Mut Somoeun, 2014
THE INFLUENCE OF PRINCIPAL LEADERSHIP
AND ENGAGEMENT OF SCHOOL COMMITTEE TOWARD THE EFFECTIVENESS OF IMPLEMENTING SCHOOL-BASED MANAGEMENT
: Descriptive Study at Public Elementary Schools in Coblong Sub-district, in Bandung City, Indonesia
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu in Bandung City, Indonesia)
By: MutSomoeun (1206808)
ABSTRACT
School-based management (SBM) is an educational reform through decentralizing the decision-making authority from the central office to local school. However, the effectiveness of SBM implementation is based on principal leadership in performing roles and responsibilities and participation of school committee.
The purpose of this study is to analyze how the influence of principal leadership and engagement of school committee have been implementing at the public elementary schools in Coblong sub-district in Bandung city.
The method used in this study is the descriptive-quantitative approach with techniques of statistical calculation and correlation of data analysis. The data are collected by giving questionnaires to 72 respondents (36 principals and 36 school committees) with population of 36 public elementary schools. The closed-ended questionnaires are used with five options of Likert Scale by focusing on three
dimensions of principal’s major roles, including: instructional leadership, community leadership, and visionary leadership; and five dimensions of school
committee’s major roles, including: making school policies, policy appraisal,
provision of financial resources, public relation, and educational planning and evaluation.
The results of this study found that: (1) the influence of principal leadership has high impact (36.24%) on the effectiveness of implementing school-based management; (2) the engagement of school committee has high impact (37.45%) on the effectiveness of implementing school-based management; and (3) both the influence of principal leadership and engagement of school committee have high impact (49.14%) on the effectiveness of implementing school-based management.
Based on results, it can be concluded that the principal’ performances and
school committees’ participations at those public elementary schools in Coblong
sub-district in Bandung city are at high level.
Mut Somoeun, 2014
THE INFLUENCE OF PRINCIPAL LEADERSHIP
AND ENGAGEMENT OF SCHOOL COMMITTEE TOWARD THE EFFECTIVENESS OF IMPLEMENTING SCHOOL-BASED MANAGEMENT
: Descriptive Study at Public Elementary Schools in Coblong Sub-district, in Bandung City, Indonesia
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
KETERLIBATANKOMITE SEKOLAH TERHADAP EFEKTIVITAS PELAKSANAAN MANAJEMEN BERBASIS SEKOLAH (Studi Deskriptif di Sekolah Dasar Negeri di Kecamatan Coblong,
di Kota Bandung, Indonesia)
By: Mut Somoeun (1206808)
ABSTRAK
Manajemen berbasis sekolah (MBS) adalah reformasi pendidikan melalui desentralisasi otoritas pengambilan keputusan dari kantor pusat ke sekolah-sekolah lokal. Namun, efektivitas pelaksanaan MBS didasarkan pada kepemimpinan kepala sekolah dalam menjalankan peran dan tanggung jawab dan partisipasi darikomite sekolah.
Tujuan dari penelitian ini adalah untuk menganalisis bagaimana pengaruh kepemimpinan kepala sekolah dan keterlibatan komite sekolah telah menerapkan di sekolah dasar negeri di Kecamatan Coblong di kota Bandung.
Metode yang digunakan dalam penelitian ini adalah pendekatan deskriptif-kuantitatif dengan teknik perhitungan statistik dan korelasi analisis data. Data dikumpulkan dengan memberikan kuesioner kepada 72 responden (36 kepala sekolah dan 36 komite sekolah) dengan populasi 36 sekolah dasar negeri. Kuesioner tertutup-berakhir digunakan dengan lima pilihan dari Likert Scale berfokus pada tiga dimensi peran utama kepala sekolah, termasuk: kepemimpinan instruksional, kepemimpinan masyarakat, dan visioner kepemimpinan; dan lima dimensi peran utama komite sekolah, termasuk: kebijakan pembuatan sekolah, penilaian kebijakan, penyediaan sumber daya keuangan, humas, dan perencanaan dan evaluasi pendidikan.
Hasil penelitian ini menemukan bahwa: (1) pengaruh kepemimpinan kepala sekolah memiliki dampak yang tinggi(36.24%) pada efektivitas pelaksanaan manajemen berbasis sekolah; (2) keterlibatan komite sekolah memiliki dampak yang tinggi(37.45%) pada efektivitas pelaksanaan manajemen berbasis sekolah; dan (3) kedua pengaruh kepemimpinan kepala sekolah dan keterlibatan komite sekolah memiliki dampak yang tinggi (49.14%) pada efektivitas pelaksanaan manajemen berbasis sekolah.
Hasilnya dapat disimpulkan bahwa 'pertunjukan dan komite sekolah' para pelaku partisipasi di sekolah-sekolah dasar negeri di Kecamatan Coblong di kota Bandung berada pada tingkat tinggi.
Mut Somoeun, 2014
THE INFLUENCE OF PRINCIPAL LEADERSHIP
AND ENGAGEMENT OF SCHOOL COMMITTEE TOWARD THE EFFECTIVENESS OF IMPLEMENTING SCHOOL-BASED MANAGEMENT
: Descriptive Study at Public Elementary Schools in Coblong Sub-district, in Bandung City, Indonesia
117
Mut Somoeun, 2014
THE INFLUENCE OF PRINCIPAL LEADERSHIP
AND ENGAGEMENT OF SCHOOL COMMITTEE TOWARD THE EFFECTIVENESS OF IMPLEMENTING SCHOOL-BASED MANAGEMENT
: Descriptive Study at Public Elementary Schools in Coblong Sub-district, in Bandung City, Indonesia
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
What’s Missing? Center for Mental Health in Schools, Dept. of Psychology, UCLA, Los Angeles.
Howard Adelman and Linda Taylor (June, 2011). What Every Leader for School Improvement Needs to Know About Student and Learning Supports. Center for Mental Health in Schools, Dept. of Psychology, UCLA, Los Angeles.
Jamie Wallin, Ph.D (2003). Improving School Effectiveness. ABAC Journal Vol. 23, No.1 (January - April, 2003), The University of British Columbia.
Christakis Georgiou Yiasemis (June 2005). Understanding School Effectiveness and School Improvement in Cyprus: A study of the perceptions of stakeholders.The University of Warwick Istitue of Education.
The Wallace Foundation (2012). The Making of the Principal: Five Lessons in Leadership Training.
Rahim Jamal Jones (06/01/2007). The Principal's Role in Building Teacher Leadership Capacity in High-Performing Elementary Schools: A Qualitative Case Study. University of South Florida.
Shelly Habegger (Sept/Oct 2008). The Principal’s Role in Successful Schools:
Creating a Positive School Culture. Ohio: www.naesp.org
Adeyemi, T. O. (2008). Organizational Climate and Teachers' Job Performance in Primary Schools in Ondo State, Nigeria: Analytical Survey. Asian Journal of Information Technology, 139-145.
Ahmed, M. (2012). A Study of the Factors Affecting the Professional Performance of Teachers at Higher Education Level in Khyber Pakhtukhwa. Academic Research International.
