CHAPTER II THEORITICAL REVIEW
A. The Nature of Translation
1. The Definition of Translation
Catford in Rachmadie (1988: 1) says that translation is the
replacement of textual material in one language (SL) by equivalent
textual material in another language (TL). Savory in Rachmadie (1988:
1) adds that translation is made possible by an equivalent of thought that
lies behind its different verbal expression. According to them, translators
should use the closest natural equivalence either in the meaning or in the
style of the receptor’slanguage.
The most comprehensive understanding about translation is
described by Newmark (1988: 3-4) in his book entitled A Textbook of Translation. He gives a new insight of translation by considering the dynamic nature of it. He completely describes that it involves ten
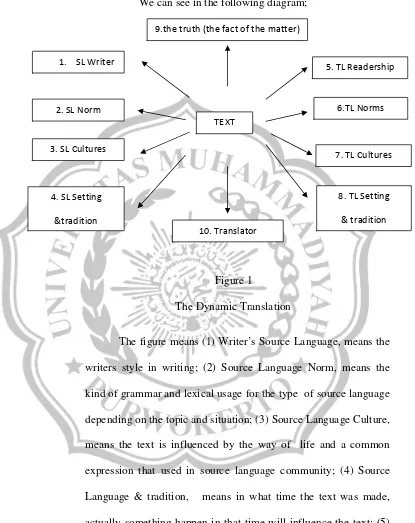
We can see in the following diagram;
Figure 1
The Dynamic Translation
The figure means (1)Writer’s SourceLanguage, means the
writers style in writing; (2) Source Language Norm, means the
kind of grammar and lexical usage for the type of source language
depending on the topic and situation; (3) Source Language Culture,
means the text is influenced by the way of life and a common
expression that used in source language community; (4) Source
Language & tradition, means in what time the text was made,
actually something happen in that time will influence the text; (5)
Target Language, means that the possible expectation and the
reader style in reading a text; (6) Target Language Norm, means
the kind of grammar and lexical usage for the type of Target
Language depending on the topic and situation; (7) Target
Language Culture, means the text is influenced by the way of life
and a common expression that used in Target Language
community; (8) Source Language & tradition, means in what time
the text was made, actually something happen in that time will
influence the text; (9) the fact or the truth is being described; and
(10) the subjective view of the translator or translation assumption
with the text.
It can be concluded that basically translation is transferring
the meaning from one text into another text with the change of the
form; form of source language (SL) is replaced by the form of
target language (TL). There should not be extraneous information,
change of meaning, or distortion of the fact of the source text.
Translation is regarded as field of research that needs a skill ti
practice. A process of translation is related to the term of source
language (SL) and Target Language (TL). The main skill to
practice translation is the ability to process the data or information
in source language then transfer it to target language.
2. The Meaning of Translation
Meaning is an essential thing in the process of translation
process. A translator should be able to analyze a discourse or text to get
suitable meaning of the whole discourse (Nababan, 1999: 47).
The meaning of translation is described as follows:
a. Lexical Meaning
Lexical meaning is the meaning of the language elements as a
symbol or event. It can also said that lexical meaning of the language
elements as written in dictionary, for example the word house means
rumah, bangunan, parlemen. The meaning will be seen if the whole sentence has known.
b. Grammatical Meaning
It is the meaning that is inseparable with the context. Moreover,
Grammatical meaning is the relation between language element in
bigger unit, such as the relation between a word and the other ones a
phrase or sentence. For example word book means buku, pesan or
memesan, look the sentence below: - You have a book.
- You book a room in the hotel.
c. Situational or Contextual Meaning
It is a meaning related to the element or surrounding it. Each word of
language has meaning based on the situation or context. It can be
seen in wordfire: - Fire! ( kebakaran!)
- Fire? (butuhapi/korek?)
