DISCOURSE ANALYSIS OF ENGLISH LECTURERS’
SUGGESTION FOR ENGLISH INTENSIVE STUDY
PROGRAM OF IAIN SALATIGA IN THE ACADEMIC
YEAR OF
A GRADUATING PAPER
Submitted to the board of examiners as a partial fulfillment of the
requirements for the degree of Sarjana Pendidikan (S.Pd)
English Education Department of Teacher Training and Education Faculty
State Institute for Islamic Studies of Salatiga
By:
SUGENG ISKANDAR - -
ENGLISH EDUCATION DEPARTMENT
TEACHER TRAINING AND EDUCATION FACULTY
STATE INSTITUT FOR ISLAMIC STUDIES OF
DECLARATION
Bismillahirrahmanirrahim,
In the Name of Allah the Most Gracious the Most Merciful.
Hereby, the writer declares that this graduating paper is written by the writer himself under the title “Discourse Analysis of English Lecturers‟ Suggestion for
English Intensive Study Program of IAIN Salatiga in the Academic Year of
”. This paper does not contain any materials which have been published by
other people and it does not cite any other people‟s ideas except the information from the references.
This declaration is written by the writer to be understood.
Salatiga, August th
The Writer,
Sugeng Iskandar
Ruwandi, M.A.
The Lecturer of English Education Department
State Institute for Islamic Studies (IAIN) Salatiga
ATTENTIVE COUNSELOR‟S NOTE
Case: Sugeng Iskandar’s Graduating Paper
Dear,
Dean of Teacher Training and Education Faculty
Assalamu‟alaikum wr.wb.
After reading and correcting Sugeng Iskandar‟s graduating paper entitled
DISCOURSE ANALYSIS OF ENGLISH LECTURERS’ SUGGESTION FOR
ENGLISH INTENSIVE STUDY PROGRAM OF IAIN SALATIGA IN THE
ACADEMIC YEAR OF , I have decided and would like to propose that
this paper can be accepted by the Teacher Training and Education Faculty. I hope this paper will be examined as soon as possible.
Wassalamu‟alaikum wr.wb.
Salatiga, August th
Counselor,
Ruwandi, M.A.
MINISTRY OF RELIGIOUS AFFAIRS
STATE INSTITUTE FOR ISLAMIC STUDIES (IAIN) SALATIGA TEACHER TRAINING AND EDUCATION FACULTY
Jl. TentaraPelajar No. Telp.( ) Fax. KodePos Salatiga
Website: http://iainsalatiga.ac.id e-mail: administrasi@iainsalatiga.ac.id
A GRADUATING PAPER
DISCOURSE ANALYSIS OF ENGLISH LECTURERS’ SUGGESTION FOR ENGLISH INTENSIVE STUDY PROGRAM OF IAIN SALATIGA IN
THE ACADEMIC YEAR OF
WRITTEN BY: SUGENG ISKANDAR
NIM:
Has been brought to the board of examiners of English education department of state institute for Islamic studies (IAIN) Salatiga on September th , and hereby considered to complete the requirements for the degree of Sarjana Pendidikan (S.Pd).
Board of Examiners, Head : Rr. Dewi Wahyu Mustikasari, M.Pd. Secretary : Ruwandi, M.A.
First examiner : Sari Famularsih, M.A. Second examiner : Noor Malihah, Ph.D.
Salatiga, September th Dean of Teacher Training and
Education Faculty
Suwardi, M.Pd
MOTTO
LIVE ONCE LIVED MEANING
DEDICATION
This graduating paper is sincerely dedicated to:
My beloved parents in my life, Mr. Askan Iskandar and Mrs. Atik Trisnawati, thank you for everything you struggle for me. The words could not explain how
important you are in my life.
My beloved older sister Lina Suciana, she always supports and advises me to continue my study to the higher level.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Bismillahirrahmanirrahin,
In the Name of Allah The Most Gracious the Most Merciful. The Lord of the universe. Because of Allah, the writer could finish this graduating paper.
Graduating paper entitled “Discourse Analysis of English Lecturers‟ Suggestion for English Intensive Study Program of IAIN Salatiga in the Academic Year of
” is presented to the Teacher Training and Education Faculty of IAIN
Salatiga as one of the requirements for Sarjana Pendidikan (S.Pd) of English Education Department of Teacher Training and Education Faculty of IAIN Salatiga.
However, this success would not be achieved without those supports, guidance, advices, helps, and encouragement from individual and institution. It is an appropriate moment for the writer to deepest gratitude for:
. Dr. Rahmat Hariyadi, M.Pd. as the Rector of IAIN Salatiga.
. Suwardi, M.Pd. as the Dean of Teacher Training and Education Faculty of IAIN Salatiga.
. Noor Malihah, Ph.D., as the Head of English Education Department of IAIN Salatiga.
. Ruwandi, M A. as his Consultant. Thanks for all the times in guiding this graduating paper.
. Setia Rini, M.Pd. as my academic counselor who always supports him to finish his study on time and to continue to the master degree.
. All my lecturers of International Class Program of IAIN Salatiga. They have taught and guided him in studying to be a better person and
Eventually, this graduating paper is expected to be able to provide the reader a useful knowledge and information. So, the writer is pleased to accept more suggestion and contribution for the improvement of this graduating paper.
Salatiga, August th
The writer,
Sugeng Iskandar
ABSTRACT
Iskandar, Sugeng. . “Discourse Analysis of English Lecturers‟ Suggestion for
English Intensive Study Program of IAIN Salatiga in the Academic Year of
”. Graduating paper. English Education Department, Faculty of
Teacher Training and Education, State Institute for Islamic Studies of Salatiga. Consultant: Ruwandi, M A.
Keywords: discourse analysis, English lecturers‟ suggestion of English intensive study
program, suggestion strategy, suggestion modification.
This research is aimed to study about the kind of suggestion strategies and the internal and external modification strategies of suggestion also the frequent strategies and the frequent internal and external modification produced by English lecturers in the classroom activity in other to bring up English lecturers‟ pragmatic awareness.
Within the classroom activity, the writer choses the English lecturers which they were teaching in English intensive study program in IAIN Salatiga and they had already at least year of English teaching experiences. In the framework of task-based language teaching, lecturers may adopt the instrument provided about teaching situation. Certainly, the writer uses the pragmatic analysis and qualitative approach.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
COVER ... i
DECLARATION ... ii
ATTENTIVE COUNSELOR’S NOTE ... iii
PAGE OF CERTIFICATION ... iv
MOTTO ... v
DEDICATION ... vi
ACKNOWLEDGMENT ... vii
ABSTARCT ... ix
TABLE OF CONTENTS ... x
LIST OF TABLES AND FIGURE ... xii
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION
A. Background of the Study ... B. Problem of the Study ... C. Objectives of the Study ... D. Significance of the Study ... E. Definition of Key Terms ... F. Organization of Graduating Paper ... CHAPTER II THEORITICAL FRAMEWORK
. Research on Speech Act of Suggestion ... . Taxonomy of Suggestion Strategy ... . Taxonomy of Downgraders to Soften Suggestion ... . Internal and External Modifiers of Suggestion ... CHAPTER III RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
A. Research Location ... B. Research Approach ... C. Subject of the Study ... D. Technique of the Data Collection and Instrument ... E. Unit of Analysis ... F. Procedures of Analysis ... G. Technique of the Data Analysis ... CHAPTER IV FINDINGS AND DISCUSSION
A. Data Findings ... . Suggestion Strategies of English Lecturers‟ Suggestion ... . English Lecturers‟ Perspective on Suggestion Strategies ... . Internal and External Modifiers Used by English Lecturers ... B. Data Analysis ...