118
Mut Somoeun, 2014
THE INFLUENCE OF PRINCIPAL LEADERSHIP
AND ENGAGEMENT OF SCHOOL COMMITTEE TOWARD THE EFFECTIVENESS OF IMPLEMENTING SCHOOL-BASED MANAGEMENT
: Descriptive Study at Public Elementary Schools in Coblong Sub-district, in Bandung City, Indonesia
Chinelo O. Duze (2012). The Changing Role of School Leadership and Teacher Capacity. Journal of Emerging Trends in Educational Research and Policy Studies (JETERAPS) 3 (1): 111-117, Scholarlink Research Institute
Journals, 2012 (ISSN: 2141-6990)
Bush, T. (2003). Theories of Educational Leadership and Management (3rd Ed.). London: Sage Publications Ltd.
Mohd Rozi Ismail (2012). Teachers’ Perceptions of Principal Leadership Styles
and How They Impact Teacher Job Satisfaction. Colorado State University, Fort Collins, Colorado.
Education Improvement Commission (November 2000). School Improvement Planning for Principals, Teachers and School Councils. A Handbook (ISBN 0-7794-0284-7), http://eic.edu.gov.on.ca
Frank D. Barnes (2004). Inquiry and Action: Making School Improvement, Part of Daily Practice. Annenberg Institute for School Reform at Brown University
Michael Fullan and Nancy Watson (August, 1999). School-based Management: Reconceptualizing to Improve Learning Outcomes. Final paper prepared for The World Bank, Ontario Institute for Studies in Education, University
of Toronto
Dandan Chen (September 2011). School-Based Management, School Decision-Making and Education Outcomes in Indonesian Primary Schools. The World Bank, East Asia and Pacific Region Education Sector Unit
A. De Grauwe (2004). School-based management (SBM): does it improve quality? UNESCO: Background paper prepared for the Education for All Global Monitoring Report 2005, The Quality Imperative.
Bambang Sumintono, Nora Mislan and Hamdan Said (Vol. IV, No.1, June 2012).
Gregory J. Palardy (01 March 2008). School Effectiveness and School Improvement. An International Journal of Research, Policy and Practice. University of California, Riverside, CA, USA
Cythia L. Uline, Daniel M. Miller and Megan Tschannen-Moran (Oct 1998).
School Effectiveness: The Underlying Dimensions. International Journal: Educational Administration Quarterly, Vol.34, No.4 (Oct 1998) 462-483
Hugh Watson Consultin (June 2004). Report on Evaluation of School-Based Management.
Pam Sammons (2006). Embracing Diversity: New challenges for School Improvement in a Global Learning Society International Congress for School Effectiveness and Improvement (Fort Lauderdale Florida 4th January 2006). The University of Nottingham, School of Education
Sarah Jennings Rosenberg and Helen F. Ladd (April 29, 2011). The Challenges in Implementing School Improvement Grant Models in Rural High Schools.
The Sanford School of Public Policy, Duke University
Geoff N Masters (April 2012). Measuring and Rewarding School Improvement.
Australian Council for Educational Research, The Commonwealth
Department of Education, Employment and Workplace Relations
(DEEWR)
Yong Zhao, David Lustick, and Wenzhong (Eric) Yang (2005). Research and the Five Dimensions of Effective Schools: A Self-Assessment Guide for the Chinese Educator. US-China Center for Research on Educational Excellence and Michigan State University, East Lansing, Michigan
Geoffrey D. Borman, Laura Rachuba, Amanda Datnow, Marty Alberg, Martha
MacIver, Sam Stringfield, & Steve Ross (September 2000). Four Models of School Improvement: Successes and Challenges in Reforming Low-Performing, High-Poverty Title I Schools. Johns Hopkins University and University of Memphis
Anit Somech (2010). Participative Decision Making in Schools: A Mediating-Moderating Analytical Framework for Understanding School and Teacher Outcomes. SAGE: www.sagepublications.com
Sello Mokoena (2011). Participative Decision-making: Perceptions of School Stakeholders in South Africa. Journal of Social Science, 29 (2): 119-131 (2011) published by University of South Africa
Bonggani Phumlani Mpungose (December 1999). Participative Decision Making and Conflict Management in Schools. The University of Zululand
World Bank (December 2007).Guiding Principles for Implementing School-based ManagementPrograms. Web: www.worldbank.org/education/economicsed Paul Gertler, Harry Patrinos and Marta Rubio-Codina† (May 2008). Empowering
Parents to Improve Education: Evidence from Rural Mexico. World Bank Policy Research Working Paper 3935
Joyce B. Castle and Coral Mitchell (July 2001). Roles of Elementary School Principals in Ontario: Tasks and Tensions. Published by Brock University Sello Mokoena (2012). Effective Participative Management: Does It Affect Trust
Levels of Stakeholders in Schools? Kamla-Raj: Journal Social Science, 30(1): 43-53 (2012)
Ai Shoraku (2008). Educational Movement Toward School-Based Management in South-East Asia: Cambodia, Indonesia and Thailand. UNESCO: Education for All Global Monitoring Report 2009
Raihani (2007). Education reforms in Indonesia in the twenty-first century.
University of Melbourne, Australia: International Education Journal, 2007,
8(1), 172-183. ISSN 1443-1475 © 2007 Shannon Research Press.
Felipe Barrera-Osorio, Tazeen Fasih and Harry Anthony Patrinos (2009).
Decentralized Decision-Making in Schools. The Theory and Evidence on School-Based Management. © 2009 The World Bank, Washington, D.C. MINEDUC (July 2008): Roles, duties and responsibilities of school management
team. Mineduc School Management, ©NCDC.
Howard Adelman, Ph.D.Linda and Taylor, Ph.D. (Revised September 2007):
Fostering School, Community Involvement. ©2008,Hamilton Fish Institute on School and Community Violence and Northwest Regional Educational
Laboratory. All Rights Reserved
Martin Prew (2009): Community Involvement in School Development Modifying School Improvement Concepts to the Needs of South African Township Schools. SAGE Publications, London, Los Angeles, New Delhi, Singapore and Washington DC. BELMAS Vol 37(6) 824–846; 345562
Eric Zachary and Shola Olatoye (2001): A Case Study: Community Organizing For School Improvement In The South Bronx. Institute For Education & Social Policy. New York University, School of Education, Copyright © March 2001
Amy C. Berg, Atelia Melaville, and Martin J. Blank, (2006): Community and Family Engagement. Coalition for Community Schools, National Association of Elementary School Prinipals. Washington, DC 2008
Center for Great Public Schools (2003): Parent, Family, CommunityInvolvement in Education. Washington, D.C.
Cara Stillings Candal (September 2009), School-Based Management: A Practical Path to School District Reform. Center for School Reform, Pioneer Institute, Public Policy Resesarch
Terry-Ann Rodriguez, and John R. Slate (2006), Site-Based Management: A Review of the Literature, Part II: Past and Present Status. Anthony Middle School and University of Missouri, Kansas City
RAND (2012): Transforming Indonesia’s Centralized Education System to
School-Based Management. Santa Monica, California, USA
Bill Mulford (April 2003), School Leaders: Changing Roles and Impact on Teacher and School Effectiveness. University of Tasmania
1
Mut Somoeun, 2014
THE INFLUENCE OF PRINCIPAL LEADERSHIP
AND ENGAGEMENT OF SCHOOL COMMITTEE TOWARD THE EFFECTIVENESS OF IMPLEMENTING SCHOOL-BASED MANAGEMENT
: Descriptive Study at Public Elementary Schools in Coblong Sub-district, in Bandung City, Indonesia
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu A. Background of Research
The world of educational system has been timely transformed in order to
seek a better development of education quality for serving the peoples’ needs to
job market access. In the 21st century of education, the school-based management
(SBM) has been viewed largely as a political reform that transfers a central power
over management of budget, personnel and curriculum to individual schools. The
reform aims to drive greater school improvement by fostering principal’s roles
and involving stakeholders to school communities through putting the hard work
and generating significantly better results for their students. The education reform
helps create a school system that is geared towards improvement and results.
