PROCEEDINGS OF
2015 INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON INFORMATION &
COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY AND SYSTEMS (ICTS)
Surabaya, September 16
th, 2015
(ISSN: 2338-185X)
(ISBN: 978-1-5090-0095-1)
Organized by
Department of Informatics
Faculty of Information Technology
2015 INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON INFORMATION &
COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY AND SYSTEMS (ICTS)
Copyright and Reprint Permission:
PROCEEDINGS OF
2015 INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON INFORMATION &
COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGY AND SYSTEMS (ICTS)
EXECUTIVE BOARD
Joni Hermana
Rector
Agus Zainal Arifin
Dean of Faculty of Information Technology
Nanik Suciati
Head of Department of Informatics
Keynote Speakers
Shinobu Hasegawa (Japan Advanced Institute of Science and Technology)
Simon Perrault (National University of Singapore)
Tomohiko Igasaki (Kumamoto University)
Scientific Committee
John Batubara
Paul Strooper
Tsuyoshi Usagawa
Akira Asano
Yoshifumi Chisaki
Keiichi Uchimura
Katsuhisa Maruyama
Pitoyo Hartono
DoHoon Lee
SungWoo Tak
Han-you Jeong
Stephanne Bressan
Kai-Lung Hua
Iping Supriana
Supeno Djanali
Handayani Tjandrasa
Riyanarto Sarno
Joko Lianto Buliali
Arif Djunaidy
Mohd Shafry Mohd Rahim
Mohd Shahrizal Sunar
Kuncoro Wastuwibowo
Ford Lumban Gaol
Karen Blackmore
Ilung Pranata
Siska Fitriani
Gou Koutaki
Ahmad Hoirul Basori
Kutila Gunasekera
Nanik Suciati
Chastine Fatichah
Royyana Muslim Ijtihadie
Tohari Ahmad
Beben Benyamin
Agus Zainal Arifin
Waskitho Wibisono
R.V. Hari Ginardi
Siti Rochimah
Daniel Oranova Siahaan
Soegianto Soelistiono
Indah Agustien
Arif Muntasa
I Gede Pasek Suta Wijaya
Faisal Rahutomo
Fitri Utaminingrum
I Komang Somawirata
A.N. Afandi
Heru Sukoco
General Co-Chair
Darlis Herumurti
Radityo Anggoro
Finance Chair
Dwi Sunaryono
Secretary Chair
Abdul Munif
Organizing Committee
Adhatus Solichah A
Baskoro Adi Pratomo
Diana Purwitasari
Dini Adni Navastara
Hudan Studiawan
Isye Arieshanti
Ratih Nur Esti Anggraini
Victor Hariadi
Wijayanti Nurul Khotimah
ISSN: 2338-185X
ISBN: 978-1-5090-0095-1
CONTACT ADDREESS
Department of Informatics
Faculty of Information Technology
Institut Teknologi Sepuluh Nopember (ITS) Surabaya
Gedung Teknik Informatika, ITS
Jalan Teknik Kimia, Kampus ITS Sukolilo, Keputih, Surabaya, Indonesia 60111
Tel. (+62)-31-5939214 Fax. (+62)-31-5913804
! "
# $ % & " "$
' (
$ )
%* '
'
+ , $ $ -* # #( $
./. 0$ . 1 , ($ ,
$ + $ . #$ , ($ ,"$ 1
0 ' ( 2
1 0' *
$ 3 1 $ 4 $ $ ,%
1 5 ' " #"
$ & *%0 $& *% $
( $ 6"7 $ # 3 $ 2
+ $+ + '
" ( * " ( *
8'0 ( * $0$9$1$
$- $0 $0"$$0 ': *%
) % ( *
'$ ) % % ;
+'"2 *$+ $+#$+'%%'
" *
' % & " ., '
'-6( '0
" * (" "
'
3$ *
'
Table of Contents
KN-Keynote Speech
KN-1
How ICT Changes Quality Assuarance in Graduate Education and Research? - From Knowledge Transfer
to Cognitive Skill Improvement -
(1 - 2)
Shinobu Hasegawa
KN-2 Interaction with Wearable Computers: Challenges and Perspectives
(3 - 4)
Simon Perrault
KN-3
Measurement and Processing for Potential of Unbalanced Complex Kinetics of Heart Rate Variability
(5
-6)
Tomohiko Igasaki
T1-Track 1
T1-1
Detection of Alzheimer's Disease using the Statistical Approach from 3D Magnetic Resonance Image
(7
-10)
Devvi Sarwinda, Ibnu Daqiqil Id
T1-2
Ultrasound B-mode Imaging using Adapted Time of Flight for Ultrasound Fat Measurement Sensor
(11
-16)
Norlida Buniyamin, M. Hazwan Abdul Halim, Zainuddin Mohamad
T1-3 Support Vector Machine with Multiple Kernel Learning for Image Retrieval
(17 - 22)
Muhammad Athoillah, Isa Irawan, Elly Imah