. Suggestion Strategies of the English Lecturers‟ Suggestion ...
. Internal and External Modifiers Used by English Lecturers ... C. Discussion ... D. Summary ... CHAPTER V CLOSURE
A. Conclusions ... B. Suggestions ... BIBLIOGRAPHY
CURRICULUM VITAE
LIST OF TABLES AND FIGURES
Table . Force levels of directives
Table . Taxonomy of suggestion linguistic realization strategies Table . Taxonomy of downgraders selected to soften suggestions
Table . List data of the subjects
Table . Taxonomy of the suggestion strategies Table . External and internal modification strategies Table . Strategy of English lecturers‟ suggestion linguistic Table . English lecturers‟ suggestion perspective on interviewing Table . Distribution of English lecturers‟ suggestion from WDCT
questionnaire
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
This chapter represents an introduction to the study of speech act about suggestion production that produced by English lecturers of English Intensive Study Program as an explicit instruction in the teaching process. It describes how the writer conducts this study about Speech Act competence toward lecturers‟ utterance of suggestion while teaching in the class of English Intensive Study Program in IAIN Salatiga. The fundamental details of study are described as following topics: Background of the Study, Problem of the Study, Objectives of the Study, Significance of the Study, Scope of the Study, Definition of Key Terms, and Organization of Graduating Paper.
A. BACKGROUND OF THE STUDY
English Intensive Study Program or usually called as “SIBI”. This term is an Indonesian abbreviation from several words is “Studi Intensif Bahasa Inggris” in IAIN Salatiga which held by language service unit of IAIN Salatiga. This is the program which helps the first and second semester students to learn about English language intensively and obligated to the all students of IAIN Salatiga. This program
is aimed to increase students‟ quality especially in English language proficiency to
confront the globalization era which an English language became an international language in the all aspects of interaction with the people in this world.
teacher/lecturer has six areas of classroom activity that can be summarized as an information provider, role model, facilitator, assessor, planner, and resource developer.
According to the English learning about speech act suggestion as the theory of this research, it will need lecturers that expert in English language to perform this theory in the class activity. Therefore, the writer will conduct a research toward English lecturers‟ utterance of IAIN Salatiga about their suggestion act production while teaching activity to students to convey suggestion utterance and English
lecturers‟ perception about the kind of suggestion strategies that used in the teaching
activity. English lecturer of English intensive study program is a person who teaches about English language in the program of English Intensive Study Program.
English lecturer of English Intensive Study Program is a central figure for students in the classroom. He plays the important role to conduct learning and teaching processes of the classroom activities. He also creates the atmosphere of the classroom, whether it is comfortable for the students or not. According to Harden and Crosby ( ), a lecturer has six areas of classroom activities that can be summarized as an information provider, role model, facilitator, assessor, planner, and resource developer.
Reviewing the lecturer as a role model, Squires ( ) and Alexander ( , cited in Dogarel and Nitu, ) notes that lecturers may not see themselves as models, and may even regret the very idea as pretentious and paternalistic, but it is difficult for learners not to be influenced by the living example set before them. For the reason, it doesn‟t matter what the lecturer‟s role in the classroom, he always acts as the model and the center of students‟ attention (Bruner, ). It is lectures‟
appropriately. Students get models of language not only from textbooks, reading materials and of all sorts and from audio and video tapes, but also from the lecturer‟s way of teaching and speaking (Harmer, ). The students will adopt what their lecturer usually speaks in the classroom. A lecturer should be continuously conscious of his potential as the model for language use. The language that lecturer uses and the way he uses can have a powerful influence on students‟ language development, their motivation to use language, and the development of their facility for language.
A lecturer uses two types of communication to transmit the message to the students in the class. The types are verbal and nonverbal communication. Tubbs and Moss ( ) stated that verbal communication is all kinds of oral communication that use one word or more. On the other hand, nonverbal communication refers to a process of communication form without using words to generate meaning (Pearson, et al., ; Pan, ). Many of the research in communication studies (Anderson ; McCroskey, Richmond, Plax, & Kearney, , cited in Seachou, )
discover that verbal and nonverbal communication affect cognitive, affective, and behavioral learning. Therefore, a lecturer should consider their communication ways that produces different effects to the students.
Generating good communication with the students could be fascinating and challenging at the same time. This situation could happen because the student might have a different interpretation when the lecturer produces utterances. The meanings of the word “utterance” are an action of saying or expressing something aloud and an
or a change of speaker (Crystal, ). Schiffrin ( ) considered that utterance is units of language production as quoted below.
Regardless of these difficulties, the view that I will take in this book is that discourse can best be thought of as “utterances”. I will view utterances as units of language production (whether spoken or written) that are inherently contextualized; whether (or how) they are related to sentences (Schiffrin, ).
Therefore, the teachers have to negotiate the meaning between them. In
producing utterances, such as “Would you like to take the chalks?”, “Please, close
the door!” or “Could you be silent?”, the teacher is not only produce the grammatical
and lexical forms of what is said (McCarthy, ) but also produce actions to ask the students to perform actions. Action produced by utterances is called speech acts (Allen and Perrault, ).
Searle ( , cited in Wardhaugh, ) declares that speech acts can be divided into three different kinds. There are utterance acts, propositional acts, and illocutionary acts. In this study, I will focus on the discussion of Illocutionary act. Illocutionary acts have to do with the intents of speakers. It includes report, announce, predict, admit, ask, reprimand, suggest, order, propose, express, congratulate, promise, thank, exhort, and request (Leech, ).
Based on the explanation above, the writer would like to conduct a study about the types of suggestion modification used by English lecturers of English Intensive Study Program and the various strategies by which suggestion strategies are produced in the classroom entitled “DISCOURSE ANALYSIS OF ENGLISH
LECTURERS‟ SUGGESTION FOR ENGLISH INTENSIVE STUDY PROGRAM
B. PROBLEM OF THE STUDY
Based on the background of the study, the writer will attempt to analyze the study of speech act competence about the taxonomy of suggestion linguistic realization strategies and internal and external modification strategies. Further, the writer has formulated the problems of the study to answer the following questions:
. What are the kinds of suggestion strategies produced by English lecturers of English intensive study program?
. What are the internal and external modifiers of suggestion produced by English lecturers of English intensive study program?
. What is the most frequent suggestion strategies and the internal and external modifiers of suggestion used by English lecturers of English intensive study program?
