IMPROVE STUDENTS’ ACHIEVEMENT IN LEARNING
ENGLISH
(A Classroom Action Research to the Second Grade of State Islamic Junior High School Kaliangkrik Magelang in the Academic Year of 2009/2010)
A GRADUATING PAPER
Submitted to the Board of Examiners in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements For the Degree of Sarjana Pendidikan Islam (S.Pd.I.)
in the English and Education Department
By:
NOK SITI FATIYATUL MUHARROMAH NIM. 113 06 006
ENGLISH DEPARTMENT OF EDUCATION FACULTY STATE ISLAMIC STUDIES INSTITUTE (STAIN)
SALATIGA
DEPARTMENT OF RELIGIOUS AFFAIRS
STATES ISLAMIC STUDIES ISTITUTE
(STAIN SALATIGA)
Jl. Tentara pelajar 02 Phone (0298) 323 706 Salatiga 50721 Website: www.stainsairtiga.ac.id E-mail: administrasi@stainsalatiga.ac.id
Dr. H. Sa'adi. M. Ag Salatiga. July 28th, 2010 The Lecturer of Educational Faculty
State Islami c Studies Institute of Salatiga
ATTENTIVE COUNSELOR NOTES
Case: Nok Siti Fatiyatul M uharromah’s Graduating Paper
Dear
The Head of State Islamic Studies Institute of Salatiga Assalamu’alaikum Wr.Wb.
After reading and correcting Nok Siti Fatiyatul Muharromah’s graduating paper entitled “THE USE OF JIGSAW TEACHING STRATEGY TO IMPROVE STUDENTS’ ACHIEVEMENT IN LEARNING ENGLISH OF THE SECOND YEAR STUDENTS OF MTs N KALIANGKRIK, MAGELANG IN THE ACADEMIC YEAR OF 2009/2010”. I have decided and would like to propose that if it could be accepted by educational faculty. 1 hope it could be examined as soon as possible.
Wassalamu’alaikum Wr. Wb.
SALATIGA
JI. Tentara Pelajar 02 Phone (0298) 323706 Salatiga 50721
Website: www.stainsalatiga.ac.id E-mail: administrasi@stainsalatiga.ac.id STATEMENT o f c e r t i f i c a t i o n
Nok Siti Fatiyatul Muharromah’s graduating paper, the student number is 11306006, entitled “The Use of Jigsaw Teaching Strategy to Improve NI?. 19580827 198303
DEPARTMENT OF RELIGIOUS AFFAIRS
STATE ISLAMIC STUDIES INSTITUTE ( STAIN) SALATIGA Jl. Tentara Pelajar 02 Phone (0298) 323706 Salatiga 50721 Website: www.stainsalatiga.ac.id E-mail: administrasi@stainsalatiga.ac.id
DECLARATION
In the name ofAllah, the Lord o f Mercy, the Giver o f Mercy
Hereby the writer fully declares that the graduating paper is made by the writer herself and it is not containing materials written or has been published by other people and other people’s ideas, except the information from the references.
The writer is capable to account for the graduating paper if in the future the graduating paper can be proved of containing other’s ideas or in fact the writer imitates the other’s graduating paper.
Likewise, the declaration is made by the writer and the writer hopes that the declaration can be understood.
Salatiga, August 5th 2010 The Writer,
Q n ' t U e ' m hM f y ie th tc * te * d cU ^ d
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
In the name o f Allah, the Lord ofMercy, the Giver o f Mercy.
All praises due to Allah The Lord of universe, who does always give His creation His Mercy. I testify there is no God other than Allah and Muhammad is His Messenger. Prayer and peace be upon him, the master of all messenger, The Prophet Muhammad, and upon all his family and companions, who leads human being to the right path, Islam, the path of the prophets and messengers.
Many peoples help and give her valuable contribution to accomplish this graduating paper. Therefore, in this very glad occasion, she is very thankful to these people as presented below:
1. Dr. Imam Sutomo, M.Ag, the Rector of State Islamic Studies Institute (STAIN) Salatiga
2. Dr. Sa’adi, M. Ag, the consultant of the graduating paper. As her attentive counselor, her adviser, and her problem solver who always supports her till the graduating paper has done.
3. All lecturers of English Department who had given the knowledge patiently.
4. All teachers and students in MTs N Kaliangkrik, for Mr. Aris thank you so much for your guidance.
5. Her beloved family, mother, father, older and younger sisters, older brothers, nephew and nieces who always give everything she needs to support her study materially and spiritually.
my study.
7. The big family of STAIN Salatiga especially for all members of TBI A ’06, who couldn’t mentioned one by one for their togetherness during study in there
8. All of Mends in IMM Kota Salatiga for their motivation in her life. 9. All of “you” who know me.
Salatiga, 6 Agustus 2010
NOK SITIFATIYATUL M. NIM. 113 06 006
ABSTRACT
Nok Siti Fatiyatul Muharromah. 11306006. THE USE OF JIGSAW TEACHING STRATEGY TO IMPROVE STUDENTS’ ACHIEVEMENT IN LEARNING ENGLISH (A Classroom Action Research to the Second Grade of State Islamic Junior High School Kaliangkrik Magelang in the Academic Year of 2009/2010). Graduating Paper. Salatiga: Sekolah Tinggi Agama Islam Negeri, August 2010.
Keywords: jigsaw teaching strategy, English achievement, motivation.
Cover page... i
Attentive counselor notes... ii
Statement of certification... iii
Declaration... iv
M otto... v
Dedication... vi
Acknowledgment... vii
Abstract... ix
Table of contents... x
List of table... xiii
CHAPTER I. INTRODUCTION... 1
A. Background of the Study... 1
B. Limitation of the Study... 3
C. Statement of the Problem... 3
D. Objective of the Study... 4
E. Benefit of the Research... 4
F. Review of Previous Research... 5
G. The Method of Research... 7
H. The Outline of The Research Paper... 13
CHAPTER II. THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK... 15
A. DEFINITION... 15
1 Jigsaw Teaching Strategy 2 English Achievement... 3 Motivation...
15
17 19
B. HYPOTHESIS... 22
CHAPTER III. RESEARCH REPORT... 24
A. General Situation of MTs N Kaliangkrik in the Academic year of 2009/2010 ... 24
1 The Location of M tsN Kaliangkrik... 24
2 The Situation of Educational Facilities and Tools... 25
3 The Situation of the Teachers and Staffs... 25
4 The Situation of the Students... 28
5 Organization Structure... 28
B. The Subject of the Study... 30
CHAPTER IV. THE IMPLEMENTATION OF THE STUDY... 31
A. Field Notes... 31
1. Cycle 1... 31
2. Cycle 2... 38
3. Cycle 3... 45
B. Verbal Score of Students’ Achievement... 50
1. Verbal Score of Cycle 1... 50
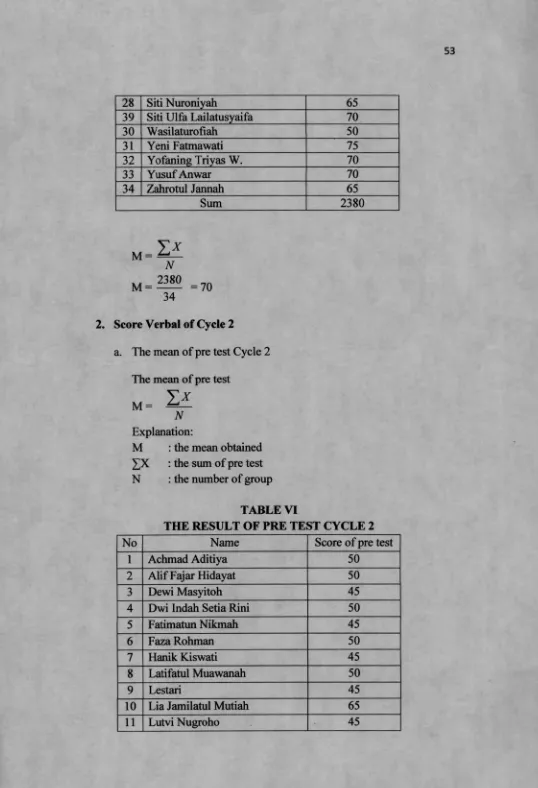
2. Verbal Score of Cycle 2... 53
3. Verbal score of Cycle 3... 56
4. The Result of the Mean Score of Pre Test and Post Test... 59
B. Implication... 61 C. Suggestion... 61
LIST OF TABLE
Table I: Educational facilities and tools in MTs N Kaliangkrik
Table II: the situation of the teachers and staffs of MTs N Kaliangkrik Table III: The situation of students of MTs N Kaliangkrik
Table IV: The score of pre test 1 Table V: The score of post test 1 Table VI: The score of pre test 2 Table VII: The score of post test 2 Table VIII: The score of pre test 3 Table IX: The score of post test 3
Table X: The mean score of pre test and post test
A. Background of the Study
English is an international language used by many different peoples in the world. It plays an important role in an international communication. It can be as a medium in study of science, politics, economics, education and culture, technology etc which are usually written in English.
