I. Introduction
This section sets the stage for the research by outlining the context of tofu preservation in Indonesia, highlighting the prevalent and dangerous use of formalin as a preservative. The researchers establish the problem of short shelf life and the associated health risks, thus justifying the need for a safer alternative. This section introduces the research objectives which are to evaluate the efficacy of sodium benzoate, potassium sorbate, and acetic acid as tofu preservatives and to determine the optimal combination for extending shelf life while maintaining consumer acceptability. The introduction effectively frames the study within a larger context of food safety and public health, making it relevant for educating students on the importance of safe food preservation practices and the application of scientific methods to address real-world challenges. This aligns with learning outcomes related to problem identification, hypothesis formulation and the significance of research in solving practical problems.
1.1 Background
The background details the challenges associated with preserving tofu, a highly perishable food. It explains the widespread, illegal use of formalin, its health risks, and the urgent need for a safe alternative. This section emphasizes the practical context of the research, demonstrating the direct relevance of the research to solving a significant problem in food production and distribution. Pedagogically, it helps students understand the societal impact of scientific research, particularly in fields like food science and technology where public health is paramount. This directly relates to learning outcomes concerning problem-solving within the context of real-world applications of scientific knowledge.
1.2 Research Objectives
Clearly stated research objectives are presented. The primary aim is to evaluate the effectiveness of specific preservatives (acetic acid, sodium benzoate, and potassium sorbate) in prolonging tofu's shelf life. The secondary objective is to identify the optimal combination of these preservatives while ensuring consumer acceptance. The clarity and precision of these objectives are crucial for establishing a strong research foundation. From an educational perspective, this subsection highlights the importance of well-defined research questions and the necessity of formulating clear and measurable objectives for research projects. This is relevant to learning outcomes concerning research design, methodology, and the process of conducting scientific inquiry.
1.3 Research Benefits
The researchers articulate the potential benefits of their study. The findings are expected to provide a safe and legal alternative to formalin for tofu preservation, benefiting both producers and consumers. This section highlights the practical implications of the research and its contribution to solving a real-world problem in the Indonesian food industry. From a pedagogical standpoint, this subsection underlines the practical applications and societal impact of scientific research. Students learn the importance of considering the relevance and potential benefits of their research, directly linking to learning outcomes regarding critical thinking, impact assessment, and the responsible conduct of research.
II. Literature Review
This section provides a comprehensive review of the relevant scientific literature on tofu, the chosen preservatives (sodium benzoate, potassium sorbate, and acetic acid), and their antimicrobial properties. It includes details about the chemical properties of the preservatives, their mechanisms of action against microorganisms, and their permitted levels of use in food. The literature review effectively establishes the theoretical framework and background knowledge upon which the research is based, thus demonstrating the academic rigor of the study. Pedagogically, this section underscores the importance of conducting thorough literature reviews in scientific research. It showcases how researchers synthesize existing knowledge to inform their research questions and methodologies. This is closely aligned with learning outcomes concerning literature review techniques, critical evaluation of scientific literature, and the integration of existing knowledge into research projects.
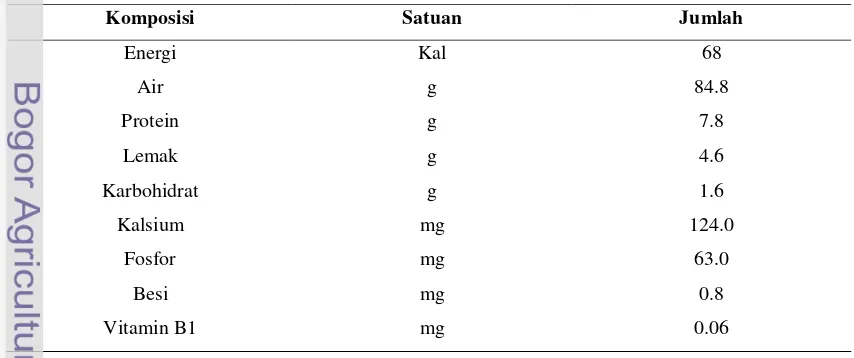
2.1 Tofu
This subsection provides a detailed description of tofu, its production process, nutritional composition, and its susceptibility to microbial spoilage. It covers the chemical composition of tofu and its implications for preservation. This establishes a foundational understanding of the subject matter and the challenges involved in preserving this specific food product. From an educational standpoint, students gain knowledge of food processing techniques, food chemistry, and the importance of understanding food properties when designing preservation strategies. This is closely aligned with learning outcomes related to food science, technology and understanding of food preservation challenges.