C. OBJECTIVES OF THE STUDY
The focus of this study is on English lecturers‟ suggestion of English Intensive
Study Program of IAIN Salatiga and the objectives of the study are listed below: . To describe and analyze about the kinds of suggestion strategies produced by
English lecturers of English intensive study program.
. To describe and analyze about the internal and external modifiers of suggestion produced by English lecturers of English intensive study program. . To find the most frequent suggestion strategies and the internal and the
external modifiers of suggestion used by English lecturers of English intensive study program.
D. SIGNIFICANCE OF THE STUDY
According to Creswell ( : ), the significance of the study should describe the importance of the study for selected audiences. Therefore, the writer expects that this study meaningfully contributes to give some benefits to the
discourse analysis focused on English lecturers‟ suggestion of English Intensive
Study Program. They are:
. Theoretically
This form of the study will provide the reader how is the role of suggestion types and strategies in the speech act competence. The results of this study can provide information to the English lecturers of English Intensive Study Program dealing with what they should deliver to the students from their utterances of suggestion. Thus, this study can become a guideline for the English lecturers to improve their materials.
. Practically
knowledge on the discourse analysis of the English lecturers‟ suggestion of English Intensive Study Program.
E. DEFINITION OF KEY TERMS
. Discourse
The term of the word “discourse” was derived from the Latin verb
„discurrere‟ which means „to run back and forth‟. Discourse is a term used in
linguistics to refer to a continuous stretch of language larger than a sentence. Moreover, Tannen ( , cited in Schiffrin, ) explains about the definition of discourse as language beyond the sentence:
Discourse – language beyond the sentence – is simply language – as it occurs, in any context (including the context of linguistics analysis), in any form (including two made-up sentences in sequence; a tape recorded conversation, meeting, or interview; a novel or play). The name for the field „discourse analysis‟, then, says nothing more or other than the term „linguistics‟ the study of language.
In addition, Crystal ( ) explains that discourse is a set of utterances which connected with speech events such as a conversation, a joke, a sermon, an
interview. On the other hand, the word analysis was derived from Latin „analusis‟
which means „unloose‟. Analysis was detailed study or examination of the
. Suggestion Act
According to Searle ( ), suggestion act belongs to the group of directive speech acts which the speaker‟s purpose is to get the hearer to commit him herself
to some future course of action. Puts more simply, directives are attempts to make the world match the words. Bach and Harnish‟s ( ) definition of directives also implies that the speaker‟s attitude and intention when performing an utterance
must be taken as a reason for the hearer‟s action. In this sense, suggestion acts are
regarded as an imposition upon the hearer by affronting his/her negative face (Banerjee and Carrel ).
F. ORGANIZATION OF GRADUATING PAPER
This linguistic study contains five chapters, namely: introduction, theoretical framework, research methodology, findings and discussion, and conclusion (closure).
Chapter I is introduction. It contains the background of this study that
describes the reason why the writer conducts the study on the discourse analysis of
English lecturers‟ suggestion of English intensive study program. This chapter also
contains statement of the problems, objective of the study, the significance of the study, the definition of key terms, and organization of the paper.
Chapter II is theoretical framework. It presents the explanation of beliefs
Chapter III describes the research methodology. It tells about why and how
this study used descriptive quantitative research as the type of this study. The design of the research, subject of the research, data collection, data analysis, and procedure of the research are also presented in this chapter.
Chapter IV is findings and discussion. It presents the data findings that have
been gained through documentation and recorder from the English lecturers of English intensive study program (SIBI) regarding their beliefs about grammar teaching. This chapter also covers the discussion of the data findings.
Chapter V is closure. It contains the conclusion which covers also the closure
CHAPTER II
THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
This chapter presents the comprehensive theories which will be the basis for this study. It takes a part as the foundation in determining the extent of the research. Since the research concerns on the discourse analysis of English lecturers‟ suggestion of English Intensive Study Program, this research will be included into some theories of suggestion strategies that according to the concepts of pragmatics area such as speech acts and the study of discourse analysis. This chapter likely covers the discussion of discourse analysis, review of utterance theories, and review of speech acts, theories of suggestion and internal external modifiers of suggestion.
A. DISCOURSE ANALYSIS
Discourse analysis is a board term for the study of the ways in which language is used in texts and contexts. Also called discourse studies. According to Abraham and Harpham Developed in the s, discourse analysis is concerned with “the use of language in a running discourse, continued over a number of sentences, and involving the interaction of speaker (or writer) and auditor (or reader) in a specific
situational context, and within a framework of social and cultural conventions” (A
Glossary of Literary Terms, ).
etc. identified by discourse analysis to characterize different social and cultural factors which aid in the interpretation and understanding of different texts and types of talk.
The scope of discourse analysis is not restricted only with the description and analysis of written data, but also the organization of spoken from such as talk, conversation, communicative event, etc. (McCarthy, , cited in Jabber and Jinquan). Furthermore, cook ( , cited in Prokopova, ) states that discourse analysis examines how wide are the discussion of it by considering its textual, social, and psychological context that become meaningful for the users.
Therefore, there are so many definitions related to the discourse analysis. It has different definitions according to different fields or academic disciplines, but most of them explain that the definition of the discourse analysis is about the meaning beyond the sentences, the study of language use, and the investigation of what that language is used for in social practice (Brown and Yule, ; Schiffrin, ; Gee, ).
B. REVIEW OF UTTERANCE THEORIES
There is not a consensus to give clear explanation about the definition of an utterance. Some experts provided several different descriptions dealing with the discussion. According to Hurford et al. ( ), utterance is any stretch of talk before and after which there is silence on the part of that person. It is used by a particular speaker, on a particular occasion, of a piece of language, such as a sequence of sentences, or a single phrase, or even a single word.
speaking without interruption by speech of the other, constituting a single turn. Then, it has semantic completion, defines a single speech act and separated by a pause.
Utterance could be said as core point in speech. Utterance means what is said by any one person before or after another person begins to speak. It commonly defines as a sequence of words within a single person‟s turn at talks. (Richards and
Schmidt, ). It means that when people have a conversation, utterance exists in it. It is also executed in order to have some effects on the hearer. This effect typically involves modifying the hearer‟s beliefs or aims. It produced an action and
took a result or effect to perform actions for the hearers. In addition, Capone ( , cited in Mey, ) in the book of Concise Encyclopedia of Pragmatics also explains the purpose of utterance‟s use in the conversation between speaker and hearer
“To speak a language is to express thoughts in the form of linguistic utterances that employ words and follow combinatorial rules. When a person A speaks communicatively, she transmits a thought to a hearer H with a certain official aim and possibly with other consequential effects. By an utterance, a speaker can inform the hearer of a certain situation, express an inner state of mind (emotions or feelings), or modify the behavior of the recipient. In all cases, a certain thought is expressed by the vocalization of an utterance. (Capone, )”.
