1964: 119) states “the teacher needs to rely on certain criteria of vocabulary selection in order to meet the needs of various goals and conditions.” In the vocabulary selection, teacher should recognize the criteria of vocabulary for his/her students. He/she should understand the objective which will be achieved, learners’ level, background of the students, needs of learning, and learning source.
2.1.3 Children Language and Learning
2.1.3.1 Children as Active Processors
those structures, which are accounted for by the underlying rule system they already posses. The child as active language processor and hypothesis builder is a more powerful explanation of language acquisition than the child as an imitator. From the above explanation, we recognize that children construct their information in their brain, as the learning of language takes part. Lindfors also proposes that children learn from the simpler syntactic unit of language to the more complex one. Word is a simple syntactic unit which can help the children to communicate their idea to be understood by other people in their surroundings.
2.1.3.2 The Principle of Children Language Learning
The children ability to learn a language is different from adult’s ability. The children have their own principles in learning a language. Hudelson (1991: 2) states four basic principles of children language learning, they are learning by doing, learning in social contexts, learning with experimenting and using the language, and learning through social interaction. Here are the explanations for each principle.
1) Learning by doing
accomplishing the meaningful task” (Hudelson, 1999: 20). Therefore, teacher is necessary to encourage the children to use the language in the meaningful tasks. 2) Learning in social context
Vygotsky’s work related to language learning postulates that “children learn in social context, in groups where some members know more than other” (Hudelson, 1991: 2). From this principle, it can be concluded that besides learning through hands-on experiences, children also need to use the language in interacting with other children and adult. In the English Foreign Language learning, it is suggested that teacher uses English as much as possible.
3) Learning with experimenting and using the language
“First and second language acquisition occurs through learners figuring out how the language works, through learners making and testing out hypotheses about the learning” (Hudelson, 1991: 2). This means that learners need to be given chances to use the language as much as they can. While using the language, children will make mistakes. Making mistakes is natural and inevitable part in language learning” (Hudelson, 1991: 2). The teacher should not punish the children who make mistakes but he should correct the mistakes.
4) Learning through social interaction
Children have their own characteristics in learning a language. It is important for the English teachers of Elementary school to know the children’s principles in learning a language. Those principles will help the teacher in creating pleasant and enjoyable teaching learning activities.
2.1.3.3 The Principle for Teaching English to Children
The way of teaching children in elementary school is different from adult’s way. Brewster (2004: 39) explains the ten principles for teaching young learners. The principle s may give direction and guidance to teach language to children effectively.
Here are the ten principles of teaching young learners: 1) Starting where the child is
Children in the classroom have experience of life, knowledge about their world and at least one language. The teaching material and activities should relate to their world and experience.
2) Encouraging social interaction
Brewster states “learning is an interactive process” which involves both teacher and students in sending and transmitting the message. Primarily, children are active participants in the classroom. Therefore, the teacher should encourage students to interact with others, as language is a means of social interaction.
3) Supporting negotiation of meaning and collaborative talk early
4) Allowing the children to be active
The teacher guides the students to be active in learning process by giving challenging materials and asking them to take a risk in learning. The teacher should allow the children to encounter challenges and risks. The challenges and taking the risks will train students to become independent, motivated, and succeed to progress.
5) Pitching input within the zone of proximal development
It is explained before that the children need to encounter challenges and to take risks in their language learning. The teacher can give the children language input beyond their linguistic level to give them opportunity for challenges and risks. The challenges and risks can be led to the successful learning.
6) Introducing language at discourse level
Children obtain pleasure when studying a new language through stories, songs, and play. Those are examples of activities to introduce language at discourse level. Those are examples of how learners can be exposed to comprehensible, meaningful language at discourse level.
7) Planning meaningful and purposeful activities within a clear familiar context The teacher should tell the students the purposes of doing an activity. Therefore, they know what activities that can support and foster themselves to be more independent. This can be done by introducing pair work and group work, the use of dictio naries and reference materials. The familiar context will enable teacher and learners to do meaningful activities.
In teaching learning process, the teacher is required to facilitate the students all the time by giving them chances to study by themselves. This will make the students more independent.
9) Developing a supportive, non-threatening, enjoyable learning environment The teacher should create comfortable learning atmosphere in the class to support the learning activities. The enjoyable environment can be created by valuing all learners as individuals, supporting challenges and risks, working on relevant and interesting topics, doing meaningful and purposeful activities and also discipline.
