LEXICAL RELATION FOUND IN
“
AN EDUCATION
”
MOVIE
SCRIPT BY NICK HORNBY
THESIS
Submitted as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Sarjana Degree of English Department Faculty of Arts and Humanities States Islamic
University Sunan Ampel Surabaya
By:
FAIQATUL AZIZAH Reg. Number A03212039
ENGLISH DEPARTMENT
FACULTY OF ARTS AND HUMANITIES STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY OF SUNAN AMPEL
LEXICAL RELATION FOUND IN
“
AN EDUCATION
”
MOVIE
SCRIPT BY NICK HORNBY
THESIS
Submitted as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Sarjana Degree of English Department Faculty of Arts and Humanities States Islamic
University Sunan Ampel Surabaya
By: Faiqatul Azizah Reg. Number A03212039
Thesis Advisor
Dr. Mohammad Kurjum M, Ag NIP. 196909251994031002
ENGLISH DEPARTMENT
FACULTY OF ARTS AND HUMANITIES STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY OF SUNAN AMPEL
ABSTRACT
Azizah. Faiqatul. 2016. Lexical Relation found in A script movie “An Education” by Nick Hornby. English Department, Faculty of Arts and Humanities, State Islamic University Sunan Ampel Surabaya. Advisor : Dr. Mohammad KurjumM,Ag
Key Term : Lexical Relation, Movie Script, and Saeed’s Theory
This analysis focused on analyzing the classification of words that have
relationship each other and how the conceptual meaning of them. The relationship could be called as lexical relation. The researcher limits this study to use six types from eight types of lexical relation. They were homonym, polysemy, synonym, antonym, hyponym and meronym. The researcher found 12 pairs of antonym, 11 pairs of synonym, 9 words of hyponym with 4 words superordinate, 5 words are homonym, 4 words are polysemy and 3 words are meronym. There are four conceptual meanings of six lexical relations. First, all of the data are kinds of lexical relation. Secondly, classification of the sound and spell of words found in homonym and polysemy. Thirdly, the classification of the sameness and opposite meaning of words found in synonym and antonym. Fourth, using hierarchical diagram and classification in part of whole and kinds of something.
INTISARI
Azizah. Faiqatul. 2016. Lexical Relation found in A script movie “An Education” by Nick Hornby.Sastra Inggris, Fakultas Adab dan Humaniora, Universitas Islam Negeri Sunan SunanAmpel Surabaya.
Dosen Pembimbing : Dr. Mohammad KurjumM,Ag
Kata Kunci : Hubungan Leksikal, Skrip Film, dan Teori Saeed
Analisis ini focus untuk menganalisis kata yang memiliki hubungan dengan kata lain dan bagaimana arti konseptual pada kata-kata tersebut. Hubungan pada kata ini disebut sebagai hubungan leksikal. Peneliti membatasi penelitian ini untuk menggunakan enam tipe dari delapan tipe yang ada. Diantaranya adalah homonim, polisemi, sinonim, antonym, hiponim dan meronim. Peneliti menemukan 12 pasang kata yang memiliki hubungan sebagai
antonym, 11 pasang sinonim, 9 kata hiponim dengan 4 kata sebagai superordinate dan 5 kata sebagai homonim, 4 kata polisemi dan 3 kata sebagai meronim. Makna konseptual yang ditemukan pada skrip film ini dapat disimpulkan menjadi empat kesimpulan. Kesimpulan pertama adalah semua data yang ditemukan dikategorikan sebagai jenis dari hubungan leksikal. Kedua, pengklasifikasian kata berdasarkan bunyi dan bentuk kata ditemukan pada homonim dan polisemi. Yang ketiga adalah pembagian kata berdasarkan persamaan kata dan kata yang berlawanan makna dapat ditemukan pada sinonim dan antonym. Yang keempat adalah penggunaan diagram hirarki untuk mengelompokkan kata yang menjadi bagian dari suatu benda dan jenis dari sesuatu.
Peneliti menganalisis hubungan leksikal pada skrip film yang berjudul An Education yang ditulis oleh Nick Hornby. Film ini diadaptasi dari pengalaman pribadi seseorang bernama Lynn Barber. Penelitian ini menggunakan pendekatan deskriptif kualitatif untuk
Examiner Approval Page ... vii
Acknowledgement ... viii
Table of Contents ... x
List of Table ... xii
Abstract ... xiii
Intisari ... xiv
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION ... 1
1.1 Background of The Study ... 1
1.2 Statement of Problem ... 6
1.3 Research Objectives ... 7
1.4 Significance of The Study ... 7
1.5 Scope and Limitation ... 7
1.6 Definition of Key Terms ... 8
CHAPTER 2 REVIEW RELATED THEORY ... 10
2.2.1 A Semantic Study: The Case of Adjective of Fashion Used in Elle Magazine ... 22
2.2.2 Semantic Analysis on the English Translation of Surah Al-Mudatsir ... 23
CHAPTER 4 FINDINGS AND DISCUSSION ... 28
4.1 The types of lexical relation found in Nick Hornby’s An Education movie script ... 28
4.1.1 Homonym ... 28
CHAPTER 5 CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION ... 60
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
This chapter presents the explanation of background of study, research
questions, research objectives, significances of study, scope and limitation and
definition of key terms.
1.1Background of the Study
Meaning has important roles in our daily communication. In some cases,
meaning is not as simple as our thought. Sometimes people want to know the
meaning of new words either they probably has some meanings or specific
meaning. The ways of identifying a meaning is looking at the dictionary or
referring to preceding sentence. As Hurford and Heasley (1983, p. 1) said “the
meaning is so vague, insubstantial and elusive”. The reason of their proposed
statement is that they ask people to be careful thought about the language and the
way to use it. Moreover, in the linguistic science, the branch that concerned with
meaning in language is semantics. As Yule (2006, p. 100) states “Semantics is the
study of the meaning of words, phrases, and sentences”.
The research of semantic analysis was done by the student of University of
Sunan Ampel Surabaya in different area such as in a song (Srudji, 2014) and
Quranic English translation of Surah Al–Mudatsir (Lutfiah, 2015). Both of them
analyzed semantics holistically, which was referred to know what the meaning of
2
analyze on the other area, that is on a movie, so that this present research focuses
to analyze meaning of word in a movie script by Nick Hornby‟s An Education.
Relate to this research, the researcher specifies to get understanding on
how the relation of words, and absolutely it relates to lexical semantic. Saeed
(1997) states:
“The traditional descriptive aims of lexical semantics have been: (a) to represent the meaning of each word in the language; and (b) to show how the meanings of words in a language are interrelated” (p.53).
In the same chapter, Saeed (1997) explained that the meaning of a word
clarified through understanding its relations with other words in the language. In
other word, lexical semantic is the how a word are related with other words in the
language. Based on the definition above, the researcher concludes that lexical
semantic and lexical relation has similar definition.
