However, developmentally, probiotic-based functional food can play a key role in the growth and development of the child's mental and physical health. The presence of glucose and sucrose in a functional food can significantly reduce the severity of pain in the host body.
TOP 1%
Introduction
There are additional adverse implications for cognitive health that are estimated to be 30% common among the overweight and obese adult population [5, 6]. The potential of modifiable lifestyle factors is important as no effective pharmacological agents have been identified for improving cognition or delaying the progression of cognitive decline [9].
An overview of MIND diet
Personal nutrients in foods have been controversially related to cognitive function, which include some vitamins, carotenoids, long-chain n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) in kinds of fish and shellfish, whole-grain foods rich in polyphenols, nuts, olive oil, coffee, fruits and vegetables [10-12].
Potential mechanism of the MIND diet
Role of MIND diet and protocol
Benefits of the MIND diet
The intake of the designated unhealthy foods, ghee, butter, sweets and pastries, full-fat cheese, and fried or fast foods should be limited. Food groups recommended in the MIND diet have been found to boost brain health as it is a rich source of fiber and packed with all the necessary nutrients such as vitamin E, folic acid, omega-3 fatty acids, carotenoids and flavonoids.
Components of MIND diet and its role to health 1 Green leafy vegetables
- All other vegetables
- Berries
- Nuts
- Vegetable oils
- Whole grains
- Seafood
- Beans
- Poultry
- Wine
Omega-3 fatty acids are responsible for physiological functions associated with neurogenesis, neurotransmission and neuroinflammation. Beans are rich in protein, carbohydrates, fibre, B vitamins and omega fatty acids, antioxidants and minerals.
Conclusion
Mushrooms and their bioactive molecules exhibit antitumor activity that can be extremely beneficial in the treatment of various rare diseases. Polyphenols, alkaloids and many other biomolecules in edible mushrooms demonstrate their effectiveness in the treatment of various neurodegenerative diseases [32].
Mushroom active compounds against cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) Cardio Vascular Diseases (CVDs) are a category of heart and blood diseases,
Lucidum extract scavenges free radicals and also increases the levels of glutathione and antioxidant enzymes [33]. A study assessed the effect of different mushroom-like Lentinus edodes, Auricularia polytricha and Flammulina velutipes preparations on the levels of cholesterol in the rats, which showed that the preparation of dried mushrooms significantly reduced plasma cholesterol levels.
Antidiabetic activity of mushroom biomolecules
In addition, the extraction and purification of the active ingredient from these mushrooms may lead to the development of a potent antiatherosclerotic drug [36]. Mushroom polysaccharides and fibers act as prebiotics that help in the treatment of diabetic patients [45].
Anticancer activity
Bioactive compounds present in Ganoderma species are a potential alternative to fight breast cancer. Agarikon.’ The fruiting bodies of the mushroom are used as medicine in Western Europe, North America and Asian countries for the treatment of stomach cancer, asthma, cough and pneumonia [74].
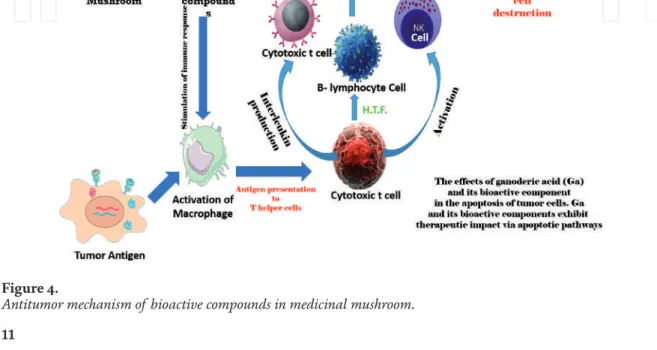
Biomolecules of mushrooms in neurodegenerative diseases (NDs) Bioactive molecules in mushrooms also prevent the progression of different NDs
Effect of maitake (Grifola frondosa) D fraction on the control of the T-lymph node Th-1/Th-2 ratio. Edible mushrooms are precious components of the eating plan because of their appealing taste, fragrance and nutritional benefits.
Mushroom cultivation
Mushroom peptides have the same amino acid composition as animal protein [9, 10], which is particularly important in light of the high intake of protein from dietary animal sources, especially in industrialized countries. The study of the biological component of mating-type DNA in the creation of strains cannot be overestimated with excellent yield and tolerance to bacterial diseases [28, 29], infectious infections [29, 30] and pathogenic organisms [31, 32]. If growers are unable to produce viable eggs, most of the mushroom growth process will stop.