C. REVIEW OF SPEECH ACTS
. Definition of Speech Acts
Speech act is a kind of verbal communication. The words speech acts are derived from two words „speech‟ and „act‟. Speech is the utterance that occurs and act means action. That is the reason why people have to interpret the meaning of communication or language through speech acts. People do not only produce utterances which contain grammatical structure and lexical form when they speak, but also perform action through those utterances (McCarthy, ). Similarly, Austin ( ) states that speech acts are an act refers to the actions that is performed in producing an utterance. Based on these opinions above, it can be concluded that speech act is the act performed by a speaker in uttering a sentence. The functions of the speech act itself is to state the speaker‟s intention to the
hearer.
Yule ( ) proposes that speech acts is performed action via utterance. Another definition from Soekemi ( ) mentions that speech act is a theory which analyses the role of utterance in relation to the behavior of speaker and listener in interpersonal communication.
According to Austin ( ), speech act is theory of performative language in which to say something is to do something. In brief when speakers are saying words, they not only produce utterance containing words and grammatical structure, but they also perform action in those utterances.
physical condition, attitudes, abilities, beliefs and the relationship existing between the speaker and the listener.
According to Searle ( , cited in Justova, ), an American language philosopher, speaking a language is performing speech acts, acts such as making statements, giving commands, asking questions, making suggestion or making promises. He states that all linguistic communications involve speech acts. In other words, speech acts are the basic or minimal units of linguistic communication.
. Theory of Speech Acts
Sadock ( ) mentioned that Austin was a former expert who begins the modern study of speech acts. Speech act theory was developed by Austin in an endeavor to explain how particular utterances apply within natural language. He begins the study engaging monograph „How to Do Things with Words‟, the published version of his William James Lectures delivered at Harvard in . The book is a cited work starts with the observation included the certain sorts of sentences such as “I christen this ship the Joseph Stalin; I now pronounce you
man and wife”. These both sentences seem designed to do something rather than
to say something. Such sentences are dubbed by Austin with performative and, on
the contrary, dubbed with constative for such sentences like “my daughter is
called Elizabeth” that only to say something and make statement or assertion.
In addition, Austin ( ) was interested in how words produced not only to provide information and facts, but also how these words performed action. For instance, the different both utterances like “I see a boy” and “I promise that I will
come tomorrow”. In the first utterance, the speaker provides information about
only gives information about plans tomorrow, but also offers a promise. The verb “promise” has a different function of the force contained within the words. Austin
classified the special types of „force-word‟ as performatives, which clearly
different with normal statements and assertion like in the first example. The other
examples of „force-word‟ includes „beg, warn, apologize, declare, etc.‟ Then, by
using these words of performatives, the speaker is performing the utterances which are called speech acts.
. Types of Speech Acts
There are three types of speech acts:
) Locutionary Acts
A locutionary act is the performance of an utterance, and hence of speech act. The term equally refers to the surface meaning of an utterance, because according to Austin ( ) “How to Do Things with Words”, a speech act should be analyzed as a locutionary act (i.e. the actual utterance and its ostensible meaning, comprising phonetic, phatic and rhetic acts corresponding to the verbal, syntactic and semantic aspects of any meaningful utterance). It can be recognized by the hearer.
Example:
If someone says „knock the door!‟ the locutionary acts is the
realization of the speaker‟s utterance.
) Illocutionary Acts
An Illocutionary act is performing an act in saying something, what is done in uttering the word, the function of the word, the specific purpose that
the speaker‟s have in mind. Searle ( ) set up the following classification
a) Assertive: an illocutionary act that speech acts commit to a speaker to the truth of the expressed proposition. The acts are stating, claiming, hypothesizing, describing, telling, insisting, suggesting, asserting, and asserting that something is the case.
Example:
Stating: staff and VIP permitted here
b) Directive: an illocutionary act for getting the addressee to do something by responding to an utterance or by performing some physical actions. The acts are ordering, commanding, defying, advising, asking, begging, challenging, daring, demanding, forbidding, insisting, inviting, permitting, recommending, requesting, suggesting, etc.
Example:
Command: Close the door please!!!
Forbid, Prohibit Don‟t close the door!!!Don‟t go to the party!
c) Expressive: an illocutionary act that expresses the speakers feeling and attitudes toward events or affairs. The acts are congratulating, thanking, deploring, condoling, welcoming, apologizing.
Example:
Condoling : I am sorry to hear that.
Congratulating : Hey Bro, congrats for your success
Example:
Naming : I named my baby Amanda.
e) Verdictive: an illocutionary acts in which the speaker makes an assessment or judgement about the acts of another, usually the addressee. The acts are ranking, assessing, appraising, condoning. Verdictive verbs include accuse, charge,excuse, thank in the explicit.
Example:
Assessing: you have low score in undestanding Syntax.
) Perlocutionary Acts
Perlocutionary act is an act that is uttered to affect the listener. An utterance that is uttered by someone often has effect to the listener. Which can be expected or unexpected affect that created by the speaker. So, in other word, a perlocution is listener behavioral response to the meaning of the utterance, not necessarily physical or verbal response, perhaps merely a mental or emotional response.
There is an example of speech acts. A child refuse to lie down and go to sleep, then his mother says, “I‟ll turn your light off”. The locutionary act is
. Speech Acts Function
In contrast to Austin, who focused more on the speaker‟s intention in their
speaking, Searle more focuses on how listeners respond what are the speakers intended to (Wardaugh, ). The concept of the illocutionary act is central
to Searle‟s understanding of speech acts. According to Wardaugh ( ),
“Searle has concentrated his work on speech acts on how a hearer perceives a
particular utterance to have the force … an utterance”. Searle ( ), as mentioned by Celce-Muria and Olstain ( ), proposes five functions to describe the illocutionary acts. These are:
a.
RepresentativesRepresentatives commit the speaker to the truth value of the expressed proposition. These kinds of speech acts state what the speaker believes to be the case or not (Yule, ). Representatives are statements of fact including assertion, conclusion, description, reporting, explanation, etc. consider the following examples of representatives:
) The sun sets to the west.
) Adam Levine is not a dancer but a top singer.
) It‟s cloudy here.
b.
Directives) You should say something to her. ) Go to the bathroom right now!
) Would you mind to hang out with me?
c.
CommissivesCommisives commit the speaker‟s intention to some future course of action. It can be performed by himself or as or the representation of a member of a group. They are promises, threats, refusals, pledges, etc (Yule, ). These are the examples of commissive acts:
) I will not come to your wedding party. ) I promise I will never make affair again. ) I will back as soon as possible.
d.
Expressives
Expressives are used to show, state, and express the speaker‟s
physiological feelings. It refers to the speaker‟s experiences, whether is his
own experiences or the hearer‟s experiences. It can be the statement of
pleasure, pain, likes dislike, joy, or sorrow (Yule, ). Expressives are among the most important speech acts for English foreign and second language learners Celce-Muria and Olstain ( ). The following will show the examples of expressive:
) Congratulations, you got the top position. ) I am sorry, betrayed my promise.
e.