SBM is normally referred to the encouragement of all involved parties/
stakeholders to get involved in school-site managing or making decisions for
school improvement. In another word, it is to foster the principal leadership (roles
and responsibilities) of the local school principals to build good communications
among school committee and all stakeholders by promoting their participations
(participative decision-making) within the school (World Bank, 2007). SBM was
adopted as a political reform that shifted the balance of power from the central
office to the community level or the school sites (Murphy & Beck, 1995).
SBM implementation is to drive the effectiveness of school and extends to
which the schools themselves can perform their core functions such as technical
and economics, human and social, political, culture, and educational. In this sense,
the effectiveness of the school shows effective school performance in improving
the high quality of education (Teguh Sihono and Rohaila Yusof, 2012). They
further explained that SBM is a form of some formal decision making authority in
planning for schools’ main functional areas such as budget planning, personnel
and programs which is delegated to and often distributed among the site-level
Mut Somoeun, 2014
THE INFLUENCE OF PRINCIPAL LEADERSHIP
AND ENGAGEMENT OF SCHOOL COMMITTEE TOWARD THE EFFECTIVENESS OF IMPLEMENTING SCHOOL-BASED MANAGEMENT
: Descriptive Study at Public Elementary Schools in Coblong Sub-district, in Bandung City, Indonesia
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
principal, teachers, parents and at time, students (high school), and community
residents is created so that site participants can get directly involved in the wide
school decision-making.
In Indonesia, the implementation of SBM was triggered by the fact that
Indonesian educational stakeholders had been struggling with the quality of
national education over the last two decades leading to the financial crisis in 1997,
which created severe economic and social problems (Nurkolis, 2005; Mulyasa,
2004; Departemen Pendidikan Nasional, 2001). For these reasons, the Indonesian
Ministry of National Education appointed a Komisi Nasional Pendidikan (KNP)
or the Commission of National Education (CNE) in February 2001. The KNP
worked until December 2001 with responsibilities to: (1) formulate the policy
recommendations to have a better quality of education; (2) provide inputs to
government about educational decentralization. The work of this Commission of
National Education (CNE) would become a basis from which to comprehensively
reform the Indonesian education. One of the recommendations of the KNP is to
develop educational councils at district level and school councils at school level.
Developing the educational council and school councils is one of the educational
decentralization policies, aimed at devolving power and authority from central
government to district authorities and schools, resulting in improvements of
democratic principles, community participation, equity, and accommodation of
the diverse local interests and needs (Departemen Pendidikan Nasional, 2001: 26).
Indonesia first applied SBM in 1999; the central government established a
Commission of National Education (Journal of NTT Studies, 2009) in February
2001 on the basis of Law 22/1999 for decentralizing education. The commission
recommended the formation of school councils at the school level to improve
quality of national education. The government then embarked on the formation of
school councils in Western Sumatera, Eastern Java, and Bali. On the basis of these
Mut Somoeun, 2014
THE INFLUENCE OF PRINCIPAL LEADERSHIP
AND ENGAGEMENT OF SCHOOL COMMITTEE TOWARD THE EFFECTIVENESS OF IMPLEMENTING SCHOOL-BASED MANAGEMENT
: Descriptive Study at Public Elementary Schools in Coblong Sub-district, in Bandung City, Indonesia
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
principles in schools, creating higher levels of parental participations in school
governance, and improving the quality of national education.
Until 2002, the government provided a set of guidelines to establish
mandatory corporate governing body type school councils (the SBM-principles,
Decree No. 044/U/2002 on the Education Board and School Committees) by
defining the school committee as a community representative body at school level
with members from parents, community leaders, education professionals, private
sector, education associations, teachers, NGOs and village officials. Furthermore,
the Education Act 20/2003 (art. 56) states that community shall take part in the
quality improvement of educational services, which include planning, monitoring,
and evaluation of educational programs through Educational Council and School
Council/Committee.
Through decentralization of education reform, Indonesia’s SBM design incorporates some features that are considered as essential to SBM effectiveness
(Barrera- Osorio et al., 2009). First, the Indonesian reform is designed to provide a
high level of autonomy to schools and encourage broad participation of the local
community in school affairs. School principals and teachers are provided with
increased autonomy to make decisions across key school areas related to school
operations, budget, and education. However, the central government maintains
authority over the hiring, assignment, and firing of civil service teachers. Second,
SBM in Indonesia provides schools with the autonomy to exercise power in
resource allocation over a block of discretionary funds, called BOS (Bantuan Operasional Sekolah). The BOS allows schools to cover operational costs based on annualper student basis. It is also administered with few restrictions, thereby
facilitating autonomous SBM resource allocation regarding the disbursement of
funds according to school priorities across almost all school activities (except
paying bonuses to teachers, rehabilitation of facilities, and building new rooms or
Mut Somoeun, 2014
THE INFLUENCE OF PRINCIPAL LEADERSHIP
AND ENGAGEMENT OF SCHOOL COMMITTEE TOWARD THE EFFECTIVENESS OF IMPLEMENTING SCHOOL-BASED MANAGEMENT
: Descriptive Study at Public Elementary Schools in Coblong Sub-district, in Bandung City, Indonesia
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
the creation of school committees, BOS teams and teaching boards that are made
up of teachers, parents and community leaders. These groups serve to assist and
advise principal and provide recommendation on the design and implementation
of educational programs, policies, and the management of funds. Fourth, the
reform encourages schools to engage in self-evaluation and monitoring of their
processes. Under this SBM model, schools are expected to inform stakeholders
for their decisions, and to be accountable for their decisions through monitoring
by education districts, school committees, parents, and the immediate community
(Vernez, G., Karam, R. &Marshall, J., 2012).