Considering the important role of English, the researcher believes that learning English is very important. In Indonesia, English is the first foreign language which is taught in secondary school as a compulsory subject. Harmer (2001, p. 56) describes in teaching-learning process there are some components involved. There are teachers, learners, syllabus, objectives, classroom management, teacher student interaction, grouping, structuring and task or activities.
Breen and Candlin (1980, p.99) describe teacher roles. The first is to facilitate the communication process between all participants in the classroom, and between these participants and the various activities and texts. The second role is an independent participant within the learning teaching group. The role is closely related to the objectives of the first role and arises from it. These roles imply a set of secondary roles for the teacher; first, as an organizer of resources and as resources himself, second
2
as a guide within the classroom procedure arid activities. A third role for the teacher is that of researcher and learner, with much to contribute in terms of appropriate knowledge and activities, actual and observed experience of the nature of learning and organizational capacities.
The problem of research here is that students' motivation to learning English is average. Therefore, they are passive in teaching- learning process. Based on researcher' experiences that less of students' motivation is that they feel English is very difficult. Beside that, less of teaching strategy that use by teacher in English class. Teacher feared students would get bad value in final examination, because English is one of foreign language as a compulsory subject in secondary final examination. As a result, little attention is direct to teaching for English teaching-learning process.
Teaching-learning English, we develop four language skills, namely listening, speaking, reading and writing. The four skills are developed in integrated manner. Based on Junior High School Curriculum 2004, the function of English is as a communication instrument to get information. In daily context, English is as an instrument to make an interpersonal relation, to exchange of information and also comforting the language aesthetics in England culture.
the first grade and in second grade, they increase their English understand to prepare final examination in the third grade. Not all of students have high motivation to learn English. The researcher is aware there are many factors to increase it. One of the aspects is teaching strategy in teaching- learning process that is by dividing students into several groups.
From discussion above, the researcher is interested in carrying out a research dealing with students' motivation. The students' motivation will encourage them to a good language skill and English value in final examination in the third grade. Because of that, the researcher takes courage to write a graduating paper with title "THE USE OF JIGSA W TEACHING STRATEGY TO IMPROVE ENGLISH ACHIEVEMENT"
(Classroom Action Research at the Second Grade of MTs N Kaliangkrik, Magelang in the academic year of 2009/2010).
B. Limitation of the Problem
The writer has limitation this research to know whether the jigsaw teaching strategy can improve students’ achievement in learning English. The material is limited to taught at the second grade of MTs N Kaliangkrik Magelang in the academic year of 2009-2010 exactly at class A.
C. Statement of the Problem
4
2. How is the development of teaching learning using jigsaw teaching strategy the second grade of MTs N Kaliangkrik Magelang in the academic year of 2009-2010?
3. How far does jigsaw teaching strategy improve students' achievement in learning English of the second grade of MTs N Kaliangkrik Magelang in the academic year of 2009-2010?
D. Objective of the Study
1. To find out the students' achievement in learning English of the second grade of MTs N Kalianngkrik Magelang in the academicyear of 2009- 2010 before using jigsaw teaching strategy.
2. To find out of the development of teaching learning using jigsaw teaching strategy in learning English of the second grade of MTs N Kaliangkrik Magelang in the academic year of 2009-2010.
3. To find out the result of students' achievement in learning English after using jigsaw teaching strategy of the second grade of MTs N Kaliangkrik Magelang in the academic year of 2009-2010.
E. Benefit of the Research
The result of the research will be beneficial as follow: 1. Methodologically
2. Theoretically
The result of this research can be used as a starting point in improving the researcher' teaching ability. The result of this research also can be used as one of the references in conducting a research on English language teaching, especially of Jigsaw Teaching Strategy in English teaching-learning strategy.
3. Practically
The result of this research will improve the students' motivation to learn English. The result of this research will improve the school quality especially in English teaching-learning process.
F. Review of Previous Research
_ I n this research, the writer reviews several researchers conducted by the previous writer references as comparison. The first review related to this research, and the title is A STUDY ON THE CORRELATION BETWEEN STUDENT'S MOTIVATION AND THEIR ACHIEVEMENTS
OF ENGLISH which has been researched in 2003 by Farida Naiturrahmah. In her thesis, analyze about student's motivation in their achievements in learning English. Based on Farida, the correlation between motivation and achievement is significantly positive.
The second review related to this research, and the title is THE
INVESTIGATION BETWEEN LOWER CLASS CHILDREN'S
MOTIVATION IN LEARNING ENGLISH AND THEIR ACHIEVEMENT
6
research concluded that both of them have motivation. But the children from the lower class do not have motivation in learning English because they have not got a chance and they are lack of expense (their parents could not pay for an English course or a good private school). Most of the children sere studying at public school and they didn't/t got English lesson until they are in 4th grade.
The third review related to this research and the title is THE
INFLUENCE OF CLASSROOM MANAGEMENT TOWARDS
STUDENTS’ ENGLISH ACHIEVEMENT which has been researched by Triyono, the student of State Islamic Studies Institute (STAIN) of Salatiga in 2004. In this thesis he conducted that good classroom management influence student’s English achievement.
The forth review relates with the research, entitled THE INFLUENCE OF TEACHER COMPETENCE IN TEACHING TOWARDS
ENGLISH STUDENTS’ ACHIEVEMENT which has been researched by Witanto, the student of STAIN Salatiga in 2004. In this thesis he founds that there is a significant correlation between teachers’ competence in teaching towards students’ achievement.
The fifth review relates with the research, entitled THE INFUENCE OF TEACHERS’ TEACHING STRATEGIES TO THE
founds that there is correlation between teachers teaching strategy and students’ English achievement.
G. The Method of Research
1. Type of Research
The research method used in this study is class action research. There are some definitions of action research. The fist definition is given by Kemmis and Me Taggart in Hadley’s book (2003, p.ii) describe action research as a systematic and collaborative effort aimed at solving classroom problems. This has been a surprisingly durable definition that has stood the test of time, even though some recently prefer to downplay the element of problem solving in action research in order to emphasize the importance of teacher reflection for understanding their students’ culture of learning.
8
Wallace (1994, p.4) states that classroom action research is
basically a way of reflecting on your teaching (or teacher-training, or management of an English department, or whatever it is you do in ELT). It is done by systematically collecting data on your everyday practice and analyzing it in order to come to some decisions about what your future practice should be.
2. The Procedure of Research
This study used classroom action research, so in this case the writer used some steps at classroom action research’ module. There are three cycles in this action research. In each cycle the procedures are as follows:
a. Planning
The activities in the planning are:
1) Preparing materials, making lesson plan, and designing the steps in doing the action.
2) Preparing list of students’ name and scoring 3) Preparing teaching aids
4) Preparing sheets for classroom observation 5) Preparing a test
b. Action
1) Giving pretest
A. DEFINITION
1. Jigsaw Teaching Strategy
The jigsaw classroom is a cooperative learning technique with a
three-decade track record of successfully reducing racial conflict and increasing positive educational outcomes. Made Wena (2009, p. 103) describes that cooperative learning jigsaw model was developed by Elliot Aronson from Texas University of United State. This strategy is used if the materials of learning are divided into some parts and the materials should not in a series. The strength of this teaching strategy can be all students active in the teaching learning process and also teaching to others.
1. Steps of Jigsaw Teaching Strategy
According Aronson, et al (in www.iigsaw.or.id) the jigsaw classroom is very simple to use. The jigsaw classroom has 10 easy steps, they are:
a. Divide students into 5 or 6 people’s jigsaw groups. The groups should be diverse in terms of gender, ethnicity, race, and ability. b. Appoint one student from each group as the leader. Initially this
person should be the most mature student in the group. c. Divide the day's lesson into 5-6 segments.
16
d. Assign each student to learn one segment, making sure students have direct access only to their own segment.
e. Give students time to read over their segment at least twice and become familiar with it. There is no need for them to memorize it.
f. Form temporary "expert groups" by having one student from each jigsaw group join other students assigned to the same segment. Give students in these expert groups time to discuss the main points of their segment and to rehearse the presentations they will make to their jigsaw group.
g. Bring the students back into their jigsaw groups.
h. Ask each student to present her or his segment to the group. Encourage others in the group to ask questions for clarification. i. Float from group to group, observing the process. If any group is
having trouble (e.g., a member is dominating or disruptive), make an appropriate intervention. Eventually, it's best for the group leader to handle this task. Leaders can be trained by whispering an instruction on how to intervene, until the leader gets the hang of it.
j. At the end of the session, give a quiz on the material so that students quickly come to realize that these sessions are not just fun and games but really count.
