Directory UMM :Data Elmu:jurnal:A:Agricultural & Forest Meterology:Vol105.Issue4.Dec2000:
Teks penuh
Gambar
Dokumen terkait
The SALSA Program is a multi-agency, multi-national research effort that was initiated at the USDA Agricultural Research Service (ARS) South- west Watershed Research Center (SWRC)
First, remote-sensing investigations are discussed, especially those directed toward taking full advantage of the capabilities of the new generation of satellites
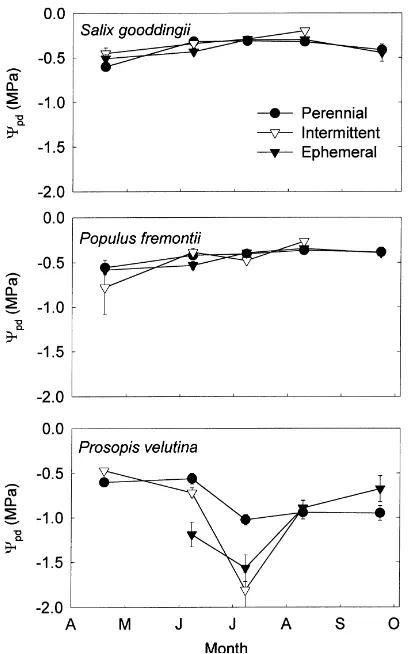
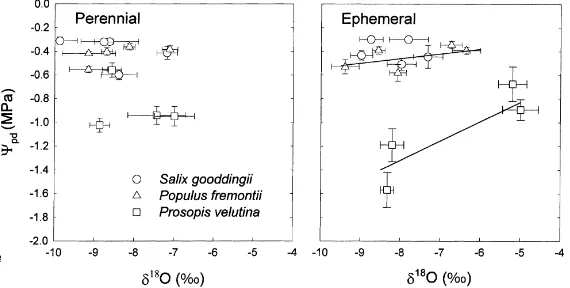
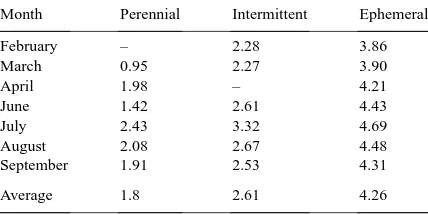
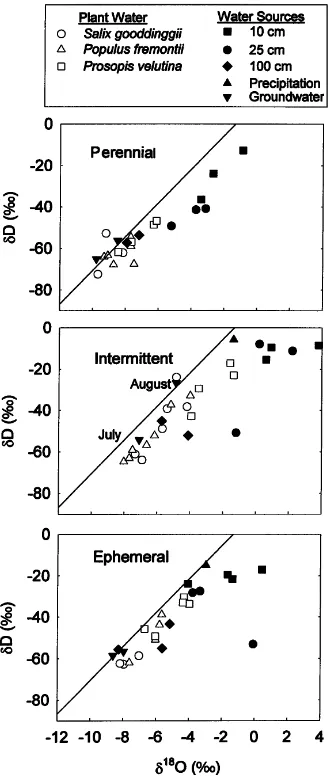
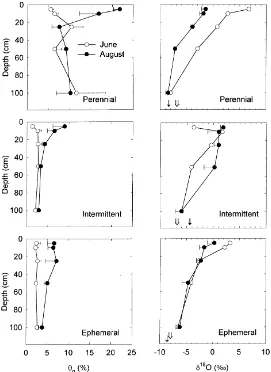
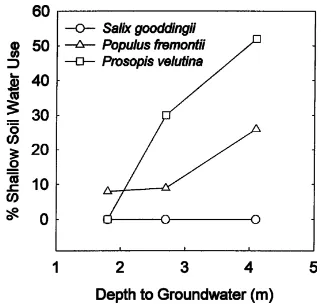
The vegetation communities were a perennial, floodplain sacaton grassland (Sporobolus wrightii) and a tree/shrub grouping composed largely of mesquite (Prosopis velutina).
Contrary to the electrical analogy, where soil and vegetation controls on evaporation are reproduced with the help of empirical surface resistances (allowing for the calculation of
In Table 1a, 1b and 1c we present the values of effective scintillometer height associated with each method, the corresponding time average value of sensible heat flux as well as
Keywords: Aerodynamic gradient method; Eddy covariance; Continuous ammonia denuders; Bi-directional fluxes; Passive flux samplers.. ∗
Comparison of stomatal NH3 compensation points determined on the basis of apoplastic NH4 + and H + concentrations (horizontal bars) and measured atmospheric NH3 concentrations ( d )
Micrometeorological measurements above the canopy indicated that gaseous Cl compounds were emitted for most of the time, and this was supported by the source/sink distributions