Furthermore, Yule (2006, p. 104) said “word have some functions depend
on their position of the other word”. It means that words not only can be related as
„containers‟ of meaning, or fulfilling „roles‟ in events, but also have „relationship‟
with other words or lexical relation. Nevertheless, the researcher agrees with Yule
(2006, 104) who stated that every day we often use lexical relation in our
communication to explain the meaning of words in term of their relationship.
When, Anna asked meaning of the word “dog” and “poodle”. Rina might say that
poodle is kind of animal because “poodle” is kind of “dog” and “dog” is kind of
3
the researcher wants to add the knowledge about word and how its relations with
the other words.
In recent research, lexical relation has been analyzed in some subjects such
as: in the English book Jackets (Smoliana, 2013), Al-Qur‟an (Surianto, 2010),
novel (Sibuea, 2008; Gultom, 2009; Riantika, 2009), movie script (Mongi, 2015),
newspaper (Aginta, 2009), magazine (Mistiningsih, 2014). Although, this present
research is regarding to Mongi‟s research (2015), the researcher uses different
kind of movie and theory.
Some linguists have different classification of types of lexical relation.
Mongi (2015) in her research used Palmer‟s theory (1976) to analyze the types of
lexical relation and Leech‟s theory (1981) to analyze meaning properties. Palmer
(1996, p.85 – 108) classified the types of lexical relation into six types: hyponym,
synonym, antonym, relational opposites, polysemy and homonym. However, Saeed
(1997, p. 63 - 71) classified it into eight types: homonym, polysemy, synonym,
opposites (antonym), hyponym, metonyms, member-collection and portion-mass.
Furthermore, the researcher used Saeed‟s theory (1997) because the additional
explanations in his theory can help the researcher to get more comprehension
about it and it is a renewal of Palmer‟s theory.
Yule (2006, 100) clarified that the investigation of the meaning of words
in a language is normally relates with conceptual or denotation meaning than
associative meaning. Further, Yule (2006) defined “conceptual meaning is basic
4
meaning of word is only based on the meaning of word should be, so that it refers
to original meaning of a form in a language. However, if it is not need personal
aspect of meaning or context of word that is treated as associative meaning or
connotation meaning.
We can use various subjects to analyze lexical relation, because we can
find word in everywhere included in movie script. Movie script is the written text
of a film, including instruction for the actors and direction in movie. Furthermore,
in this research, the researcher chose a movie script by Nick Hornby with the title
An Education because semantics and lexical are relate with word in text. Beside
that, the researcher wants to apply Saeed‟s theory in other subject than the
previous study which used Jason Mars‟s song lyrics.
The form of movie script arranges into two parts, narration and dialogue.
Narration is words that are heard as part of movie, television show, etc and that
describe what is being seen (Merriam-Webster‟s Learner‟s Dictionary). Actually,
the existance of narration in a movie is really important because it will explain the
plot and what the actor should to do. Thus, the researcher focused on the narration
because it is much more data of lexical relation than dialogue. Dialogue is
conversation which is written for a book, play or film (Cambridge Advance
Learner‟s Dictionary).
An Education is a phenomenal movie which is adapted by personal
experience of British Journalist, Lynn Barber. This movie achieved the
5
and the best director. An education tells about a 16th years old schoolgirl, Jenny
(Carey Mulligan) who was seduced by a Jewish and married man, David (Peter
Sarsgaard). Jenny almost lost her ambition to take education in Oxford because
she felt that David was worldly beyond her imagination. An original review by
Knegt said that Jenny‟s story was the most universal because it is about a teenager
transforming into adult. However, a teenager on 13 – 16 years old is dangerous
age because they involve in instable emotion and other psychological changes.
The researcher chose this movie script to be analyzed because some
factors. The first was because the researcher found many data in the script as the
main focus by the researcher. Nick Hornby often used words with similar
meaning and be in contact with other words. The second is the story. This movie
was based on true story and has the important value. Nick Hornby adapted the
story by Lynn Barber when she was a teenager in post-war Britain. This movie
tells about a school girl who seduced and leaved her school because she wants to
marriage with a marriage man.
There are some researchers have done with lexical relation. Firstly, a thesis
by Sri Handayani Gultom (2009) entitled “an analysis of meaning properties and
lexical relations in The Rainbow by D.H. Lawrence”. She focused to analyze the
types and the dominant types of meaning properties and lexical relation. She used
systematic random sampling to collect data. Besides that, she used descriptive
qualitative method and supported the quantification. Descriptive qualitative
6
Secondly, a thesis was written by Rosmaidar and Dewi Purnamasari in
Jurnal Ilmiah Bina Bahasa (2011) and she analyzed the lexical relation used in
Jason Mars‟s song lyric. In this research, they analyzed the types of lexical
relation used Saeed‟s theory and the interpretation of the researcher towards the
finding of data.
In the present study, the researcher uses different subject and theory, as the
gap of previous studies. The researcher analyzes An Education movie script as the
subject of this research. Furthermore, the researcher applies Saeed‟s theory (1997)
to analyze the types of lexical relation and Yule‟s theory (2006) to analyze the
conceptual meaning. For addition, the researcher also uses the other supporting
theories.
From the explanation above, the researcher intend to analyze the types of
lexical relation by Saeed‟s theory and the conceptual meaning in movie script of
An Education by Nick Hornby. The researcher looks for the meaning of every pair
of words which is based on definition in dictionary to get accurate meaning and to
explain the reason of the relation and help the researcher to know the conceptual
meaning of some words.
1.2 Research Question
Based on the background study, the researcher finds two research question,
7
1. What types of lexical relations are found in An Education movie script
by Nick Hornby?
2. What are the conceptual meanings of a lexical relation found in An
Education movie scriptby Nick Hornby?
1.3 Research Objectives
The objectives of this research are:
1. To classify types of lexical relation are found in An Education movie
script by Nick Hornby.
2. To describe the conceptual meanings of each lexical relation are found
in An Education movie script by Nick Hornby.
1.4 Significances of the Study
The researcher hopes this study can give some significances:
1. The researcher, English students and teachers can get additional
information about lexical relations.
2. This research can be reference or previous study for, student or the
future researcher who will research about semantic, especially about
lexical relation.
1.5 Scope and Limitation
The researcher focuses to take the data in the narration of movie script. It
8
eight types based on Saeed‟s theory, but the researcher just takes six types to be
analyzed. That is because member-collection and portion-mass limited of the
references.
1.6 Definition of the Key Terms
The researcher gives some the definition of key terms to make clear and to
avoid misunderstanding.
