Candida albicans
Potensi Antimikroba Daun Bunga Pukul Empat (Mirabilis jalapa L.) Terhadap
Staphlococcus aureus, Escherichia coli dan Candida albicans
Mira Andam Dewi, Wiwiek Indrayani, Ennie Riben Sihite Faculty of Pharmacy, Universitas Jenderal Achmad Yani, Cimahi
Faculty of Pharmacy, Universitas Padjajaran, Jatinangor e-mail: [email protected]
ABSTRAK
Bunga pukul empat (Mirabilis jalapa Linn.) merupakan salah satu tanaman yang secara empiris digunakan seba-gai obat tradisional untuk pengobatan bisul, debit, luka, eksim, dan gatal-gatal. Tujuan dari penelitian ini adalah untuk menentukan aktivitas antimikroba ekstrak air, ekstrak etanol, fraksi n-heksana, fraksi etil asetat dan fraksi air daun bunga pukul empat terhadap Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli dan Candida albicans. Ekstraksi daun dilakukan dengan maserasi dan dekok. Ekstrak etanol tebal diikuti oleh ekstraksi cair-cair menggunakan pelarut n-heksana dan etil asetat. Tes aktivitas mikrobia dilakukan dengan menggunakan metode difusi perforasi. Hasil penelitian menunjukkan bahwa ekstrak air memiliki potensi antimikroba lebih besar dari ekstrak etanol dan fraksi lainnya dalam menghambat Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli dan Candida albicans dengan konsentrasi Mini-mum Inhibitory (MIC) untuk setiap mikroba 5% b/ v, 40% b / v dan 60% b/ v dengan diameter zona bening yang 15,70 mm, 14,53 mm, dan 14.10 mm. Tetrasiklin, amoksisilin, nistatin yang digunakan sebagai pembanding meng-hambat mikroba dengan konsentrasi yang lebih kecil dari ekstrak dan fraksi daun. Flavonoid, polifenol, saponin, tanin, kuinon, monoterpenoid-seskuiterpenoid dan steroid senyawa yang memiliki aktivitas sebagai antimikroba.
Kata kunci: bunga pukul empat (Mirabilis jalapa Linn.), aktivitas antimikrobia, konsentrasi daya hambat minimum
ABSTRACT
Four o’clock flower (Mirabilis jalapa Linn.) is one of the plants that are empirically used as a traditional medicine for the treatment of ulcers embankment, discharge, sores, eczema, and itching. The aim of the research was to determine the antimicrobial activity of water extract, ethanol extract, n-hexane fraction, ethyl acetate fraction
and water fraction of leaves of Four o’clock flower against Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli and Candida albicans. The extraction of leaves was done by maceration and decoction. Ethanol extract thick followed by liq-uid-liquid extraction using the solvent n-hexane and ethyl acetate. Microbial activity assays performed by using
diffusion perforation method. The results showed that the water extract has a potential antimicrobial greater
than the ethanol extract and other fractions in inhibiting Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli and Candida albicans with Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) for each microbial 5%w/v, 40%w/v and 60%w/v with a
diameter of clear zone are 15.70 mm, 14.53 mm, and 14.10 mm. Tetracycline, amoxicillin, nystatin were used as
comparison inhibit microbes with smaller concentrations of extracts and fractions of leaves. Flavonoids, polyphe-nols, saponins, tannins, quinones, monoterpenoid-seskuiterpenoid and steroids compounds that have activity as an antimicrobial.
Keywords : four o’clock flower leaf (Mirabilis jalapa Linn.), antimicrobial activity, Minimum Inhibitory
the Sumedang, West Java. Staphylococcus
au-reus B.90, B.86 bacterium Escherichia coli and the yeast Candida albicans R.66 of the Depart -ment of Chemical Engineering FTI - ITB Labo-ratory of Microbiology and Bioprocess Tech-nology.
Method
Preparation of extract
Dried leaves of M. jalapa was extracted by two methods i.e. maceration for 24 hours using 96% ethanol and boiling water extract (decoction). Each extract was evaporated in a rotary evaporator (vacuum rotary evapora -tor) to obtain concentrated extracts, and then evaporated on a water bath until it forms a thick extract and weighed.
The condensed ethanol extracts was separately and dissolved in methanol: water
(2:8) and after it was put in a separating funnel with the addition of n-hexane (1:1), shake gen -tly until well blended, then allowed until just split into 2 fractions comprising fraction of n-hexane and water fractions. N-n-hexane fraction was separated the water fraction was
extract-ed further using ethyl acetate (1:1). Each frac -tion was evaporated on a water bath, until the viscous fractions were obtained.