According the World Bank (RAND, 2012:1-4), although the Indonesian
government has broadly implemented SBM policy since 2003, the national survey
was conducted throughout the country with 400 principals in 2010 indicated that
most principals consulted with teachers, districtstaff, and other school principals
before making decisions,community and parent participation in school
decision-makingwas very limited. Members of school committees, whichwere designed to
facilitate parental and community involvementin education, rarely participated in
school affairs. The survey revealed that school committeeparticipated in decisions
in 44 percent of schools. Principals mainly viewed the school committee as an
intermediarybetween the schools and parents, and the school committeemembers
expressed attitudes of noninterference withschool matters and deference to school
staff. Commonly, parents similarlyexpressed deference to school staff, and most
principals andteachers reported feeling little or no pressure from parents
toimprove school performance. As a result, parents and community members are
not participating as fully as envisioned, and the decision-making authority of
principal at school level was: 88% in recruiting and hiring teachers; 99% in setting
school vision and goal; 88% in developing school curriculum; 65% in setting
school calendar; 88% in selecting textbooks; 96% in student administrating; and
Mut Somoeun, 2014
THE INFLUENCE OF PRINCIPAL LEADERSHIP
AND ENGAGEMENT OF SCHOOL COMMITTEE TOWARD THE EFFECTIVENESS OF IMPLEMENTING SCHOOL-BASED MANAGEMENT
: Descriptive Study at Public Elementary Schools in Coblong Sub-district, in Bandung City, Indonesia
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
policy change toward local autonomy, districts still strongly influenced school
policies and practices.Principals reported that they rarely made decisions
withoutseeking district approvalout of fear of making a mistakeor appearing
authoritarian. Thefindingshown that the district influence was equal to/greater
than that of teachersin all areasaveraging 3.2 to 3.6 on a scale of 4—except
inclassroom instructional practices. Principals frequently had meeting with district
staff, which indicated thedistrict’scontinued prominent role in school
decision-making.
B. Problem Identification and Research Formulation
1. Problem Identification
Based on background of the study in educational reform above, it is seen
that Indonesia started implementing school-based management and enforced the
effectiveness of implementation, especially delegating the local authoritative
power (decentralizing) to the school communities or local schools. In this regard,
the empowerment of local schools is transferred to the individual schools for
implementing school-based management (SBM) by strengthening the principal
leadership (roles and responsibilities) and promoting the engagements of school
committee through participative decision-making (PDM). Here, the term PDM
refers to the involvements of stakeholders or shared decision-making and shared
responsibilities among the principal, and school committee, (teachers, parents, and
community residents) who are the key actors toward the effectiveness of SBM
implementation.
SBM is a model of management providing more autonomy to individual
schools and enhancing the direct involvements of school communities (head
teachers, teachers, students, staff, parents and society) in making decisions to
improve the quality of schools under the policy of the Indonesian Ministry of
Mut Somoeun, 2014
THE INFLUENCE OF PRINCIPAL LEADERSHIP
AND ENGAGEMENT OF SCHOOL COMMITTEE TOWARD THE EFFECTIVENESS OF IMPLEMENTING SCHOOL-BASED MANAGEMENT
: Descriptive Study at Public Elementary Schools in Coblong Sub-district, in Bandung City, Indonesia
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
paradigm of decentralization of education which is being applied to solve the
ineffectiveness of the centralistic educational paradigm formerly implemented.
Centralistic management of education does not educate the school management to
creatively develop the school organization, develop the curriculum, manage
facilities and learning resources, nor develop community participation. SBM
makes the school community an active participant involved in making decisions
in relation to school programs including curriculum and its learning strategies.
In general, there are two pillars to help SBM implementation succeed the
effectiveness; the influence of principal leadership and the engagement of school
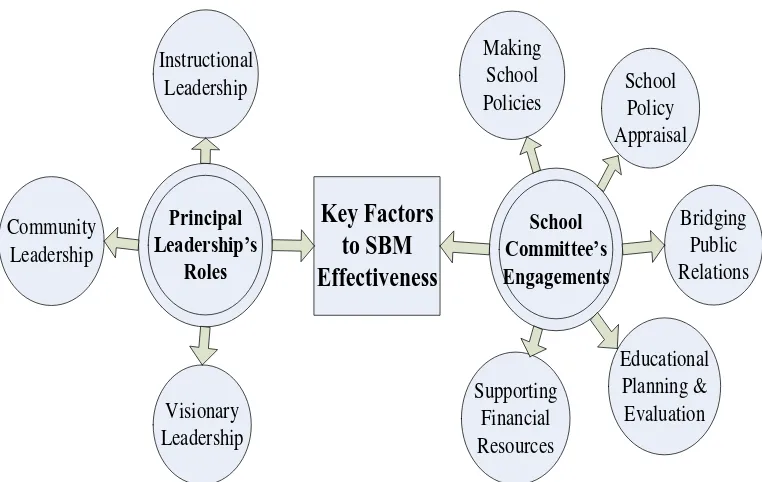
committee. The principal leadership refers to the performance of principal’s roles
and responsibilities such as role in instructional leadership, community leadership,
and visionary leadership (Michael Usdan, Barbara McCloud, and Mary
Podmostko, 2000). And the engagement of school committee refers to power and
authority related to empowerment to: formulate and approve the school policies;
formulate and approve the school’s mission and vision; formulate and approve
annual school programs including annual school budget; design strategic planning
for school development; determine learning standards in the school; decide on the
provision of incentives to the principal, teachers, and administrative staff; develop
school potential factors for increasing student achievements both academic
(school examinations) and non-academic (religious life, sports, arts, skills which
are appropriate to school environment such as agricultural skills, weaving skills,
and simple technology); raise school funds for the purpose of financing the
school; mobilize school resources both financial and non-financial (human power
for school building and facilities, ideas and recommendations); encourage more
participation of school stakeholders in formulating, implementing, and monitoring
school policies; create a transparent, accountable, and democratic atmosphere in
the school for the purposes of quality education in the school; respond to the
Mut Somoeun, 2014
THE INFLUENCE OF PRINCIPAL LEADERSHIP
AND ENGAGEMENT OF SCHOOL COMMITTEE TOWARD THE EFFECTIVENESS OF IMPLEMENTING SCHOOL-BASED MANAGEMENT
: Descriptive Study at Public Elementary Schools in Coblong Sub-district, in Bandung City, Indonesia
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
between school and external organizations for improving educational processes
and outcomes; identify and solve school problems; and evaluate school policies
and programs including the control of school buildings and facilities as well as
school grants (SBM policy by the Indonesian Ministry of Education, 2002). These
authorities can be briefed into the four major roles: (1) An advisory agency in
determining and/ approving school policies, at the school level; (2) A supporting
agency in supporting the school both in financial and non-financial matters; (3) A
controlling agency for transparency and accountability at school level; and (4) A
mediator between school, government, and community. In another word, the key
roles of school committee are: (1) Making school policies; (2) School policy
appraisal; (3) Supporting financial resources; (4) Bridging public relations; and
(5) Educational planning and Evaluation (Foxborough Public School, 2008; and
Triton Regional School, 2013).
To enforce SBM effectively, the Indonesian Education Act 20/2003 (art.
56) also defines that a school committee is an independent body established to
provide advice, directions and support for personnel, facilities and equipment, and
monitoring of a school. However, Indonesia still faces many problems in the real
practice such as some local schools do not establish school committee or less
participation from stakeholders, and even principal leadership’s role seems to be
in low performance so far, which must be more developed (World Bank, 2010).
Up to 2004, the SBM guidelines clarified that the school has to elect the
school council (participative decision makers) with a minimum of nine members
depending on the size of the school. The membership of a school council should
comprise of community representatives, principal, teachers, school foundations,
and local governments. The community representatives should consist of: (1)
parents; (2) public figures, (3) educational experts; (4) industries or businesses;
(5) professional organization of teachers; (6) representatives of alumni; and (7)
Mut Somoeun, 2014
THE INFLUENCE OF PRINCIPAL LEADERSHIP
AND ENGAGEMENT OF SCHOOL COMMITTEE TOWARD THE EFFECTIVENESS OF IMPLEMENTING SCHOOL-BASED MANAGEMENT
: Descriptive Study at Public Elementary Schools in Coblong Sub-district, in Bandung City, Indonesia
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
three representatives only from teachers, school foundations, and Advisory Body
for the Village Governance, there is no limitation of the total number elected from
the representatives of the community members. And each school council has the
authority to elect school council executive and standing committees. The council
executive of each school council consists of at least the Council President,
Secretary, and Treasurer. It is ruled out that a school principal cannot be elected as
the Council President, while the executive members and standing committees are
elected from and by school council members. Depending on the need of the
schools, the standing committees of the school councils can be elected for: (1)
Finance; (2) School Quality Control; (3) Partnership Networks and Information
System; and (4) Buildings and School Facilities.