2.2 Sodium Benzoate
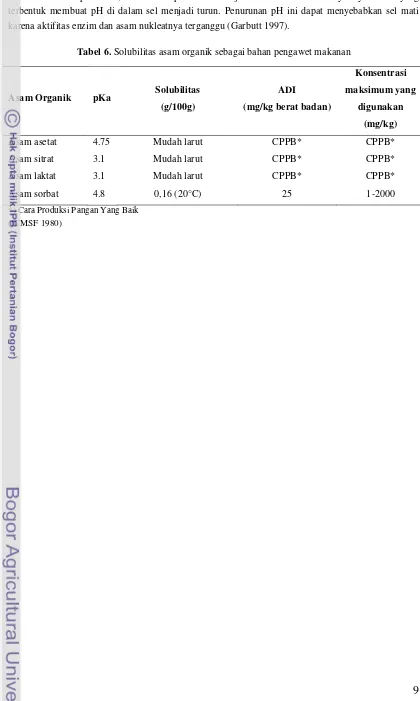
The properties and antimicrobial mechanism of sodium benzoate are discussed. Information about its effectiveness, pH dependence, and permissible daily intake (ADI) is provided. This subsection provides specific knowledge about one of the chosen preservatives, its chemical properties, and its effectiveness against microorganisms. Students learn about the specific mechanisms of action of food preservatives and their role in controlling microbial growth in food systems. This contributes to learning outcomes on food preservation techniques and understanding of food chemistry.
2.3 Potassium Sorbate
Similar to the previous subsection, this section focuses on potassium sorbate, detailing its characteristics, antimicrobial activity, pH dependence, and ADI. This parallels the sodium benzoate discussion, providing a comparative analysis of two common food preservatives. Students gain a comparative understanding of different food preservatives, expanding their knowledge of various preservation strategies and their effectiveness against different types of microorganisms. This directly links to learning outcomes related to food preservation techniques and their effectiveness.
2.4 Acetic Acid
This subsection explains the antimicrobial properties of acetic acid, its mechanism of action, and its safety profile. The information on its pH-dependent activity and its potential as a food preservative is emphasized. This final preservative is discussed in detail, expanding the range of preservation methods discussed. Students can develop a holistic understanding of several methods of food preservation and the scientific reasoning behind using specific preservatives for different foods. This supports learning outcomes related to the selection of appropriate preservation strategies based on scientific principles and product-specific needs.
III. Materials and Methods
This section describes the materials and procedures used in the research. It details the preparation of the tofu samples, the different preservative treatments, the analytical methods used (Total Plate Count, texture analysis, color measurement, pH measurement, and organoleptic testing), and the statistical analysis performed. This section is vital for demonstrating the scientific rigor and reproducibility of the research. From a pedagogical perspective, this section is crucial for teaching students about research methodology, experimental design, data collection techniques, and data analysis. This directly supports learning outcomes regarding the development and implementation of experimental designs, data collection, analysis and interpretation, and reporting of scientific findings.
3.1 Materials and Equipment
A detailed list of the materials (e.g., tofu, preservatives, agar plates, etc.) and equipment (e.g., texture analyzer, chromameter, pH meter, etc.) used in the experiments is provided. This ensures transparency and enables readers to understand the resources and tools used in the study. Pedagogically, this section helps students learn about the types of materials and equipment used in food science research and how to select appropriate tools for specific experiments. This relates to learning outcomes on experimental techniques and the selection of appropriate equipment.
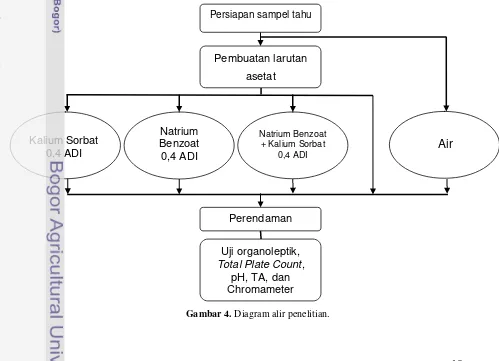
3.2 Research Methods
This subsection outlines the experimental design, detailing the different treatments applied to the tofu samples and the rationale behind those treatments. The description of the two-stage research process (sample preparation and shelf life analysis) is included. The methodology is clearly explained to enhance understanding and replicability of the study. Pedagogically, this section teaches students about the process of designing scientific experiments and about the selection of appropriate methods to test hypotheses and answer research questions. It highlights the importance of designing rigorous and well-controlled experiments. This directly relates to learning outcomes on experimental design, hypothesis testing, and research methodology.
