ABSTRACT
Puspitasari, Dian. (2016). A Study on Code Switching Used by an English Teacher in Teaching English to the Eighth Grade Students of SMP N 2 Mlati. Yogyakarta: English Language Education Study Program, Sanata Dharma University.
Indonesia is one of the multilingual countries in the world. In Indonesia, English is not the first language because Indonesian has various languages, such as Indonesian language and many regional languages. English is considered as international language which is important to be mastered in this globalization era. In Indonesian multilingual society, code switching is a common phenomenon which mostly occurred. In accordance with the English learning, code switching could be beneficial to both the students and the teacher. It helps the students to understand the teacher’s explanation and helps the teacher to transfer the material to the students. Seeing that English is not students’ first language, the use of code switching by the English teacher in SMP N 2 Mlati is needed to help the students in the English teaching and learning process.
This research addressed two research questions. First, what are the types of code switching used by an English teacher in teaching English to the eighth grade students of SMP N 2 Mlati? Second, what are the functions of code switching used by an English teacher in teaching English to the eighth grade students of SMP N 2 Mlati?
The approach of this research was qualitative since it sought to understand and interpret human or social behavior. The data were gathered from direct and indirect observation of the English teaching and learning process in the classrooms. The researcher conducted the observation in one meeting for each class. The data gathered were analyzed by using some theories. The types of code switching were based on Poplack’s theory, while the functions of code switching were based on Jingxia’s theory.
The findings of this research showed that there were 84 cases of code switching used by an English teacher in teaching English to the eighth grade students of SMP N 2 Mlati. The researcher found three types of code switching used by the English teacher. In addition, the researcher also found five functions of teacher’s code switching in English teaching and learning process. The findings showed that the type of code switching which mostly was used by the English teacher during the English teaching and learning process was inter-sentential code switching. Meanwhile, the result showed that the English teacher mostly did code switching for managing the class, such as admonished the students, asked the students to do an exercise, or asked a student to read and answer a question. Moreover, the English teacher also often did code switching to translate unknown vocabulary items.
ABSTRAK
Puspitasari, Dian. (2016). A Study on Code Switching Used by an English Teacher in Teaching English to the Eighth Grade Students of SMP N 2 Mlati. Yogyakarta: English Language Education Study Program, Sanata Dharma University.
Indonesia adalah salah satu negara multilingual di dunia. Di Indonesia, Bahasa Inggris bukan merupakan bahasa utama karena Indonesia memiliki banyak bahasa, seperti Bahasa Indonesia dan beragam bahasa daerah. Bahasa Inggris dianggap sebagai bahasa internasional yang penting untuk dikuasai dalam era globalisasi. Dalam masyarakat multilingual di Indonesia, alih kode merupakan suatu fenomena yang biasa terjadi. Sehubungan dengan pembelajaran Bahasa Inggris, alih kode dapat bermanfaat bagi siswa dan guru. Alih kode membantu siswa memahami penjelasan guru dan membantu guru dalam menyampaikan materi kepada siswa. Melihat bahwa Bahasa Inggris bukan bahasa ibu siswa, penggunaan alih kode oleh guru Bahasa Inggris di SMP N 2 Mlati diperlukan untuk membantu siswa dalam proses belajar mengajar Bahasa Inggris.
Penelitian ini dilaksanakan untuk membahas dua rumusan masalah. Yang pertama, tipe alih kode apa saja yang digunakan oleh guru Bahasa Inggris dalam mengajar Bahasa Inggris kepada siswa kelas delapan di SMP N 2 Mlati? Yang kedua, apa fungsi penggunaan alih kode yang dilakukan oleh guru Bahasa Inggris dalam mengajar Bahasa Inggris kepada siswa kelas delapan di SMP N 2 Mlati?
Penelitian ini menggunakan pendekatan kualitatif karena penelitian ini berusaha untuk memahami dan menafsirkan tingkah laku manusia atau sosial. Data diperoleh dari hasil observasi langsung dan tidak langsung pada saat proses belajar mengajar Bahasa Inggris. Peneliti melakukan observasi pada satu pertemuan untuk setiap kelas. Data yang diperoleh kemudian dianalisis dengan menggunakan beberapa teori. Tipe alih kode dianalisis menggunakan teori Poplack. Fungsi alih kode dianalisis menggunakan teori Jingxia.
Hasil penelitian menunjukkan bahwa terdapat 84 kasus alih kode yang dilakukan oleh guru Bahasa Inggris dalam mengajar Bahasa Inggris kepada siswa kelas delapan di SMP N 2 Mlati. Peneliti menemukan tiga tipe alih kode dan lima fungsi alih kode yang digunakan oleh guru bahasa Inggris. Hasil penelitian menunjukkan bahwa tipe alih kode yang paling sering digunakan oleh guru Bahasa Inggris selama proses belajar mengajar adalah inter-sentential code switching. Sedangkan hasil penelitian menunjukkan bahwa guru Bahasa Inggris paling sering menggunakan alih kode untuk mengatur kelas, seperti menegur siswa, memerintah siswa untuk mengerjakan latihan, atau meminta siswa membaca dan menjawab pertanyaan. Selain itu, guru Bahasa Inggris juga sering menggunakan alih kode untuk mengartikan kosakata yang tidak dikenal.
CODE SWITCHING USED
BY AN ENGLISH TEACHER IN TEACHING ENGLISH
TO THE EIGHTH GRADE STUDENTS OF SMP N 2 MLATI
A SARJANA PENDIDIKAN THESIS Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements
to Obtain the Sarjana Pendidikan Degree in English Language Education
By Dian Puspitasari Student Number: 111214131
ENGLISH LANGUAGE EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAM DEPARTMENT OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDUCATION FACULTY OF TEACHERS TRAINING AND EDUCATION
SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY YOGYAKARTA
i
CODE SWITCHING USED
BY AN ENGLISH TEACHER IN TEACHING ENGLISH
TO THE EIGHTH GRADE STUDENTS OF SMP N 2 MLATI
A SARJANA PENDIDIKAN THESIS Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements
to Obtain the Sarjana Pendidikan Degree in English Language Education
By Dian Puspitasari Student Number: 111214131
ENGLISH LANGUAGE EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAM DEPARTMENT OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDUCATION FACULTY OF TEACHERS TRAINING AND EDUCATION
SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY YOGYAKARTA
ii
A Sarjana Pendidikan Thesis on
CODE SWITCHING USED
BY AN ENGLISH TEACHER IN TEACHING ENGLISH
TO THE EIGHTH GRADE STUDENTS OF SMP N 2 MLATI
By Dian Puspitasari Student Number: 111214131
Approved by
Advisor
iii
A Sarjana Pendidikan Thesis on
CODE SWITCHING USED
BY AN ENGLISH TEACHER IN TEACHING ENGLISH
TO THE EIGHTH GRADE STUDENTS OF SMP N 2 MLATI
By Dian Puspitasari Student Number: 111214131
Defended before the Board of Examiners on April 11, 2016
and Declared Acceptable
Board of Examiners
Chairperson : P. Kuswandono, Ph.D. Secretary : Ch. Lhaksmita Anandari, S.Pd., Ed.M.