2. English Achievement
a. Definitions of achievement
The meaning of achievement is similar with the Dutch word
prestige that means that result of something done. Heni in her thesis (2005) says that achievement is a concrete result of an action done by an individual. It can be measured directly by using a test. The result can be seen and felt at a certain time. Basically, achievement is the proof of effort reached.
Hornby (1987) say: achievement is something done with an effort and skill successfully. In general, achievement is a personal accomplishment, attainment of goal go by the individual or the society in educational psychology. Achievement is perhaps the most commonly used to measure achievement effect. However, the common use of testing is acceptable by education decision makers.
The acceptable credibility of testing as measurement device appears and has four characteristics as follows:
1) It is seemingly an objective measurement.
2) Test result is to infer students’ and inter-groups comparisons. 3) Testing has been a traditional characteristics of educational
systems and has been assumed to promote students’ discipline and effort, and
18
Nasution (1984, p.37) states that measurement of achievement can be do in five ways, those are as follows:
1) Main level of achievement
2) Average or distribution of achievement 3) Group achievement
4) Achievement and effect size
b. The Factors of Achievement
Teaching is consciously effort of teachers to make students learn and reach an achievement. Muhibbin (1987, p. 46) states that there are two factors that influence English achievement. The factors of achievement according to the theory of psychology are influenced by internal and external factors:
1. The internal factors
The internal factors consist of physical and psychological moods. Physical modes cover health, fatigue, and sensory factors. Psychological factors consist of observation, reaction, fantasy, associative intelligence, emotion, motivation, desire, attention, and interests.
2. The external factors
consist of parents’ sittings, play mates, study mates, teacher, principal, and staff.
c. The Classification of Achievement.
The learning achievement is classified as follows: 1) Cognitive achievement level
The cognitive achievement level concerns knowledge, comprehension, recalling, application, analysis, synthesis, evaluation and memory.
2) Affective achievement level
The affective achievement level involves receiving, responding, valuing, characteristics, organization, intention, attention, and internalization.
3) Psychomotor achievement level
Psychomotor achievement level consists of movement, basic skill movement, perceptual movement harmony, complex skill movement, speech behaviors, and expressive and interpretative movement.
3. Motivation
2000: 160-166). Marion William and Richard Burden suggest that motivation is a 'state of cognitive are usual' which provokes a 'decision to act' as a result of which there is 'sustained intellectual and/or a physical effort' so that the person can achieve some 'previously set goal' (William and Burden 1997: 120). According to Fieldman (1996) motivation is concerned with the factors that direct and energize the behavior of human and other organism.
In discussion of motivation an accepted distinction is made between extrinsic and intrinsic motivation (Harmer, 2001: 51), that is motivation which comes from outside and from inside. Extrinsic motivation is caused by any number of outside factors, for example, the need to pass an exam, the hope of financial reward, or the possibility of future travel. Intrinsic motivation, by contrast, comes from within the individual. Thus a person might be motivated by enjoyment of the learning process itself or by a desire to make themselves feel better,
a. Sources of Motivation
Harmer (2001) says that sources of motivation are the society we live in, significant others, the teacher and the method.
1) The society we live in: outside any classroom there are attitudes to language learning and the English language in particular.
2) Significant others: a part from the culture of the world around
students, their attitude to language learning will be greatly affected by the influence of people who are close to them. 3) The teacher: clearly a major factor in the continence of a
student's motivation is the teacher.
4) The method: it is vital that both teacher and the students have some confidence the way teaching and learning take place. When either loses this confidence, motivation can be disastrously affected, but when both are comfortable with the method being used, success is much more likely.
b. Forms of Motivation
Brown (2000) has two different clusters of attitudes divided into two basic types of motivation: instrumental and integrative motivation:
1) Instrumental Motivation
Motivation to acquire a language as means for attaining instrumental goal: furthering a career, reading technical material, translation, and so forth.
2) Integrative Motivation
25
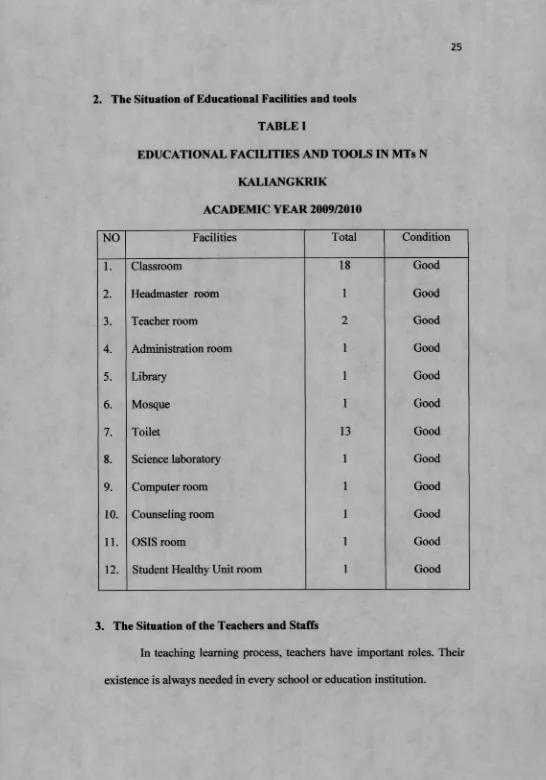
2. The Situation of Educational Facilities and tools
TABLE I
EDUCATIONAL FACILITIES AND TOOLS IN MTs N
KALIANGKRIK
ACADEMIC YEAR 2009/2010
NO Facilities Total Condition
1. Classroom 18 Good
2. Headmaster room 1 Good
3. Teacher room 2 Good
4. Administration room 1 Good
5. Library 1 Good
6. Mosque 1 Good
7. Toilet 13 Good
8. Science laboratory 1 Good
9. Computer room 1 Good
10. Counseling room 1 Good
11. OSIS room 1 Good
12. Student Healthy Unit room 1 Good
3. The Situation of the Teachers and Staffs
TABLE II
LIST OF TEACHERS AND STAFFS OF MTs N KALIANGKRIK
NO NAME STATUS
1. Abdul Ghofar, S. Pd Headmaster 2. Dra. Nur Wafirotullaela Teacher
3. Siti Mursidah Teacher
4. Muchtasor, BA Teacher
5. Noor Hamida, S. Pdi Teacher 6. Drs. Imam Subarkah Teacher 7. Dra. R. Umi Hanik, M. Pd Teacher 8. Akhmad Hasyim, S. Pdi Teacher 9. Lilik hidayati, S. Pdi Teacher 10. Ninik Muminingsih, A. Md Teacher
11. Drs. Djuni Teacher
12. Mifitakhul Karimah, S. Pdi Teacher 13. Aris Suranto, A. Md Teacher
14. Robiah, S. Pd Teacher
CHAPTER III
RESEARCH REPORT
A. General situation of MTs N Kaliangkrik
1. The Location of MTs N Kaliangkrik
The location of MTs N Kaliangkrik is on Jl. Mayor Ismulloh No.
18 Beseran Kaliangkrik for second and third grade and at Torip, Beseran for first grade. This school was built in July 14, 1969. The width of this location is about 2402 m2 for building and 8823 m2 for field.
The total number of students of MTs N Kaliangkrik in the academic year 2009/2010 is 648 students. They consist of 239 students of the first grade, 206 students for second grade and 203 students for third grade. MTs N Kaliangkrik has 18 classrooms which cover the first grade having 6 classrooms, second grade has 6 classrooms and third grade has 6 classrooms.
B. The Subject of the Study
The subject of this research is second year students of MTs N
THE IMPLEMEMT ATI ON OF THE STUDY
A. FIELD NOTES
In this research implementation, we (the teacher and the writer) has arranged three cycles. In each cycle the steps are planning, acting, observing and reflecting.
1. Cycle 1
a. Planning
The activities are preparing:
1) Materials, making lesson-plan, and designing the steps in doing action.
2) List of students’ name
3) Teaching aids (charts, picture) 4) Sheet for classroom observation 5) Tests (pretest and posttest)
b. The implementation of the action
On Wednesday, the third of March 2010 the teacher and the observer (the writer) entered their English class. The situation was: Teacher: “Assalamu’alaikum... ”
Student: “Wa’alaikumsalam...”
Teacher: “Good morning every body”
Student: “Good morning, Sir. How are you?” Teacher: “I am fine, and you?
Student: “I am fine thank you.”
Teacher: “Who is absent today?” Student: “No one sir.”
Teacher: “Students, you will study about recount text. Do you know recount text? What is the purpose of recount text?” (All of the students were silent, but after few minutes there was student in the comer answered).
Student: “To retell past even”
Teacher: “Yes, recount text is to retell past even”
Then the teacher introduced the mode of presentation in studying recount text. The steps are follows:
1) Divide students into six groups. 2) Divide recount text for each group.
3) Assign each student to learn one recount text.
4) Give students time 40 minutes to read over their text.