3.3 Analytical Methods
This section details the specific analytical methods employed for each parameter. It includes descriptions of the Total Plate Count method, texture analysis, color measurement, pH measurement, and organoleptic testing, along with the statistical analysis (ANOVA and Duncan's multiple range test). This detailed explanation enhances understanding and reproducibility. From a pedagogical point of view, this subsection is valuable for teaching students about different analytical techniques used in food science and the statistical tools used to analyze data. Students learn how to select appropriate analytical methods for their research and how to interpret the statistical results. This strengthens learning outcomes concerning data analysis, statistical interpretation, and reporting of scientific findings.
IV. Results and Discussion
This section presents the findings of the research, including the results of the Total Plate Count, texture analysis, color measurement, pH measurement, and organoleptic tests. It interprets the data and discusses the implications of the results in relation to the research objectives. The discussion section critically evaluates the findings in relation to the existing literature and explains any discrepancies or unexpected results. It places the findings within the broader context of food preservation research. This section is crucial for demonstrating the researchers' ability to analyze data, interpret results, and draw meaningful conclusions. From a pedagogical perspective, this is an excellent opportunity for students to learn about data interpretation, critical thinking, and the process of drawing evidence-based conclusions. It emphasizes the importance of discussing the limitations of the study and suggesting directions for future research. This directly connects to learning outcomes on data interpretation, critical analysis, and conclusion drawing.
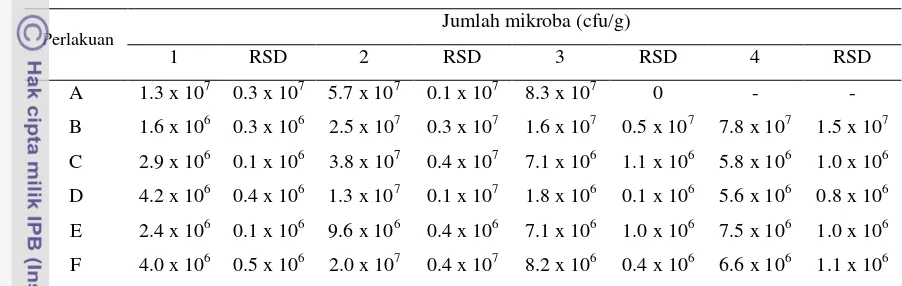
4.1 Total Plate Count
The results of the Total Plate Count (TPC) analysis are presented and discussed, focusing on the effectiveness of the different preservative treatments in reducing microbial growth. The impact of different combinations of preservatives on microbial load is analyzed and interpreted. Students can learn to interpret microbial data, understand the significance of microbial counts in food quality, and the link between preservative use and microbial control. This relates to learning outcomes in microbiology and food safety.
4.2 Texture Analysis
The results of the texture analysis are presented, showing the effects of the preservatives on the texture of tofu. The changes in texture over time and in relation to the different treatments are discussed. Students learn about the methods used to assess food texture, its influence on consumer acceptance, and the importance of considering sensory attributes in food preservation. This enhances learning outcomes in sensory science and food quality.
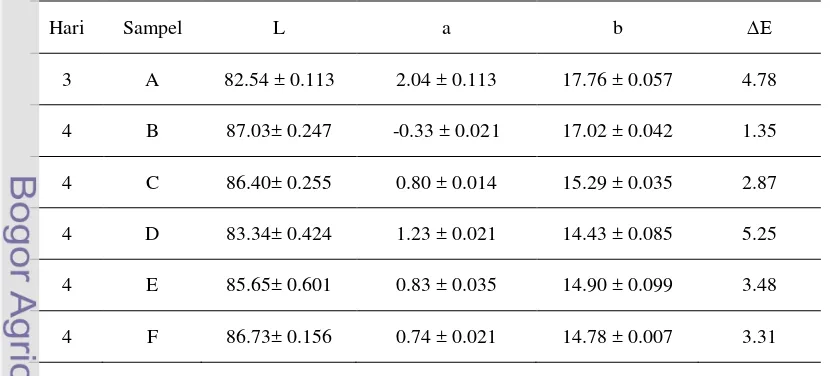
4.3 Color Measurement
The color changes in the tofu samples over time and under different preservative treatments are reported and interpreted. The findings are linked to consumer acceptability. This section highlights the importance of considering visual aspects of food quality. Students learn how to quantify color changes, the importance of visual appeal in food, and the impact of preservation methods on sensory attributes. This contributes to learning outcomes in sensory science and food quality.