Preparation of suspensions of bacteria
Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli on Nutrient Agar media were incubated at
35-37 °C for 18-24 hours. The medium used for
the rejuvenation of the yeast Candida albicans
is the Sabouraud Dextrose Agar incubated at 25-30 °C for 72 hours. The cultures were then suspended with 3-4 mL of 0.95% NaCl, and put
into tube. The calculation of the concentration of bacteria performed using ultraviolet
spec-trophotometer, in order to obtain 25% trans
-mittance at a wavelength of 580 nm.
Antimicrobial Test
A total of approximately 1.0 mL micro -bial test put in sterile petri dish, then added
15 mL of agar medium and sterilized. Each cup had 6 holes prepared by using a perforator to be filled with 6 different concentrations of test
solutions.
INTRODUCTION
The development of antimicrobial drugs is one of the most important advances
in medicine, as an effective treatment against
serious infections. It has improved the qual-ity of life and enable progress in many areas of medicine as well as in the pharmaceutical industry. Indonesia is a country rich in tropical plants that are widely used as raw material for the drug, which is used for the maintenance of health, prevention or treatment of a
dis-ease. This is one of the efforts to improve the health of the community with a more afford -able cost, because of the nature of materials can be easily obtained in the neighborhood. In addition, traditional medicines derived from plants proved relatively safe as long as how to use it correctly with the proper dose and with appropriate indications as well. Natural
medi-cine also causeless side effects compared to
chemical drugs. The human body is relatively easier to accept drugs from natural materials compared with chemical drugs. One of the me-dicinal plants used in traditional medicine is
four o’clock flower (Mirabilis jalapa L.). Fire-works at four believed to cure several diseases
including inflammation of the tonsils (tonsilli
-tis), inflammation of the prostate gland, acute
arthritis, urinary tract infections, vaginal
dis-charge (leucorrhea), erosion of the cervix, dia -betes mellitus, worming, itching, acne medica-tion, and eczema or scabs. The leaves of four
o’clock flowers can be used as embankment boil (maturatif), vaginal discharge, sores, ec -zema, diuretics, itching and diabetes mellitus. This plant has not been widely studied, where-as the usability and usefulness are important. Antimicrobial activity of leaf as antimicrobi-als were tested against Gram-positive bacteria
Staphylacocus aureus, Gram-negative bacteria
Escherichia coli and the yeast Candida albi-cans.
MATERIALS AND METHOD Materials
Four o’clock flower leaves (Mirabilis
Each hole was filled as much as 50.0 mL test solution. All the filled cup test was incubated for 24 hours at a temperature of 35-37°C for
Staphylococcus aureus
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Determination of plant
Leaves flowers at four o’clock was de -termined Bandungense Herbarium, School of Biological Sciences and Technology, Institute of
Technology Bandung (ITB). The results of de -termination showed that plants studied were
Mirabilis jalapa L., family Nyctaginaceae.
The antibacterial activity
The results of microbiological testing showed Minimum Inhibitory Concentration
value (MIC)
Material test Microbial
Staphlococcus aureus Escherichia coli Candida albicans
Water Extract
Ethanol Extract
Fraction of water
Fraction of Etil Asetat
Fraction Of n-heksan
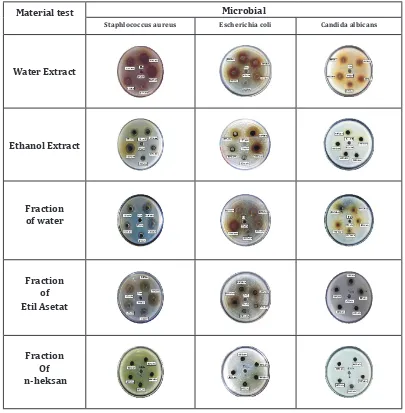
Figure 1. Antimicrobial activity of M. jalapa extract and fraction
Weak inhibition against Candida albicans were-compared to Staphylococcus aureus and Escheri-chia coli. Candida albicans cells were generally larger than bacterial cells, the hyphae and the abil-ity to grow very fast compared to microbes.