10)Testing and assessing in the way that we teach
The teacher conducts the test and assessment to know the development of students’ ability and the progress they make in their learning.
2.1.4 Elementary School Students
The fifth grade students of Elementary school are the subjects of this research, their characteristic s including how they learn, the principle of children language learning and also the principle of teaching English to children will be discussed.
2.1.4.1 Fifth Grade Students
operational period which extends from about 6 to 7 to 11 or 12, and the formal operational period which continues from approximately 11 to 12 through adulthood or old age. The fifth grade students are in the concrete operational period.
This includes the fifth grade students of elementary school. They are considered in the intermediate grade because they are in the last three year. Their development characteristics found in this period are physical, intellectual, emotional, and social aspect. Curiosity is an indicator of their cognitive development. They are interested in learning all kinds of thing and they want to know as many facts as possible.
2.1.4.2 The Students’ Characteristics in Learning
The thoughts of children of elementary school age develop gradually and stay calm in normal condition. They are the very stage of learning (Kartono, 1979: 140). Children have unique attitudes toward learning something because they know not necessarily in what they know.
The nature of children’s learning depends on the stage of cognitive development they have reached (Kartono, 1979: 140). In addition, memory of children of 8 to 12 years reaches the highest and greatest intensity. The ability to learn by heart is the strongest competency.
Scott and Lisbeth (1993: 3-4) identify some general characteristics of children that are related to their capability as follows:
2. They can tell the differences between fact and fiction. 3. They ask questions all the time.
4. They rely on the spoken word as well as the physical world to convey and to understand meaning.
5. They are able to make some decisions about their own learning. They have definite vie w about what they like and they dislike doing
6. They have a developed sense of fairness about what happens in the classroom and begin to question teacher’s decisions.
7. They are able to work with others and to learn from others.
From those descriptions above, it is crucial to know how they learn. It becomes a great guidance in choosing a strategy to increase students’ vocabulary retention.
2. Theoretical Framework
help the students to expose themselves with daily English words and to give them more exposure toward their needs of certain words related to their daily life.
Nevertheless, in local context as in OI 743 Petra Children Development Center, it is arduous for learners in the fifth grade of Elementary school to master English vocabulary. These students are from under average socioeconomic background. Some of students are still able to memorize some of the words but some are not. However, most students are not accustomed to memorize effectively. Even though, they are able to memorize the sound of the words, it is sometimes difficult for them to write into right spelling.
As a result of the research objective that is to find an appropriate strategy to teach English vocabulary in OI 743 Petra Children Development Center, some principles must be taken into consideration. Firstly, words of daily life communication will vary in nature; according to Brooks (1962), “Learner’s vocabulary is divided into two groups, active and passive.”
Active vocabulary is the vocabulary that the learner should use in speaking and writing. While passive vocabulary is vocabulary the learner needs to recognize in listening and reading. This research covers both vocabularies. This fact is supported by Nation (2002: 6). He proposes all words are created equal.
where the child is, (2) Encouraging social interaction, (3) Supporting negotiation of meaning and collaborative talk early, (4) Allowing the children to be active, (5) Pitching input within the zone of proximal development, (6) Introducing language at discourse level, (7) Planning meaningful and purposeful activities with in a clear, familiar context, (8) Helping learners to become more independent and autonomous, (9) Developing a supportive, non-threatening, enjoyable learning environment and (10) Testing and assessing in the way that we teach.
The third, the researcher recommends direct learning toward English words. Nation (1990: 2) defines direct vocabulary learning as the learners do exercises and activities that focus their attention on vocabulary. Some examples of those activities are word-building exercises, guessing words from context when it is done as a class exercise, learning words in list and vocabulary games.
The fourth, the researcher considers the learning of vocabulary which is done in 743 OI Petra Children Development Center as productive learning. Productive learning supports the students to produce the foreign word by speaking and writing. It requires more time than receptive learning. For productive learning, “saying the words aloud brings faster learning with better retention” (Wallace, 1991: 29). For instance the teacher shows a picture of an elephant and asks the student to write the English word. By being productive and direct toward the English words, learners are provided with the supporting atmosphere to ease them in their vocabulary learning.
based on many factors. The examples of the factors are time needed to learn, number of words to be learned, the difficulty of words, and the repetition of the words.