DeclarationsDeclarations are kinds of speech acts that change the world via utterance (Yule, ). The speaker has to have a special institutional role in a special context to perform a declaration. It‟s only effective when stated
by the appropriate authority. It includes declaring war, marrying, firing and hiring from employment, etc. the examples of declarations are as follows:
) Umpire: the shuttle cock is out!
) The dictatorial leader: I declare a war with your clan.
D. THEORIES OF SUGGESTION
Suggestion belong to the group of directive speech acts which according to Searle ( ), are those the speaker‟s purpose is to get the hearer to follow what the
aim of the speaker by the action in the future. Bach and Harnish‟s ( ) definition
of directives also implies that the speaker‟s attitude and intention when performing
an utterance must be taken as a reason for the hearer‟s action. Moreover, one relevant feature affecting directives in opposition to other speech act, such as representatives or commissives (Searle ), refers to the necessary interaction between the speaker and the hearer in order to get the speech act performed. As Trosborg ( : ) points out, “only in the case of directives is the hearer‟s subsequent act (getting
things done) part of the speaker‟s intentions. As stated by Thomas ( ), both
speaker and hearer are to be taken into account when producing directive speech acts.
another. Taking into account the assumption that there are different kinds of directives, Haverkate ( ) provides a specific definition for exhortative speech acts which also implies that the speaker wants the hearer to do something. This author distinguishes between impositive and non impositive directives. The former group includes more threatening acts, such as requesting, pleading and ordering, whereas non-impositives directives refer to suggestions and instructions. The main difference between these two groups lies in the fact that the benefits obtained by carrying out an impositive speech act are exclusively for the speaker, whereas the objective of the non-impositive speech acts is to benefit the hearer. Thus, a clear distinction between request and suggestions is important, since both speech acts belong to the same category of directives and as suggested by Thomas ( ), one relevant principal of pragmatics involves the fact that some speech acts may overlap. For this reason, previous literature addressing directives has already distinguished request and suggestion on the basis of the benefit of the action (Searle ; Rintell ; Edmonson and House ; Banerjee and Carrell ; Trosborg ). As Rintell
( ; ) states, “in a suggestion, the speaker asks the hearer to take some action
which the speaker believes will benefit the hearer, even one that the speaker should desire”.
. Directives
Directives express the speaker‟s attempt to get the hearer doing something
because of the speaker‟s intention. Searle ( ) gives the notion of
directives as the utterance that uttered by the speaker to get the hearer doing
what the speakers wants to do to him or her. Austin‟s behabitives and exercitives
are including in this Searle‟s directives. Directives include in the form of asking,
inviting, permitting, advising, etc. that give the direction to the hearer to do something in accordance with the speaker‟s instruction.
The forms of directives are various because they different way to get the hearer do what the speaker wants or intends to do. The speaker as a person who forces the hearer to do something can choose the way how he/she states the directives. According to Holmes ( , cited in Mustikasari, ), there are several scales of directives that show different various level of directives to force the hearer do the speaker‟s intention. It can be showed by the figure below.
Figure Force Levels of Directives
Speech function : Directive
Speech act : Command, order
Request
Advise, recommend
Invite
Suggest
Hint
Increasing force
The above figure shows the levels of speech act force. The force‟s levels
are getting higher from the bottom to the top. The level of force that starts from the lower to the higher position is hint, suggest, invite, advise/recommended, request, and command/order. The discussion about the levels of suggestion will be presented in the further explanation.
. Research on Speech Act of Suggestion
With regard to research dealing with the speech act of suggesting, Schmidt et al. ( ) claim that suggestions have received less attention in comparison to the speech act of requesting, this has been extensively investigated. In their own words, the authors ( : - ) state that “in analyzing commercials as suggestions, we are somewhat hampered by the lack of detailed studies of this speech act and requests have been investigated intensively, but the speech act of suggestion, a cousin of the request, has been much less studied”. Moreover, most
of the research that has dealt with this speech act, as well as the studies that have regarded suggestions as advice acts, consist of cross-cultural pragmatic studies (Rintell ; Boatman ; Banerjee and Carrell ; Altman ; Hu and Grove ; Wierzbicka ; Hinkel , ), with only a few studies from the field of ILP (Bardovi-Harlig and Hartford , ; Koike , ; Alcon ; Matsumura , ). A detailed description of these studies is provided in the two subsections that follow.
. Taxonomy of Suggestion Strategy
other hand, they adopt the variety of pragmalinguistic formulae that have been examined in previous research on pragmatics (Edmonson and House, ; Wardhaugh, ; Banerjee & Carrel, ; Koike, ; Tsui, ; Schmidt et al., ; Koester, ; among others) and Bardovi-Harlig and Hartford‟s ( ) maxim of congruence, which involves the appropriateness of the specific strategies according to the speaker‟s status relative to one another in a given
situation. For the clear information about taxonomy of suggestion strategies,
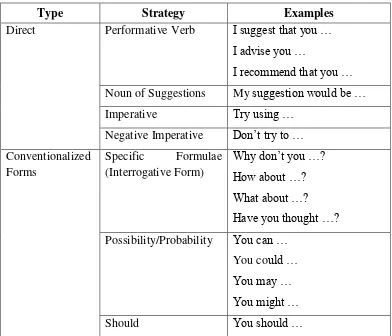
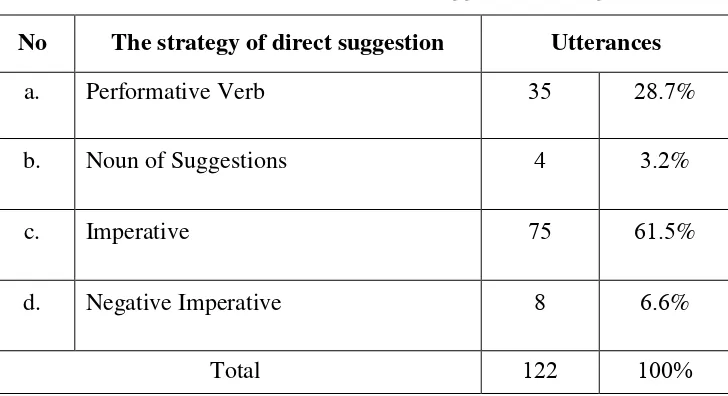
Table . presents such taxonomy of suggestion linguistic realization strategies from Fauzul Aufa, ( ; ) in international journal on studies in English language and literature (IJSELL) which is divided into three main types: ( ) direct; ( ) conventionalized; and ( ) indirect forms.