Manual or motorized cutters are used to cut the upper leafy part and part of the strong stem towards the roots to make straw bundles 45 cm long and 10 cm wide.
Challenges in mushroom cultivation
Global mushroom cultivation prospects
The introduction of fresh varieties of mushroom cultivation for commercial purposes has resulted in a rapid expansion of the mushroom business worldwide during the last two decades.
Nutritional value
Phenolic compounds
While the other FA was found only in trace levels, with the exception of Lactarius deliciosus, which has a high concentration of stearic acid (C18:0) [51].
The therapeutic effect of mushrooms
Fungi accumulate bioelements with free radicals and anti-inflammatory properties such as zinc, copper, iron and selenium [84].
Mushroom and chronic diseases
- Impact of mushroom on cardiovascular diseases
- Edible mushrooms and obesity
- Effect of mushroom on cancer
- Role of mushroom in diabetes
- Effect of mushroom on immune system
- Mushrooms’ effect on bone health
- Neurodegenerative diseases and mushroom
Some fungal species have been shown to have anti-inflammatory effects [108], and edible mushrooms have been used to obtain natural anti-inflammatory chemicals. Ganoderma induce dried fruit bodies by cell growth in the G2-M cell cycle phase, which is caused by cell proliferation. Many mushrooms have been shown to control blood glucose levels clinically and/or experimentally and to alter the course of diabetes problems without causing negative effects [41, 132].
Edible mushrooms are high in polyphenols, polysaccharides, vitamins, carotenoids and minerals, all of which have antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties [154].
Conclusion
- Medicinal mushroom in phytotherapy
- Medicinal mushrooms in folk medicine
- Mushrooms as a delicacy food in Cameroon
- Usage of medicinal mushrooms
Evaluation of antioxidant and antiglycation effects of Lactarius Deterrimus and Castanea Sativa extracts on hepatorenal injury in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Most of the mushroom benefits that have been researched and investigated using the scientific method are those that have been recognized to produce bioactive metabolites that. Different species of mushrooms have been reported as nutritious and tasty food in many parts of the world and have been documented by many researchers [24–26].
The nutritious property of mushrooms is also another way through which it can be beneficial to the health of the person who eats mushrooms [27].
Some example species of mushrooms that have been studied for medicinal properties
- Coriolus versicolor
- Lentinula edodes
- Tremella fuciformis
- Ganoderma lucidum
- Auricularia auricula and Arabis polytricha
- Boletus edulis
- Cordyceps sinensis
- Fomitopsis officinalis
- Pleurotus ostreatus
The survival of the treatment of PSK has shown the potential to increase the survival rate within 5 years by 21 and 52%, respectively [36]. This species is widely distributed in North and South America, Europe and part of the African dense moist forest where they grow on the hardwood. The species is very popular and widely used in Chinese and Japanese traditional pharmacopoeia for the past 4000 years for the treatment of several diseases of the liver, hypertension, peptic ulcer, arthritis, chronic hepatitis, insomnia, bronchitis and asthma [9, 48 ].
The mushroom's ear-like shape is linked to the returned spirit of Judas, which serves as a reminder of his betrayal [27, 50].
Carnivorous fungi
- Common toxic mushrooms
- Psychoactive mushrooms
- Mushroom bioactive metabolites of therapeutic potential
There was no significant change for total cholesterol and its high and low density lipoprotein fractions in plasma, as well as the calculated atherogenic index. Some scientific works have supported these claims, as well as the long-lasting effects of the induced spiritual experiences [24, 77]. Psilocybin, a naturally occurring chemical in certain psychedelic mushrooms such as Psilocybe cubensis, has been studied for its potential in treating mental disorders such as obsessive-compulsive disorder [77].
In the study, one-third of the volunteers reported that ingesting psychedelic mushrooms was the single most spiritually significant event of their lives [79].