T1-4 Porn Picture Files Scanning Method Based On The Number of Picture Files In A Directory
(23 - 28)
Ario Yudo Husodo, I Gede Pasek Suta Wijaya
T1-5
Analysis Of Cement Sales Forecast Pattern Changes In Cement Indonesia Ltd (Persero) Using Artificial
Neural Network :East Java Sales Area
(29 - 34)
Wiwik Anggraeni, Avia Riska Syofiani
T1-6 Spinal Curvature Determination from X-Ray Image using GVF Snake
(35 - 40)
Madha Christian Wibowo, Tri Arief Sardjono
T1-7 A New Implementation Of Cultural Algorithms based on Inter-Personal Interaction Influence
(41 - 48)
Arash Zaeim, Mahdi Hassani Goodarzi, Mahdi Masoomzadeh
T1-8
Teeth Segmentation on Dental Panoramic Radiographs Using Decimation-Free Directional Filter Bank
Thresholding and Multistage Adaptive Thresholding
(49 - 54)
Rarasmaya Indraswari, Agus Zainal Arifin, Dini Adni Navastara, Naser Jawas
T1-9
Protein Family Identification using Markov Chain as Feature Extraction and Probabilistic Neural
Network (PNN) as Classifier
(55 - 60)
Toto Haryanto, Rizky Kurniawan, Sony Muhammad
T1-10 Calving Events Detection and Quantification from Time-lapse Images in Tunabreen Glacier
(61 - 66)
Sigit Adinugroho, Dorothée Vallot, Pontus Westrin, Robin Strand
T1-11 General Pattern Identification of Debugging System
(67 - 72)
Falahah Suprapto, Iping S Suwardi, Kridanto Surendro
T1-12 Color Correction Using Improved Linear Regression Algorithm
(73 - 78)
T1-13 Improving Tibia and Femur Segmentation Recovery Based on Double Labelling Technique
(79 - 82)
Kardiva Indah Pangestuti, Eko Mulyanto Yuniarno, I Ketut Eddy Purnama
T1-14 Document Subjectivity and Target Detection in Opinion Mining Using HMM POS-Tagger
(83 - 88)
Amir Hamzah, Naniek Widyastuti
T1-15
Identification of Oil Palm Plantation in Ikonos Images using Radially Averaged Power Spectrum
Values
(89 - 94)
Soffiana Agustin, R.V. Hari Ginardi, Handayani Tjandrasa
T1-16
K-Medoids Algorithm on Indonesian Twitter Feeds for Clustering Trending Issue as Important Terms in
News Summarization
(95 - 98)
Diana Purwitasari, Chastine Fatichah, Isye Arieshanti, Nur Hayatin
T1-17 Fast Discrete Curvelet Transform And HSV Color Features For Batik Image Classification
(99 - 104)
Nanik Suciati, Agri Kridanto, Mohammad Farid Naufal, Muhammad Machmud, Ardian Yusuf
Wicaksono
T1-18 An Epileptic Attack Detection Based on The Princple Components Analysis (PCA)
(105 - 108)
Siswandari Noertjahjani, Adhi Susanto, Risanuri Hidayat, Samekto Wibowo
T1-19 Images Processing of Facial Expression to Predict the Customer Opinion towards a Product
(109 - 112)
Adang Suhendra, Anneke Annassia Putri Siswadi, Astie Darmayantie
T1-20
Implementation of Naïve Bayes Method for Product Purchasing Decision using Neural Impulse Actuator
in Neuromarketing
(113 - 118)
Tryono Taqwa, Adang Suhendra, Matrissya Hermita, Astie Darmayantie
T1-21 Classification of Textile Image using Support Vector Machine with Textural Feature
(119 - 122)
Ratri Pawening, Rohman Dijaya, Thomas Brian, Nanik Suciati
T2-Track 2
T2-1
Ease of Use Analysis of In-Game Interface Design in DotA 2 for Beginners Using Saw Method
(123
-126)
Arvyn Dila Wijaya, Fuad Baskara, Mutiara Romana Kusuma, Richard Simon Bernhard
T2-2
Human Body Electromagnetics Radiation for Physical and Psychological Conditions of Down Syndrome
and Non-Down Syndrome Person
(127 - 132)
Zunairah Hj Murat, R.S.S.A. Kadir, Nadiah Kamaruzaman, Mastura Rosdi
T2-3
Improving Concentration Through Picture Selecting Game Based on Kinect Sensor for Student with
Intellectual Deficiencies
(133 - 136)
Dandhi Kuswardhana, Nenden Nur'Aeni, Juhanaini, Shinobu Hasegawa
T2-4 Review of A Framework for Audiovisual Dialog-Based in Human Computer Interaction
(137 - 140)