5) Form temporary “expert group” consist of students who have same recount text. Give students time 40 minutes to discuss the main point of their text and to rehearse the presentation they will make to their jigsaw group.
6) Bring students back into their jigsaw groups.
7) Ask each student to present her or his text to the group. Encourage others in the group to ask question for clarification.
33
Before the lesson, the teacher gave pretest to the class for about 40 minutes. After pre test, he began to teach recount text with the steps stated before. He told the students:
Teacher: “Okay class, you will study recount text. Before we start our lesson, I would like divide you into six groups. Each group consists of six students, except for fifth and sixth group only five students. Do you understand?”
Students: “Yes sir.” (Many students do not answer the teacher’s question)
Teacher: “Anak-anak, kalian akan belajar tentang teks recount. Sebelumnya saya akan membagi kalian menjadi enam
kelompok. Setiap kelompok terdiri dari enam siswa
kecuali kelompok lima dan enam hanya lima siswa.
Paham?”
Student: “Geh/Ya pak. ” (Yes sir)
Teacher: “Sekarang mulai berhitung dari kamu (siswa yang duduk di pojok depan) satu sampai enam. Setelah itu membuat
kelompok misal kelompok satu dengan kelompok satu.
Tetapi sekarang waktu tinggal lima menit, buat
kelompoknya kita lanjutkan pertemuan depan saja
one. But, now we have just five minutes so make group we continue next meeting, okay?).
Students: “Yes sir.”
Teacher: “Okay students, we will continue next Monday. Thanks for your attention, Wassalamu’alaikum... ”
Students: “Wa’alaikumsalam...”
On Monday, the eighth of March 2010, they entered the English class, this was the situation:
Teacher: “Assalamu’alaikum... ” Student: “Wa’alaikumsalam...”
Teacher: “Good morning every body”
Student: “Good morning, Sir. How are you?” Teacher: “I am fine, and you?
Student: “I am fine thank you.” Teacher: “Who is absent today?” Student: “No one sir.”
Teacher: “Students, we will continue the lesson that we have made groups. Do you remember?”
Student: “Yes sir.”
Suddenly, some of students asked their pretest value. Student: “Pak, berapa nilai yang kemarin? ” (Sir, how is my
35
Teacher: “Besok akan saya bagikan, sekarang kalian buat
kelompok separti pertemuan kemaren.” (Tomorrow I will distribute them. Now, make groups like we have made on the last meeting).
Student: “Yes sir.”
Teacher: “baiklah, kalian sudah presentasi teks kalian di kelompok
yang baru. Waktu juga sudah habis. Untuk pertemuan
yang akan datang kita kan bermain dengan quis tanya
jawab dan posttest. ” (Well, you have presented your text in new groups, time is also over. For next meeting, we will play with quiz and posttest). Wassalamu ’alaikum...
Student: “w a’alaikumsalam....
On Wednesday, the tenth of March 2010 they entered their last English class for first cycle. The situation was:
Teacher: “Assalamu’alaikum... ” Student: “Wa’alaikumsalam...”
Teacher: “Good morning every body”
Student: “Good morning, Sir. How are you?” Teacher: “I am fine, and you?
Student: “I am fine thank you.” Teacher: “Who is absent today?” Student: “No one sir.”
Teacher: “okay class, before we are going to the post test, I will give quiz.”
Student: “kuis nopo pak/kuis apa pak? (What kind of quiz?) Teacher: “kuis sederhana, saya akan memberikan beberapa
pertanyaan kemudian jika kalian bisa mejawab
22
c. Elements of Motivation
Brown (2000) also says there are six desires or needs of human
organisms are commonly identified which under gird the construct of motivation:
1) The need for exploration, for seeing "the other side of motivation", for probing the unknown.
2) The need for manipulation, for operating-to use skinner's term-on the environment and causing chance.
3) The need for activity, for movement and exercise, both physical and mental.
4) The need for stimulation, the need to be stimulated by the environment, by other people, or by ideas, thoughts, and feelings. 5) The need for knowledge, the need to process and internalize the
results of exploration, manipulation, activity, and stimulation, to resolve contradictions, to quest for solutions to problems and for self-consistent system of knowledge.
6) Finally, the need for ego enhancement, for the self to be known and to be accepted and approved of by others.
B. HYPHOTESIS
27
21. Chalimah, S. Pd Teacher 22. Sri Rahayu. S. Pd Teacher 23. Samik Saputri, S. Pd Teacher 24. Siti Muawanah, S. Pd Teacher 25. Siti Kotijah, S. Pd Teacher 26. Siti Aisyah, S. Pd Teacher 27. Siti Chamidatus S., S, Ag Teacher
28. Suharto, S. E Teacher
29. Sri Wahyuni, S. Pd Teacher 30. Maesaroh, S. Ag Teacher 31. Masruri S., S.S Teacher 32. Hamzah Fatulloh, S. E Teacher 33. Roflatul Munthofiah, S. Pdi Teacher 34. Nur Rohmah, S. Pdi Teacher 35. Irine Mulyaningsih, S. Pd Teacher 36. Abdullah Al Kafi, S. Ag Teacher 37. Tajudin Masnuh, S.S Teacher 38. Retno Sujiwati, A, Md Teacher 39. Sarwo Mulyono, S. Pd Teacher 40. Sobari Dwi Imanto, S. Pdi Teacher
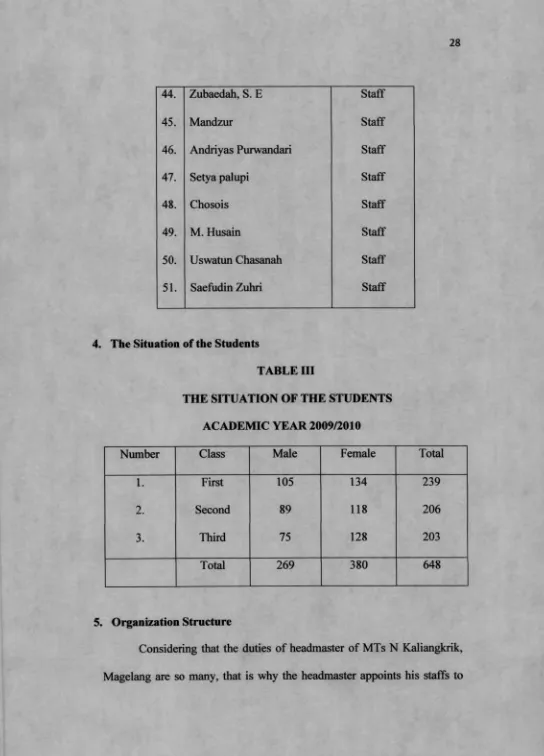
41. Nur Khayati Staff
42. M. Faturrakhman Staff
44. Zubaedah, S. E Staff
45. Mandzur Staff
46. Andriyas Purwandari Staff
47. Setya palupi Staff
48. Chosois Staff
49. M. Husain Staff
50. Uswatun Chasanah Staff
51. Saefudin Zuhri Staff
4. The Situation of the Students
TABLE III
THE SITUATION OF THE STUDENTS
ACADEMIC YEAR 2009/2010
Number Class Male Female Total
1. First 105 134 239
2. Second 89 118 206
3. Third 75 128 203
Total 269 380 648
5. Organization Structure
29
run on of educational activities. The organization structure consists of some delegation lines with different duties, as following table:
Paham? ” (Simple quiz, I will some questions then if you
can answer before you have to raise your hand. Understand?)
Student: “yes sir.”
Teacher gave six questions orally. 83% of the question students can answer. The questions were: what kind of the text is it, what does the text tell us about, what is the purpose of the text, identify the schematic structure of the text, find the meaning of new vocabulary in the text, what tense are used in the text!. After finished quiz, they continued to the post test for about 40 minutes,
c. Observation
In the first cycle, the writer and her collaborator observed the teaching learning process. By monitoring the student’s activity in this action the teacher and the writer can see that the students were rather nervous then they presented to others. In first group some students presented not correctly so some students did not understand. The class situation was rather noisy, because it was first time for them in English class using jigsaw teaching strategy and monitored by an observer. But they looked happy and active.
38
test 84% of students can answer teacher’s question, while the average of post test is 70.
d. Reflection
After analyzing the result of the action in cycle 1, the writer can conclude that it is very important for the teacher to be careful with the student’s understanding; the teacher can give the students more explanation about the meaning of text to improve student’s achievement. He must give support the students who didn’t answer the teacher’s question to improve student’s motivation in learning English.
Action 1 has given rather satisfactory result because the averages of post test only 70. The problems in this cycle are some students are difficult to understand the meaning of text, some sentences are written not correct and some students look not active because shy to say in English. It is very important to continue to the next cycle to improve student’s achievement and motivation in other skill like speaking. The teacher and the writer used the same teaching strategy but in different theme.