In phytochemical screening, water extracts as the most effective extract in inhibiting the growth of Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli and
Can-dida albicans, showed that it contained flavonoids,
polyphenols, saponins, tannins, quinones and ste-roids. Then followed the fraction of ethyl acetate and water fractions that provided good resistance showed that it contained flavonoids, polyphenols, saponins, tannins, quinones and steroids. Ethanol extract provided barriers against Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli, but the concentration Minimum Inhibitory (MIC) was smaller than the water extract,
water fraction and ethyl acetate fraction,
be-cause the only ethanol extract contains fla -vonoids, polyphenols, quinones and monot-erpenoid-seskuiterpenoid. n-Hexane fraction did not provide barriers against microbial test. This can be due to the content of the
compounds in the n-hexane fraction only fla -vonoids. It showed that the antimicrobial
ac-tivity is affected by the metabolites contained
in extracts and fractions, so the Minimum
In-hibitory Concentration different extracts and
fractions against certain microbes. Polyphe-nolic compounds, saponins, tannins, quinones and steroids. Ethanol extract provided barriers against Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli, but the concentration Minimum Inhibitory
(MIC) was smaller than the water extract, wa -ter fraction and ethyl acetate fraction, because
the only ethanol extract contains flavonoids,
polyphenols, quinones and monoterpenoid-seskuiterpenoid. n-Hexane fraction did not provide barriers against microbial test. This can be due to the content of the compounds
in the n-hexane fraction only flavonoids. It showed that the antimicrobial activity is affect -ed by the metabolites contain-ed in extracts and fractions, so the Minimum Inhibitory
Concen-tration different extracts and fractions against
certain microbes. Polyphenolic compounds, saponins, tannins, quinones, monoterpenoid-seskuiterpenoid and substances believed to be steroids that have antimicrobial activity in test substance.
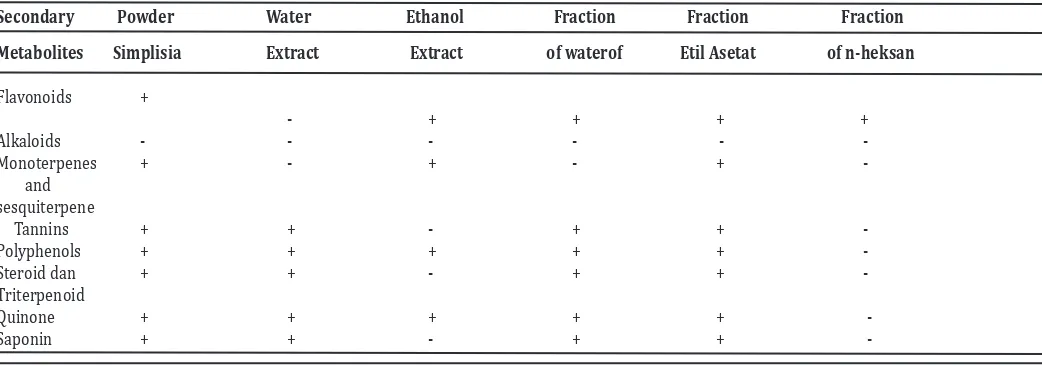
Table 1. Screening phytochemicals of simplisia, extracts and fractions of M. jalapa leaves
Secondary Powder Water Ethanol Fraction Fraction Fraction
The test results of antibacterial activity of water extract, ethanol extract and fractions of
Mirabilis jalapa L. showed that water extract was
the most potent one in inhibiting the growth of
Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli and
Candi-da albicans compared with ethanol extract, water
fraction, ethyl acetate fraction and n-hexane frac-tion with Minimum inhibitory Concentrafrac-tion (MIC) for each microbial 5% w/v, 40% w/v and 60% w/v with consecutive inhibition diameter 15.70 ± 0.62 mm; 14.53 ± 0.10mm, and 14.10 ± 0.51 mm. Sec -ondary metabolites were thought to have antimi-crobial activity against microbes were flavonoids, polyphenols, saponins, tannins, quinones, monot-erpenoid - seskuitmonot-erpenoid and steroids.
REFERENCES
Wijayakusuma,H, Hidup Sehat Cara Hembing, Penerbit Elex Media . Komputindo,Jakarta. 1995. Hal 1-2
Moch. Rachdie Pratama, Pengaruh Ekstrak Ser buk Kayu Siwak (Salvadora persica) Ter hadap Pertumbuhan Bakteri Streptococ
cus mutans dan Staphylococcus aureus
dengan Metode Difusi Agar, Institut Teknologi Sepuluh Nopember, 2005. Dalimartha, Setiawan. Atlas Tumbuhan Obat
Indonesia, Jilid IV, Puspa Swara, Jakarta. 2006. Hal 46-48
Jawetz, Melnick & Adelberg., Mikrobiologi
Kedokteran, Edisi 23, Alih bahasa Edi Nu -groho & R.F. Maulany.EGC. Jakarta. 2007. 180, 208, 214-215, 279, 291, 658-660 Pelczar, M.J. and E.C.S. Chan, Dasar-dasar
Mik-robiologi, Jilid II, terjemahan Ratna S Hadioetomo, T. Imas, S. Sutarmi Tjitroso-mo, Sri Lestari, Penerbit UI Press, Jakar-ta. 1988, 487-490, 548-549, 952-957. Staf Pengajar Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas
Indonesia, Mikrobiologi Kedokteran, Edisi Revisi, Binarupa Aksara, Jakarta, 1993. 30, 103-111.