Semantic is one of branch of linguistic that focuses in study of meaning. It is not only learns how meaning express, but also meaning organize, the relation
and the properties of lexicon semantically. (Kreidler, 1998)
Lexical relation is the relationship between two or more words or phrases in some aspects. There are form, meaning, sound, and others. Saeed (2003) said
that relationship in lexical relations not only relation between two word literally,
but also a system.
Conceptual meaning is the original meaning of form in a language. Conceptual meaning covers those basic, essential components of meaning that are
conveyed by the literal use of a word. (Yule, 2006: 100)
Script movie is called be screenplay. It is the text for a film, including the words to be spoken by the actors and instructions for the cameras (Cambridge
Advanced Learner‟s Dictionary Third Edition). That contains dialogue and
9
An Education is an movie by Lone Scherfig. The screenplay is written by Nick Hornby that is inspired by Lynn Barber‟s true story.
CHAPTER II
REVIEW RELATED THEORY
In this chapter, the researcher focuses in two points. The first is theoretical
bases. It contains a description of several theories, which is support the researcher
does the present research. The second is some previous studies related with this
topic, theory and others. Then, the researcher explains about the similarities and
differences between the research and others.
2.1 Theoritical Framework
Theoritical framework contains the main theory of this research, the relevant
studies and sources which is relate with this research. It also explains about the
supporting theories and resources.
2.1.1 Semantics
Historically, semantics based on a detailed account was found in 1948.
There were two historical semantics. First, the divination which was never occur
about the term semantick in the phrase semantick philosophy in seventeenth
century which was introduced in a paper read to the American Philological
Association in 1894 entitled “Reflected meaning: a point in semantics”. Second,
M. Bréal, the France stated that term sémantique had been formed from the Greek
in the previous years. In 1900, it appeared a phenomenal little book which was
neglected Bréal’s book entitled Semantics: studies in the science of meaning. In
11
concerned with changing of meaning from a historical point of view which is
study about the change of meaning at the time (FC book. 1971).
Semantics defines as one of the branched of linguistics studying about the
meaning or content of language in morphemes, words, phrases, and sentences.
Lyon (1968: P.54) stated “…. And the expression-plane of language can be
described in terms of (at least) two levels: that of sounds and that of words”. To
introduce now the terms generally used by linguists: the sound of a given
language are described by phonology; the form of its words and the manner of
their combination in phrases, clauses and sentences by grammar; and the meaning,
or content of the words (and of the units composed of them) by semantics. Every
branch of linguistic has different specifications.
By Hurford and Heasley (1983: p. 1) stated that semantics is the study of
meaning in language. The aims of semantic are to explain and to clarify of the
nature meaning. For instance, the meanings of words ladder, staircases, stairs and
step. They have a similar meaning. The following are meaning of them by
Cambridge Advanced Learner Dictionary. 1) The word ladder means a piece of
equipment used for climbing up and down, which consists of two vertical bars or
pieces of rope joined to each other by a set of horizontal steps; 2) The word
staircases meansa set of stairs inside a building usually with a bar fixed on the
wall or onto vertical poles at the side for you to hold on to; 3) The word stairs
means a set of steps which lead from one level of a building to another; 4) The
word step means one of the surfaces that you walk on when you go up or down
12
Kreidler (1998: 3) defines semantic as a systematic study of meaning and
linguistic semantic is the study of how languages organize and express meanings.
2.1.2 Lexical Relation
By definition on dictionary, lexical relation is related of word. Yule (2006)
states
“Words is not only can be treated as “container” of meaning, or as fulfilling “roles” in events, they can also have “relationship” with each other” (p. 104)
The relationship between two or more words is called lexical relation. The
relationship are based on forms, meanings, sounds, and others. The meaning of
word in terms of its relationship to other words is treated as the analysis of lexical
relations (Yule, 2006: p. 102).
In other book, Saeed (1997, p. 63) called the lexicon or word as a network.
As he explains,
“A particular lexeme may be simultaneously in a number of these relations, so, that it may be accurate to think of the lexicon as a network, rather than a listing of words as in a published dictionary” (63).
2.1.3 Types of Lexical Relation
The most familiar types are antonym and synonym. There are six types of
lexical relation by Saeed (1997) that is analyzed by the researcher. They are
13
2.1.3.1 Homonym
A homonym is a relation between minimum two words where is identical
of the pronunciation and spelling but unrelated meaning. As Saeed (1997: p. 63)
stated that homonyms are unrelated senses of the same phonological word. Two
ways to distinguish different types of homonym. They are depending on the
syntactic categories and spelling. Look at the following examples:
a) Lexemes of the same syntactics category and with the same spelling. For
instance, lap (n) means circuit of a course and lap(n) means part of body
when sitting down. (Cambridge Advances Learner’s Dictionary)
b) Of the same category, but with different spelling. For instance, ring(v) and
wring (v).Ring means to make a telephone call to someone and wring
means to hold something tightly with both hands and twist it by turning
your hands in opposite directions(Cambridge Advances Learner’s
Dictionary).
c) Of the different categories, but with the same spelling. For instance , keep
(verb) and keep (noun).Keep (v) means to delay someone or prevent them
from doing something;and keep (n) means the cost of providing food,
heating and other necessary things for someone. (Cambridge Advances
Learner’s Dictionary)
d) Of different categories and with different spelling. For instance, not(adv)
and knot (n).Not [nɒt]means used to form a negative phrase after verbs like
14
Both of them are identical pronunciation but different spelling, meaning
and categories.
Based on the following explanation, homonym is defined as pronunciation
and spelling are identical, but unrelated meaning. In others is identical in
pronunciation but spelling is different.
2.1.3.2 Polysemy
Polysemy is two or more words with the same form and related meanings.
In other hand, it can be defined as one form (written or spoken) with multiple
meanings that are all related by extension. Saeed (2003) argued that polysemy
deals with multiple senses of the same phonological word, but its invoked if the
senses are judge to be related.
The examples are:
The word “date” (= a point in time). It means kind of date is polysemous
in term of particular day and month (= on a letter), an arranged meeting
time (= an appointment), a social meeting (= with someone we like), and
even a person (= that person we like).
In dictionary, polysemy listed under the same lexical entry. Based on the
example above, date is lexical entry (a point in time) that has some lexemes. Entry
can be called as head of the word in a dictionary. In polysemy, there have one
15
2.1.3.3 Synonym
Synonym is relation between words with similar meaning. That are
different phonological words which have the same or very similar meaning
(Saeed, 2003).It can be adjective, noun, verb or adverbs.
For example are:
- Adjective (good = fine)
- Noun (bag = briefcase)
- Verb (watch = view)
- Adverb (weak = low).
Although definition of synonym is word relation with sameness of
meaning. Sameness or similar means that not the perfect synonym that the
meaning is same absolutly. There have not the same meaning exactly in two
words (Palmer, 1981: p. 89). For example the identical twin has the close
similarity physically. Exactly, they have differences each other. It is maybe in part
of they body, their hoby, their feeling and other. They also have difference
characteristics. In synonym, there are at least five ways in which they can be seen
to differ.