2. Cycle 2
a. Planning
The activities are preparing:
2) List of students’ name 3) Teaching aids
4) Sheet for classroom observation 5) Tests (pretest and posttest)
b. The implementation of the action
Based on the result of cycle 1, it is necessary for the teacher to continue the next cycle.
On Monday, the twenty second of March 2010, the teacher and the writer (the observer) entered their English class. They revised the steps of teaching strategy in cycle 1. There were some students who have difficult to understand the meaning of text, like text with title “Fishing in the harbor”, so the teacher asked a student to present again, then the teacher explain each of text meaning. Beside, there were soma students who wrote short answer sentences wrongly in post test. In this case, the teacher correct students’ mistake. The last problem is miscommunication between the teacher and the writer. In cycle 2 they did correction for steps of teaching strategy. The steps are follows:
1) Divide students into six groups.
2) Appoint one student as a leader for each group. 3) Divide the material for each group.
4) Assign two students to learn one material.
40
6) Form temporary “expert group” consist of students who have
same recount text. Give students time 40 minutes to discuss the main point of their material and to rehearse the presentation they will make to their jigsaw group.
7) Bring students back into their jigsaw groups.
8) Ask each student to present her or his material to the group. Encourage others in the group to ask question for clarification. 9) Give students test orally and exercise.
Before the teacher started the lesson, he gave pretest to them. The materials in cycle 2 is about short transactional. The situation was as follows:
“Students, today we will discuss about grammar. Before we start our lesson, I will divide you into six groups like last meeting”. The class situation was noisy. “Listen to me please! Dengarkan! Baiklah, nanti setiap kelompok akan mendapatkan tiga materi,
setiap materi akan dipelajari dua siswa kecuali untuk kelompok
About 40 minutes the students have studied the materials. They have had note their material. “Okay class, time is over, we will continue to next meeting on Wednesday. Thanks for your attention,
Wassalamu ’alaikum...
’’The students answered: "Wa’alaikumsalam... ”
On Wednesday, the twenty fourth of March 2010, they entered their English class. This was the situation:
Teacher: “Assalamu’alaikum... ”
Student: “Wa’alaikumsalam... ” Teacher: “Good morning every body”
Student: “Good morning, Sir. How are you?” Teacher: “I am fine, and you?
Student: “I am fine thank you.” Teacher: “Who is absent today?” Student: “No one sir.”
Teacher: “Okay class, in this meting we will continue the lesson that we have studied last meeting. Do you remember?” Student: “Yes sir”
Student: “Yes sir” (the class situation was very noisy because the
students made rounds with tables and chairs).
Teacher: “your task is discus your material, so you have same assumption with other, if you do not understand with your material you can ask with your friend or me”
Student: “yes sir” (many students do not answer the teacher’ question)
Teacher: “Tugas kalian adalah berdiskusi tentang materi kalian, jadi kalian memiliki asumsi atau kesepahaman yang sama
tentang materi yang kalian dapat, jika kalian ada yang
kurang paham bisa bertanya pada temanmu atau saya,
pahan sekarang? ”
Student: “yes sir”
The students began discussed with their friend in new group. The class was rather quite. They looked very happy and seriously. They made summary, sample sentences and wrote the meaning of new words on the note book. Some students did not understand with their material, so they asked to the teacher. The teacher gave 40 minutes to discus.
Teacher: “okay students, time is up for your discussion. Now you back to your old group. Then, you share your material to others. So, all of students understand with three materials. Let’s start now!
Student: “yes, sir”
After the teacher gave question orally, he gave them post test for about 40 minutes,
c. Observation
In the second cycle, observation is also carried out during the implementation of the action. The writer and the teacher can see that some students wrote the example sentences wrongly. When they made sample sentence for expressing agreement, they wrote “I am agree”, using adjective “he has a beautiful classic small house”, using present future tense they wrote “she will goes to Bali”. The students found difficulties in compose a sentence using adjective like determiner, opinion, size, age, shape, color, and noun. Some students pronounced not correctly for “mountain” [mawntan] they pronounced [montein], “sky” [skai] they pronounced [skie], “shall” [syael] they pronounced [syall], “tonight” [ta’nait] they pronounced [tu’nait], “determiner” [di’tarmanar] they pronounced [de’tarmainar].
43
The class situation was noisy because the students moved
their chair and table. They presented their material to others, they looked nervous but happy. That situation was going about 40 minutes.
Teacher: “students, time is over. Thanks for your attention, we will meet again on Monday for quiz and post test.”
Student: “ulangan lagi pak? Tentang ini? (Exercise again sir? About these?).
Teachers: “of course, wassalamu’alaikum... ”
Students: “w a ’alaikumsalam... ”
On Monday the fifth of April 2010, it is the last meeting in the cycle 2. They entered English class. The situation was as follows:
Teacher: “Assalamu’alaikum... ”
Student: “Wa’alaikumsalam...”
Teacher: “Good morning every body”
Student: “Good morning, Sir. How are you?” Teacher: “I am fine, and you?
Student: “I am fine thank you.” Teacher: “Who is absent today?”
Student: “No one sir.”
d. Reflection
By analyzing the result of action 2, the teacher can conclude that the students can improve their motivation in English class. Since they can answer oral test well, it indicates that they have more motivation to learn English. But in post test only 65% of students can do it, the average just only 59. That is may be caused by time schedule was not good. Second meeting until third meeting to do post test was a week intervening, the time used to try out third grade. It is necessary for her to continue to the next cycle. Besides to improve students’ achievement in learning English, they are able to make simple sentences easier than before, the teacher and the writer used the same teaching strategy but different materials because in classroom action research the materials must continue.
3. Cycle 3
a. Planning
The activities are preparing:
1) Materials, making lesson-plan, and designing the steps in doing action.
2) List of students’ name
3) Teaching aids (charts, real things, pictures) 4) Sheet for classroom observation
46
b. The implementation of the action
On Monday, the seventh of April 2010 the teacher and the writer entered their English class, and then he introduced the mode of teaching strategy in learning English. The steps were as they did before (in cycle 2).
There were many problems in cycle 2. Some students had wrong pronunciation, wrote some words or sentences wrongly and the time is not good there was distance in second and third meeting. The skills in cycle 3 are speaking and listening with materials using positive degree of comparison, tag question and using adjective clause. The class situation was as follows:
Teacher: “Assalamu’alaikum... ”
Student: “Wa’alaikumsalam...”
Teacher: “Good morning every body”
Student: “Good morning, Sir. How are you?” Teacher: “I am fine, and you?
Student: “I am fine thank you.” Teacher: “Who is absent today?” Student: “No one sir.”
task. After the students had finished the pretest he collected and began to teach them.). Okay class, time is up!
Teacher: “well, like on the cycle 2, I will divide you into six groups, and then each group will get three materials, and each material will studied by two students. The materials are using positive degree of comparison, tag question and using adjective clause, please open your LKS page 64 to
68!
Suddenly the bell was ringed; it means that the time is up. The teacher said: t\we will continue on Wednesday. Thanks for your attention, wassalamu ’alaikum, Students answered together:
w a’alaikumsalam... ”
The next meeting on Wednesday twelfth April 2010, she entered her English class; she continued the lesson the yesterday before. She gave follow up by asking the students to mention what the materials on the Monday meeting.
Teacher: “okay class, please make group like on the Monday meeting and studied those materials”
Student: “yes sir”.
48
using adjective clause some students asked what is different between use of ‘that’ and ‘which’. They looked enjoy with that situation. After 40 minutes, the discussion finished.
Teacher: “okay students, now you make three new groups first group for using positive degree of comparison, second for tag question and third group for using adjective clause. Understand?
Students: “yes miss.”
The class situation was noisy but after they found their groups the condition was quiet again. They looked rather enjoy and confident. They were rather active in the discussion process. When the students did the discussion, she walked around the class to check the students’ task. After 40 minutes the students had finished the discussion and the have had some notes.
Teacher: “well, your time is to present your material. Now, please stand up and make around. Every group has to have one student as leader to presents in front of your friends. Okay?”
Student: “yes miss.”
using adjective clause have presentation, while group using
positive degree have not presentation because the time was over. Teacher: “okay student, time is over, we will continue this
presentation on Monday, and also on the next meeting we will do oral test like quiz and post test. Thank you so much, wassalamu’alaikum... ”
Student: “w a’alaikumsalam...”
The last meeting on Monday the fourteenth April 2010 the teacher entered English class. That meeting used to continue the last group to present and oral test. After that he gave them post test about 40 minutes,
c. Observation
The teaching learning process in cycle 3 was increasing. The students who were passive (quiet) and shy in cycle 1 and cycle 2, they looked confident eager to speak up in front of class fluently. In written form process there were some students who found difficulties. Class situation was more active (teacher and students) and the students were not nervous and shy like in cycle before, but she believed that that in all the actions in learning English there are some problems.