Hasanudin, Marina Agathya, Muhammad Brilliant Subaweh, Rizky Akbar, Sri Supadmini
T2-5 3D ITS Campus on the Web: A WebGL Implementation
(141 - 144)
Anny Yuniarti, Ardian Atminanto, Anggi Mardasatria, Ridho Rahman Hariadi, Nanik Suciati
T2-6
Sitting to Standing and Walking Therapy for Post-Stroke Patients using Virtual Reality System
(145
-150)
Wijayanti Nurul Khotimah, Rizka Wakhidatus Sholikah, Ridho Rahman Hariadi
T2-7
Visualization Model of Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) Telematics Services Potentiality Map in
Indonesia
(151 - 156)
Eneng Tita Tosida, Sufiatul Maryana, Hermawan Thaheer, Ferdy Arrahman
T2-8 First Aid Simulation Game With Finite State Machine Model
(157 - 162)
T2-9
Batik Classification using Neural Network with Gray Level Co-occurence Matrix and Statistical Color
Feature Extraction
(163 - 168)
Christian Sri Kusuma Aditya, Mamluatul Hani'ah, Rizqa Raaiqa Bintana, Nanik Suciati
T3-Track 3
T3-1 A Multi-Strategy Approach for Information Extraction of Financial Report Documents
(169 - 174)
Siti Mariyah, Dwi Hendratmo Widyantoro
T3-2 Analysis of Virtual Worker Website freelancer.com
(175 - 180)
Axelyo Primastomo, Eva Utari Cintamurni Lubi, Ferdi Areanto, Gerry Hadiwijaya, Rina Noviana
T3-3
An Evaluation of Twitter River and Logstash Performances as Elasticsearch Inputs for Social Media
Analysis of Twitter
(181 - 186)
Pingkan P. I. Langi, Widyawan, Warsun Najib, Teguh Bharata Adji
T3-4
Synchronizing Learning Material on Moodle and Lecture Based Supportive Tool: The REST Based
Approach
(187 - 192)
Irwan Kautsar, Shin-Ichiro Kubota, Yasuo Musashi, Kenichi Sugitani
T3-5
A Study of Students’ Acceptance Toward Mobile Learning in Higher Education Institution in
Indonesia
(193 - 196)
Sary Paturusi, Arie Lumenta, Yoshifumi Chisaki, Tsuyoshi Usagawa
T3-6
Improving the Accuracy of COCOMO’s Effort Estimation Based on Neural Networks and Fuzzy Logic
Model
(197 - 202)
Riyanarto Sarno, Johannes Sidabutar, Sarwosri
T3-7
Decomposition Using Refined Process Structure Tree (RPST) and Control Flow Complexity Metrics
(203
- 208)
Indra Gita Anugrah, Riyanarto Sarno, Ratih Nur Esti Anggraini
T3-8 A Conceptual Information Technology Framework to Support Rice Farming in Timor Leste
(209 - 214)
Edio Da Costa, Handayani Tjandrasa, Supeno Djanali
T3-9
Mobile Apps for Schedulling of Medical Staff in Emergency Condition using Integer Programming
(215
-218)
Ahmad Saikhu, Victor Hariadi, Laili Rochmah
T4-Track 4
T4-1 Traffic Congestion Distribution in Social Opportunistic Networks
(219 - 224)
Bambang Soelistijanto
T4-2
Increasing the capacity of the secret data using DE pixels blocks and adjusted RDE-based on Grayscale
Images
(225 - 230)
Mohammed Hatem Ali Al-Huti, Tohari Ahmad, Supeno Djanali
T4-3 Modification of Key Scheduling For Security Improvement in XTEA
(231 - 236)
Osvari Arsalan, Achmad Imam Kistijantoro
T4-4 Prototype of Cloud Based Document Management for Scientific Work Validation
(237 - 240)
Agus Muliantara, Ngurah Agus Sanjaya Erawan, I Made Agus Setiawan, I Made Widiartha
T4-5
Design and Implementation of Digital Signal Processing Algorithm on ARM Cortex M4 Microcontroller
Based Pulse Oximetry System
(241 - 244)
Pratondo Busono
Pratondo Busono
T4-7 An Efficient Grid-Based Framework for Answering Tolerance-Based Skyline Queries
(251 - 256)
2015 International Conference on Information, Communication Technology and System
PROTOTYPE OF CLOUD BASED DOCUMENT
MANAGEMENT FOR SCIENTIFIC WORK
VALIDATION
Agus Muliantara
1), Ngurah Agus Sanjaya, I Made Widiartha, I Made Agus Setiawan
Computer Science Department, Udayana University
Badung, Bali, Indonesia
1)