Member : Agustinus Hardi Prasetyo, S.Pd., M.A. Member : Drs. Pius Nurwidasa Prihatin, M.Ed., Ed.D. Member : Yohana Veniranda, M.Hum., M.A., Ph.D.
Yogyakarta, April 11, 2016
Faculty of Teachers Training and Education Sanata Dharma University
Dean
iv
“For nothing is
impossible with God.”
(Luke 1: 37)
This thesis is dedicated to my beloved parents,
v
STATEMENT OF WORK’S ORIGINALITY
I honestly declare that this thesis, which I have written, does not contain the work
or parts of the work of other people, except those cited in the quotations and references, as a scientific paper should.
Yogyakarta, April 11, 2016 The Writer,
vi
LEMBAR PERNYATAAN PERSETUJUAN
PUBLIKASI KARYA ILMIAH UNTUK KEPENTINGAN AKADEMIS
Yang bertanda tangan di bawah ini, saya mahasiswi Universitas Sanata Dharma:
Nama : Dian Puspitasari
Nomor Mahasiswa : 111214131
Demi pengembangan ilmu pengetahuan, saya memberikan kepada Perpustakaan Universitas Sanata Dharma karya ilmiah saya yang berjudul:
CODE SWITCHING USED
BY AN ENGLISH TEACHER IN TEACHING ENGLISH
TO THE EIGHTH GRADE STUDENTS OF SMP N 2 MLATI
Beserta alat yang diperlukan (bila ada). Dengan demikian, saya memberikan kepada Perpustakaan Universitas Sanata Dharma hak untuk menyimpan, mengalihkan dalam bentuk lain, mengelolanya dalam bentuk pangkalan data, mendistribusikannya secara terbatas, dan mempublikasikannya di internet atau media lain untuk kepentingan akademis tanpa perlu meminta ijin maupun royalti kepada saya selama tetap mencantumkan nama saya sebagai penulis.
Demikian pernyataan ini saya buat dengan sebenarnya.
Dibuat di Yogyakarta Pada tanggal: 11 April 2016
Yang menyatakan,
vii ABSTRACT
Puspitasari, Dian. (2016). A Study on Code Switching Used by an English Teacher in Teaching English to the Eighth Grade Students of SMP N 2 Mlati. Yogyakarta: English Language Education Study Program, Sanata Dharma University.
Indonesia is one of the multilingual countries in the world. In Indonesia, English is not the first language because Indonesian has various languages, such as Indonesian language and many regional languages. English is considered as international language which is important to be mastered in this globalization era. In Indonesian multilingual society, code switching is a common phenomenon which mostly occurred. In accordance with the English learning, code switching could be beneficial to both the students and the teacher. It helps the students to
understand the teacher’s explanation and helps the teacher to transfer the material
to the students. Seeing that English is not students’ first language, the use of code
switching by the English teacher in SMP N 2 Mlati is needed to help the students in the English teaching and learning process.
This research addressed two research questions. First, what are the types of code switching used by an English teacher in teaching English to the eighth grade students of SMP N 2 Mlati? Second, what are the functions of code switching used by an English teacher in teaching English to the eighth grade students of SMP N 2 Mlati?
The approach of this research was qualitative since it sought to understand and interpret human or social behavior. The data were gathered from direct and indirect observation of the English teaching and learning process in the classrooms. The researcher conducted the observation in one meeting for each class. The data gathered were analyzed by using some theories. The types of code
switching were based on Poplack’s theory, while the functions of code switching were based on Jingxia’s theory.
The findings of this research showed that there were 84 cases of code switching used by an English teacher in teaching English to the eighth grade students of SMP N 2 Mlati. The researcher found three types of code switching used by the English teacher. In addition, the researcher also found five functions
of teacher’s code switching in English teaching and learning process. The findings showed that the type of code switching which mostly was used by the English teacher during the English teaching and learning process was inter-sentential code switching. Meanwhile, the result showed that the English teacher mostly did code switching for managing the class, such as admonished the students, asked the students to do an exercise, or asked a student to read and answer a question. Moreover, the English teacher also often did code switching to translate unknown vocabulary items.
viii ABSTRAK
Puspitasari, Dian. (2016). A Study on Code Switching Used by an English Teacher in Teaching English to the Eighth Grade Students of SMP N 2 Mlati. Yogyakarta: English Language Education Study Program, Sanata Dharma University.
Indonesia adalah salah satu negara multilingual di dunia. Di Indonesia, Bahasa Inggris bukan merupakan bahasa utama karena Indonesia memiliki banyak bahasa, seperti Bahasa Indonesia dan beragam bahasa daerah. Bahasa Inggris dianggap sebagai bahasa internasional yang penting untuk dikuasai dalam era globalisasi. Dalam masyarakat multilingual di Indonesia, alih kode merupakan suatu fenomena yang biasa terjadi. Sehubungan dengan pembelajaran Bahasa Inggris, alih kode dapat bermanfaat bagi siswa dan guru. Alih kode membantu siswa memahami penjelasan guru dan membantu guru dalam menyampaikan materi kepada siswa. Melihat bahwa Bahasa Inggris bukan bahasa ibu siswa, penggunaan alih kode oleh guru Bahasa Inggris di SMP N 2 Mlati diperlukan untuk membantu siswa dalam proses belajar mengajar Bahasa Inggris.
Penelitian ini dilaksanakan untuk membahas dua rumusan masalah. Yang pertama, tipe alih kode apa saja yang digunakan oleh guru Bahasa Inggris dalam mengajar Bahasa Inggris kepada siswa kelas delapan di SMP N 2 Mlati? Yang kedua, apa fungsi penggunaan alih kode yang dilakukan oleh guru Bahasa Inggris dalam mengajar Bahasa Inggris kepada siswa kelas delapan di SMP N 2 Mlati?
Penelitian ini menggunakan pendekatan kualitatif karena penelitian ini berusaha untuk memahami dan menafsirkan tingkah laku manusia atau sosial. Data diperoleh dari hasil observasi langsung dan tidak langsung pada saat proses belajar mengajar Bahasa Inggris. Peneliti melakukan observasi pada satu pertemuan untuk setiap kelas. Data yang diperoleh kemudian dianalisis dengan menggunakan beberapa teori. Tipe alih kode dianalisis menggunakan teori Poplack. Fungsi alih kode dianalisis menggunakan teori Jingxia.