The last, the researcher proposes the cognitive strategies as the learners involved in manipulation or transformation of material to be learned; in other words, the learner interacts directly with what is to be learned (Wenden and Rubin, 1987: 72). Cognitive strategies can vary in the amount of learner’s interactions or transformations involved; greater involvement is thought to result in increased learning. Quoted in Wenden and Rubin (1987), Brown and Paliscar (1982) divide cognitive strategies into several kinds. They are repetition, resourcing, directed physical response, translation, grouping, note taking, deduction, recombination, imagery, auditory representation, key word, contextualization, elaboration, transfer, and differencing.
In this research, the researcher uses imagery as the strategy to teach vocabulary. Here are some alternatives of imagery strategy through demonstration or picture. They are (1) using an object, (2) using a cut-out figure, (3) using gesture, (4) performing an action, (5) photographs, (6) blackboard drawing or diagrams and (7) pictures from books. As a specific strategy which is used in this research, the researcher chooses pictures as the media in teaching English words to the fifth grade students in 743 OI Petra Children Development Center.
29
CHAPTER III
METHODOLOGY
This chapter discussed the methodology of the research. In this research, there were six points which were going to be explained. They were method of the research, research participants, research instruments, data gathering techniques, data analysis technique, and research procedure.
3.1 Method
The research used CAR (Classroom Action Research) during the process. As it was cited in Sagor (2005: 1), “action research is a disciplined process of inquiry conducted by and for those taking the action. The primary reason for engaging in action research is to assist the actor in improving or refining his or her actions.” In this research, the researcher investigated an appropriate teaching strategy to improve students’ achievement in their English vocabulary learning in OI 743 Petra Children Development Center.
Hughes (1989: 9) stated that there are four types of test; they are proficiency test, achievement test, diagnostic test, and placement test. Since the research was aimed to observe the progress of the student after the treatment, achievement test was considered appropriate to be applied. As it was stated in Hughes (1989: 10) that
Achievement tests are directly related to language courses, their purpose being to establish ho w successful individual student, groups of students, or the course themselves ha ve been in achieving objective. They are two kinds: final achievement tests and progress achievement test. Based on the goal of the research that was to observe progress of the students, the researcher used progress achievement test. In the meantime, the researcher used journal during the treatment period to collect the word data as the main source of the research data. The journal consisted of important questions related to students’ progress in their retention of English vocabulary learning. It was called Triangulation Matrix. These two data gathering techniques helped the researcher to maintain validity and reliability of the data.
3.2 Research Participants
3.2.1 Research Subject
The subjects of this research were students of the fifth grade of Elementary School in OI 743 Petra Children Development Center. These subjects were chosen based on some considerations. The first, the students cooperated easily in the research. Second, they tended to be active in following and joining the lesson. In addition, English course program was provided in the main program of OI 743
seventh, and tenth grade students. Among those grades, only the fifth grade students faced difficulties in learning English vocabulary. This problem became the main issue which established the research question.
3.2.2 Research Setting
Considering the availability of the subjects of the research, the researcher determined OI 743 Petra Children Development Center as the main place for conduc ting the research. English course program was designed to help students to improve their English achievement in their formal school. The subjects attend ed the English course program once in a week. For the fifth grade, the class was scheduled on Sunday. The class used to be in an open space class. The place was large and appropriate for any teaching activities. This research was held on April up to May. The first research was conducted on April 23rd, 2007 and reviewed on April 30th, 2007. The second research was conducted on May 21st, 2007 and reviewed on May 28th, 2007.
3.3 Research Instruments
changes which occurred in teaching and learning process as an evaluation toward English vocabulary teaching strategy. In order to obtain the data, the researcher also used a test as a tool for data gathering. The test was in the form of an achievement test. The achievement test was weekly quiz. It was used to measur e student’s achievement in their English vocabulary learning.
3.4 Data Gathering Technique s
Data in this research were collected from the weekly progress report journal of the researcher. It was called Triangulation Matrix. During the teaching process, the researcher gathered the data of the progress of students in their English vocabulary learning. At the end of class, the data were carefully evaluated and used to determine the success of the strategy which was used in the research. It was necessary to record the progress and the changes that were made by the students.
Another data gathering technique which was used to provide the data was a test. It measured students’ achievement in their English vocabulary learning. The test consisted of questions that were related to English vocabulary of the previous topic. The previous topic was given a week before the test. The achievement test was a weekly quiz. The weekly quiz was used as the data gathering technique to collect data. Based on the weekly observation and the quiz result the researcher could evaluate the result of the strategy which was used for to teach English words.