Table . Taxonomy of suggestion linguistic realization strategies (from Fauzul Aufa, ; )
Type Strategy Examples
Direct Performative Verb I suggest that you … I advise you …
Need You need to …
Conditional If I were you, I would … Indirect Impersonal One thing (that you can do)
would be …
Here‟s one possibility …
There are a number of options that you …
It would be helpful if you … It might be better to … A good idea would be … It would be nice if …
Hints I‟ve heard that …
The first type of suggestion involves that of direct strategies, in which the speaker clearly states what he/she means. Direct suggestions are performed by means of performative verbs, a noun of suggestion, imperatives and negative imperatives (e.g. I suggest that you buy a new computer). The type of conventionalized forms used to make suggestions still allow the hearers to understand the speaker‟s intentions behind the suggestion, since the illocutionary force indicator appears in the utterance, although this second type of suggestion realizations is not as direct as the first type. Within this group, there is a greater variety of linguistic realizations to be employed, such as the use of specific formulae, expressions of possibility or probability, suggestions performed by means of the verbs should and need, and the use of the conditional (e.g. Have you thought about buying a new computer?). Finally, the group of indirect suggestions refers to those expressions in which the speaker‟s true intentions are
suggestion. The use of different impersonal forms has been regarded as a way of making indirect suggestions and the use of hints is considered the most indirect type of comment that can be employed in order to make a suggestion (e.g. it would be helpful if you bought a new computer).
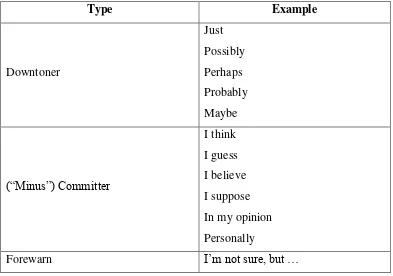
. Taxonomy of Downgraders to Soften Suggestion
Apart from the linguistic realizations employed to make a suggestion, it is also important to pay attention to those modification devices that serve to soften the suggestion. As the writer has already mentioned, suggestions are Face-Threatening Act (FTA) and as such should be softened and mitigated in order to „minimize the threat to the hearer‟s face‟.
In order to account for the use of modification devices in the chapter, we have considered the classification proposed by House and Kasper ( ), since their study on the use of modality markers was the first to examine the use of these markers to either mitigate (downgraders) or intensify (upgraders) the force of the speech act. Specifically, the authors define downgraders as those markers that play down the impact that a speaker‟s utterance may have on the hearer,
Table . Taxonomy of downgraders selected to soften suggestions
The first type that of downtoners consists of sentence modifiers which are used by the speaker in order to soften the impact his/her utterance is likely to have on the hearer (e.g. You could perhaps buy a new computer). The second type, minus committer, refers to a type of modifier employed by the speaker to lower the degree of his/her commitment to the state of affairs referred to in the utterance by explicitly showing his/her personal opinion (e.g. in my opinion, you should buy a new computer). The third type, that of forewarn, expresses a kind of anticipatory device used by the speaker to forewarn the hearer about possible negative reactions to the act he/she is about to employ. This downgrader usually consists of a preliminary metacomment about what the speaker is going to do in order to soften what could be a potential offence. For this reason, forewarn
makes use of the conjunction but before stating the actual speech act (e.g. I‟m
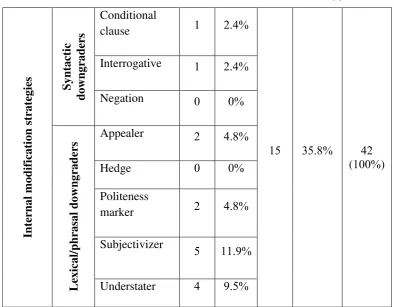
. Internal and External Modifiers of Suggestion
Internal and external modifiers of suggestion also known as “suggestion
modification” which are used to soften or strengthen the speech act of
suggestion. The speaker will have appropriate and successful suggestions using these mitigating devices because the speaker will successfully perform the socially accepted suggestions.
According to Fauzul Aufa‟s ( ) journal which adopted his resources of his theory from Trosborg ( ), there are two modifications of suggestion that can be discussed for further theory of the suggestion types. Certainly, the modifications make the suggestions more appropriate and polite in certain contexts. They are:
a.
Internal ModifiersInternal Modifiers refer to the tools employed to soften the
impositive of the suggestion‟ utterances. Trosborg ( ) distinguished
two types of Internal Modifiers:
) Syntactic Downgraders
Syntactic downgrader is the structure of the sentence that is used to soften and decrease the imposition of suggestion‟s utterance.
As Trosborg ( ) states that syntactic downgraders have three categories of suggestion, namely conditional clause, interrogative,
and negation.
a) Conditional Clause
Employed by speakers to distance themselves from the suggestion.
Example:
I would like to ask, if you could maybe to do this firsthand?
b) Interrogative
The structure of the sentence used to downtone the impact of the suggestion by appealing to the hearer‟s consent.
Example:
Could you point me the clear solutions for this problem?
c) Negation
The structure of the sentence employed by speakers to downtone the force of the suggestion by indicating their lowered expectations of the suggestion being given.
Example:
You couldn‟t repeat what you have explained
please?
) Lexical/Phrasal Downgraders
According to Trosborg ( ), lexical/phrasal downgraders have five categories, namely appealer, hedge, politeness marker, subjectivizer, and understater. Here, I will specify each of those categories.
a) Appealer
This category used by the speakers to appeal the hearer‟s
Example:
You know, you shouldn‟t drink too much
alcohol…..
b) Hedge
This category used to indicate tentativeness, possibility and lack of precision.
Example:
Is it possible if we can arrange a meeting during holidays somehow?
c) Politeness marker
This category employed by the speakers to bid for their hearer‟s cooperation.
Example:
Could you give more explanation, please? d) Subjectivizer
Explicitly, this category expressed by the speaker to show his or her subjective opinion to the state of affairs referred to in the proposition.
Example:
I believe morality is important than appearance e) Understater
Example:
That might be a bit better for us than the junk food……
b.
External ModifiersExternal modifiers are also called as “supportive moves” of the suggestion utterances. They are additional devices used to support the suggestion‟s utterances. In contrast to internal modifiers in which using the
head act of suggestions or the actual suggestions, external modifiers are preceding and or following the head act of suggestions. In addition, they support the head act in order to make the speaker suggestion‟s utterances
are being vaguer for the hearer (Achiba, ; Blum-Kulka et al., , cited in Al-Gahtani and Alkahtani, ). According to Trosborg ( ), an external modifier has four categories, namely grounder, preparatory, imposition minimizer, and disarmer. The writer will specify each of those categories in the following below.
) Grounder
The function of this category is to provide reasons, explanations, and justifications for the suggestions.
Example:
Emm, unfortunately, I really don‟t understand this topic
here….
) Preparator
Example:
May I give you a suggestion?
) Imposition Minimizer
The function of this category is to reduce the imposition placed on the hearer by the suggestion offered.
Example:
I will return them immediately, the next day….
) Disarmer
The function of this category is to remove any potential objection the hearer might raise.
Example:
I am not trying to be smart, but I just need you to….
CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
This chapter represents the methodology and method of the research which will be discussed and explained through the points that was provided in the research methodology area. The writer will use the method of descriptive quantitative approach that will help this research by using a questionnaire sheets that named by Written Discourse Completion Task (WDCT) which contains some situations practiced by the English lecturers of English intensive study program in the classroom activity and interviewing section. The contains of this chapter are research location, research approach, subject of the study, technique of the data collection and instrument, unit of analysis, procedures of analysis, and technique of the data analysis.