Hasil penelitian menunjukkan bahwa terdapat 84 kasus alih kode yang dilakukan oleh guru Bahasa Inggris dalam mengajar Bahasa Inggris kepada siswa kelas delapan di SMP N 2 Mlati. Peneliti menemukan tiga tipe alih kode dan lima fungsi alih kode yang digunakan oleh guru bahasa Inggris. Hasil penelitian menunjukkan bahwa tipe alih kode yang paling sering digunakan oleh guru Bahasa Inggris selama proses belajar mengajar adalah inter-sentential code switching. Sedangkan hasil penelitian menunjukkan bahwa guru Bahasa Inggris paling sering menggunakan alih kode untuk mengatur kelas, seperti menegur siswa, memerintah siswa untuk mengerjakan latihan, atau meminta siswa membaca dan menjawab pertanyaan. Selain itu, guru Bahasa Inggris juga sering menggunakan alih kode untuk mengartikan kosakata yang tidak dikenal.
ix
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
First of all, I would like to express my gratitude to the Greatest Jesus Christ for His guidance and blessings, so that I can finish my thesis. I thank Him for all the ways and strengths that He gave to me during the ups and downs in the process in finishing my thesis.
My deepest gratitude goes to my advisor, Agustinus Hardi Prasetyo,
S.Pd., M.A., for his guidance, time, motivation, patience, and suggestion until the final writing of this thesis. I sincerely thank my academic advisor, Yuseva
Ariyani Iswandari, S.Pd., M.Ed., for her care and guidance started from the first time I entered this study program. I also thank all lecturers and the staff of the English Education Study Program for the knowledge they shared and guidance during my study in Sanata Dharma University. I would also thank Y. Mei Setyanta, S.Pd., M.Hum. for the opportunity given to me to conduct the research in his English classes.
I would like to express my deepest gratitude to my beloved parents Djoko
Septiabudi and (Almh) Sih Djuwarjanti, my sisters, Kristin Nugraheni and Ratna Setiawati, my brother, Sat Herry Sucahyo, and also my niece, Agastya Eirena Kusumawicitra. I thank them for all the love, prayer, guidance, advices, support, motivation, and reinforcement during my ups and downs. I truly thank my best friend in life, Anjar Bayu Saputra, for his love, support, and patience
x
I also take this opportunity to express my gratitude to my friends, especially Tamtam, Badra, Devita, Rosa, and Vika. I thank them for the all the
crazy times that we spent together. I also want to express my gratitude to all of my friends in PBI batch 2011, Tetangga Masa Gitu, and Patriot. Then, I would not
forget anyone who had supported me that I cannot mention. I send my thanks to them.
xi
TABLE OF CONTENTS
TITLE PAGE ... i
APPROVAL PAGES ... ii
DEDICATION PAGE ... iv
STATEMENT OF WORK’S ORIGINALITY ... v
LEMBAR PERNYATAAN PERSETUJUAN PUBLIKASI... vi
CHAPTER II. REVIEW ON RELATED LITERATURE A. Theoretical Description ... 7
1. Bilingualism and Multilingualism ... 7
2. Code Switching ... 10
a. The Types of Code-Switching ... 10
b. The Functions of Code-Switching ... 13
c. Code-Switching in Language Teaching ... 17
xii CHAPTER III. METHODOLOGY
A. Research Method ... 20
B. Research Setting ... 21
C. Research Participant ... 21
D. Research Instruments and Data Gathering Technique ... 21
1. Research Instruments ... 21
2. Data Gathering Technique ... 23
E. Data Analysis Techniques ... 25
F. Research Procedure ... 26
CHAPTER IV. RESEARCH FINDINGS AND DISCUSSION A. Research Findings ... 28
1. The Types of Code Switching ... 28
2. The Functions of Code Switching ... 30
B. Research Discussion ... 32
1. The Types of Code Switching Occurred in the Classrooms ... 32
a. Tag-Switching ... 32
b. Inter-sentential Code Switching ... 34
c. Intra-sentential Code Switching ... 39
2. The Functions of Code Switching Occurred in the Classrooms ... 42
a. Translating Unknown Vocabulary Items ... 42
b. Explaining Grammar ... 44
c. Managing Class ... 45
d. Emphasizing Some Points ... 47
e. Indexing a Stance of Empathy or Solidarity Toward Students ... 48
CHAPTER V. CONCLUSIONS AND RECOMMENDATIONS A. Conclusions ... 51
xiii
REFERENCES ... 54
xiv
LIST OF TABLES
Table 3.1. The Sample of the Checklist of Code Switching Cases ... 22 Table 4.1. The Data Findings of the Types of Code Switching in the Classrooms ... 29 Table 4.2. The Data Findings of the Functions of Code Switching in the
xv
LIST OF APPENDICES
1
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
This chapter is an introductory part. This chapter presents research background, research problems, problem limitation, research objectives, research
benefits, and definition of terms.
A. Research Background
Students acquire English from many resources. In schools, they mostly acquire English from their English teachers. It makes the English teacher plays a
vital role towards students’ understanding in English learning because English is
not students’ mother tongue. Sometimes, the students find difficulties in understanding some English words, phrases, and sentences because they are lack
of vocabularies. It becomes teacher’s responsibility to make students understand about the materials given. In the English teaching and learning process, teacher
should use clear language to deliver information and knowledge to the students and vice versa.
In order to make the students understand, the teacher sometimes needs to
shift from English as the second language to the students’ first language when
teaching the students. Lightbown (2001) states that the shift from one language to
The researcher has observed the case of code switching when the researcher did Internship Program (Program Pengalaman Lapangan) in SMP N 2
Mlati. The teachers there often use code switching to Indonesian or Indonesian when they explained the materials. The teachers also code switch when they gave
instructions, advices, or jokes to the students. The researcher experienced the phenomenon of code switching at the first time of teaching English in the eighth grade of SMP N 2 Mlati. The researcher used English language to teach the
students, but they often seemed confused and said “Bu ngomongnya jangan cepet-cepet, diulangin lagi Bu.” (“Do not speak too fast, Miss. Can you repeat your
sentences?”) or “Artinya apa Bu? Nggak dong.” (What does it mean, Miss? I do
not understand.”). Some students also lack English vocabularies. After that
moment, the researcher taught using two languages; English and Indonesian. The
researcher taught in English first, and then explained it again in Indonesian when the students seemed confused with the materials given by the researcher. By using
two languages in teaching English, the students understood what the researcher explained.
Based on the researcher’s experience during Internship Program, the researcher found that some students had less motivation in learning English. They did not understand what the teacher said and they were shy to ask more
explanation from the teacher. Sometimes, they did not pay attention to the
teacher’s explanation. It affected their score, they got unsatisfying scores. Since
teach them. It was possible for the teacher to do code switching because it was beneficial to both students and teacher.