3.5 Data Analysis Technique
The data of the research were numeric and word data. They were taken from the treatments, which were given by the researcher. This treatment was aimed to solve students’ difficulty in English vocabulary learning in OI 703 Petra
Children Development Center. Treatment provided the result, which was required for data analysis. This research chose weekly journal and weekly quizzes as the data gathering techniques to observe the improvement of students’ retention in their vocabulary learning. Accordingly, the results of weekly observation and quiz were the result of the research. They measured progress of students’ retention in their English vocabulary learning.
In order to be able to observe the progress of the students, the researcher set up standard of the amount of the vocabulary items. The standard was thirteen English words out of fifteen English words, which were used in the English vocabulary learning. From the standard amount of the vocabulary which was used, the researcher was able to measure students’ vocabulary retention from their weekly quizzes scores. The calculation of the numeric data used the following formula:
Note: Mn : Mean (an indicator of central tendency of the sources set) The Mean was counted using the formulation below:
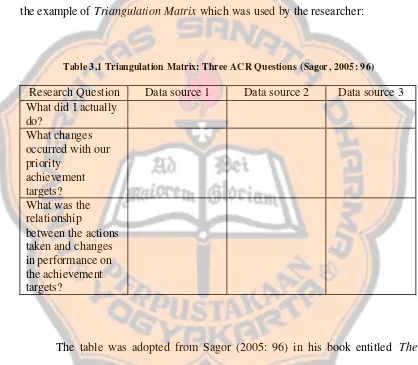
As professional, the researcher expected the result of data which could influence decisions on teaching and learning to be both valid and reliable. Therefore, the researcher also used a data gathering technique, it was a weekly journal to collect the word data. Sagor (2005: 93) stated the strategy used most frequently by action researchers was called Triangulation Matrix. Table 3.1 was the example of Triangulation Matrix which was used by the researcher:
Table 3.1 Triangulation Matrix: Three ACR Questions (Sagor, 2005: 96)
Research Question Data source 1 Data source 2 Data source 3 What did I actually
3.6 Research Procedure s
1. The first action was to choose the place of the research.
2. The researcher asked the letter of permission from Sanata Dharma University to conduct a research and delivered it to OI 743 Petra Children Development Center.
3. The researcher formulated the problems that appeared in the class and based on the improvement of the students, the researcher picked-up the most crucial problem to be solved. It was done as identifying the focus of the research. Considering the use of the research next in the future, the topic chosen was more on application of certain strategy in language teaching.
4. The researcher took sample of research subjects.
5. The researcher constructed an observation to investigate the major problem in student’s vocabulary retention and to establish the achievement targets in learning English vocabulary.
6. The researcher analyzed the observation data and selected achivement target. 7. The researcher established assessment criteria and based the action on theories
in language learning.
8. In order to achieve the goal of the research, the researcher formulated and determined the research question.
9. The researcher chose and created the data gathering technique s (data-collection plan) which were used to collect the data.
11.The researcher decided the schedule of English teaching and conducted the teaching.
12.The researcher observed the teaching process toward progress based on the strategy which was used for teaching English vocabulary.
13.The researcher conducted weekly quizzes as tools to measure students’ retention in the ir English vocabulary learning. The last step was analyzing the data, revising theories of actions, and formulating the final report for future action.
The above procedures referred to the Action Research Cycle proposed by Sagor. The figure was adopted from Sagor (2005: 96) in his book entitled The Action Research Guide Book.
Figure 3.1 The Action Research Cycle (Sagor, 2005: 96)
Stage 1: Clarifying Vision
Stage 3: Implementing Action and Collecting Data Stage 4:
Develop a theory of action Plan future action
Revise theory of action
Analyze the data
Take action Create a data-collection plan
38 CHAPTER IV
RESEARCH RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS
In this chapter, the researcher discussed on the implementation of a certain strategy to teach English words, discussion, and other findings. The process of English vocabulary teaching could be observed in the section of implementation of the chosen strategy. Hence to obtain the results of the research, the data of English words teaching were processed and analyzed in discussion section. In addition, there were other impacts of the use of the chosen strategy. The researcher recorded the impacts of the chosen strategy in the findings sections as additional information.