Abstract— One of the main tasks of lecturer is to conduct research faculty and publish research results in a scientific paper. To avoid plagiarism, University of Udayana commissioned the University Quality Assurance Agency (BPMU) and each faculty to validate the scientific work of lecturers. At the university level work files are uploaded through the system, while at the faculty level are still using physical file. If the validation process at both the faculty and the university can be done through one door, then the time and cost required can be minimized. However, scientific work digitizing system also has shortcomings because it takes a large storage media. Therefore we need an information system validation scientific work that is supported by the efficient management of storage media.
This study will be conducted over two years with a case study in the scientific validation process in Unud. In the first year, the study was divided into several processes such as system need analysis, system architecture design, implementation code, test and evaluation. At this stage of the second year, the study will focus on further exploration technologies Cloud Computing and Cloud Storage.
Outcomes achieved in this study is the first year: Scientific Validation System, International Seminar Dissemination, Publication in the National Accredited Journal. While in the second year: Scientific Work System Applications, International Seminar Dissemination, Publication in the National Accredited Journal.
Keywords— system for scientific paper validation, cloud based document management
I. INTRODUCTION
As mandated in UU No. 14 year 2005 on Teachers and Lecturers, lecturers are expressed as professional educators and scientists with the main task of transforming, developing, and disseminating science, technology, and arts through education, research, and community service (Chapter 1 Article 1 paragraph 2). Meanwhile, professionals are expressed as jobs or activities carried out by someone and become a source of income that requires expertise, skills, or skills that meet
certain quality standards or norms and require professional education.
A case of plagiarism in 2010 by a professor gave setbacks to education in Indonesia and should be taken as a lesson to prevent it from happening again in the future. The president and professors of the university are encouraged to give insight to prospective professors to act commendable and have individual awareness that a professor is a respectable position both in academia and in the community. Improvements should be made on the process of achieving the rank of a professor and must be accompanied by a rigorous selection process.
Udayana University, as the largest state university in Bali, are concerned with preventing plagiarism among its lecturers. The Regulation of the Udayana University President number 2 in 2012 stated that all scientific papers of lecturers that will be used for academic needs (promotion and academic positions) must be validated in stages. The validation process starts from the Faculty / Department and ends at the University. This move is expected to create a better scientific culture, and prevent the occurrence of scientific dishonesty in the university. On the other hand, the policy of Directorate General of Higher Education (DIKTI) also explicitly states that if there is scientific fraud such as plagiarism in any scientific works that are used for gaining academic promotion, then the sanction is given not only to the perpetrator, but also to the institution in which the entire promotion and academic positions which occurred in the same year will be disallowed.