By applying code switching in English learning, it helped the students to
understand the teacher’s explanation. Moreover, code switching also helped the
teacher to communicate with the students. When the students understand the material which the teacher delivered, they became motivated and active during the class activities. They were not afraid to ask and answer the questions. By seeing
the case that occured in SMP N 2 Mlati, the researcher felt that the implementation of code switching in English learning might be important and beneficial for the
students to understand the materials.
In this study, the researcher was interested to conduct a study on code switching done by an English teacher in teaching English. The researcher chose
this topic because of her personal experience when she did Internship Program.
She found the phenomena of code switching in teacher’s utterances. The English
teacher often did code switching to the students who were multilingual when he
taught English lesson. Moreover, the intensity of teacher’s code switching was
different according to the class and situation. It motivated the researcher to conduct a research about the implementation of code switching in education world, especially in SMP N 2 Mlati.
B. Research Problems
In this study, the researcher would like to address two questions related to
1. What are the types of code switching used by an English teacher in teaching English to the eighth grade students of SMP N 2 Mlati?
2. What are the functions of code switching used by an English teacher in teaching English to the eighth grade students of SMP N 2 Mlati?
C. Problem Limitation
This research is specified to the use of code switching in teaching English in the classroom. It involves not only code switching between English and
Indonesian, but also English and Indonesian. In this research, the researcher will focus on the types and the functions of code switching spoken by the English teacher when teaching English.
This research was conducted in SMP N 2 Mlati. It discussed code switching only in SMP N 2 Mlati, especially in English subject of the eighth grade
students. It was not discuss code switching in other subjects or other places.
D. Research Objectives
This study about code switching used by English teacher of SMP N 2 Mlati has some goals which have to be reached. The goals are presented below:
1. To identify the types of code switching used by an English teacher in teaching English to the eighth grade students of SMP N 2 Mlati.
2. To find out the functions of code switching used by an English teacher in
E. Research Benefits
The researcher expects that this study can give the benefits to the readers,
the English teachers, the students, the future English teachers, and also the next researchers.
1. The Readers
By reading this thesis, the researcher hopes that the readers understand the types and the functions of code switching. Moreover, the readers will have new
and wider knowledge about the advantages of the use Indonesian towards English language in English teaching and learning through code switching.
2. The English Teachers
The result of this study can be used as reflection for the English teachers whether they have applied code switching or not when they are teaching the
students. It is because code switching is important to be used in English teaching and learning, especially for ESL/EFL students.
3. The Students
The implementation of code switching in English teaching and learning
can improve students’ understanding and help the students to learn English better
because they understand some words, phrases, and sentence that are difficult or not familiar for them.
4. The Future English Teachers
The researcher expects that this study can give an image to the future
English subject, so they must be able to make a plan and strategy in order to help the students understand about the materials given.
5. The Next Researchers
The researcher hopes that this study will give a contribution for the future
research development and encourage the future researchers to conduct further study on sociolinguistics, especially on code switching.
F. Definition of Code Switching
The researcher would like to define some terms related to the definition of
code switching. Hoffman (1991) states that code switching involves the alternate use of two languages or linguistic varieties within the same utterance or during the same conversation. This statement is supported by Richard (1985) who suggests
that code switching is a term in linguistics referring to replacement between two or more languages in a single conversation, stretch of discourse, or utterances
between people who have more than one language in common. In short, code switching is a linguistics term that refers to the use of two or more languages in
the same utterance or conversation in the multilingual society. In this study, code switching refers to the preference of the English teacher of SMP N 2 Mlati to switch the language (English to Indonesian or English to Javanese) in the English
7 CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
This chapter reviews important studies to support the present research. The
aim of this chapter is to give the basic principles of the formulated problems. This chapter consists of two main parts, theoretical description and theoretical framework. Theoretical description gives explanation of underlying theories
related to the use of code switching in English language teaching. In addition, theoretical framework discusses the theories that have been employed.
A. Theoretical Description
In this section, some theories are elaborated. The theories that are
elaborated are bilingualism and multilingualism, and the theory of code switching. The elaborations of each theory are presented below.
1. Bilingualism and Multilingualism
The theories of bilingualism and multingualism become important since these are the backgrounds of code switching phenomenon. Living in a multicultural society deals with different cultures and languages.People who live
in a multicultural society often use code switching to signal two different identities at once. For this reason, the researcher provides several explanations
Most people as speakers usually occupy more than one language and require a selected language whenever they choose to speak with others. The
phenomenon of people having more than one code (language) is called bilingualism or multilingualism (Wardhaugh, 1986).
Bilingualism exists in almost all countries in the world, in all different classes of society and in all age groups (Grosjean, 1982). The term bilingualism has relative meaning since the definitions of bilingualism are almost as many as
the researchers who have studied bilingualism. In the popular view, bilingualism
was defined as “native-like control of two or more languages” (Bloomfield, 1933). It means that a person should be able to use two or more languages as well as a native speaker. In contrast, a bilingual is anyone who possesses a minimal competence in only one of the four language skills, listening comprehension,
speaking, reading, and writing, in a language other than his mother tongue (Macnamara in Hamers & Blanc, 2000). For example, an Indonesian who knows
Hiragana (a Japanese syllabary) without being able to understand or write is a bilingual.
The bilinguals mostly have their own dominant language. The dominant language is the language that tends to be the strongest. This language is not always the first or native language of the bilingual (Byram, 2000). However, a
bilingual can also be fluent in both languages without being able to function as a monolingual in either of their languages (Romaine, 1995). On the other hand,
bilinguals do not become fluent in both their languages since it depends on the level of fluency that a bilingual needs to be able to communicate. Some people
become equally fluent in both languages, while others do not since in their lives they just need to be really fluent in one language. It can also be that a bilingual
does not continue to study one of the languages but still can use it in oral conversation (Grosjean, 1982). However, people are still called bilingual, since most of the once that are bilingual regularly use both languages, even if they do
not have native-like competence in both languages (Byram, 2000).
Multilingualism is a powerful fact of life around the world, a circumstance
arising at the simplest level, from the need to communicate across speech communities (Edwards, 1994). The definition of multilingualism is about the practice of using more than one language, to varying degrees of proficiency,
among individuals and societies. It includes individuals who use one language at home and others outside the house. It also includes people who can function much
better in one language but who can still communicate in another language or other languages. It also refers to societies and nation-states that use more than one language in a variety of situations to varying degrees.
Basically, multilingualism is the use of two or more languages in any given situations, either by an individual speaker or by a community of speakers.