50
English. The improvement can be seen through the result of
activity from cycle 1, cycle 2, and cycle 3.
d. Reflection
After analyzing the result of cycle 1, cycle 2, and cycle 3, it can be concluded that using jigsaw teaching strategy can motivate the students to involve activity in learning English in the class. The result of the written test is also good. The mean score of students is 72,08, before the teacher did action the mean score was 58,03.
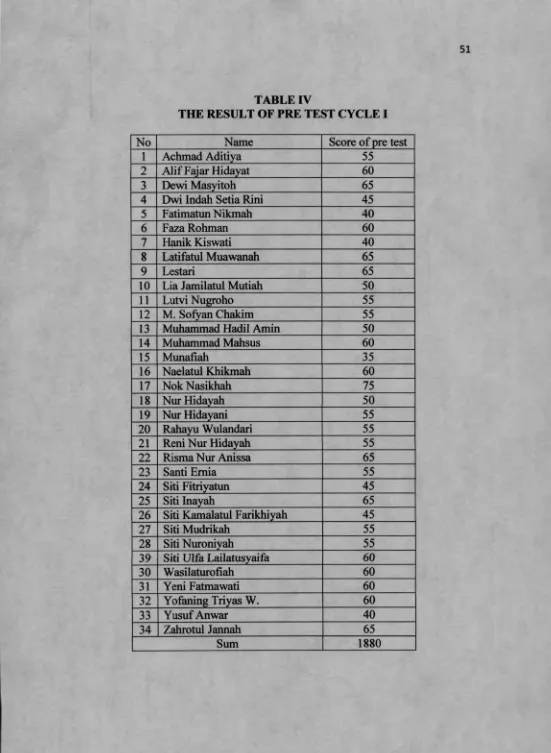
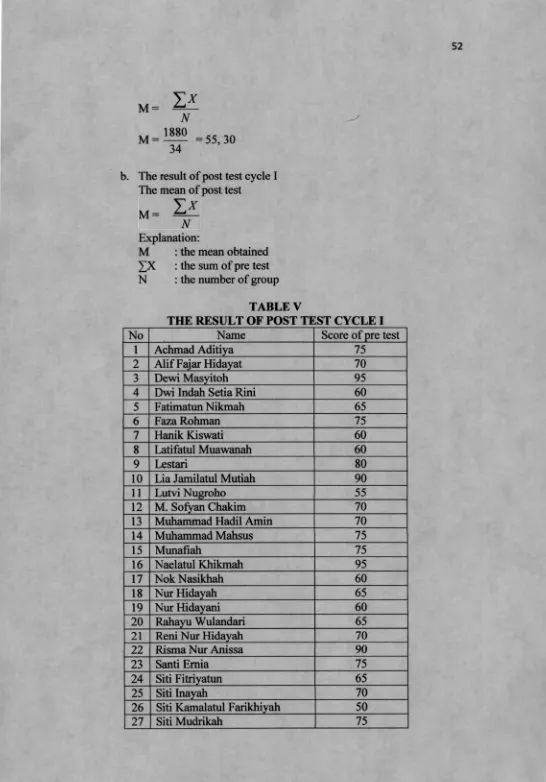
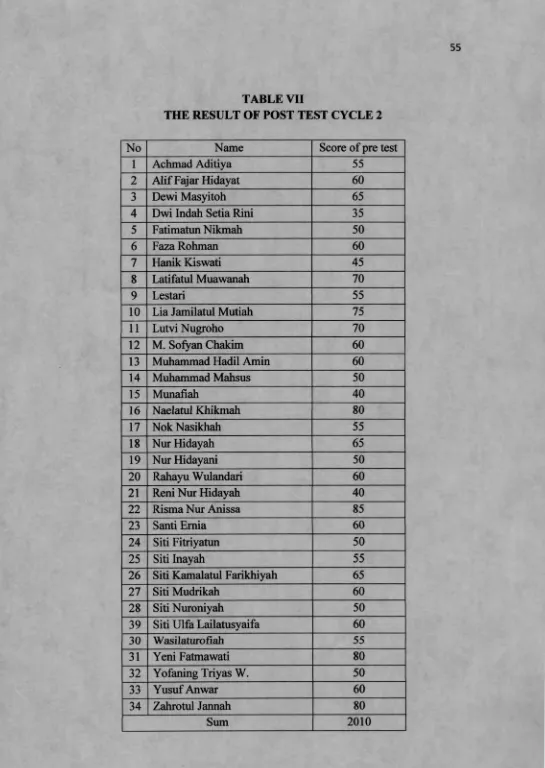
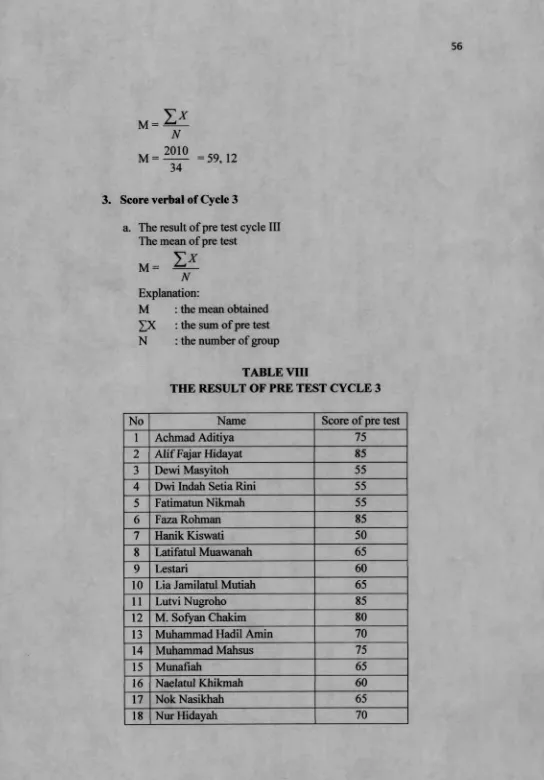
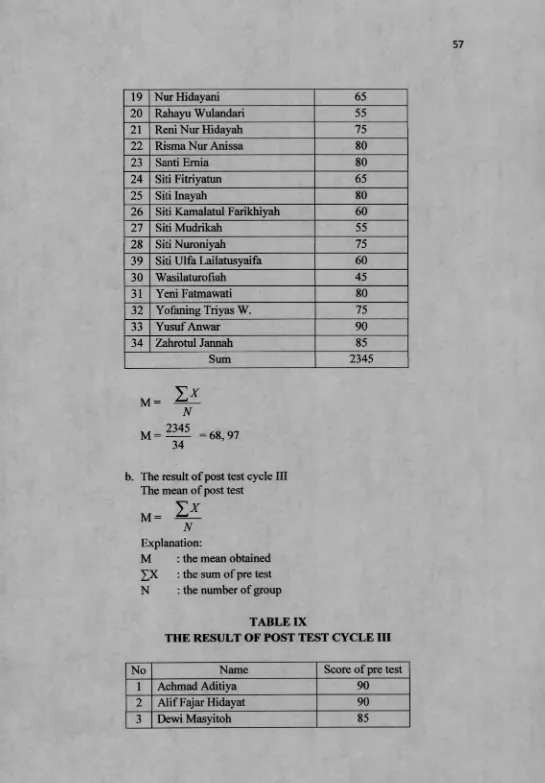
The result of pre test, post test and oral test were used to know the score of English achievement. She gave pretest to students before she taught and she gave post test after she taught for each cycle. The mean score of pre test in cycle 1 is 55,30, cycle 2 is 50,59, and cycle 3 is 68,97. So the mean score of pre test is 58,03, while the score of post test in cycle 1 is 70, cycle 2 is 59,12, and cycle 3 is 87,21. So the mean score of post test is 72.08. She also gave oral test to students during the teaching learning process in each cycle.