4.1Research Findings
4.1.1 The Implementation of the Chosen Strategy
Two cycles had been conducted in order to search for an appropriate strategy to improve English words retention in OI 743 Petra Children Development Center. The second cycle was aimed to verify the first cycle since the first cycle proved that the strategy of the first research had been successful in improving students’ retention in memorizing English words they learned. The cycles were the Action Research Cycles proposed by Sagor (2005: 96) in his book entitled The Action Research Guide Book.
May 28th, 2007. The class was conducted for one hour. It started at 16.00 p.m. and finished at 17.00 p.m. The place was in OI 743 Petra Children Development Center. The subjects of this research were the fifth grade students of elementary school.
The class consisted of 20 students and 5 students were chosen as the subjects of the research. They were selected with the consideration that the students were at the same level and had similar characteristics. The researcher chose three girls and two boys. This proportion was based on the number of the total students who were observed. The students consisted of 20 students with the number of the class was dominated by girls. The class consisted 2/3 of girls and 1/3 of boys.
Dealing with the learning activities inside of the class, the researcher had set the lesson plans for the meetings. In the class, the researcher provided the students with exercises. They were written and oral exercises. The researcher drilled the students orally to pronounce the English words correctly. It was done as an oral exercise. Then for the written exercise, the researcher proposed the use of fill- in-the blanks practice. The class was ended by reviewing the English words.
also supported by the principle for teaching English to children theory in which the researcher should start where the child was and supported negotiation of meaning a collaborative talk early. In an oral practice, students were facilitated with the chance to exchange their ideas or opinions to train them in negotiating meaning and collaborative talk.
Wenden and Rubin (1987: 71) stated that “learning strategies are techniques, approaches, or deliberate actions that the students take in order to facilitate the learning and recall both linguistic and content area information. ” Based on the effectiveness of imagery to retain memory, the researcher considered picture as an appropriate strategy to improve students’ retention in learning vocabulary. This strategy was proven to be effective enough in improving students’ mastery in their English vocabulary learning.
4.1.1.1 The First Cycle
4.1.1.1.1 Clarifying Vision
In the initial stage of clarifying vision of the research, the researcher identified a crucial problem that occurred in OI 743 Petra Children Development Center. The identification led into the focus of the research. This research focused on a strategy that was appropriate to teach English words toward the fifth grade students of OI 743 Petra Children Development Center. The students could not memorize the English words they learned. The percentage of the words that they could memorize was only 50% out of 100%. The result was considered poor thus it was important to be solved. In the first cycle, the researcher had chosen pictures as the strategy to teach English words.
The second stage, the researcher selected achievement target. The students were expected to be able to memorize 80% out of 100% English words they learned. During the research, students were given fifteen English words in each meeting. From those fifteen English words, students were expected to memorize fourteen English words. If during the process students could achieve the target, they were considered successful in their English vocabulary learning.
Children Development Center. Out of fifteen English words, students used to be able to memorize five up to six words. Therefore, the strategy should facilitate the students to achieve fourteen words out of fifteen English words.
4.1.1.1.2 Articulating Theories
This research was based the research on theories of children language and learning, theories of ten principles of teaching young learners, and theories of English language teaching. These theories were used as references in achieving the objective of this research problem formulation question. The theories were used as a guidance to search for an appropriate strategy to teach English vocabulary.
of a strategy that was used to teach English vocabulary and construction of lesson plans.
Theories of ten principles of teaching young learners helped the researcher to adopt his teaching based on students’ age. The principles gave direction and a guidance to teach language to children effectively. They are (1) starting where the child is, (2) encouraging social interaction, (3) supporting negotiation of meaning and collaborative talk early, (4) allowing the children to be active, (5) pitching input within the zone of proximal development, (6) introducing language at discourse level, (7) planning meaningful and purposeful activities with in a clear familiar context, (8) help ing learners to become more independent and autonomous, (9) developing a supportive, non-threatening, enjoyable learning environment and (10) testing and assessing in the way that we teach. The above theories were applied in this research and used to help the researcher to teach English words. Each point of these theories facilitated the researcher to explain English words and to conduct the teaching.
Figure 4.1 The Relation in Communication Process (Nation, 1990:3)
Encoding Decoding
In this research, the information source to teach English words was the teacher’s brain. The transmitter was the teacher’s voice when the teacher gave a verbal explanation, the teacher’s hands when the teacher drew or pointed to a picture, the teacher’s body when the teacher gave a demonstration and a real object when the teacher showed it to the class.