Based on this, Udayana University through the Quality Assurance Agency (BPMU) published a guide or manual procedures to validate the scientific work. The standard operating procedure (SOP) for validating scientific work in Udayana University include steps required and things that need to be validated as well as the duties and functions of the Scientific Validation Team. The SOP is made with reference to the regulations of the Minister, DIKTI and also regulations of the President of Udayana University. It is expected that each faculty to know and comply with the steps in validating the publication of scientific works (BPMU, 2012).
2015 International Conference on Information, Communication Technology and Systems (ICTS)
However, in practice, there is still an issue on the validation process between the faculty and the university. The scientific work files that have been uploaded through the current system was not used in the execution of validation. Thus, the validation process still needs the hard copy of the scientific paper.
Based on this problem, it is necessary to develop a system that is able to perform validation and review in an integrated manner and only use softcopy of the scientific paper. This approach would gain some advantages, among others:
1. Paperless, because we only use the softcopy version of the article.
2. Safe, no file would be lost.
3. Better searching, by using the integrated system, each person who takes part in the validation process will have a better way of searching for files..
II. CLOUD TECHNOLOGY
Cloud computing is a subscription-based service that provides access to the storage space and computer resources connected to the network. One-way to understand cloud computing is to think about the experience of using email. Email service providers like Yahoo, Gmail, Hotmail, etc., take care of the problems associated with the software and hardware needed to support personal email account users. When the user wants to access email so he only needs to open the browser on his computer, typing in their email address and login providers. The most important part of the process is the
availability of internet access. Email users are not physically stored on his personal computer, he can access it anywhere with an internet connection.
III. SCIENTIFIC WORK VALIDATION IN
UDAYANA UNIVERSITY
The scientific work is valid if it meets two aspects: eligibility and authenticity. Aspects of eligibility generally include several criteria: knowledge coverage, insight aspiration, recency, exposure, analysis and synthesis of scientific work, contribution for advancement of science and technology. Existing flow of validation process in Udayana University can be seen in Figure 1.
IV. SYSTEM DESIGN
At this stage, the system will be built and installed within the single web server. The main objective is to focus on the process of realizing the scientific work validation system. To support the implementation of this first phase, the research is divided into several sub-phases.
A. Requirement analysis
Elicitation of system requirements is done in this stage. In order to achieve that, the results of the preliminary study are evaluated and the validation process is further studied. Related parties are also interviewed, including the agency who is responsible for coordinating the process of scientific work
validation (BPMU).
1
Fig. 1. Flow diagram for validation of Scientific works
1
This research was funded by BOPTN-Udayana University with contract number 103.43/UN14.2/PNL.01.03.00/2014, March 3rd 2014
All possible processes and procedures that have been identified are confirmed and checked for its correctness with BPMU. Identification of functional and non-functional requirements of the system is based on interviews and studies that have been done before. The functional and non-functional requirements of the system are then used as the basis for determining the modules and features of the system. It also serves as a guide in the design process OF both the platforms that will be used later as well as application development framework and its software architecture.
B. Architecture design
At this stage, we will conduct software architectural design based on the functional and non-functional requirements that have been defined in the previous stage. In the first year, the research will be focused on the development of minimal features that the system must meet (functional requirements). Thus, the system functional requirements will be prioritized, but we will still provide room for customization to meet the non-functional requirements of the system such as system access speed and the level of safety and the possibility of other non-functional requirements.
The tools and technologies to develop the software will also be selected as well as the language to be used (web-based system using CodeIgniter framework and object-oriented programming). For the first phase, an overview of the system design of scientific work validation can be seen in Figure 2.
Fig. 2. Validation Flowchart
C. Implementation
With the completion of the design of the software to be developed, then the next phase is implementation. The implementation process will be carried out following software development standards (Coding Style Convention), so that the software code is more manageable later. In addition, the programming process will also use version control to manage changes of the code. Using version control will ensure that we have history of changes made to the code.
D. Testing and Evaluation
To ensure that the features implemented will run smoothly, it needs to be tested. Experiments carried out by testing must-have features one by one (black box). In addition, testing will also carried out by using scenarios that have been previously defined. The scenarios represent real life environment where the application will be used. Testing results will then be evaluated and improved and can also be collected and used as considerations for the next development iteration process.