A. RESEARCH LOCATION
This research is conducted in the campus of IAIN Salatiga at Jl. Tentara Pelajar No. SALATIGA Central Java, Indonesia. IAIN Salatiga located in the central of Salatiga city and near to the public park named Pancasila. IAIN Salatiga is the only one of Islamic campus in Salatiga because there are two institutions has been constructed in Salatiga, namely; Satya Wacana Christian University (UKSW) and State Islamic Institute for Islamic Studies (IAIN) Salatiga.
B. RESEARCH APPROACH
This study uses a descriptive quantitative approach. Descriptive analysis means to analyze the data which has been described; it is the study based on the English
lecturer‟s suggestion utterances of English Intensive Study Program taken from
The analysis in quantitative approach concerning in calculating and understanding the result of found data.
This study is quantitative approach model, since the writer describes the phenomena of the study in numbers and measurements of it instead of words. Creswell ( ) states that quantitative research is descriptive the numbers in which the writer is interested calculating, numbering and understanding gained through numbers. The data of the study are collected in the form of the numbers rather than the words.
In this study, the writer used the analysis of discourse as a tool to analyze a set
of selected suggestion‟s utterances of the English lecturer of English Intensive Study
Program from WDCT questionnaire. The objective of this study using WDCT
instrument (QUESTIONNAIRE) is to inform the speaker‟s pragmalinguistic
knowledge about the speech act suggestions with its strategies and linguistic forms where the result can be implemented (Kwon, ). Bebee and Cummings ( ) also describe a WDCT as highly effective instrument to collect the strength data for discourse studies. In addition, Houck and Gass ( ) explain that the using of WDCT allows the writer to collect a large amount of data in a short period. Therefore, WDCT is an appropriate way to collect the data for this study since the purpose of this study is to show the result of the subject‟s utterances of suggestion
and it takes a short time to elicit the data.
C. SUBJECT OF THE STUDY
competence about speech act of suggestion‟s utterances. The selection of the subjects
was done on the basis of the following criteria:
. They were English lecturers of English Intensive Study Program of IAIN Salatiga in the Academic Year of .
. They were enrolled in English Language Education or assistants of English lecturer of English Intensive Study Program in teaching English subject.
. All the subjects had already at least year of English teaching experiences. . All the subjects are Indonesian lecturers of English as a Foreign Language.
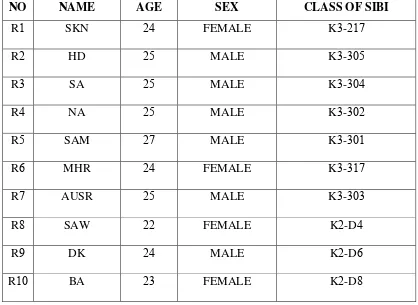
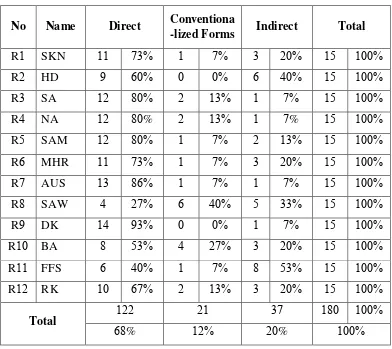
The list data of the subjects is presented in the table . . The writer only writes
down the initial of the subjects‟ name because of keeping the confidence of them.
Besides that, the writer confidentially keeps the identity of the subjects in order to make the subjects are comfortable to give the data.
Table . List data of the subjects
NO NAME AGE SEX CLASS OF SIBI
R SKN FEMALE K -
R HD MALE K -
R SA MALE K -
R NA MALE K -
R SAM MALE K -
R MHR FEMALE K -
R AUSR MALE K -
R SAW FEMALE K -D
R DK MALE K -D
R FFS FEMALE K -C
R RK MALE K -A
The writer prefers to choose the lecturers of English Intensive Study Program because the lecturers are the alumni of English Education Department of IAIN Salatiga that use English fully in the teaching and learning process. It will effect on
the suggestion‟s utterances that they produce because of their habitual activities. For
the reason, the writer would like to analyze the strategies of the teachers‟ suggestion to the students.
D. TECHNIQUE OF THE DATA COLLECTION AND INSTRUMENT
The data is collected using a Written Discourse Completion Task (WDCT) questionnaire. A WDCT questionnaire is a pragmatics instrument containing a set of very briefly described situations in which aims to elicit a certain data of speech act research (Kogetsidis, ; Varghese and Billmyer, ). In this task, the lecturers are asked to respond appropriately in written form based on the situational description given on the questionnaire paper. The questionnaire consists of certain
situations that enable the subjects to produce the suggestion‟s utterances. The
questionnaire is followed by some situations and blank spaces. Therefore, the writer asks them to give responses and write what they would say in each situation with
lecturer‟s suggestion. English lecturers have to imagine that the speakers in the real
situation. For example in WDCT questionnaire:
Situation
Your answer:
………......
Situation
You teach your students in the classroom. In the middle of your teaching there was a student who feels sleepy, so you want him to pay attention to your explanation of the lesson. What suggestion would you make in this situation?
Your answer:
………......
Based on the situations above, the subjects are guiding to produce the suggestion utterances in the blank spaces provided. They have to answer WDCT questionnaires in English. The writer will take two weeks to conduct a research and to get a data from the subjects.
E. UNITS OF ANALYSIS
The units of analysis are both of the categorization and classification of main levels of suggestion strategies and the internal and external modification strategies of suggestion.
. Lecturer‟s Utterances
In this sub of units analysis, the writer will analyzes the utterances of the lecturer through the questionnaire that given to the lecturers as the respondents. The writer will choose every utterance that given in the written form on the questionnaire sheets to analyze into the taxonomy of the suggestion strategies and the internal and external modification strategies.
. Lecturer‟s Suggestion Perceptions
In this analysis, the writer will focus on the lecturers‟ suggestion
to know their perceptions of the suggestion based on the taxonomy of suggestion and the internal and external modification strategies of the suggestion.
F. PROCEDURES OF ANALYSIS
Interpreting the data is classifying and calculating it based on the theoretical framework of main and supporting theories. They are Martinez-Flor, on the categorization and classification of main levels of suggestion‟s directness strategies and Trosborg ( ) on the internal and external modification strategies.
G. TECHNIQUE OF THE DATA ANALYSIS
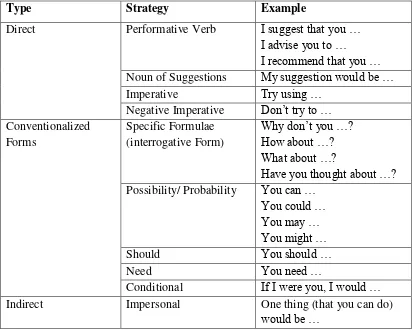
The data collected were reduced and analyzed according to a modified taxonomy of the suggestion strategies by Martinez-Flor ( ) that I have taken from
Fauzul Aufa‟s ( ) English Journal that I provide in table . .