In multilingual communities, children generally learn their ethnic language first, and later add other languages for purposes, such as education, business, or for communication with a wider range of people. For example: Javanese can speak
English as their foreign language, even some people can speak Japanese, Spanish, Dutch, etc. In short, bilingualism means two languages are used by someone
alternately to communicate with others, while multilingualism refers to the ability of people who use more than two languages.
Many bilinguals and multilinguals were having difficulties with their languages. Sometimes, they often move from one language to another within a single utterance. It is called by code switching. The explanation of code switching
will be presented in the next part.
2. Code Switching
According to Gal (1998), the function of code switching as “a
conversational strategy used to establish, cross or destroy group boundaries; to create, evoke, or change interpersonal relations with their right and obligations”. Code switching becomes the concern of this study, especially the types and the
functions of teacher’s code switching. For this reason, the researcher provides
some theories in understanding the types of code switching, the functions of code switching, and the use of code switching in language teaching.
a. The Types of Code Switching
There are many types of code switching that exist in sociolinguistics study. According to Van Dulm (2007), code switching can be viewed from a
grammatical perspective, as well as from a sociolinguistic perspective. Grammatically, there are three types of code switching. Hoffmann (1991)
which involves a situation in which a bilingual attaches a tag from one language to an utterance in another language.
From a sociolinguistic perspective, there are two types of code switching, namely metaphorical and situational code switching (Van Dulm, 2007).
Metaphorical code switching refers to the process in which a bilingual speaker changes codes because of the change in what is being talked about. In contrast, situational code switching refers to the process in which a
bilingual person often switches from one code to another depending on whom that person is talking to. This statement is supported by Gumperz (1982), he
introduces the concepts of situational and metaphorical switching. Situational switching involves change in participants and/or strategies, while metaphorical switching involves only a change in topical emphasis.
According Poplack (1980) there are three types of code switching, those are tag-switching, inter-sentential, and intra-sentential. Tag-switching is when a
person inserts a tag phrase from one language into the second language, for instance greeting phrases and parting phrases. This type of code-switching is
very simple and does not involve a great command of both languages, since there is a minimum risk of violation of grammatical rules. Here is the example of tag-switching from a Portuguese-English bilingual:
[1] I look like Lilica, you know, nunca paro! (I look like Lilica, you know, I never stop!).
The second type of code switching is inter-sentential. It involves a switch
another. For instance, the title of Shana Poplack’s paper used in this study (2000) is a perfect example of inter-sentential switching:
[2] Sometimes I’ll start a sentence in Spanish y termino en español
(Sometimes I’ll start a sentence in Spanish and finish in Spanish).
The third and the most complex type of code switching is intra-sentential, which is the code switching occurs within the clause or sentence boundary. Here is the example of Portuguese-English bilingual’s speech:
[3] Yeah, I don’t know o meu lugar nesse mundo…so, something that is weird, like a, like a, I guess it’s… (… I don’t know my place in this
world…)
Moreover, Myers-Scotton (2002) distinguishes code switching into two other types, namely classic and composite code switching. Classic code switching
occurs when the utterance obeys the morphosyntactic rules of only one of the languages of the bilingual, which demonstrates that the speaker has fully acquired
and is capable of using the morphosyntactic patterns of one of the languages. Nevertheless, in the case of classic code switching speakers are sufficiently
proficient in the second language to insert free morphemes of it in a sentence which is otherwise utterly ruled by the first language, or to produce lexical islands in the second language. Composite code switching occurs when the morphemes
belonging to both languages are used and more specifically the morphosyntactic structure of the utterance is influenced by rules of both languages. This happens
b. The Functions of Code Switching
Code switching is used for various functions. Here are the functions of
code switching from three different linguists; those are Gumperz, Jingxia, and Sert.
According to Gumperz (1982), he enumerates six specific functions of conversational code switching: quotation, addressee specification, interjection, reiteration, message qualification, and personalization vs. objectification.
1) Quotation is defined in terms of its framing of reported speech.
2) Addressee specification is defined in terms of a local interactional function of
switching without reference to surface form
3) Interjection is labeled and defined in terms of the switched element’s syntactic function in a sentence.
4) Reiteration is defined in terms of referential functions as well as the metadiscursive function of emphasis.
5) Message qualification is labeled specifically in terms of its metadiscursive function but it is described in terms of sentence structure
6) Personalization vs. objectification is not defined in terms of surface shape or local contextualization functions but in terms of more abstract metaphorical function.
In 2010, another researcher, Jingxia, formulates the function of code switching in more specific. Jingxia (2010) specifies the functions of code
1) Translating Unknown Vocabulary Items
To convey the meaning of foreign language through translation may be an
efficient way of helping the learner feels natural in an EFL classroom. Translation of words and phrases may occur during the interaction between the teacher and
students. The teacher switches to the first language when the students seemed not understand. Sometimes, translating vocabulary happened when the teacher used other teaching strategies in English before or after translating the word or phrase.
2) Explaining Grammar
Whether first language or second language, it is better to explain grammar
as a practical issue. According to Duff and Polio (1990), teachers are very unwilling to teach grammar in the target language for various reasons, such as time-saving, grammar-oriented exams, and worries about too much pressure on
the studies. Martin-Jones (2000) also reported that teachers teach grammar in L2-L1-L2 sequence. To the students, esp. non-English-major students, they are not
very familiar with the terms of English grammar. If the teachers use grammatical terms in English to explain the complicated sentence structure, he is running the
risk of making more trouble for it takes more time and causes problems with the
students’ understanding.
3) Managing Class
The ways in which the teacher organizes the class also involve a choice of language. When the teacher gives directions of the activities, the teacher switches
students did something that violated classroom discipline, the teachers tends to switch to the first language for criticism and maintenance of discipline. The
teachers’ displeasure expressed in the first language seemed to be more serious
threat.
4) Emphasizing Some Points
Important messages can be reinforced or emphasized when they are transmitted in the L1 (Macaro, 1997). The use of first language can lay stress on
some instructions or direct students’ attention to important contents. Code -switching to the first language can be used to give emphasis.
5) Indexing a Stance of Empathy or Solidarity Towards Students
The teachers appear to switch to build solidarity and intimate relations with the students and to show some concerns when students seemed to have
problems. This finding is consistent with Duff and Polio (1990) statement, they conclude that many of the teachers resorted to the L1 for rapport building with the
students and “to temporarily background their role as a teacher, to perhaps
foreground their role as an empathetic peer, and to digress from instructional
sequences”. When the teacher asked the question, the student was so nervous and
anxious that he didn’t know how to answer the question. He was scared of being
criticized. Instead of reminding him solely in English, the teacher consciously
switched to the first language to encourage the student and help him build his confidence. Although the frequency of code-switching for solidarity or empathy is
6) Facilitating Students’ Understanding by Quoting Others’ Words
Quoting others’ words is also used in the switching. It is more efficient,
powerful, and specific to cite the language originally used by other people compared with its near-synonymous counterpart. To express the idea and feeling
directly and vividly, the teacher quotes other’s words. Thus, the students might
have deeper understanding about what the teacher said and the teacher could get more resonance from the students as well.