The researcher used one type of cognitive strategies which was called imagery. Imagery could be done by demonstrations and using pictures as it translated the idea in the information source. In addition, English language teachers could help their learners to grasp the concept. It was done by varying the situation in which it was demonstrated and by giving verbal definition as well as nonverbal one in learning English vocabulary.
The above explanation stated that imagery was used by correlating new information to visual concepts in memory via familiar easily retrievable visualizations, phrases or locations. Those visual concepts were suitable and helpful for students in memorization of English words. They were used to choose a strategy to teach English words.
Information Source
Information Destination Receiver
4.1.1.1.3 Implementing Action and Collecting Data
The first stage of implementing action and collecting data in the research was determination of research question. The question was formulated as “What is the teaching strategy that is appropriate to improve the achievement of the fifth grade students in their vocabulary learning in OI 743 Petra Children Development Center?” Thus, the research focused on a strategy that was effective to teach English words.
The second stage, based on the research question, the researcher started to create a data-collection plan. Data collection plan which was used were
Triangulation Matrix and weekly quizzes. The Triangulation Matrix was used to collect the qualitative data which became the main source data of the research. The Triangulation Matrix was a journal. These data collection plans were used to record the process of applying the chosen strategy to teach English vocabulary. The data were words. All of changes and progress of students were recorded in details. Weekly quizzes were given in order to measure students’ achievement in their English vocabulary learning and to pursue the initial standard. The initial standard was the strategy worked if it could improve students’ English vocabulary retention. It meant that students were required to be able to memorize up to fourteen out of fifteen English words.
effective or not. In order to record students’ progress and to measure students’ achievement, the researcher used Triangulation Matrix and weekly quizzes.
The first research was conducted on April 23rd, 2007 and reviewed on April 30th, 2007. The class was conducted for one hour; it started at 16.00 p.m. and finished at 17.00 p.m. The place was in OI 743 Petra Children Development Center. The subjects of this research were the fifth grade students of elementary school. The class consisted of 20 students and 5 students were chosen as samples. 5 students were selected because they were considered as an appropriate number that could represent the total number of the class. They were selected based on the consideration that the students were at the same level and the y had similar characteristics. The researcher chose three girls and two boys. This proportion was based on the number of the students. The students consisted of 20 students and the numbers of the class were dominated by girls. The class consisted 2/3 of girls and 1/3 of boys.
4.1.1.1.4 Reflecting and Planning Informed Action
The first stage of reflecting and planning informed action in this research was analyzing data. Based on the data the researcher found that students were able to memorize fourteen out of fifteen English words. Students were also more active in joining the class. They seemed more interested when pictures took place in the teaching. Moreover, the pictures also helped the students to understand the translation of each English word.
results of data analysis of research subjects in their English words learning achievement, they were able to achieve the initial standard.
Students’ characteristics in OI 743 Petra Children Development Center were suit able to the use of pictures in learning English words. They were interested in the use of imagery stuffs as the strategy to teach English words. By concentrating on the visual objects, the researcher could lead the subjects to focus their mind on the English words they learned.
4.1.1.2 Second Cycle
4.1.1.2.1 Implementing Action and Collecting Data
The first stage of implementing action and collecting data in the cycle was determination of the aim of the second cycle. The second cycle verified whether the strategy used in the first cycle worked effectively in the second cycle or not. The strategy worked if the students could memorize fourteen out of fifteen English words. In order to record the progress of the students and to measure students’ achievement, the researcher used Triangulation Matrix and weekly quiz. The main data were Triangulation Matrix data and the supporting data were the weekly quizzes result.
The verification cycle was conducted on May 21st, 2007 and reviewed on May 28th, 2007. The class took for one hour; it started at 16.00 p.m. and finished at 17.00 p.m. The place was in OI 743 Petra Children Development Center. The subjects of this research were the fifth grade students of elementary school. The class consisted of twenty students. Out of twenty, five students were chosen as the subjects of the research. They were selected based on the consideration that the students were at the same level and they had similar characteristics. The researcher chose three girls and two boys. This proportion was based on the number of students. The students consisted of twenty students with the number of the class was dominated by girls. The class consisted of 2/3 of girls and 1/3 of the class was boys.
oral exercises. The researcher drilled the students orally to pronounce the words correctly. It was done as an oral exercise. Then for the written exercise, the researcher proposed to use fill in the blanks practice. The class was ended with reviewing the English words given.