Table . Taxonomy of the Suggestion Strategies taken from Fauzul Aufa‟s ( ) English Journal and adopted from Martinez-Flor ( )
Type Strategy Example
Direct Performative Verb I suggest that you … I advise you to …
I recommend that you … Noun of Suggestions My suggestion would be …
Imperative Try using …
Here‟s one possibility … There are a number of options that you …
It would be helpful if you … It might be better to … A good idea would be … It would be nice if …
Hints I‟ve heard that …
In the present study, suggestions were examined according to the type of strategies, internal, and external modifications. The suggestion head acts were codified based on three degrees of directness:
. Direct Forms (DF)
. Conventionalized Forms (CF) . Indirect Forms (IF)
Each level of directness comprised various strategies. For example, in CF suggestions, the suggestion perspective was analyzed according to the specific formulae, such as the use of interrogative forms, or the use of modal to show possibility e.g. can, may, could, and might, or whether the suggestion uses should or
need, or by usingconditional forms, e.g. if I were you, I would …
Table . External and Internal Modification Strategies from Fauzul Aufa‟s ( ) English Journal which adopted from (Trosborg, )
External Modification Strategies
Name Function Examples
Grounder Provides reason, explanations, and justifications for the suggestions
Erm, unfortunately, I really don‟t understand this topic here …
Preparator Short utterance that intends to prepare the hearer for the suggestions
Disarmer Remove any potential objection the hearer might raise
I am not trying to be smart, but I just need you to …
Internal Modification Strategies
Type Name Function Examples
Syntactic Interrogative Used to downtone the
impact of the suggestion
Negation Employed by speakers to downtone the force of the
hearer‟s cooperation please? Subjectivizer Explicitly expressed by
the speaker to show his or her subjective opinion to the state of affairs referred to in the proposition
I believe morality is important than appearance …
Understater Adverbial modifiers used to underrepresent the state of affairs referred to in the proposition
That might be a bit
better for us than the junk food …
On the other hand, External Modifications involved four supportive moves that either will proceed or follow a suggestion head act, namely: grounders, preparators, imposition minimizers, and disarmers. While the Internal Modifications divided into two downgraders, namely: syntactic downgraders and lexical/phrasal downgraders. The two downgraders also have many names for each downgraders, for the names of Syntactic Downgraders has three names are conditional clause, interrogative and
CHAPTER IV
FINDINGS AND DISCUSSION
This chapter will describe about the linguistic pragmatic study on speech act suggestion and the result of the research that the writer will combine and proves between his research and the object of linguistic study. This chapter has two sections that present
the data findings and its analysis of English lecturers‟ suggestion. The first section is the
presentation of data findings. It consists of English lecturers‟ suggestion strategies, the
use of internal and external modifiers of suggestion, and English lecturers‟ perspective
about suggestion strategies. The second is about the data analysis. The third is the discussion of the data findings. Finally, the writer summarizes the data findings and analysis of the data. This section consists of the analysis of the research questions.
A. DATA FINDINGS
In this section, the writer would like to present the main data that have been elicited from WDCT questionnaire of English lecturers‟ suggestions. From the data
findings, the writer grouped them based on the taxonomy of suggestion linguistic
realization strategies from Fauzul Aufa‟s ( ) English Journal which adopted from
. Suggestion Strategies of English Lecturers’ Suggestion
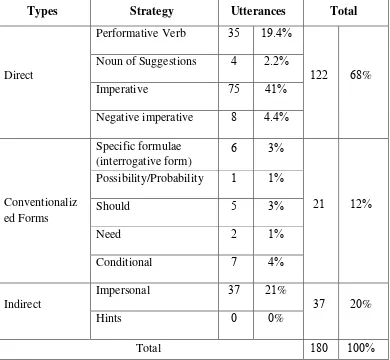
Based on the research data, the writer found that globally English lecturers of English Intensive Study Program often produced the direct suggestion strategy rather than conventionalized forms and indirect strategy. The occurrence of direct strategy is % of the data as the first strategy. For the occurrence of conventionalized form as the second strategy is %. Finally, the occurrence of indirect suggestion is %. It existed as the third strategy that frequently occurred on the chart. The distribution of English lecturers‟ suggestion can be shown in table . .
Table . Strategy of English Lecturers‟ Suggestion Linguistic
Types Strategy Utterances Total
Table . demonstrates that the direct suggestion is the most frequent ( %) as a strategy of request rather than conventionalized form ( ) and
indirect suggestion ( %). The result of this study contradicted to Fauzul Aufa ( ), he has found about EFL learners‟ suggestion strategies. Fauzul Aufa
( ) investigated his research about „the use of Discourse Completion Task
(DCT) as explicit instruction on Indonesian EFL learners‟ production of
suggestion acts that studying university in Queensland‟. He found that an indirect strategy is more frequent than two other suggestion strategies and also in the form of Internal and External suggestion strategies, he found that the internal modification strategies is more frequently used by Indonesian EFL learners. The writer supposes that this difference is a matter of grammatical and pragmatical issue especially in suggestion strategies emerged of the data source. Fauzul collected the data from the native speaker of Indonesian EFL learners who study in university in Queensland that produced Indonesian suggestions while he collected the data from the native speaker of Indonesian EFL learners that
produced English suggestions. Fauzul‟s study involved the subject participants
The writer involved the lecturers as subject that produced suggestions to the students. And based on the data information, they preferred to choose direct suggestion as a strategy to convey their intention to the students. The writer would like to describe the detail information about the distribution of English
lecturers‟ suggestion strategy in the following section.
. English Lecturers’ Perspective on Suggestion Strategies
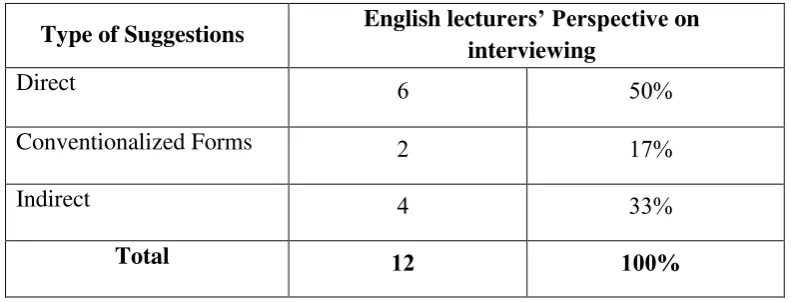
Here, the writer will provide for the reader about the data result of the research from interviewing and questionnaire sheets which has been formulated in the next table with the explanation.
From the table . below is the result of interviewing section, it can be seen that the English lecturers preferred to choose direct suggestion strategy
whether conventionalized forms or indirect suggestion strategy. The writer has conducted an interview to twelve English lecturers of English intensive study program to give their opinions about the most appropriate suggestion‟s strategy used to the students.
Table English Lecturers‟ Suggestion Perspective on Interviewing
Type of Suggestions English lecturers’ Perspective on
interviewing
Direct
Conventionalized Forms
Indirect