B. VERBAL SCORE OF STUDENT’S ACHIEVEMENT
1. Verbal Score of Cycle 1
a. The result of pre test cycle I The mean of pre test
M =
N
No Name Score of pre test
1 Achmad Aditiya 55
2 Alif Fajar Hidayat 60
3 Dewi Masyitoh 65
4 Dwi Indah Setia Rini 45
5 Fatimatun Nikmah 40
6 Faza Rohman 60
7 Hanik Kiswati 40
8 Latifatul Muawanah 65
9 Lestari 65
10 Lia Jamilatul Mutiah 50
11 Lutvi Nugroho 55
12 M. Sofyan Chakim 55
13 Muhammad Hadil Amin 50
14 Muhammad Mahsus 60
21 Reni Nur Hidayah 55
22 Risma Nur Anissa 65
23 Santi Emia 55
24 Siti Fitriyatim 45
25 Siti Inayah 65
26 Siti Kamalatul Farikhiyah 45
27 Siti Mudrikah 55
28 Siti Nuroniyah 55
39 Siti Ulfa Lailatusyaifa 60
30 Wasilaturofiah 60
31 Yeni Fatmawati 60
32 Yofaning Triyas W. 60
33 Yusuf Anwar 40
34 Zahrotul Jannah 65
52 The mean of post test
Explanation:
M : the mean obtained £ X : the sum of pre test N : the number of group
TABLE V
THE RESULT OF POST TEST CYCLE I
No Name Score of pre test
1 Achmad Aditiya 75
2 Alif Fajar Hidayat 70
3 Dewi Masyitoh 95
4 Dwi Indah Setia Rini 60
5 Fatimatun Nikmah 65
6 Faza Rohman 75
7 Hanik Kiswati 60
8 Latifatul Muawanah 60
9 Lestari 80
10 Lia Jamilatul Mutiah 90
11 Lutvi Nugroho 55
12 M. Sofyan Chakim 70
13 Muhammad Hadil Amin 70
14 Muhammad Mahsus 75
21 Reni Nur Hidayah 70
22 Risma Nur Anissa 90
23 Santi Emia 75
24 Siti Fitriyatun 65
25 Siti Inayah 70
26 Siti Kamalatul Farikhiyah 50
28 Siti Nuroniyah 65 39 Siti Ulfa Lailatusyaifa 70
30 Wasilaturofiah 50
31 Yeni Fatmawati 75
32 Yofaning Triyas W. 70
33 Yusuf Anwar 70 The mean of pre test
Y *
THE RESULT OF PRE TEST CYCLE 2
No Name Score of pre test
1 Achmad Aditiya 50
2 Alif Fajar Hidayat 50 1
3 Dewi Masyitoh 45
4 Dwi Indah Setia Rini 50
5 Fatimatun Nikmah 45
6 Faza Rohman 50
7 Hanik Kiswati 45
8 Latifatul Muawanah 50
9 Lestari 45
10 Lia Jamilatul Mutiah 65
12 M. Sofyan Chakim 50
13 Muhammad Hadil Amin 55
14 Muhammad Mahsus 50
21 Reni Nur Hidayah 45
22 Risma Nur Anissa 75
23 Santi Emia 55
24 Siti Fitriyatun 60
25 Siti Inayah 45
26 Siti Kamalatul Farikhiyah 60
27 Siti Mudrikah 60
28 Siti Nuroniyah 45
39 Siti Ulfa Lailatusyaifa 45
30 Wasilaturofiah 45
31 Yeni Fatmawati 75
32 Yofaning Triyas W. 50
33 Yusuf Anwar 45 The mean of post test
No Name Score of pre test
1 Achmad Aditiya 55
2 Alif Fajar Hidayat 60
3 Dewi Masyitoh 65
4 Dwi Indah Setia Rini 35
5 Fatimatun Nikmah 50
6 Faza Rohman 60
7 Hanik Kiswati 45
8 Latifatul Muawanah 70
9 Lestari 55
10 Lia Jamilatul Mutiah 75
11 Lutvi Nugroho 70
12 M. Sofyan Chakim 60
13 Muhammad Hadil Amin 60
14 Muhammad Mahsus 50
21 Reni Nur Hidayah 40
22 Risma Nur Anissa 85
23 Santi Emia 60
24 Siti Fitriyatun 50
25 Siti Inayah 55
26 Siti Kamalatul Farikhiyah 65
27 Siti Mudrikah 60
28 Siti Nuroniyah 50
39 Siti Ulfa Lailatusyaifa 60
30 Wasilaturofiah 55
31 Yeni Fatmawati 80
32 Yofaning Triyas W. 50
33 Yusuf Anwar 60
34 Zahrotul Jannah 80
56 The mean of pre test
M =
THE RESULT OF PRE TEST CYCLE 3
No Name Score of pre test
1 Achmad Aditiya 75
2 Alif Fajar Hidayat 85
3 Dewi Masyitoh 55
4 Dwi Indah Setia Rini 55
5 Fatimatun Nikmah 55
6 Faza Rohman 85
7 Hanik Kiswati 50
8 Latifatul Muawanah 65
9 Lestari 60
10 Lia Jamilatul Mutiah 65
11 Lutvi Nugroho 85
12 M. Sofyan Chakim 80
13 Muhammad Hadil Amin 70
14 Muhammad Mahsus 75
15 Munafiah 65
16 Naelatul Khikmah 60
17 Nok Nasikhah 65
19 Nur Hidayani 65
20 Rahayu Wulandari 55
21 Reni Nur Hidayah 75
22 Risma Nur Anissa 80
23 Santi Emia 80
24 Siti Fitriyatun 65
25 Siti Inayah 80
26 Siti Kamalatul Farikhiyah 60
27 Siti Mudrikah 55
28 Siti Nuroniyah 75
39 Siti Ulfa Lailatusyaifa 60
30 Wasilaturofiah 45
31 Yeni Fatmawati 80
32 Yofaning Triyas W. 75
33 Yusuf Anwar 90
b. The result of post test cycle III The mean of post test
M =
THE RESULT OF POST TEST CYCLE III
No Name Score of pre test
1 Achmad Aditiya 90
2 Alif Fajar Hidayat 90
4 Dwi Indah Setia Rini 90
10 Lia Jamilatul Mutiah 90
11 Lutvi Nugroho 80
12 M. Sofyan Chakim 90
13 Muhammad Hadil Amin 75
14 Muhammad Mahsus 90
21 Reni Nur Hidayah 90
22 Risma Nur Anissa 90
23 Santi Emia 90
24 Siti Fitriyatun 85
25 Siti Inayah 85
26 Siti Kamalatul Farikhiyah 95
27 Siti Mudrikah 80
28 Siti Nuroniyah 90
39 Siti Ulfa Lailatusyaifa 90
30 Wasilaturofiah 90
31 Yeni Fatmawati 90
32 Yofaning Triyas W. 90
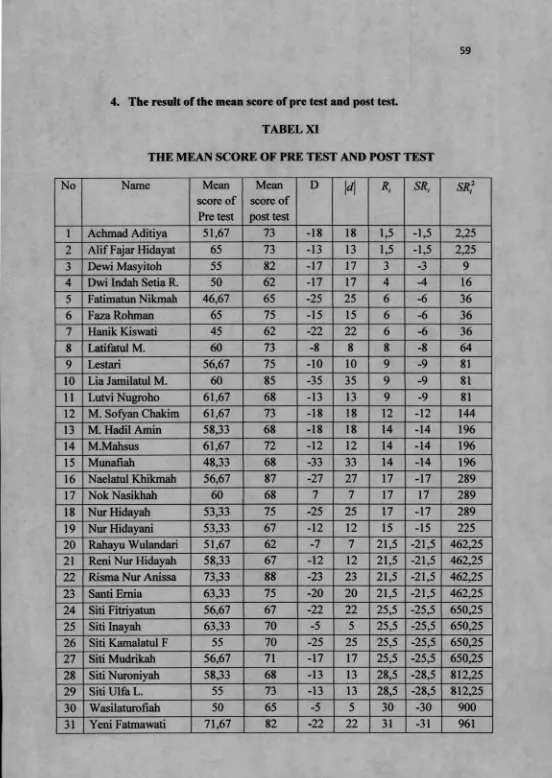
4. The result of the mean score of pre test and post test.
TABEL XI
THE MEAN SCORE OF PRE TEST AND POST TEST
No Name Mean
1
Achmad Aditiya 51,67 73 -18 18 1,5 -1,5 2,252
Alif Fajar Hidayat 65 73 -13 13 1,5 -1,5 2,253 Dewi Masyitoh 55 82 -17 17 3 -3 9
4 Dwi Indah Setia R. 50 62 -17 17 4 -4 16
5 Fatimatun Nikmah 46,67 65 -25 25 6 -6 36
6 Faza Rohman 65 75 -15 15 6 -6 36
15 Munafiah 48,33 68 -33 33 14 -14 196
16 Naelatul Khikmah 56,67 87 -27 27 17 -17 289
17 Nok Nasikhah 60 68 7 7 17 17 289
18 Nur Hidayah 53,33 75 -25 25 17 -17 289
19 Nur Hidayani 53,33 67 -12 12 15 -15 225
20 Rahayu Wulandari 51,67 62 -7 7 21,5 -21,5 462,25 21 Reni Nur Hidayah 58,33 67 -12 12 21,5 -21,5 462,25 22 Risma Nur Anissa 73,33 88 -23 23 21,5 -21,5 462,25
23 Santi Emia 63,33 75 -20 20 21,5 -21,5 462,25
24 Siti Fitriyatun 56,67 67 -22 22 25,5 -25,5 650,25
25 Siti Inayah 63,33 70 -5 5 25,5 -25,5 650,25
26 Siti Kamalatul F 55 70 -25 25 25,5 -25,5 650,25 27 Siti Mudrikah 56,67 71 -17 17 25,5 -25,5 650,25 28 Siti Nuroniyah 58,33 68 -13 13 28,5 -28,5 812,25
29 Siti Ulfa L. 55 73 -13 13 28,5 -28,5 812,25
30 Wasilaturofiah 50 65 -5 5 30 i cn O 900
60
32 Yofaning Triyas W. 61,67 70 -10 10 32,5 -32,5 1056,25 33 Yusuf Anwar 58,33 75 -35 35 32,5 -32,5 1056,25
34 Zahrotul Jannah 70 77 -12 12 34 -34 1156
Sum 197333 2451 -572 586 588 -544 13472,5
Y S R i
t = r =
JsW
-5 4 4 Vl 3472,5
-5 4 4 116,07 = -4, 69
dlt = (n, + n 2-2 ) = (34 + 34 - 2) = 66 -» a = 0,05 -> t(0 05;66)
= -1671
A. Conclusion
1. From the mean score verbal shows that the mean of pre test is 58,03
2. Based on the reflection on ach cycle shows that students’ activities at English class indicate that students were motivated and interested in learning English. It is indicated in oral test the percentage of students who can answer is 83% in first cycle, 86% in second cycle and 95% in third cycle.