4.1.1.2.2 Reflecting and Planning Informed Action
The first stage of reflecting and planning informed action in this research was analyzing the data. Based on the data, the researcher found that students were able to memorize up to fourteen out of fifteen English words with the same strategy as in the first cycle. Students were also more active in joining the class. They were more interested when pictures took place in the teaching. Moreover, the pictures also helped the students to understand the translation of each English word.
4.3Discussions
The strategy was used based on some considerations. They were the characteristics of students in 743 OI Petra Children Development Center and some related theories. They were theories of children language and learning, theories of ten principles of teaching young learners and theories of English language teaching. In addition, Triangulation Matrix explained the enthusiasm of the students in joining the class activities. It was proven from Triangulation Matrix data that pictures reinforced students’ interest in learning English words.
Triangulation Matrix data explained that there were changes in students’ achievement in learning English words. Students were able to memorize in average 14 English words out of 15. The achievements of the students were the same as the standard which had been set at the beginning of the first cycle.
Table 4.1 The weekly quiz scores of the subject
Number of correct items Name Meeting 1 Meeting 2
It could be concluded that most of the students were able to memorize fourteen English words out of fifteen in average. Hence, the researcher proposed the use of pictures as the strategy to teach English words toward students of the fifth grade in OI 743 Petra Children Development Center. The Triangulation Matrix data and the quiz results showed the effectiveness of this strategy in English vocabulary teaching. As for conclusion, the problem formulation of this research had been answered based on the results of both the Triangulation Matrix
data and the quiz result of the second meeting. Both data supported the use of pictures to teach English words in OI 743 Petra Children Development Center.
4.4Other Findings
In the teaching and learning process, the researcher found that there were effects of using pictures as the teaching strategy to teach English words in OI 743
atmosphere during the teaching and learning activities. The class was much livelier due to the enthusiasm of the students in joining all of the class activities. The students’ gave their attention to the researcher’ explanation more instead of talking by themselves. Moreover, the researcher presented interesting pictures that made the class and the learning much more interesting.
The second, pictures could reduce explanation in teaching English words. The researcher did not spend much time in explaining the meaning of the English words. The students guessed easily the meaning of English words based on the pictures which were used in the teaching process. By using pictures, the researcher only presented the pictures and gave little explanation to the students. Just at a glance, the students could be able to find the meaning of the English words by looking at the pictures.
The last, during the research the researcher also found that the students were so enthusiastic and interested in the strategy. It was proven that they were curious in knowing the next topic. It happened as they were interested in the pictures which were used in the teaching of English words. When the students enjoyed and felt interested in the class, they were willing to memo rize the English words. It seemed that pictures used in the class were able to make the students involved in the learning activities. The learning was facilitated if the students discovered rather than remembered and repeated what was to be learned.
54 CHAPTER 5
CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS
This chapter concludes the research by presenting conclusions drawn from the findings and the data analysis discussed in chapter 4. The next is by proposing suggestions toward any future English teachers that might face the same problem. Chapter 5 concludes the way to teach English words to the fifth grade students in OI 743 Petra Children Development Center.
5.1 Conclusions
Based on the research findings and the data analysis, there were two conclusions drawn in the research. First, the use of pictures in English vocabulary teaching for the fifth grade students in OI 743 Petra Children Development Center was proved to be effective to teach English words. Weekly quizzes results and Triangulation Matrix data showed the improvement of students’ achievement in learning English words. The students could memorize the English words easily when pictures were used in the teaching process. They could memorize around 14 English words out of 15. It meant that pictures worked effectively to teach English words in OI 743 Petra Children Development Center.
improve their retention better than without pictures and they did not face any difficulties. Students were also more enthusiastic in joining the lesson. They were active in taking part during the class. Thus, the assignments that related with pictures in memorizing English words worked effectively because of the students’ interest in pictures.
5.2 Suggestions
Based on the data analysis in chapter 4 and the conclusions, this research recommends pictures as an effective strategy to teach English vocabulary to the fifth grade students in OI 743 Petra Children Development Center. Since students are more enthusiastic in joining the lesson when pictures are used, it is recommended that pictures should be used in any of English teaching at elementary level in OI 743 Petra Children Development Center. In addition, pictures are interesting. They improve optimally students’ retention in their English learning.
copying from books. It is suggested by the researcher that the teacher of the fifth grade students should use pictures to teach English words in OI 743 Petra
Children Development Center.