E. Results and Discussion 1) Requirements analysis
At this stage, the system requirements analysis is conducted by interviewing the users, in this case BPMU and reviewers.
a)Functional requirements
The functional requirements are 1) the system must be web based, 2) the ability to delegate a reviewer for a scientific work, 3) online grading for reviewers, 4) lecturers are able to upload his papers online. The system is expected to perform basic database functions such as Create, Read, Update, Delete (CRUD) on research type. The types of research are Dosen Muda, Hibah Udayana, Kajian Wanita, Hibah Bersaing, Hibah Pascasarjana, Hibah Pekerti, Hibah Kompetensi, Insentif Dasar, Hibah Strategis Nasinoal, Fundamental, and Hibah
Kerjasama. The system is also expected to perform data management on type of publication, publication’s category (local, national, or international). System can record the number of authors in a scientific work. It also has to keep track of comments history for each scientific work. The system is able to perform an assessment of the scientific work.
b)Non-functional requirements
The system is able to perform news, announcements and guidelines management. A survey to reviewers is also conducted in this stage. The survey is carried out to find a review model that can improve the comfort of the reviewer in conducting the review process.
2) System design and implementation a)System flow
Once we obtained the functional and non-functional requirements of the system, the next step is to design the system flow. The flow of the scientific work validation system can be seen inFigure 2.
b)Entity relationships diagram (ERD)\
Entities involved in the scientific work validation system are lecturers, scientific works, reviewers and validators. The ERD of the system is shown in Figure 3.
Fig. 3. Overview of ERD System
3) System features
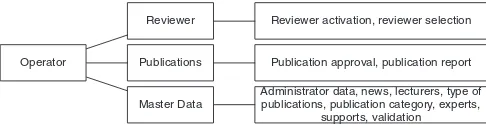
There are four main roles in the systems: operator, lecturer, administrator and reviewers. Each of these roles needs specific features and they are shown in Figure 4, Figure 5 and Figure 6.
Operator
Reviewer
Publications
Master Data
Reviewer activation, reviewer selection
Publication approval, publication report
Administrator data, news, lecturers, type of publications, publication category, experts,
supports, validation
Fig. 4. Operator functionalities
Lecturer Publications
Publications data, print list of publications, check publications
status, print validation result
Fig. 5. Lecturer’s functionalities
Year and Semester Master Data
Master Admin
Master of Fields
Data Admin
Administrator
News, guidelines, lecturer, faculty, group, static page, of• ce, department, rank,
signature of approval, level
Master of Fields
Type of publications, publications category, publications status
Fig. 6. Administrator’s functionalities
The system is not only used by those who competent in computer and information technology, but also those who are competent in other fields. This became the basis of the interface model that is carefully designed in order for the navigation and control menu to be understood easily.
Figure 7 shows an example of the menu interface. This menu is used to select reviewer. The validation system has been tested using black box method. Black box analysis is carried out on all functionalities of each user category. Results of the black box testing indicate that the entire system has functioned properly. This proves that the system can perform all required functions.
Fig. 7. Reviewer selection interface
F. Conclusion
The conclusions obtained from the research are:
a. There are two main requirements of the system: BPMU as the organizers of the validation process and reviewers want the validation process to be simple. b. Scientific work validation system developed in this
research has functioned properly and met the requirements of scientific work validation at the Udayana University. This can be seen from the result analysis of testing the system’s features.
c. The system is able to improve BPMU’s performance in terms of efficiency and effectiveness as a quality improvement media in Udayana University.
G. References
[1] BPMU Universitas Udayana,2012, “Standar Operasional Prosedur Validasi Karya Ilmiah”, Universitas Udayana
[2] CAT, 2010. “Cloud Computing Basics”. http://www.south.cattelecom.com/Technologies/CloudComputing/00716 26948_chap01 .pdf. 27 April 2013.
[3] Direktorat Jenderal Pendidikan Tinggi, 2010, “Pedoman beban kerja dosen dan evaluasi pelaksanaan tridharma perguruan tinggi”,Departemen Pendidikan Nasional.
[4] Huth, A., Cebula, J. 2011. “The basics of cloud computing”. Carniege Mellon University.