While Jingxia specifies the functions of code switching in teaching-learning process, Sert also specifies it in the classroom. According to Sert (2006),
the functions of teachers’ code switching in the classroom are as follows: topic switch, affective functions, and repetitive functions.
1) Topic Switch
The teacher alters his/her language according to the topic that is under discussion. This is mostly observed in grammar instruction, that the teacher shifts
his language to the mother tongue of his students in dealing with particular grammar points, which are taught at that moment.
2) Affective Function
It serves for expression of emotions, which is very much useful to build a good rapport with students. Students should understand the correct emotion when
3) Repetitive Function
The teacher switches code to mother tongue of the students in order to
clarify meaning, and in this way stresses importance on the foreign language content for better comprehension.
c. Code Switching in Language Teaching
In learning a language, it is important not only to learn isolated areas of a second language (L2) but to be able to use those areas simultaneously when
talking, reading, writing or listening in your second language (Cook, 2001). It means that in learning a language, people have to use language simultaneously
in their daily activities. According to Cook (2001), it is important not to prevent students from using their first language but to encourage them to use the second language in as many situations as possible and to find out when and why
code-switching should occur.
Ellis (1984) says that it is important for second language and foreign
language teachers to expose learners to as many language functions as possible in the target language. She argues that the use or overuse of the mother
tongue by second language and foreign language teachers will deprive learners of valuable target language input.
Code switching is used to create close relationships between students and
their teachers (Jingxia, 2010) and students find classroom interaction more natural and easy when code-switching is allowed (Cook, 2001). In formal situations, code switching can be used to make the teaching more effective. When
useful to translate or explain some concepts further in the students’ L1 (Lin,
2013). Code switching leads more efficient teaching for the simple reason that the
students can understand faster and more thoroughly. Hence, teachers’ code
switching is an important tool for explanations and instructions (Cook, 2001).
Grammar and vocabulary learning can also be facilitated by code-switching (Jingxia, 2010). Kumar and Narendra (2012) find that grammar instruction was
the area that contained the largest amount of code-switching.
B. Theoretical Framework
The use of code switching in bilingual or multilingual classroom is important. There are a lot of theories about the types of code switching defined by
the linguists, such as Poplack (1980),Gumperz (1982), Myers-Scotton (2002), and Van Dulm (2007). Each linguist has their own classification of the types of code switching. The researcher employed the theory of Poplack (1980) in defining the
types of code switching. Poplack’s theory is the most appropriate in classifying
the types of code switching in the context of English teaching and learning
process. There are tag-switching, inter-sentential switching, and intra-sentential switching that are going to be used in this research.
In categorizing the functions of code switching, the linguists have their
own categorization. There are some theories about the functions of code switching from Gumperz (1982), Sert (2006), and Jingxia (2010). In this study, the
the functions of teacher’s code switching in the learning and teaching process in bilingual or multilingual classroom. The functions that are going to be used in this
research: translating unknown vocabulary items, explaining grammar, managing the class, emphasizing some points, indexing a stance of empathy or solidarity
towards students, and facilitating students’ understanding by quoting others’
20 CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
This chapter presents discussion of the method used in the research. This chapter consists of several parts; those are research method, research setting, research participant, research instruments and data gathering technique, data
analysis techniques, and research procedure.
A. Research Method
This research was conducted by using qualitative research because it seeks
to understand and interpret human or social behavior about the types and the functions of code switching used by an English teacher to the eighth grade students of SMP N 2 Mlati.
Rossman and Rallis (2003) have described about qualitative researcher in the following way:
Qualitative researchers seek answers to their questions in the real world. They gather what they see, hear, and read from people and places and from events and activities. They do research in natural settings rather than in laboratories or through written surveys.
It means that qualitative research deals with natural situations and focusing on
people. The primary aim of a qualitative research is to provide a complete and detail description of the research topic. It focuses on meaning and understanding rather than numeric analysis of data. However, Seale (1999) said that the use of
results. By counting the events that are well defined and illustrated can increase the credibility of claims made by qualitative researchers. In other words, it is
possible to maintain a commitment to qualitative work and to use numbers to improve its quality.
B. Research Setting
This study was conducted in SMP N 2 Mlati. The researcher used all of the
eighth grade classes; 8A, 8B, 8C, and 8D. These classes were taught by the same English teacher. The first and the second data gathering were conducted on 21st
May, 2015. The third and the fourth data gathering were conducted on 22nd May, 2015 and 25th May, 2015.
C. Research Participant
The participant of this research was an English teacher of SMP N 2 Mlati.
The teacher was observed while teaching English in order to find out the types and the functions of code switching that exist in the English lesson.
D. Research Instruments and Data Gathering Technique 1. Research Instruments
According to Marshall and Rossman (1999), the most practical, efficient, feasible and ethical methods for collecting data need to be selected. In order to gather the data to answer the two research questions, the researcher used two
a. Observation Checklist
Schmuck (1997) states observation methods are useful to researchers in a
variety of ways. It provides researchers with ways to check for nonverbal expression of feelings, determine who interacts with whom, grasp how
participants communicate with each other, and check for how much time is spent on various activities. While observing the participant, the researcher took notes on the list of code switching cases that occurred in the classrooms.
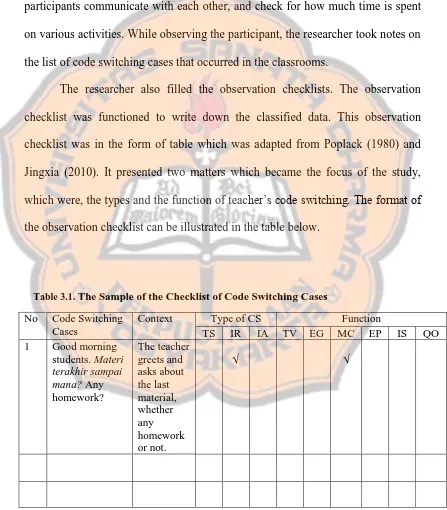
The researcher also filled the observation checklists. The observation checklist was functioned to write down the classified data. This observation
checklist was in the form of table which was adapted from Poplack (1980) and Jingxia (2010). It presented two matters which became the focus of the study, which were, the types and the function of teacher’s code switching. The format of the observation checklist can be illustrated in the table below.