First, some sets of synonym belong to different dialects of language. For
instance. The term of fall and autumn have the similar meaning. But they have
different dialect. The term fall is used in United States and autumn is used in some
16
Second, there is a similar situation, but a more prolematic one, with the
words that are used in different style. Wife or spouse are more formal than old
lady or missus.
Thirdly, some words may be said to differ only in their emotive or
evaluative meaning. Some semantics have made deals with the emotive difference
that have function to influence attitudes. Words may have different emotive
meaning in different societies. For instance, the term liberal that is good word in
Great Britain when Winston Churchill use politic a conservative. But, it is bad
word in South Africa and in some political circles in the United States. Other
examples is naive or gullible seems more critical than ingenuous.
Fourthly, some words are collocationally restricted. For example the
sentence below:
1. A big house - a large house
2. My big sister – my large sister
Fifthly, it is obviously the case that many words are close in meaning, or
that their meaning overlap. This kind of synonym is exploited by the dictionary
maker. For instance, the term mature (adjective) have possible synonym are adult,
ripe, perfect, due. Possible synonym for the term govern are direct, control,
determine, require.
The following explanation is explained with more brief by Saeed (1997: p.
17
of parameters. They may belong to different dialects, register, style of language,
colloquial, formal, literary, and others that belong to different situation.
2.1.3.4 Antonym
Saeed ( 1997: p. 66) defines “antonyms is useful to identify several
different types of relationship under a more general label of opposition”. It means
words which are opposite in meaning. However, antonym is often thought of as
the opposite of synonym, but the status of two are very different. There is no real
synonym that means the words are similar not same fully. But antonym is a
regularly and very natural feature of language.
2.1.3.4.1 Binary antonyms
Saeed ( 1997: p. 66) defines binary pairs or complementary pairs as a
relation between words such that the positive of one implies the negative of the
other. The relation of A is opposite with B. In Binary antonyms. If A yes, so B is
no and vice versa. If something is A, the other is not B: if there is not A, they are
B. Look at the following pairs of word:
1) Love–hate
2) Same–different
3) Dead–alive
(1) They are not binary antonyms because if you do not love her, you do
18
same, they are not different; if they are not the same, they are different. (3) they
also binary antonyms.
2.1.3.4.2 Gradable Antonym
Gradable antonym is a relationship between opposite where the positive of
one term does not necessarily imply the negative of the other. This relation is
typically associated with adjective (Saeed. 1997: p. 67).
Gradable antonyms have some major characteristics. First, there are
usually intermediate terms. In term hot and cold are gradable antonyms because
between hot and cold is a continuous scale of values, which may given names
such as warn, cool, or tepid.
Second, the term is usually relatives. It can compare two words. For
example a late dinosaur fossil is earlier than an early Elvis record. Third is that
some pairs one term is more basic and common. A good test for gradability can
use asking statement such as How?, how much? or very, very much. For example
of the pairs long – short, how long is it? or how short is it? is acceptable.
2.1.3.4.3 Reverse
The point of reverse antonym is movement. As Saeed (1997) states:
“the characteristics reverse relation is between terms describing movement, where one term describes movement in one direction, , and the other the same movement in opposite direction, “ (p.67).
19
motion, there words can be called reserves. They are up - down, in - out, turn –
left. Terms of any process which can be classified as reverse are inflate – deflate,
expand – contract, fill – empty, or knit – unravel.
2.1.3.4.4 Converse antonym or relational antonym
Definition of converses antonym by Saeed (1997: p. 67) is the terms which
describe a relation between two entities from alternate viewpoints. For instance as
in pairs employer and employee. Helen is Shena’s employer then we know
automatically that Shena is Helen’s employee.
A pair of words which is one of them is reversed definitely. For example is
relationship between parent and child. The existence of child because the
existence of his parent. The formula of converse antonym can be look at Kreidler
(1998: p. 105), for any two converse relational terms X and Y, if [a] is the X of
[b], then [b] is the Y [a].
Converse pairs commonly include kinship and social roles (husband of –
wife of) and directional opposites (in front of – behind). Some words like give to -
receive from is one of the pairs of converse about argument predicates. The
formula is if A gives X to B, B receive X from A.
2.1.3.5 Hyponym
Saeed (1997, p. 68) defines “hyponym includes the meaning of a more
general words”. It is less familiar than antonym or synonym, but it is important
20
is the idea that if an object is a carrot, then it is necessarily a vegetable, so
meaning of vegetable is included in the meaning of carrot.
In hyponym there are divided into two parts. The more general term is
called superordinate or hypernym. Looking at the above examples, vegetable is
superordinate of carrot.
When we talks about hyponymous relation, we are essentially looking at
the meaning of words in some types of hierarchical relationship. The hierarchical
diagram can use in set of word such as animal, insect, vegetable, flower, tree,
human artefact and others. An example of the hierarchical diagram is the
following set of words of bird.
Keastrel and sparrowhawk are hyponym of hawk and hawk a hyponym of
bird. We assumes that keastrel is a hyponym of bird (keastrel is a kind of bird).
While bird is superordinate or hypernym term. Superordinate can be called as the
higher level terms. Other part of hyponym is co-hyponym where two or more
words that share the same superordinate term. So, co-hyponym of above diagram
are crow and hawk.
Bird
Crow
Hawk
Keastrel
Sparrowhawk
etc
21
2.1.3.6 Meronymy
Meronymy is a term used to describe a part-whole relationship between
lexical items (Saeed. 1997: p. 70). The sentence frame of meronymy like X is part
of Y, or Y has X. As in a page is part of a book, or a book has pages. Definition
of meronymy by Saeed is similar with definition of metonym by Yule. But, Saeed
(1997) gives different definition about meronymy and metonymy.
Definition of metonymy by Saeed (1997: p. 78) is a referential strategy
where a speaker refers to an entity by naming something associated with it. While,
Yule (2006, p. 108) states that metonym is the relationship between words, based
on a container – content relation (can/juice), a whole-part relation (car/wheels), or
a representative – symbol relationship (king/crown).
A glance, meronymy is similar with taxonomies hierarchical diagram of
hyponym. But, meronymic hierarchical are less clear-cut and regular than
taxonomies. While differences of meronymy and hyponymy are in transitivity.
Hyponymy is always transitive, but meronymy may or may not be (Saeed: 1997,
p. 70).
2.1.4 Conceptual Meaning
Conceptual meaning covers those basic, essential components of meaning
that are conveyed by the literal use of word (Yule. 2006: p. 100). It means that
22
For example:
“Needle”
The basic component of word needle in English might include “thin,
sharp, and steel instrument”. These component would be part of the
conceptual meaning of needle.