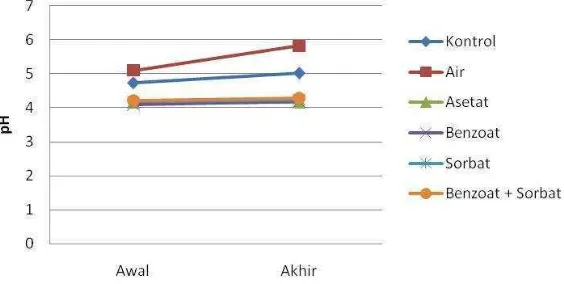
4.4 pH Measurement
The pH changes in the tofu samples are presented and discussed, linking these changes to the effectiveness of the preservative treatments and their influence on microbial growth. The relationship between pH and microbial growth is explained. Students can understand the link between pH, microbial growth, and the effectiveness of preservatives, a crucial concept in food preservation. This directly addresses learning outcomes in food microbiology and preservation.
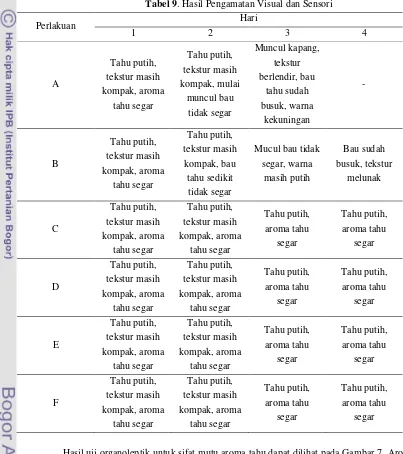
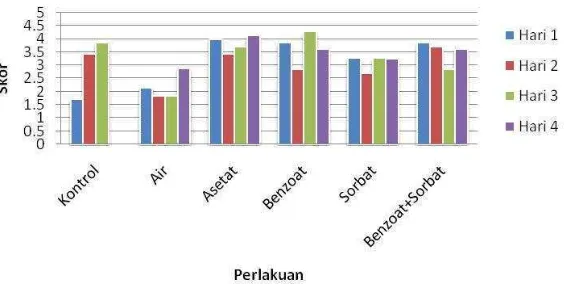
4.5 Organoleptic Test
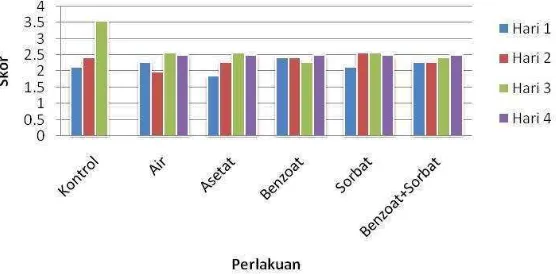
The results of the organoleptic tests (sensory evaluation) are presented and discussed, focusing on the consumer acceptability of the tofu samples under different treatments. The findings are related to texture, color, and aroma. Students learn about sensory evaluation methodologies, the importance of consumer preferences in food acceptance, and the combined effect of preservation methods on multiple sensory attributes. This strengthens learning outcomes in sensory science, food quality, and consumer behavior.
V. Conclusion and Recommendations
This section summarizes the key findings of the research and draws conclusions based on the results. The researchers state whether their objectives were met and discuss the implications of their findings for the Indonesian tofu industry. Recommendations for future research and practical applications of the findings are given. This section ties together the various parts of the research and provides a concise summary of the study's contributions. From a pedagogical perspective, this section is vital for teaching students how to synthesize information, draw conclusions, and make recommendations for future work. It highlights the importance of clear and concise communication of scientific findings. This strengthens learning outcomes related to scientific communication, conclusion writing, and recommendations for future research.
5.1 Conclusion
A concise summary of the main findings is presented, stating whether the research objectives were met and highlighting the most significant results. The key conclusions drawn from the data are clearly stated. Students learn to summarize their research findings in a clear and concise manner, highlighting the most important conclusions. This supports learning outcomes related to scientific communication and report writing.
5.2 Recommendations
Based on the research findings, practical recommendations for the Indonesian tofu industry are provided, suggesting ways to improve tofu preservation practices and reduce the use of harmful preservatives. Directions for future research are also suggested. Students learn the importance of providing practical recommendations based on research findings and suggesting areas for future research, thus enhancing their ability to contribute to knowledge development. This aligns with learning outcomes concerning scientific communication and research advancement.