- Fire! (tembak!)
d. Textual Meaning
Textual meaning is meaning that correlates to the discourse or its
subject matter. For example the word interest; in common it means
menarik,but in economics it meansbunga.
e. Socio-cultural Meaning
This is a meaning that has closed relation with the social culture of
the language user. A word of this kind often does not have the same
concept of the source language and target language. For example,
when we find the world Halloween, it will be better we write it as the
Halloween not the other because we couldn’t find the best word in
Indonesia and it’s to avoid misinterpreting of the reader.
All aspects will be taken from the result of translation test.
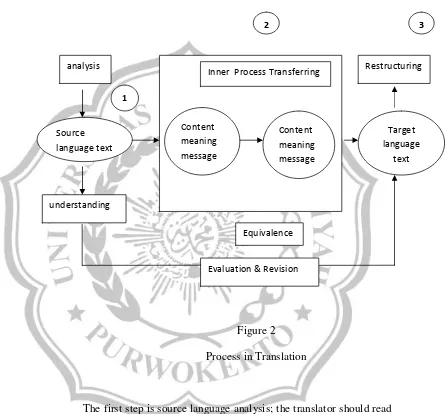
3. Process in Translation
Translation process can be defined as a series of activity
done by translator when he transfers message from SL into TL.
(Suryawinata in Nababan, 1999: 25). It can be seen in the following
figure:
Figure 2
Process in Translation
The first step is source language analysis; the translator should read
the source language text. Comprehension on the text content
requires understanding on linguistics and non-linguistics element of
minds. The last is restructuring, it means destroying the message
transfer becomes an equivalence stylistic form of target language.
4. The Principle of Learning Translation
To learn translation, a student should understand the kind
of the text or the subject matter of the text. Besides, a student should
be familiar with the equivalent words and have good sense in
analyzing the text.
Using media can help a learner learn something. Hopefully,
personal vocabulary notes can help a learner in learning process.
Having personal vocabulary notes helps one memorize the
vocabularies easily and familiar with words, then help them do the
translation process easily.
B. Vocabulary
1. The Definition of Vocabulary
Vocabulary is a list or set of words for a particular language
or a list or set of words that individual speakers of a language
might use (Brown, 1995: 1).
Mulbar (2007: 8) gives some definitions bellow;
a) Vocabulary is the content function words of language, which
understanding, spelling and the letter reading and writing
obviously.
b) Vocabulary is the words having meaning when heard or seen
even though not produced by individual himself to
communicate with other.
From the statement above the researcher take conclusion
that anything words which has a meaning in communication, not
only in speaking communication but also in writing
communication that the other person can understand the meaning
it could be a vocabulary.
2. Kinds of Vocabulary
Harmer (1993: 159) distinguishes two kinds of vocabulary,
namely active vocabulary and passive vocabulary.
a Active vocabulary refers to all words the students have learnt
and which can be used in communication.
b Passive vocabulary refers to all words which students will re
cognize them when they see them in communication.
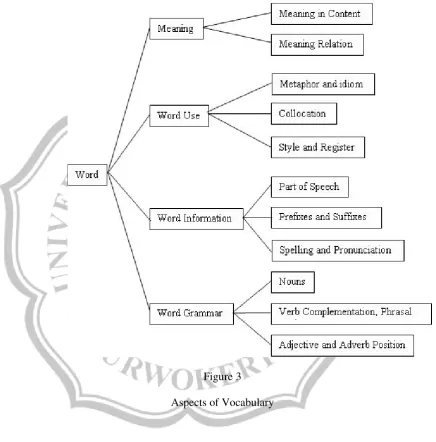
3. The Four Aspects of Vocabulary
Harmer (1993: 156-158) explains four aspects of
vocabulary that the students need to know about. The four aspects
a. Word Meaning
One word may have more than one meaning. The
meaning of a word depends on the context in which that the
word occurs. Therefore in the teaching of vocabulary, words
taught to students should be presented in variety of context to
show various meaning.
b. Word Use
The meaning of a word can be changed, stretched, or
limited by how it is used, and this is something that students
need to know about in relation to word use, Harmer (1993:
157) states that students need to recognize such as idiomatic
use, metaphorical use, and word collocation.