As Leech (1981: p. 9) divides meaning into seven kinds of meaning in his
book entitled “Semantics: the study of meaning”. He defines conceptual meaning
as widely assumed to be the central factor in linguistic communication. In these
book, he stated two reason for assigning priority to conceptual meaning are:
1. It has a complex and sophisticated organization of a kind which may
be compared with;
2. Cross-related to, similar organization on the syntactic and phonological
levels of language.
The point of the conceptual meaning are logical, cognitive or denotative
content.
2.2 Previous Study
Regarding on this study, the researcher found some other researches which
related with the topic or theory.
23
article and advertisement in Elle Magazine. Besides that, she used Kreidler’s
theory to conduct the data of lexical relation and classify the adjectives in three
types of lexical relation: synonym, antonym, and hyponym. Moreover, she used
qualitative approach to analyze the data because it is not number but word. Then,
she found thirty data of hyponym, twenty four data of synonym, and five
adjectives of antonym.
Furthermore, she collected adjective words which were indicated as
synonym, antonym, or hyponym in a different table based on the types of lexical
relation. Each of adjective analyzed used Webter’s Dictionary.
Semantic Analysis on the English Translation of Surah Al-Mudatsir
The research of Lutfiah (2015) used data from the English Translation of
Surah Al-Mudatsir. She used translation by A. Yusuf Ali. Her research was
conducted with descriptive qualitative method. She focused in two types of
meaning whether lexical meaning and sentential meaning. In lexical meaning, she
analyzed the meaning of word and how the relation of words. She defined a
sentential meaning as a meaning of a statement, command, exclamation or
question. It usually contains of subject and predicate, and begins with a capital
letter and end of punctuation mark. The last, she delivered the religious message,
CHAPTER III RESEARCH METHODS
This chapter presents research design, research instrument, data and data
source, data collection and data analysis.
3.1 Research Design
Research design explained the strategy of the research, the ways or
techniques that used by the researcher to finish the study. According to Kothari
(2004:5) in his book about research methodology, two basic research approaches
were qualitative and quantitative approaches. Qualitative approach concerned with
subjective assessment of attitudes, opinions and behaviour. Besides that, this
approach focused to use group interviews, projective techniques, and depth
interviews. While quantitative approach focused to use the formula and numeral
to quantification in collecting the data.
In this research, the researcher applied descriptive qualitative approach. It
meant that the researcher did not use the calculation with a formula to collect data,
but it used the library studies and coded to classify the types of lexical relation.
Moreover, the researcher used descriptive approach to describe the meaning of
each word that was classified as lexical relations. As Kothari (2004: 2) stated that
the major purpose of descriptive research is description of the state of affairs, as it
exists at present. Thus, the researcher only described and has no control over the
25
3.2 Instrument
The instrument of this research was the researcher herself. It means that
the researcher took the data of lexical relation from data source, classified and
identified based on the types of lexical relation and the meaning. Besides that, the
researcher used her knowledge about the topics and she is helped by some sources
or books related with the topics.
3.3 Data and Data Source
Data source of this study was script of An Education movie. Moreover, the
data of this present research was all words that contain of the types of lexical
relation. The data was taken from data source that have been selected before.
3.4 Data Collection
To collect the data, the researcher used some procedures, these were:
1. Browsing in internet
The researcher searched the script on Google with the keyword “script of
An Education movie”
2. Downloading the script
In this step, the researcher downloaded the script by copied it to Microsoft
Word. It helped the researcher to read and to look for data easily
3. Printing out the script
In this step, the researcher printed out the script that has saved before. It
26
4. Coding
The researcher was not only reading the article, but also using a coding
technique to remark the data. The purposes were easier to group the data
and to analyze the types of lexical relation. As Kothari (2004, p. 123) said
“Coding refers to the process of assigning numeral or other symbols to
answer so that responses can be put into a limited number of categories or
classes”.
Moreover, the researcher did two steps, those are:
a. Giving an underline for certain words that word odds. It referred to the
word that has not a relation with other words.
b. Marking the words by using different color pens in each types of
lexical relation. Kothari (2004: p. 123) also stated that one of standard
method was to code in the margin with a colored pencil.
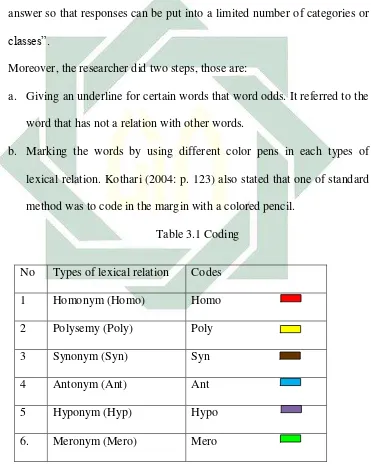
Table 3.1 Coding
No Types of lexical relation Codes
1 Homonym (Homo) Homo
2 Polysemy (Poly) Poly
3 Synonym (Syn) Syn
4 Antonym (Ant) Ant
5 Hyponym (Hyp) Hypo
27
Actually, the researcher found more than one pairs in every types of
lexical relation. Therefore, the researcher added the serial number to code each of
pairs.
3.5 Data Analysis
In analyzing the data, the researcher did some procedures. These were:
a. Identifying and classifying the pairs of words which was included in the
types of lexical relation
In identifying the pair words, the researcher rechecked of the pair words
which related the theory. The researcher was helped by the dictionary to
get an accurate data.
b. Identifying the meaning of each relation.
The researcher identified the meaning and the reason of each lexical
relation. The result related with what the function or the meaning of the
relation behind the words.
c. Analyzing the conceptual meaning
The researcher chose the types of lexical relation these were homonym,
CHAPTER IV
FINDINGS AND DISCUSSIONS
In this chapter, the researcher analyzes the types of lexical relation that
found in An Education script movie and the conceptual meaning of them.
4.1 The types of lexical relation found in Nick Hornby’s An Education movie script
In the following below, the researcher analyzes the finding of the types of
lexical relation that found in An Education movie script based on Saeed’s theory.
The six types of lexical relation are homonym, polysemy, synonym, antonym,
hyponym, and metonym.
4.1.1 Homonym
Homonym is relation of words with the same phonological words. They are
divided into homophone which is same the sound and homograph which is same
the written word. The researcher used dictionary to know the sound or
pronunciation of words. The researcher found four relationship in the script. They
are two – too, write – right, ring, four –for and sleeve.
Table 4.1 Finding of Homonym
Data Word pairs Sentences
1.
Write - right a. A couple, ... write down everything the teacher says.
29
2. Two - too Two 13 years old boys sitting between them wave too,parodically, and then blow kisses, much to Graham’s embarrassment and Jenny’s fury.
3. Sleeve a. Almost involuntarily, Jenny touches the sleeve of Helen’s velvet jacket.
b. (For a moment, the sound quality changes –
soundtrack becomes source music, seamlessly)
Jenny is studying the sleeve.