Table 3.1. The Sample of the Checklist of Code Switching Cases
Abbreviation:
IR : Inter-sentential switching
IA : Intra-sentential switching TS : Tag switching
TV : Translating Unknown Vocabulary Items EG : Explaining Grammar
MC : Managing Class
EP : Emphasizing Some Points
IS : Indexing a Stance of Empathy or Solidarity Towards Students
QO: Facilitating Students’ Understanding by Quoting Others’ Words
b. Recordings
The researcher also used recordings as the instrument of this research. The
recordings refer to the audio recordings during the English teaching and learning process in the classrooms which contained code switching cases. Then, the
recordings were used to collect the data about the types and functions of code switching occurred in the classrooms. The recordings were analyzed by using the
theories that have been employed. To ease the data analysis, the researcher used the same format of the observation checklist. The observation checklist later helped the researcher to complete and strengthen the data observation.
2. Data Gathering Technique
In gathering the research data, the researcher used observation as data
a basic method for obtaining data in qualitative research. Moreover, the goal of qualitative observation is to understand complex interactions in natural settings.
In this study, the researcher would employ techniques of direct observation and indirect observation. Direct observation means the researcher was physically
present in the field to observe the situation or phenomenon that occurred there. By doing so, the researcher could understand the characteristics of the setting, the phenomenon, and also the subject of the research. Meanwhile, indirect
observation refers to an activity that was not done in the research setting that has been determined by the researcher. The researcher would use audio recordings
from English teaching and learning process in the eighth grade classrooms.
There were several steps conducted in gathering the data. First, the researcher conducted direct observations. The researcher observed the English
teaching and learning process of the eighth grade students of SMP N 2 Mlati in all classes. This step was used in order to get the data about the types and the
functions of code switching used by the English teacher. The researcher provided observation checklists as the instrument that consists of column of code switching
cases, the types, and the functions of code switching. While observing the teaching and learning process, the researcher also recorded it.
Second, the researcher conducted indirect observation in order to get more
complete data. The researcher listened to the audio recordings and filled the observation checklist. The result of direct observation was crosschecked with the
E. Data Analysis Techniques
Data analysis is the process in which the data were analyzed by using
several techniques. The researcher analyzed the data gathered in order to gain the answers to the questions formulated in the problem formulation. In this study, the
researcher analyzed the data by using qualitative data analysis as suggested by Miles and Huberman (1994) that consist of three stages:
1. Data Reduction
Data reduction refers to the process of selecting, focusing, simplifying, abstracting, and transforming the data that appear in written up field notes or
transcriptions (Miles & Huberman, 1994). It was the process whereby the mass of qualitative data obtained were reduced and organized. At this stage, the researcher
discarded all irrelevant data and transcribed all the code switching in teacher’s
utterances that had been got from direct and indirect observation. The researcher
classified code switching in teacher’s utterances based on the types and the functions as suggested by Poplack and Jingxia.
2. Data Display
After the data were reduced, the next stage was data display. It provided an organized and compressed assembly of information that permitted conclusion drawing. To draw conclusions from the mass of data, Miles and Huberman (1994)
said that the text in the form of narrative was mostly used to display the data in qualitative research. They also suggested that a good display of data in the form of
helped the researcher to understand what happened in this research and to decide the next step in drawing conclusions.
3. Drawing Conclusions and Verifying
Conclusion drawing involved stepping back to consider the meaning of the
analyzed data. The data analysis allowed the researcher to begin and develop conclusions of the study. Then, the initial conclusions were verified in order to test the validity and reliability of findings. The researcher relied on triangulation
to enhance the credibility and dependability of the study. In this study, the researcher used data triangulation. The researcher investigated whether the data
collected by using direct observation confirmed data collected by using indirect observation.
F. Research Procedure
Based on the researcher’s personal experience, the researcher was
interested to choose code switching used by English teacher in teaching English to the eighth grade students of SMP N 2 Mlati. Then, the researcher formulated two
research problems: 1) What are the types of code switching used by the English teacher in teaching English to the eight grade students of SMP N 2 Mlati? 2) What are the functions of code switching used by the English teacher in teaching
English to the eight grade students of SMP N 2 Mlati?
As the first step, the researcher asked for permission to the institution to
observation checklists, took note, and recorded the teaching and learning activities in the classroom. Then, the researcher conducted indirect observation through
audio recordings. The researcher also filled the observation checklist in order to gain more complete and strength data. After getting the data completely, the next
step was analyzing the data. In this step, the researcher reduced the data gathered, displayed the data, and drew conclusions. The researcher also used data triangulation as the strategy to reduce bias. After that, the researcher made the
28
CHAPTER IV
RESEARCH FINDINGS AND DISCUSSION
This chapter presents the findings and discussion of the study. In this chapter, the researcher provided some analysis and discussion to answer the two
research questions of the study. There are two major parts in this chapter. The first part is the research findings and the second part is research discussion.
A. Research Findings
This part shows the findings of this study that the researcher obtained.
Since this study had two research questions, the researcher divided the research findings into two points. The first one was the types of code switching and the
second one was the functions of code switching. 1. The Types of Code Switching
In this section, the researcher presented the data of the first research
question. The first research question was related to the classification of the types of code switching used by the English teacher in teaching English to the eighth
grade students of SMP N 2 Mlati. In classifying the types of code switching used by the English teacher, the researcher employed Poplack’s theory that categorized code switching into three types. Those types are tag-switching, inter-sentential
code switching, and intra-sentential code switching.
analysis revealed that there are 84 cases of code switching in the teacher’s utterances. The researcher presented the data findings of the types of code
switching used by the English teacher in the table as follows.
Table 4.1. The Data Findings of the Types of Code Switching in the Classrooms
No Types of Code Switching Number Percentage
1 Tag-switching 4 4, 8 % 2 Inter-sentential Code Switching 42 50 % 3 Intra-sentential Code Switching 38 45,2 %
Total 84 100 %
From Table 4.1., it can be seen that the English teacher did all of the types
of code switching. It can be concluded that inter-sentential code switching is the most frequently used by the English teacher in teaching English among the other types. It is followed by intra-sentential code switching which is often used by the
English teacher. Besides, tag switching is the types of code switching which is rarely used by the English teacher in teaching English. Those are the classification
of code switching based on the types which are used by an English teacher in teaching English to the eighth grade students of SMP N 2 Mlati.
Actually, when the researcher did the observation, the teacher had already
finished all of English materials for the eighth grade students. The English teacher
only asked the students do to English exercises in the students’ worksheet and
switching in teacher’s utterances was limited. The limited cases of code switching
affected the number of the types and function of teacher’s code switching.