1) Idiomatic Use
Word meaning is frequently stretched through the use of
idiom (idiomatic expression). Such “Cats and Dogs”, can
be put into such a fixed phrase as it’s raining cats and
dogs, it means very heavy rain.
2) Metaphorical Use
Metaphor is the use of word to indicate something, which
is different from its literal meaning. Such as the word
‘hiss’ which describes the way people talk as in “Don’t
3) Word Collocation
Word meaning is also governed by collocation, that is,
which words go with each other. For example, such a word
‘wrist’ can collocate with ‘sprain’ as in ‘sprain wrist’, but
it cannot collocate with the word ‘head’. So it can not be a
collocation as ‘sprain head’. On the country, the word
‘ache’ can collocate wit ‘head’ as in ‘headache’, but it
cannot collocate with the word ‘wrist’. So, we cannot have
such a collocation as ‘wrist ache’.
c. Word Formation
Word formation refers to word forms and how they are
formed. Some words are nouns, some words are adjectives,
some words are verbs, etc. A student need to know how to form
adjectives from nouns, how to form nouns to adjectives, how to
form verbs to nouns, or from adjectives and etc. For example,
beauty (noun) changed into beautiful (adjective), or beautify
(verb) (Chew and Kaur in Mutmainnah, 2006: 11)
d. Word Grammar
Word grammar refers to such thing as the way words are
Harmer can summarize four aspects of vocabulary in the
following figure;
Figure 3
Aspects of Vocabulary
C. Personal Vocabulary Notes (PVN)
Personal Vocabulary Notes (PVN) is a way of developing students’
vocabulary in a personalized way while encouraging them to become
Making PVN is a simple activity, but not all the students are interested
in making it as their habit. To make the PVN, the students should have a book
to record vocabulary items. They may write all the new vocabularies in
English then translate it. They may also write the words in their native
language that they do not know how to say in English. Having PVN, the
students will increase their vocabulary more and more. To keep the
vocabulary, the students should try to memorize it. To understand better, they
should write sentences using their PVN. So, the students’ English can be
progress by having PVN.
The Advantages of PVN:
1. Motivation
Students are usually much more motivated to remember
their PVN than they are a set of vocabulary items they have
received from a textbook or teacher.
2. Students’ Need
PVN addresses individual student needs by encouraging
students to find the vocabulary they need to communicate and talk
about their experiences.
3. Contextualized Vocabulary Learning
The teacher is able to address a great deal of complexity
and richness without having to invent a context as the context is
already created by the student.
Especially, in large multilevel classes PVN provides the
teacher with a time-efficient way of giving attention and feedback
on language to individual students.
5. Vocabulary Awareness
PVN gives students a much deeper sense of what it is to
learn vocabulary and know a word as they get contextualized
feedback on words they are using.
6. Dictionary Skills
PVN provides a motivating context for teaching dictionary
skills again because students are researching their own words.
7. Material for a Variety of Other Skill Activities
Once student have a set of PVN the teacher can use their
vocabulary to teach many other points such as circumlocution
skills, pronunciation (ex. Word stress), grammar (ex. Parts of
speech)
D. Basic Assumptions
To learn translation, the students should understand well with the
kind of the text or the subject matter of the text. Besides, the students
should familiar with the words equivalent and have good sense in
Personal vocabulary notes makes one’s vocabulary increased
more and more. Moreover, when we make vocabulary notes from many
sources, we can familiar with many new vocabularies and understand
the sentence in textual or contextual meaning.
It means that having a habit in making personal vocabulary notes
will help the learners in language learning, especially for their
translation.
E. Hypothesis
The writer proposes a hypothesis that there is significant
correlation between personal vocabulary notes and the translation