4. For - four a. Jenny opens the door for David.
b. An ornate four poster bed occupies most of the space in the room.
5. Ring a. The doorbell rings.
b. Suddently Miss Stubbs notices something glinting on
her hand; an engagement ring.
Based on the finding above, the researcher explains them one by one at the
following explanation.
Data 1:
a) A couple, ... write down everything the teacher says. (1A. Int. Classroom. Day. Line 5 -7)
30
Write is an activity or verb to mark (letter, words, or number) on a surface
such as a paper or computer screen, using a pen, pencil or keyboard. This is to
record thoughts, facts, or messages. Pronunciation of write is (raɪt). (Cambridge
Advanced Learner’s Dictionary)
Right is a direction on toward to the side of your body that is to the east
when you are facing north. The pronunciation of it is [raɪt] and include in adjective
categories. (Cambridge Advanced Learner’s Dictionary)
Based on the explanation above, the relation of write and right is
homophone and part of homonym. It is because write and right have same spoken
/raɪt/. But, they have different category (verb and adjective) and different spelling
(write and right).
Data 2:
Two 13 years old boys sitting between them wave too, parodically, and then blow kisses, much to Graham’s embarrassment and Jenny’s fury. (4. Int school.
hall. Day. Line 4-7)
Words two and too is found in the 4th narration. They are in one sentence.
Two is category of the cardinal number “2” and it is an equivalent to the sum one
and one. Pronunciation of two is (tu:). Too (tu:) is an adverb means more or also.
(Cambridge Advanced Learner’s Dictionary)
Based on the explanation above, two and too are homophones because they
31
Data 3:
a) Almost involuntarily, Jenny touches the sleeve of Helen’s velvet jacket. (16.
Int. ST. John’s Smith Square. Night. Line 9 -10)
b) (For a moment, the sound quality changes – soundtrack becomes source
music, seamlessly) Jenny is studying the sleeve. (66. Int. Record shop. Day.
Line 3-5)
Sleeve is the part of piece of clothing that covers the arm. The pronunciation
of sleeve is [sli:v]. The second sleeve relates with stiff envelop for a record. It
means how the strong feeling when you hear the music or record. It has same
pronunciation with the first sleeve.
Sleeve at the first and second sentences categories as homonym which is
belong to homophone and homograph all at once. The reason is because they have
same syntactical categories and spelling, but they have different meaning.
Data 4:
a) Jenny opens the door for David. (36. Int. Hallway. Night. Line 1)
b) An ornate four poster bed occupies most of the space in the room. (38. Int.
Helen’s Bedroom. Day. Line 1)
Definition of for in dictionary is intended to be given to with function as
preposition in the sentence. The word for can be as preposition or conjunction. The
32
Four is one of the cardinal numbers. The position of four is between the
number “three (3)” and “five (5). It is noun. The sound of four is fᴐ:(r). (Cambridge
Advanced Learner’s Dictionary)
Based on the information above, we can know that the relation of them is
sameness of sound, but the syntactical category and the spelling are different. Thus,
it is homophone.
Data 5:
a) Suddently Miss Stubbs notices something glinting on her hand; an
engagement ring. (82. Int. Classroom. Day. Line 18 -20)
b) The doorbell rings. (91. Int. Jenny’s house. Evening. Line 10)
Ring (a) is a circular piece of jewelry worn especially on your finger, while
Ring (b) is verb that is to cause the sound of a bell. (Cambridge Advance Learner’s
Dictionary).
Both of the words ring is homonym, where the lexeme have different
syntactic category and with the same spelling. The sound is same [rɪŋ]. The
syntactic category of (a) ring is noun and (b) ring is verb.
4.1.2 Polysemy
Polysemy is a words with multiple sense or lexeme in one lexical entry. The
word is having more than one meaning. Actually, the researcher found many words
with more than one meaning, but there are take some data in the script. The words
33
Table 4.2 Finding of Polysemy
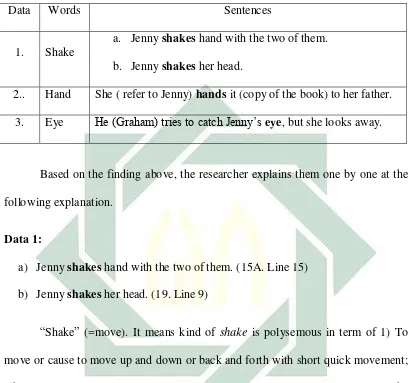
Data Words Sentences
1. Shake
a. Jenny shakes hand with the two of them.
b. Jenny shakes her head.
2.. Hand She ( refer to Jenny) hands it (copy of the book) to her father.
3. Eye He (Graham) tries to catch Jenny’s eye, but she looks away.
Based on the finding above, the researcher explains them one by one at the
following explanation.
Data 1:
a) Jenny shakes hand with the two of them. (15A. Line 15)
b) Jenny shakes her head. (19. Line 9)
“Shake” (=move). It means kind of shake is polysemous in term of 1) To
move or cause to move up and down or back and forth with short quick movement;
vibrate; 2) To sway or totter or cause to sway or totter; 3) To clasp or grasp (the
hand) of (a person) in greeting etc; 4) Shake hand to clasp hands in greeting,
agreement, etc. 5) Shake on it (informal) to shake hands in agreement,
reconciliation, etc. 6) to move backwards and forwards or up and down in quick,
short movements, or to make something or someone do this; 7) To wave or
34
Data 2:
She ( refer to Jenny) hands it (copy of the book) to her father. (55. Int. Jenny’s
House. Night. Line 6)
“Hand” (= take handle or control of something). It means kind of hand is
polysemous in term of, 1) to transmit or offer by the hand or hands; 2) To help or
lead with the hand; 3) Nautical = to furl (a sail) (Collins English Dictionary and
Thesaurus).
Data 3:
He (Graham) tries to catch Jenny’s eye, but she looks away. (58 B. Line 6)
Eye (= an organ of something). It means kind of eye is polysemous in term
of, 1) Part of body = one of the two organs in your face, which you use to see with;
2) Part of plant = a dark spot on a potato or similar plant part, from which a new
stem and leaves will grow; 3) The hole in a needle through which you put the
thread; 4) Attention or observation; 5) Opinion, judgment, point of view or
authority (Collins English Dictionary and Thesaurus).