In summary, this study is primarily focused on the two key factors which
contribute to the effectiveness of implementing SBM at school level. Those key
factors are called as independent variables: the influence of principal leadership
(X1)and the engagement of school committee (X2), which will make a positive
influence toward the effectiveness of implementing school-based management (Y)
at school level. Therefore, the movements toward the effectiveness of SBM are to
provide opportunities to all relevant stakeholders such as teachers, parents and
community members with information about their rights and responsibilities, and
about the general state of education in their community; training stakeholders in
how to use information; delegating to stakeholders (school committee), a specific
power (right to hire and fire the contract teachers/the responsibility for monitoring
teacher performance); allowing the local authorities, such as a school committee
or the principal to determine the use of school resources.
The figure below illustrates the key factors foster the effectiveness of SBM
Mut Somoeun, 2014
THE INFLUENCE OF PRINCIPAL LEADERSHIP
AND ENGAGEMENT OF SCHOOL COMMITTEE TOWARD THE EFFECTIVENESS OF IMPLEMENTING SCHOOL-BASED MANAGEMENT
: Descriptive Study at Public Elementary Schools in Coblong Sub-district, in Bandung City, Indonesia
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu Principal
(Source: School Leadership for 21st Century Initiative, Leadership for Student Learning, Oct 2000)
Figure 1.1: Factors to foster SBM Effectiveness
2. Research Formulation
Based on background and problem identification of the research above, the
problem formulations that are going to be explored and studied are primarily
focused on the influence of principal leadership (roles and responsibilities), and
school committees’ engagement in participative decision making (PDM). These are the key factors for making positive influence toward the effectiveness of
implementing school-based management. Thus, the research questions to be raised
in this research study are:
1. How is the influence of principal leadership in performing roles and
responsibilities strengthened at public elementary schools in Coblong
Mut Somoeun, 2014
THE INFLUENCE OF PRINCIPAL LEADERSHIP
AND ENGAGEMENT OF SCHOOL COMMITTEE TOWARD THE EFFECTIVENESS OF IMPLEMENTING SCHOOL-BASED MANAGEMENT
: Descriptive Study at Public Elementary Schools in Coblong Sub-district, in Bandung City, Indonesia
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
2. How is the engagement of school committee promoted at public
elementary schools in Coblong sub-district, Bandung city?
3. How far is the effectiveness of implementing SBM policy at public
elementary schools in Coblong sub-district, Bandung city?
4. How can the influences of principal leadership foster the effectiveness
of implementing SBM policy in Coblong sub-district, Bandung?
5. How can the engagement of school committee foster the effectiveness
of implementing SBM at public elementary schools in Coblong?
6. How much can the influence of principal leadership and engagement
of school committee enhance the effectiveness of SBM policy?
C. Objectives of Research
The overall aim in this research study is to describe the educational reform
through fostering the influence of the school leadership in performing key roles
and the engagement of school committee in sharing decisions and responsibilities
in school operations toward the effectiveness of implementing SBM policy at the
primary level of public schools in Coblong sub-district, in Bandung city.
With particular purpose, this study is discovered on the key factors of the
effectiveness of School-Based Management (SBM) which has been firstly applied
since 1999 in Indonesia. However, this study is explored only on the current
situations at school level in the context of school community. In this research,
therefore, the main purposes of study are:
1. To know the influence of principal leadership in performing key roles
at public elementary schools in Coblong sub-district, Bandung city.
2. To know the engagement of school committee in sharing decisions at
public elementary schools in Coblong sub-district, Bandung city.
3. To know the effectiveness of SBM policy at public elementary schools
Mut Somoeun, 2014
THE INFLUENCE OF PRINCIPAL LEADERSHIP
AND ENGAGEMENT OF SCHOOL COMMITTEE TOWARD THE EFFECTIVENESS OF IMPLEMENTING SCHOOL-BASED MANAGEMENT
: Descriptive Study at Public Elementary Schools in Coblong Sub-district, in Bandung City, Indonesia
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
4. To critically analyze the influence of principal leadership contributing
toward the effectiveness of implementing SBM policy.
5. To analyze the engagement of school committee contributing to the
effectiveness of implementing SBM policy.
6. To know how the influence of principal leadership and engagement of
school committee toward the effectiveness of implementing SBM.
D. Significance of Research
As a scientific research, the significances of this study are divided into two
sides as the followings:
1. Significance in Theory
With critical analysis and findings, this study is expected to be a useful
instrument for students, teachers, principal or researchers who are interested in
researching in field of educational administration. It will become a helpful tool to
the next generation of researchers (theoretical-proofed document). Here, the study
will come up with the new findings of the problems in implementing the concept
of school-based management (SBM) such as how performance the principals do to
improve education quality, the engagements of school committees, the challenges
to theoretical implementation failures, and the factors to achieve a success of the
school-based management.
2. Significance in Practice
This study is expected to be a significant encouragement to the key actors
of school such as: principals, supervisors, teachers, community leaders, parents/
stakeholders who involve in managing the local schools; since it gives a better
understanding of what makes a difference in improving student outcomes and
Mut Somoeun, 2014
THE INFLUENCE OF PRINCIPAL LEADERSHIP
AND ENGAGEMENT OF SCHOOL COMMITTEE TOWARD THE EFFECTIVENESS OF IMPLEMENTING SCHOOL-BASED MANAGEMENT
: Descriptive Study at Public Elementary Schools in Coblong Sub-district, in Bandung City, Indonesia
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu E. Structure of Research
Systematic writing in this study consists of five chapters in accordance
with the Guidelines for Scientific Writing of Indonesia University of Education in
2012. The research study is illustrated with the organizational structure which is
going to discuss with details in the specific chapters. Here, the structure of the
research study is to describe how the thesis is organized in order to produce an
appropriate format and research beauty with coherences as the follows:
In chapter I, the discussion starts with introduction to the research by over
viewing the main issues such as background, problem identification, problem
formulation, objectives of research, significance of research, and organizational
structure of research.
Chapter II discusses on the literature review, research framework, and
hypothesis of research. The study focuses are on issues of school leadership,
school committee, school-based management, and hypothesis of research.
Chapter III focuses on the research methodology by explaining about how
the study is conducted based on the rule of scientific method, including: research
location, population and sample; research design; operational definition; research
instrument; instrument development process; techniques of data collection; and
techniques of data analysis.
Chapter IV states about the research findings and discussions.