3. The mean score of pre test 55,30 to 70 in post test cycle 1, the mean score of pre test 50,59 to 59,12 in post test cycle 2, and the mean score of pre test 68,97 to 87,21 in post test cycle 3. The result that jigsaw teaching strategy can improve effectively students’ achievement in learning English.
B. Implication
The result of the research shows that using jigsaw teaching strategy can improve students’ motivation, interest and achievement. The implementation of jigsaw strategy is reasonable because it can give students a great motivation to speak up in learning English. Thus, jigsaw strategy is good to improve students’ achievement, interest, and motivation.
C. Suggestion
Based on the result of the study and conclusion, the writer would like to suggest as follows:
1. To the teachers
Teachers should have sensitivity toward students’ problem. Jigsaw teaching strategy can be alternative solution for students who get trouble in their motivation, not confidents and their achievement. Jigsaw teaching strategy attract students to active like brief to speak in front of class, it helps students to want to study English. It can influence student’s’ happiness and make students enjoy the learning.
2. To the students
Students should be active in teaching learning process and are not afraid of English lesson. Students should pay attention to teacher explanation, if the teacher give question they can do perfectly and they can do exercise.
3. To other researchers
BIBLIOGRAPHY
Breen, M. and C. N. Candlin. The Essentials o f a Communication Curriculum in Language Teaching. Cambridge: Cambridge University. 1980. p. 99
Brown, Douglas. Principles o f Language Learning and Teaching. Englewood Cliffs, N. J: Prentire Hill. 1980, p. 48, 160-166.
Elliot, John. Action Research fo r Educational change. Philadelpia: Open University Press. 1991. P.69.
Fieldman, Robert S. Understanding Psychology. America: me. Grow Hill Inc. 1996, p.127
Fries, Charles, C. Teaching and Learning English as a Foreign Language. United States of America: Prentice Hall. 1980. p. 112, 114, and 160-166
Hadi, Sutrisno. Metodologi Research Jilid 2. Yogyakarta: Andi Offset. P.902
Hadley, Gregory. Action Research in Action. Singapore: Publications Department, 2003. p.ii.
Harmer, Jeremy. The Practice o f English Language Teaching. New York: Longman Press. 2001. p. 51, 56 and 66
Harris, David P. testing English as a Second Language. New York: Me Grow hill book Company. 1986, p.3
Kurikulum 2004. Standar Kompetensi SM{P dam MTs. Dharma Bakti
Modul Penelitian Tindakan Kelas. Bogor: Universitas Pakuan. 2009. p.3-5.
Muhibbin, Syah. Psikologi Pendidikan dengan Pendekatan Bani. Bandung: Remaja Rosda Karya. 1987, p. 46
Nasution, S. Berbagai Pendekatan dalam Proses Belajar Mengajar. Jakarta: Bumi Aksara. 1984. p. 50
Nurhandayani, Heni. The Influence o f Teachers’ Teaching Strategies o f the English Achievement. STAIN Salatiga. 2005
Supanngat, Andi, Drs. M. Si. Statistika Dalam Kajian Deskriptif, inferensi, dan Nonparametik. Jakarta: kencana Predana Media. 2007, p.375.
Suprijanto, Drs. Ir H. Pendidikan Orang Dewasa dari Teori hingga Aplikasi.
Jakarta: Bina Aksara. 1984, p.25
Wallace, J. Michael. Action Research fo r Language Teacher. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. 1999. p. 4
Wena, Made. Strategi Pembelajaran Inovatif Kontemporer. Jakarta: Buni Aksara. 2009. p. 193
www.jigsaw.or.id
Text for number 1 to 5!
It was Sunday morning, January 2nd 2009. My friend and I went to the beach after studying hard. We wanted to refresh our mind and enjoyed the fresh air. We went there early in the morning by car. Many people were there when we arrived.
After parking the car, we walked a long the beach barefooted. We cold feel the smoothness of the sand. The cold sea water touched our feet.
Then, we looked for a place to take a rest. We rolled out the mat on the ground and had meals together. While eating, we saw many things. We saw many children built sand castles. Some of them played with their balls. We also saw many people sunbathe.
After having meals, we were interested in doing the same thing. We were so happy and really enjoyed that day.
Adapted from: Bahasa Inggris SMP. Akasia 1. The purpose of the text above is to...
a. Retell about past event b. Amuse the reader
c. Describe about the beach d. Inform the reader
2. The story tells us about... a. The condition of beach b. Go to the beach
4. The sentences of the story mainly in...form. a. Simple present tense
b. Simple past tense c. Simple future tense d. Simple perfect tense 5. The events of the text is in...
a. First and second b. Second and third c. Third and fourth d. Fourth and first
Text for number 6 to 10!
There were so many places to see in Bali that my friend decided to join the tours to see as much as possible. My friend stayed in Kuta on arrival. He spent the first three days swimming and surfing on Kuta beach. He visited some tours agent and selected two tours. The first one was to Singaraja, the second was to Ubud.
The streets are lined with tress and there are many Old Dutch houses. Then, they return very late in the evening to Kuta.
The second tour to Ubud was a very different tour. It was not to see the scenery but to see the art and the craft of the island. The first stop was at Batubulan, a center of stone sculpture. There, my friend watched young boys were carving away at big blocks of stone. The next stop was Celuk, a center for silversmiths and goldensmiths. After that, he stopped a little while for lunch at Sukawati and on to Mass. Mass is a tourist center.
My friend ten-day-stay ended very quickly beside his town tours, all his day was spent on the beach. He went sailing or surfboarding every day. He was quite satisfied.
(Taken from www. understandim text.blogspot.com)
6. The text above talks about... a. Visiting Bali
b. Places in Bali c. four to Kuta beach d. Sailing and surfing
7. Below are places in Bali, except... a. Kuta
9. The re-orientation of the text is in.. .paragraph. a. Fourth
Text for number 11 to 15.
Lat year I left New Zealand for Bunaken Island. I went there with a group of New Zealand divers. Getting there was not quite easy.
Soon after our arrival at Bunaken, we got a general briefing. It included a description about how to take pictures under water.
Then, we began our diving. In our diving, we saw groups of tiny fish. In order to identify them, we need a good guide. Without some knowledge of their habitat and behavior, it was difficult to identify.
In summary, the trip was mostly enjoyable. This place is so impressive with its marine life.
12. The sentences bellows are correct, except...
a. The writer went to Bunaken Island with a group of divers b. Diving is easy without a good guide
c. A good guide is important in our diving d. The trip was mostly enjoyable
13. “It included a description about how... ” The word it refers to... a. General briefing
b. Diving
c. New Zealand divers d. Bunaken Island
14. Where is Bunaken Island? It is in... a. New Zealand
b. Sulawesi c. Kalimantan d. Sumatera
15. The orientation of the text is in.. .paragraph. a. First
b. Second c. Third d. Fourth
Text for number 16 to 20.
Last New Year’s Eve, my family joined some other families on a fishing trip at Greenwich harbor to welcome the New Year; we went fishing so we could stay up late.
On our way to the harbor, we bought some beef mince at the butcher’s. We used the mince as bait. My parents’ friends brought the fishing rods for us to use. When we got to the harbor, some families were already there. We were a bit late because tried to find our way to the harbor and got a bit lost. We started a fishing competition. We agreed that whoever got the most fish will keep all the fish caught that night. Apparently, no one caught any big fish. We caught mostly small yellowtail fish. After fishing for nearly three hours, my mom got the most fish. All the participants gave all their fish to us. We came home with a bucketful of fish. It was not bad at all.
The next morning, we enjoyed some fresh fried yellowtail fish with steamed rice for breakfast. That was very special because we had never had fried yellowtail fish for breakfast before.
16. The text above talks about... a. New Year’s Eve
b. Fishing in the harbor c. Trip to the harbor d. Fishing competition
17. The purpose of the text above is to... a. Retell about last New Year’s Eve b. Amuse the reader