Therapeutic potential of mushrooms
- Pharmacological properties of mushrooms .1 Antioxidant property of medicinal mushrooms
One of the common metabolic disorders such as cardiovascular disease is associated with atherosclerosis, low-density lipid (LDL) oxidation, and hypercholesterolemia, plays a role in the regulation of the cholesterol level which is essential for the prevention and treatment of this disease [42, 83]. The most commonly used animal models for the study of the hypoglycemic effects of mushrooms are rats and mice with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM), induced by streptozotocin (STZ), and genetically modified non-insulin diabetic mice [13] , 92]. Consequently, there is the need for the selection of the most suitable cultivation media for obtaining the most active secondary metabolites of fungal mycelia [51].
Therefore, they are potential sources of natural antibiotics and many extrinsic bioactive compounds from the extracellular secretions of mycelium, which can inhibit bacteria [72] and viruses [3, 19].
Mushroom toxicity
- Pathophysiology of mushroom poisoning
- Mushroom liver toxicity
- Nephrotoxicity
- Toxicity evaluation, treatment, and management
- Stages of amanita poisoning
- Chemical test for mushroom toxicity
- Orellanine poisoning and symptoms
- Toxin found in certain species of Coprinus
- Gastrointestinal irritants
Cholinergic toxicity: This is caused by muscarinic mushroom in the genera Clitocybe and Inocybe. The toxin's bioactive metabolites can lead to the inhibition of aldehyde dehydrogenase which causes headache, nausea. Cases of attacks may be due to the presence of gyromitrin in Gyromitra, Paxina and Cyathipodia micropus species, although this may be less common in the latter two.
Symptoms include flushing of the neck and face, metallic taste in the mouth, tingling sensations in the extremities, numbness in the hands.
Most common toxic mushrooms in Cameroon
Conclusions
Most mushrooms are consumed directly in various menus for health and medicinal purposes, contributing to their additive and synergistic effects of bioactive compounds. The work was supported by a research mobilization grant from the Ministry of Higher Education of the Republic of Cameroon. Structures, biological activities and industrial applications of polysaccharides from the mushroom Hericium erinaceus (lion's mane): a review.
Second, we present our findings on the ability of the comb medicinal mushroom, H.
Characteristics of wild mushroom mycelia 1 Collection of mushrooms and separation of mycelia
- Ethanol extract preparation from mushroom mycelia
- Antioxidant activity of wild mushroom mycelia
- Total phenolic content of the wild mushroom mycelia
- Phenolic compounds enable the DPPH radical scavenging capacity of mushroom mycelia
In this chapter, we first discuss the antioxidant activity of 20 different species of wild mushroom mycelia [9]. The DPPH radical scavenging activity of mushroom mycelium was calculated from test lines of Trolox and 25 μM) and expressed as μmol Trolox/g dry powder. Eighty percent ethanol extracts of mushroom mycelia were used for antioxidant activity measurements using DPPH radical scavenging activity (Figure 1).
The DPPH radical scavenging activity of mushroom mycelium was calculated and expressed as trolox equivalent.
NGF synthesis of H. ramosum mycelia
- Methods
The DPPH radical scavenging activity showed a significant correlation (R) with the total phenolic content of wild mushroom mycelium extracts (Figure 3). All these results indicate that the DPPH radical scavenging ability of these extracts is driven by phenolic compounds.
Soybean fermentation using mushroom mycelia
- Antioxidant activity of fermented soybean .1 Methods
- Alpha-glucosidase inhibitory activity of soybeans fermented with mushroom mycelia
- Comparison of isoflavone concentrations in soybeans fermented with mycelia versus non-fermented soybeans
Total phenol content was higher in all fermented extracts compared to unfermented control soybeans. Both DPPH radical removal activity and antioxidant activity were higher in fermented soybeans than in unfermented soybeans (Table 1). Yeast alpha-glucosidase inhibitory activity was measured using previously reported methods [52] with modifications as described in Suruga et al.
We also used maltose as a substrate and calculated the % degree of alpha glucosidase inhibition [54].
Discussion
- Characteristics of H. ramosum mycelia and other mushroom mycelia
- Soybean fermentation of mushroom mycelia
The present findings indicate that the DPPH radical scavenging activity of the Hericaceae group, including H. We showed that fermentation using these mycelia increased the amount of the aglycone form compared to non-fermented ones. Comparison of the antitumor effect of the fruiting body and mycelium of Hanabiratake (Sparassis crispa).
Aliphatic side chain of catecholamine enhances the stimulating effect of the catechol part on the synthesis of nerve growth factor.