4.1.3 Synonym
Synonym is two words or more that have related meaning. The researcher
found 11 word pairs in the script. They were „nervous = shy, embarrassed’, „street
= road’, „beautiful = pretty’, „overcoat = jacket’, „look = stare’, „hall =
auditorium’, „girl = lady’, „start = begin’, „jumpout = getout’, „huge = large’, and
35
Table 4.3 Finding of Synonym
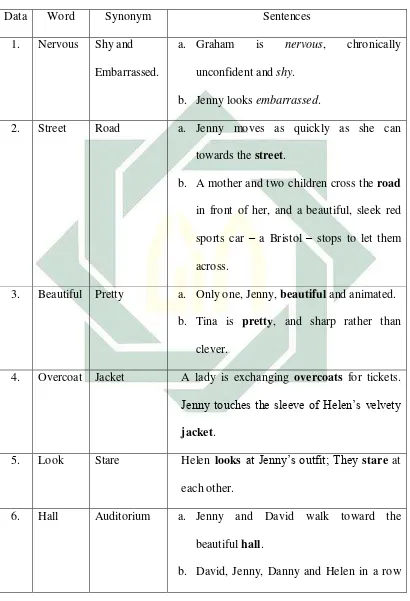
Data Word Synonym Sentences
1. Nervous Shy and
Embarrassed.
a. Graham is nervous, chronically
unconfident and shy.
b. Jenny looks embarrassed.
2. Street Road a. Jenny moves as quickly as she can
towards the street.
b. A mother and two children cross the road
in front of her, and a beautiful, sleek red
sports car – a Bristol – stops to let them
across.
3. Beautiful Pretty a. Only one, Jenny, beautiful and animated.
b. Tina is pretty, and sharp rather than clever.
4. Overcoat Jacket A lady is exchanging overcoats for tickets. Jenny touches the sleeve of Helen’s velvety
jacket.
5. Look Stare Helen looks at Jenny’s outfit; They stare at each other.
6. Hall Auditorium a. Jenny and David walk toward the
beautiful hall.
36
in the middle of the auditorium.
7. Girl Lady a. The girls walk over to another reception table;
b. A lady is exchanging overcoats for tickets.
8. Start Begin a. Tina starts to slurp the froth from her cappuccino with a spoon.
b. Jenny is in her Latin class, waiting for the
lesson to begin.
9. Jump out Get out David jumps out of the car and let Marjorie and jack out. Jenny gets out too.
10. Huge Large a. Books about ponies, a much loved teady
bear; a cello huge in the small room leans againts the wall.
b. She has been something on the doorstep,
... – a large bunch of flower.
11. Small Little a. Outside a dilapidated house covered in
scaffolding stand a large West Indian
family, mother, father, three or four
small children and a dog.
b. Jenny’s POV of the black family in one
37
Based on the finding above, the researcher explains them one by one at the
following explanation.
Data 1:
a) Graham is nervous, chronically unconfident and shy. (5. Ext. School. Day.
Line 3-4)
b) Jenny looks embarrassed. (11. Int. Jenny’s sitting room. Afternoon. Line 3)
Nervous, shy and embarrassed are related in meaning to each other. As Yule
(2006: p. 104) said that synonym can be found in two or more words with very
closely related meaning. It is an example of synonym that found at more than two
words.The meaning is not same but similar.
Nervous (adjective) means people’s feeling worried or anxious in a
particular situation. Shy (adjective) means nervous and uncomfortable with other
people. Embarrassed means feeling ashamed or to feel or cause to feel confusion or
self-consciousness. (Collins English Dictionary and Thesaurus)
Data 2:
a) Jenny moves as quickly as she can towards the street. (5. Ext.School.Day.
Line 5)
b) A mother and two children cross the road in front of her, and a beautiful,
sleek red sports car – a Bristol – stops to let them across. (6.Ext. Bus stop.
Day. Line 2)
38
or both sides. Road means a long route or way for vehicles, person, and animals to
travel on.
Data 3:
a) Only one, Jenny, beautiful and animated. (1A.Int. Classroom. Day. Line 8)
b) Tina is pretty, and sharp rather than clever. (13.Int.Coffee bar.Day. Line 6)
Beautiful and pretty are related in meaning each other. Beautiful (adjective)
means a characteristic of a girl who is very attractive and pleasant. It is shining on
the inside and out. Pretty (adjective) means a characteristic of a girl who is pleasant
to look at and has a good appearance.
Data 4:
A lady is exchanging overcoats for tickets. Jenny touches the sleeve of Helen’s velvety jacket. (16. Line 9 -10)
Overcoat and jacket are related in meaning each other. Overcoat(noun)
means a long thick coat worn in cold weather. Jacket (noun) means a short coat.
They are coat but have different model.
Data 5:
Helen looks at Jenny’s outfit; They stare at each other. (16. Line 12 and 17)
Look [verb] and stare [verb] are related in meaning each other. They have
same syntactic category that is verb. Look is an activity to direct your eyes in order
to see. Stare is an activity to look for a long time with eyes wide open. Stare it can
39
This synonymous are a sameness of an activity when someone are seeing
something.
Data 6:
a) Jenny and David walk toward the beautiful hall. (15A. Line 1)
b) David, Jenny, Danny and Helen in a row in the middle of the auditorium. (17. Line 2)
Hall (noun) and auditorium (noun) are related in meaning each other. Hall
means a building or large room used for an events involving a lot of people.
Auditorium means the part of theatre, or a similar building, which the audience sits
to watching and listening.
Data 7:
a) The girls walk over to another reception table; b) A lady is exchanging overcoats for tickets. (16. Line 7 and 8)
Girl (noun) and lady (noun) related in meaning each other. Girl means a
female child or young woman, especially one still at school. Lady means a woman
regards as having the characteristics of a good family and high school position. It
can be called as a polite or old fashioned way of referring to or talking to a woman.
Data 8:
a) Tina starts to slurp the froth from her cappuccino with a spoon. (13. Line 12)
40
Start (verb) and begin (verb) are related in meaning each other. Start means
to begin doing something. That is opposed to stop that have a possibility to be
continuing. Begin means to start to be, do, and etc. It is opposed to end. Begin is
more formal than start.
Data 9:
David jumps out of the car and let Marjorie and jack out. Jenny gets out too. (100. Jenny’s house. Night. Line 1-4)
Jumps out and gets out are related in meaning each other. Both of them
explains when a people go out or leave a building and from inside to outside
something. Jump out means to leave a closed vehicle, building, etc.
Data 10:
a) Books about ponies, a much loved teady bear; a cello huge in the small room
leans againts the wall. (2. Int. Bedroom. Day. Line 2)
b) She has been something on the doorstep, ... – a large bunch of flower. (12A.
Int/ext. Jenny’s house. Evening. Line 2)
Huge (adjective) and large (adjective) are related in meaning each other.
Huge means an extremely large in size or amount. It is used in reference to
dimensions or quantity. Large means big in size or amount.
Data 11:
a) Outside a dilapidated house covered in scaffolding stand a large West Indian
41
b) Jenny’s POV of the black family in one window, and the little old lady disappearing from another.
Small and little are related in meaning each other. Small is comparatively
little; limited in size, number, importance, and etc. Little is small quantity, extent or
duration of (Collins English Dictionary and Thesaurus).