And chapter V discusses about the conclusion and recommendations of the
53
Mut Somoeun, 2014
THE INFLUENCE OF PRINCIPAL LEADERSHIP
AND ENGAGEMENT OF SCHOOL COMMITTEE TOWARD THE EFFECTIVENESS OF IMPLEMENTING SCHOOL-BASED MANAGEMENT
: Descriptive Study at Public Elementary Schools in Coblong Sub-district, in Bandung City, Indonesia
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu A. Location, Population and Sample of Research
1. Location of Research
In order to shape the scope of the research, this study is conducted in the
certain location. Here, the research study is particularly targeted in the public
elementary schools in Coblong sub-district in Bandung city, Indonesia. And also,
the study is mainly focused on the perspectives and effectiveness of implementing
the concept of school-based management policy (SBM).
2. Population and Sample of Research
Arikunto (2010: 173) states that population is the entire subject of the
research, while Margono (2010: 118) says population is all data which become the researcher’s attention in a certain place and time. To Hinton (2005: 48) explained that the population of study can be a complete set and can also be any part of a
particular category that researchers want to conduct.
Based on the statements above, the population in this study is all the public
elementary schools where have already been effectively implemented the SBM
policy in Coblong sub-district, Bandung city, Indonesia. According to the data of
Dinas Pendidikan Kota Bandung in 2014, there are 36 public elementary schools
in Coblong sub-district; therefore all of those schools are chosen for subject study.
In addition, a total population sampling is used in this study because the
total population is very small. Total population sampling is a type of purposive
sampling technique/ non-probability sampling techniques chosen to examine the
entire population that has a particular set of characteristics (Patton, 1990, 2002;
and Kuzel, 1999; as cited in Lund Research Ltd, 2012). And the respondents for each school are two people (one principal and one head of school committee) who
are representatives of individual school and delegated with power and authority in
Mut Somoeun, 2014
THE INFLUENCE OF PRINCIPAL LEADERSHIP
AND ENGAGEMENT OF SCHOOL COMMITTEE TOWARD THE EFFECTIVENESS OF IMPLEMENTING SCHOOL-BASED MANAGEMENT
: Descriptive Study at Public Elementary Schools in Coblong Sub-district, in Bandung City, Indonesia
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
monitoring, implementing and evaluating the programs at school level through
open participations of school stakeholders based on the school-based management
policy (Indonesian Ministry of Education, the SBM guidelines 2004).
Thus, this research study will select all those 36 public elementary schools
where have been implementing the policy of school-based management (SBM).
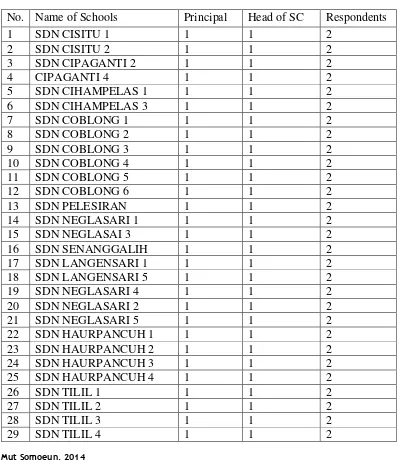
The total population in this research study is shown in the table below:
Table 3.1: Total Population of Research
No. Name of Schools Principal Head of SC Respondents
Mut Somoeun, 2014
THE INFLUENCE OF PRINCIPAL LEADERSHIP
AND ENGAGEMENT OF SCHOOL COMMITTEE TOWARD THE EFFECTIVENESS OF IMPLEMENTING SCHOOL-BASED MANAGEMENT
: Descriptive Study at Public Elementary Schools in Coblong Sub-district, in Bandung City, Indonesia
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
30 SDN TIKUKUR 1 1 1 2
31 SDN TIKUKUR 2 1 1 2
32 SDN TIKUKUR 3 1 1 2
33 SDN TIKUKUR 4 1 1 2
34 SDN TIKUKUR 5 1 1 2
35 SDN SEKELOA 1 1 1 2
36 SDN SEKELOA 2 1 1 2
Total Respondents 36 36 72
B. Research Design
In order to get the valid and reliable data, the method used in this study is
descriptive survey of a quantitative approach. This approach seeks to describe the
current status of an identified variable to provide systematic information about a
phenomenon in the research issues. The analysis and synthesis of the collected
data provide the test of the hypothesis. Systematic collection of information
requires careful selection of the units studied and careful measurement of each
variable. According to Omar (2004: 81), he states that “descriptive method can
provide research correlation, descriptive analysis method can describe the things
that reveal facts, classification and measurement, and whereas to be measured is a
fact that serves to define what happens.” Meanwhile RJ Hilsden (2001: 23) gives
a restriction on descriptive research, namely "research directed to provide the
symptoms, the facts or events in systematic and accurate information on the
properties of a particular population or region."
However, by principle, the overall structure for a quantitative design is
based on the scientific method. It uses deductive reasoning, where the researcher
forms a hypothesis, collects data in an investigation of the problem, and then uses
the data from the investigation, after analysis is made and conclusions are shared
to prove the hypotheses not false or false. With this stance, the basic procedure of
a quantitative design is: making observations about something that is unknown,
Mut Somoeun, 2014
THE INFLUENCE OF PRINCIPAL LEADERSHIP
AND ENGAGEMENT OF SCHOOL COMMITTEE TOWARD THE EFFECTIVENESS OF IMPLEMENTING SCHOOL-BASED MANAGEMENT
: Descriptive Study at Public Elementary Schools in Coblong Sub-district, in Bandung City, Indonesia
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
problem or issues; hypothesizing an explanation for those observations; making a
prediction of outcomes based on the hypotheses by formulating a plan to test the
prediction; collecting and processing data; and verifying the research findings by
making final conclusions and presenting the findings in an appropriate form.
Simply speaking, this research will be based on the hard documents,
theory interpretations, data populations (questionnaires with a total number of
population and sample selection), and data analysis. It will be relied on the
numerical data (primary and secondary data). It claims for developing knowledge,
such as cause and effect thinking, reduction to specific variables, hypotheses and
questionnaire responses, the use of measurement and observation, and the test of
theories. The research will isolate the three variables and causally relates them to
determine the magnitude and frequency of relationships.
In addition, the research study will be determined with the variables to
investigate and chooses instruments, which will respond highly reliable and valid
data. This means that the two variables of research issues: independent (X1, X2)
and dependent (Y) are inevitably correlated to the research study.
The figure below is used to determine the correlation coefficient of the
variable X1 to Y, X2 to Y, and X1 and X2 to Y of this research study:
(X1RY)
(X1X2RY)
(X2RY)
Where:
X1 = Influence of Principal Leadership
X2 = Engagement of School Committee
Y = Effectiveness of Implementing SBM
R = Correlation Coefficient between X1 and X2 to Y X1
Y
Mut Somoeun, 2014
THE INFLUENCE OF PRINCIPAL LEADERSHIP
AND ENGAGEMENT OF SCHOOL COMMITTEE TOWARD THE EFFECTIVENESS OF IMPLEMENTING SCHOOL-BASED MANAGEMENT
: Descriptive Study at Public Elementary Schools in Coblong Sub-district, in Bandung City, Indonesia
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
Based on the figure above, it means that the two independent variables of
the correlation coefficient between the influence of principal leadership (X1) and
engagement of school committee (X2) will make a change to the effectiveness of
implementing school-based management (Y). In this sense, the researcher can
draw a conclusion that the descriptive method of analysis is suitable to use in this
study, because it is in accordance with the purpose of research, which is to get an
overview on the influence of principal leadership (X1), and the engagement of
school committee (X2) toward the effectiveness of school-based management (Y).