2. The Functions of Code Switching
In this section, the researcher presented the data of the second research
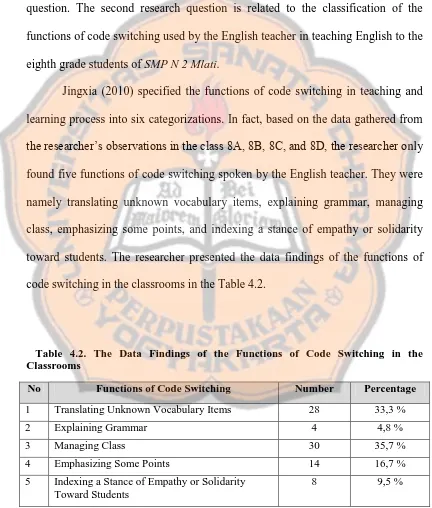
question. The second research question is related to the classification of the functions of code switching used by the English teacher in teaching English to the eighth grade students of SMP N 2 Mlati.
Jingxia (2010) specified the functions of code switching in teaching and learning process into six categorizations. In fact, based on the data gathered from
the researcher’s observations in the class 8A, 8B, 8C, and 8D, the researcher only found five functions of code switching spoken by the English teacher. They were namely translating unknown vocabulary items, explaining grammar, managing
class, emphasizing some points, and indexing a stance of empathy or solidarity toward students. The researcher presented the data findings of the functions of
code switching in the classrooms in the Table 4.2.
Table 4.2. The Data Findings of the Functions of Code Switching in the Classrooms
No Functions of Code Switching Number Percentage
1 Translating Unknown Vocabulary Items 28 33,3 % 2 Explaining Grammar 4 4,8 % 3 Managing Class 30 35,7 % 4 Emphasizing Some Points 14 16,7 % 5 Indexing a Stance of Empathy or Solidarity
Toward Students
No Functions of Code Switching Number Percentage
6 Facilitating Students’ Understanding by Quoting
Other’s Words 0 0 %
Total 84 100 %
From the Table 4.2., we can see that the English teacher did not do all of the functions of code switching in his English class. The English teacher only applied five functions of code switching, except facilitating students’
understanding by quoting other’s words. It could be affected by the situation that
the researcher had already explained in the previous section. When the researcher
did observation, the English teacher had finished all the materials. He only asked
the students to do English exercises in the students’ worksheet, and then discuss it
together. Since there was no explanation about certain material, the English
teacher did not do code switching in order to facilitate students understanding by
quoting other’s words.
Based on the table above, it can be seen that managing class and translating unknown vocabulary items are the functions of code switching which mostly was used by the English teacher in teaching English. The English teacher
did code switching to manage the class because some students did not really pay attention to the teacher. They were busy with their own businesses, so the teacher
admonished the students. Managing class also refers to the way of the English teacher when he instructed the students to do something, for example: to do the exercise, to read and answer the question, or to continue the exercise as the
unknown vocabulary items because the English teacher was more focus on translating English vocabulary during the discussion. Moreover, the students in
some classes needed teacher’s help in the English teaching and learning process,
especially to translate English vocabulary. It helped the students in understanding
the English lesson.
B. Research Discussion
In this part, the researcher provides the discussion to answer the two research questions. The researcher discussion is divided into two points. The first
one is talking about the types of code switching. The second one discusses the functions of code switching.
1. The Types of Code Switching Occurred in the Classrooms
Poplack (1980) identified types of code switching which occurred in her research, namely tag, inter-sentential, and intra-sentential switching. After
analyzing the data, the result showed that there were three types of code switching which occurred during English teaching and learning process in SMP N 2 Mlati
which included tag switching, inter-sentential code switching, and intra-sentential code switching.
a. Tag-Switching
Tag-switching involves the insertion of a tag in one language into an utterance which is otherwise entirely in the other language (Poplack, 1980).
According to the audio recordings that were made during the researcher’s
to the others. The researcher only found four cases of tag-switching that existed in English teaching and learning process to the eighth grade students of SMP N 2
Mlati. The cases were presented below.
The first case of tag-switching occurred in class 8D. In this case, the
teacher instructed the students to open their student worksheets. The English teacher said:
[2] T: Yuk, open your student worksheet now.
The English teacher inserted the tag yuk in his English sentence. The tag yuk is actually used to emphasize his utterance. From the case above, it can be said that the English teacher did tag-switching by inserting the tag yuk in the English sentence.
The second case of tag switching also occurred in 8D class. It happened
when the teacher agreed with the student’s answer. The English teacher and the
students were having a short discussion about degree of comparison.
[18] T: Yak, degree of comparison.
The case showed that the English teacher inserted the tag yak in the
English sentence. Actually, the tag yak has the same meaning as ya in Indonesian
or “yes” in English. So, it can be concluded that the English teacher did tag -switching by inserting the tag yak in his English utterance.
The third case of tag-switching occurred in 8C class. This case occurred when a student read an English text. The English teacher gave compliment and
suggestion to her. The teacher said:
From that case, we could see that the English teacher inserted the tag nduk in the English sentence. The tag nduk actually comes from Indonesian; it means “a
girl”. The English teacher did tag-switching in teaching English by inserting the tag nduk in his English sentence.
The fourth case also occurred in 8C class. The teacher and the students
were discussing the exercise in the student worksheets. The teacher instructed the student to read and answer the next number.
[52]T: Yuk, the next number. Please read it!
The teacher used the tag yuk when he instructed the students to do something. He did tag-switching by inserting the tag yuk to emphasize his
utterance.
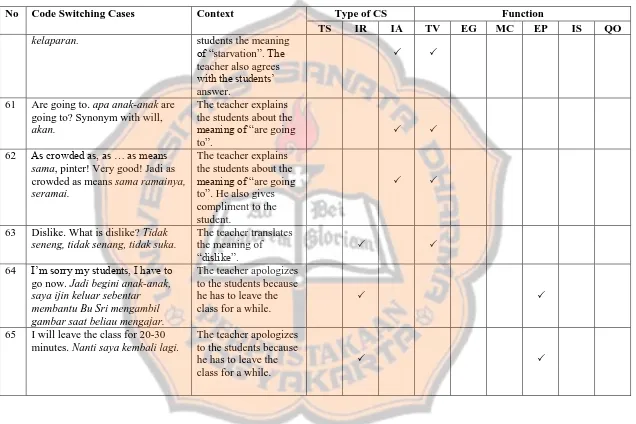
b. Inter-Sentential Code Switching
According to Myers-Scotton (1993), inter-sentential code-switching involves switches from one language to the other between sentences. Inter-sentential code switching refers to a type of code switching: the alternation in a
single discourse between two languages, where the switching occurs after a sentence in the first language has been completed and the next sentence starts with
a new language (e.g. Appel & Muysken 1987:118).
In this section, the researcher made categorization of inter-sentential code switching based on the switching of languages occurred in the classrooms. The