4.1.4 Antonym
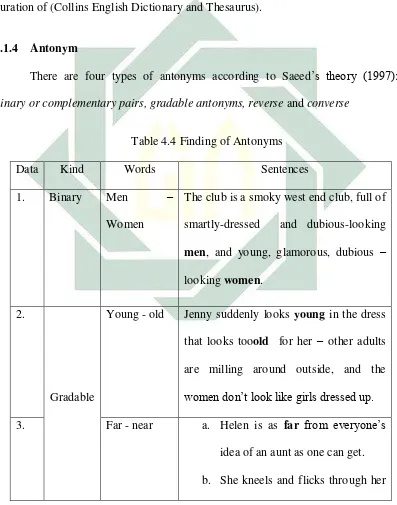
There are four types of antonyms according to Saeed’s theory (1997):
binary or complementary pairs, gradable antonyms, reverse and converse
Table 4.4 Finding of Antonyms
Data Kind Words Sentences
1. Binary Men –
Women
The club is a smoky west end club, full of
smartly-dressed and dubious-looking
men, and young, glamorous, dubious – looking women.
2.
Gradable
Young - old Jenny suddenly looks young in the dress that looks tooold for her – other adults
are milling around outside, and the
women don’t look like girls dressed up.
3. Far - near a. Helen is as far from everyone’s idea of an aunt as one can get.
42
half-dozen or so LPs on the floor
near a cheap record player ... 4. Small – large ... and Jenny walking towards it, a small 6. Open-closes a. Marjorie kicks the door open with
her foot and comes in holding a
birthday cake with seventeen
candles burning on it.
a. She follows the girls inside.
b. She stands outside the living room for a moment, listening.
b. They return to their table.
11.
related with the types of antonym at the following explanation.
4.1.4.1Binary or Complementary Pair
According to Saeed (1997: 66) said that “binary pairs is a relation between
words such that the positive of one implies the negative of the other”. It was like a
44
creatively change the form. The words cannot be used to refer the same thing at the
same time. It is impossible to use both of words.
Data 1:
The club is a smoky west end club, full of smartly-dressed and dubious-looking
men, and young, glamorous, dubious –looking women. (74. Int. Club. Night. Line 3-4)
The words men and women are categories as binary antonym. It can be used
in the same at the same time. Men are plural of man that is an adult male human
being; masculine, while women are also plural of woman. It is an adult female
human being; feminine. The people cannot be said as women and men, but it only
can be said as women or men.
4.1.4.2 Gradable Antonyms
Gradable antonym is words relation that usually find in adjective and
something that can be measured. Saeed (1997) stated that one of the characteristics
of this antonym is usage of “how” and word “very” to ask of something. In other is
the terms are usually relative.
Data 2:
Jenny suddenly looks young in the dress that looks too old for her – other adults are milling around outside, and the women don’t look like girls dressed
45
Young and old are gradable antonym. It means that not young people is not
necessarily an old people. We can use “very” to test this pairs. It is being very
young or very old. Young means suitable for young people. Old means it having
lived or existed for many years. The clothes make user looks older or dated than her
age should be.
Data 3:
a) Helen is as far from everyone’s idea of an aunt as one can get. (15A. Line 7)
b) She kneels and flicks through her half-dozen or so LPs on the floor near a cheap record player ... (2. Line 8)
From the sentence, the relation of words Far and near are gradable
antonyms. Not far is not necessarily near. It expresses distance. To know the
distance, we can use a question word “how”, to be how is far or how is near?
Far is at, to or from a great distance in space or time. Near is not far away in
distance. From the definition above, it can be conclude that far and near have
contrary meaning.
Data 4:
“... and Jenny walking towards it, a small figure in a large playground”. (24.
Ext. School. day. Line 2)
Small and large are gradable antonym. Not small is not necessarily large.
Small is an adjective that is used before describes as comparatively little, limited in
46
4.1.4.3Reverse
This words relation finds out at the term that describes a movement and
process which it can be reversed.
Data 5:
a) He winds down the other window and waves on the cars that have stopped
behind him. (6. Line 16)
b) She has been something on the doorstep, and he stoops to pick it up – a large bunch of flower.(12A. Int/ext. Jenny’s house. Evening. Line 2)
The words down and up are contrary in meaning which tell us in which
direction to move position. That is characteristic of reverse relation. Down is used
to indicate movement from a higher to a lower position. While, up is toward a
higher position.
Data 6:
a) Marjorie kicks the door open with her foot and comes in holding a birthday cake with seventeen candles burning on it. (58. Int. Jenny’s house. Evening.
Line 2)
b) Jenny closes her eyes, makes her wish, blows out her candles. (58. Line 6)
The words open and close are categories as reverse relation that describes a
movement in direction. Open is to move something to a position that is not closed,
or to make something change to a position that is not closed. Close is to (cause
47
Data 7:
She looks neither left nor right but other girls, younger girls, watch her through
the windows as she leaves. (84. Ext. School. Day. Line 5)
The words Left and right categories as reverse relation that describes motion
the following of something. Left means an adjective that means on or towards the
side of your body that is to the west when you are facing north. Right means toward
the side of your body that is to the east when you are facing north.
Data 8:
a) She follows the girls inside (32. Line 9)
b) She stands outside the living room for a moment, listening. (34. Line 1)
The words inside and outside are reverse relations that describes movement
of direction something. Inside describes as in or into a room, building, container, or
something similar. Outside describe as the position when someone is not inside a
building.
Data 9:
a) A waitress comes over to their table. (74. Int. Club. Night. Line 12)
b) Danny nudges David, and they go over to talk to him just as the champagne
arrives. (74. Line 16)
The words come and go are categories as reverse relation that describes a
movement in direction. Come is to move towards a specified person or place
48
Data 10:
a. Danny nudges David, and they go over to talk to him just as the champagne arrives. (74. Int. Club. Night. Line 16)
b. They return to their table. (76. Int. Club. Night. Line 6)
The words go and return are categories as reverse relation that describes a
movement in direction. As previous explanation that go describe as an activity to
move or process to or from a point or in a certain direction (Collins English
Dictionary and Thesaurus). Return is to come or go back to a previous place
(Cambridge Advance Learner’s Dictionary).
4.1.4.4Converse
It is a relationship between two things (or people) from alternate viewpoints
(Saeed, 1997: p. 67). It means that this relationship describe the same relationship
are mentioned in the opposite order.
Data 11:
A mother and two children cross the road in front of her, ... (6. Ext. Bus stop. Day. Line 2)
The words mother and children are converse, because if Xis the mother of
Y, Y are the children of X. Definition of mother is a female parent, while children
is a plural of child which is defined as a boy or girl between birth and adult, or a
son or daughter of any age (Cambridge Advance Learner’s Dictionary). This