C. Operational Definition
1. Effectiveness of School-Based Management (Y)
School-based management (SBM) is defined as a form of decentralization
that can improve the educational outcomes and increase client satisfaction. It also
emphasizes the individual school (represented by principals, teachers, parents, and
other members of school community) as the primary unit for improving education
and the redistribution of decision-making authority over the school operations as
the primary means by which this improvement can be stimulated and sustained
(World Bank, 2007). It is a form of educational governance at school level by
granting authority and power to all stakeholders for making shared decisions and
taking shared responsibilities (Vernez, G., & Karam, R. Marshal, J. 2012).
Thus, the effectiveness of school-based management is referred to the
successful implementation of decentralization at school level. According to Dr. K.
Pushpanadham (in the ABAC Journal Vol. 26, No. 1, 2006:43), the effectiveness
of implementing SBM would be appeared in these areas: (1) involvements of staff
in decisions about programs and organization; (2) involvements of parents and
others in the community in the school; (3) efficient and effective allocation of
resources based on the school budget; (4) strong instructional leadership and a
Mut Somoeun, 2014
THE INFLUENCE OF PRINCIPAL LEADERSHIP
AND ENGAGEMENT OF SCHOOL COMMITTEE TOWARD THE EFFECTIVENESS OF IMPLEMENTING SCHOOL-BASED MANAGEMENT
: Descriptive Study at Public Elementary Schools in Coblong Sub-district, in Bandung City, Indonesia
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
and collaboration; (6) long term academic improvement; (7) positive attitudes and
support for the school demonstrated by staff, students, parents, and the
community; (8) positive behavior modeled by the staff; (9) and the school should
be successful and effective in meeting its goals.
There are three dimensions in implementing the SBM policy. And for its
effectiveness can be measured by the authorities of school itself as the follows:
(1) Budget Management: School principal and school committee can
make decisions over expenditures, allocations, and find funds from
various sources with accountability (World Bank, 2007;
Barrera-Osorio, Fasih & Patrinos, 2009:5; and UNESCO, 2012).
(2) Staff Management: Principal and in some case with discussions
among school committees can decide to promote, compensate, hire
or terminate staff or teachers, this also include right to assign staff
(David Lustick and Jing Lei, 2005: 64; Lunenburg et al., 2006: 14). (3) Curriculum Development: Based on SBM policy, each local school
can develop its core curriculum, select textbook and improve the
instructional programs (World Bank, 2007; UNESCO, 2012).
Based on the definitions above, SBM is to foster school management by
giving more decision-making authority to parents and community with autonomy
in setting school vision, mission, goals, and policies. It requires changes in school
governance and management, strategic planning, school financing, accountability,
and the development of new skills for staff members.
2. Influence of Principal Leadership (X1)
The influence of principal leadership is a strength of school principal’s
roles and responsibilities in managing school such as assuring instruction aligned
Mut Somoeun, 2014
THE INFLUENCE OF PRINCIPAL LEADERSHIP
AND ENGAGEMENT OF SCHOOL COMMITTEE TOWARD THE EFFECTIVENESS OF IMPLEMENTING SCHOOL-BASED MANAGEMENT
: Descriptive Study at Public Elementary Schools in Coblong Sub-district, in Bandung City, Indonesia
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
Sun, Creemers and Jong (2007: 97) define principal leadership’s influence as an empowerment of school leader for managing personnel (hiring, firing, promoting
teachers and school staff members), time and finance, spiritual and human
resources support, and school improvement. The main focuses of principal are to
influence in these areas: school leadership; teacher evaluation; student disciplines;
developing, implementing, and evaluating programs; reviewing policies and
procedures; setting school schedule; hiring new teachers; building parents and
community relations; and authority delegation (Derrick Meador, 2013).
According to Michael Usdan, Barbara McCloud, and Mary Podmostko, et
al., (as cited in the School Leadership for the 21st Century Initiative, Leadership
for Student Learning, October 2000: 8), the influence of principal is done through performing the principal’s key roles. It is defined as leadership in the three key dimensions for school improvement as the followings:
(1) Instructional leadership: focusing on strengthening the teaching and
learning, the professional development (staff), data-driven decision-making and
accountability;
(2) Community leadership: manifesting in a big-picture awareness of the school’s role in society; shared leadership among educators, community partners and residents; close relations with students’ parents and others; and advocacy for school capacity building and resources;
(3) Visionary leadership: guiding or demonstrating energy, commitment,
entrepreneurial spirit, values and conviction that all children will learn at high
levels, as well as inspiring others with this vision both inside and outside the
school building. It is the action undertaken by an effective instructional principal
in four key roles in SBM implementation: designer of involvement; motivator/
coach; facilitator of change; and liaison to outside world (Priscilla Wohsteller &
Mut Somoeun, 2014
THE INFLUENCE OF PRINCIPAL LEADERSHIP
AND ENGAGEMENT OF SCHOOL COMMITTEE TOWARD THE EFFECTIVENESS OF IMPLEMENTING SCHOOL-BASED MANAGEMENT
: Descriptive Study at Public Elementary Schools in Coblong Sub-district, in Bandung City, Indonesia
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu 3. Engagement of School Committee (X2)
The term engagement shares meaning with involvement and participation.
Thus, the engagement of school committee is an involvement or participation of
the people who are elected as committee members of a school. Those elected
members have power and authority to make decisions for their school affairs. According to Queensland’s article cited by Emerson, Fear, Fox, and Sanders (in the Parent and Community Engagements Framework, 2012:2), the engagements
of school committee are to strengthen the students’ outcomes through effective
partnerships between principals, teachers, students, parents and the community.
The Indonesian Ministry of National Education (2002) states that school committee’s engagements are to get involved in these areas: an advisory agency in determining/approving educational policies at the school level; a supporting
agency in supporting school both in financial and non-financial matters at school
level; a controlling agency for the purpose of accountability and transparency at
school level; and a mediator in communicating between school, government, and
community.
However, Foxborough Public School (2008) and Triton Regional School
(Massachusetts, USA, 2013) have common ideas that the engagements of school
committee are normally to fulfill the five dimensions of roles at school level as the
followings:
(1) Policy making: the school committee is responsible for development of
the school policy as guides for administrative action and for employing
a superintendent who will implement its policies.
(2) Appraisal: the school committee is responsible for evaluating the
effectiveness of its policies and their implementation.
(3) Provision of financial resources: the school committee is responsible
for adoption of a budget that will enable the school system to carry out
Mut Somoeun, 2014
THE INFLUENCE OF PRINCIPAL LEADERSHIP
AND ENGAGEMENT OF SCHOOL COMMITTEE TOWARD THE EFFECTIVENESS OF IMPLEMENTING SCHOOL-BASED MANAGEMENT
: Descriptive Study at Public Elementary Schools in Coblong Sub-district, in Bandung City, Indonesia
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
(4) Public relations: the school committee is responsible for providing
adequate and direct means for keeping the local citizenry informed
about the schools and for keeping itself and the school staff informed
about the needs and wishes of the public.
(5) Educational planning and evaluation: the committee is responsible for
ensuring that educational objectives are set that promote continual
improvement of the educational programs.
In brief, the engagement of school committee is a participation with right in
these areas: sharing decision-making in setting school vision, mission, and goal;
planning, implementing, monitoring, and evaluating the school programs;
managing school budget; hiring, terminating, compensating; bridging relations;
promoting parental and community participation through sensitizing, involving
and effectively communicating educational information to all parents, pupils,
community stakeholders, and toward local authorities for seeking effectiveness of
quality education, student outcomes, quality teaching and building the good
environments or conditions of school.
D. Research Instrument
The research instruments used in data collection are questionnaires. In this
sense, questionnaires are a number of written questions used to obtain information
from respondents in terms of statements about personal or things that are known
(Arikunto, 2010:128). Therefore, the questionnaires of the research instrument are
given to the respondents of principals and heads of school committee.
Based on the reason above, the instrument (questionnaires) in this study
will be used in the preparation of model of Likert Scale. According to Riduwan
and Kuncoro (2007:20), Likert Scale is used to measure the attitudes, opinions
and perceptions about a person or group social events or symptoms. By using the
Likert Scale, the variables to be measured are translated into dimensions, the
Mut Somoeun, 2014
THE INFLUENCE OF PRINCIPAL LEADERSHIP
AND ENGAGEMENT OF SCHOOL COMMITTEE TOWARD THE EFFECTIVENESS OF IMPLEMENTING SCHOOL-BASED MANAGEMENT
: Descriptive Study at Public Elementary Schools in Coblong Sub-district, in Bandung City, Indonesia
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
indicators. With measurable indicators can be used as a starting point to make the
item instrument in the form of questions or statements that need to be answered by
the respondents.
In addition, the respondents will be asked to answer the closed-ended
questions regarding with these three issues: 1) Influence of Principal Leadership
(X1); 2) Engagement of School Committee (X2); and 3) Effectiveness of
School-Based management (Y) of the research study.
And to obtain information from the field study, the questionnaires will be
use with the multiple choices in a form of Likert Scale of five weighted options as
shown the table below:
Table 3.2: Value of Likert Scale
Alternative Answers Question Scores
Very High 5
High 4
High Enough 3
Low 2
Very Low 1
1. Influence of Principal Leadership (X1)
To know the level of the Influence of Principal Leadership (X1) in the
day-to-day school operations, the researcher designs a table of brief aspects of the
study variable as shown below:
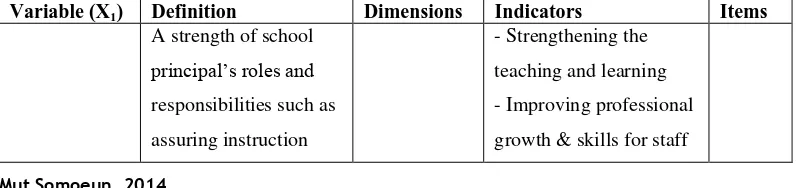
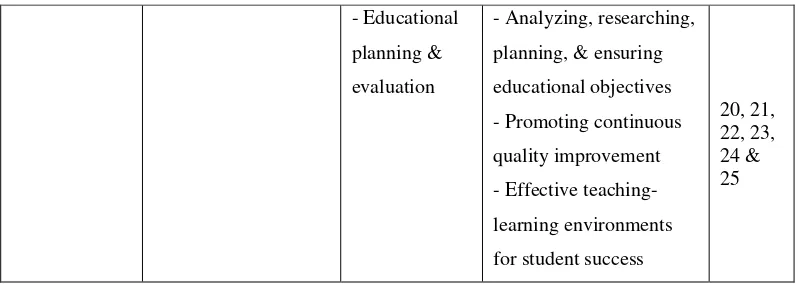
Table 3.3: Aspects of Instrument
Variable (X1) Definition Dimensions Indicators Items
A strength of school
principal’s roles and
responsibilities such as
assuring instruction
- Strengthening the
teaching and learning
- Improving professional
Mut Somoeun, 2014
THE INFLUENCE OF PRINCIPAL LEADERSHIP
AND ENGAGEMENT OF SCHOOL COMMITTEE TOWARD THE EFFECTIVENESS OF IMPLEMENTING SCHOOL-BASED MANAGEMENT
: Descriptive Study at Public Elementary Schools in Coblong Sub-district, in Bandung City, Indonesia
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
The Influence
and outside the school
- Involvement designer
of all stakeholders
- Motivator or coach of
Mut Somoeun, 2014
THE INFLUENCE OF PRINCIPAL LEADERSHIP
AND ENGAGEMENT OF SCHOOL COMMITTEE TOWARD THE EFFECTIVENESS OF IMPLEMENTING SCHOOL-BASED MANAGEMENT
: Descriptive Study at Public Elementary Schools in Coblong Sub-district, in Bandung City, Indonesia
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
- Liaison to outside
world
2. Engagement of School Committee (X2)
To know the times/ how often the Engagement of School Committee (X2)
is done in school affaires, the researcher designs a table of brief aspects of the
study variable as shown below:
Table 3.4: Aspects of Instrument
Variable (X2) Definition Dimensions Indicators Items
Mut Somoeun, 2014
THE INFLUENCE OF PRINCIPAL LEADERSHIP
AND ENGAGEMENT OF SCHOOL COMMITTEE TOWARD THE EFFECTIVENESS OF IMPLEMENTING SCHOOL-BASED MANAGEMENT
: Descriptive Study at Public Elementary Schools in Coblong Sub-district, in Bandung City, Indonesia
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
- Educational
3. Effectiveness of School-Based Management (Y)
To know the Effectiveness of School-Based Management (Y) is done in
school community, the researcher designs a table of brief aspects of the study
variable as shown below:
Table 3.5: Aspects of Instrument
Variable (Y) Definition Dimensions Indicators Items
Effectiveness
- Hiring & firing staff
Mut Somoeun, 2014
THE INFLUENCE OF PRINCIPAL LEADERSHIP
AND ENGAGEMENT OF SCHOOL COMMITTEE TOWARD THE EFFECTIVENESS OF IMPLEMENTING SCHOOL-BASED MANAGEMENT
: Descriptive Study at Public Elementary Schools in Coblong Sub-district, in Bandung City, Indonesia
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia | repository.upi.edu | perpustakaan.upi.edu
development
- Selecting textbooks
- Instructional schedule
E. Instrument Development Process
In data collection, the techniquesare needed to use the mostappropriate, so
thatit canget the valid and reliabledata. In this study, the researcherwillusesome
stepsas the followings:
1. Determination of Data Collection Tool
A tool is questionnaire will be used. Questionnaire is a list of questions to
others who are willing to respond in accordance with the user demand in granting
respondents to checklist answers to the required questions (Riduwan, 2010: 99).
Therefore, questionnaires used in this study are closed-ended questions, which
respondents have to answer the questions relate to the studied variables only.
2. Preparation of data collection tool
Data collection tool in the preparation of this study are as follows:
- Creating variable that will be investigated in accordance with the given
subject, namely variables: Influence of Principal Leadership (X1);
Engagement of School Committee (X2); and Effectiveness of
School-Based Management (Y).
- Constructing the aspects of questionnaires into questions.
- Formulatingcriteriascoresforeach itemaccording to