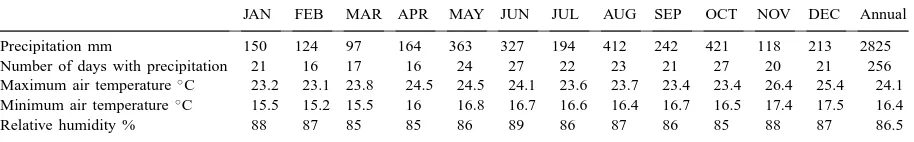
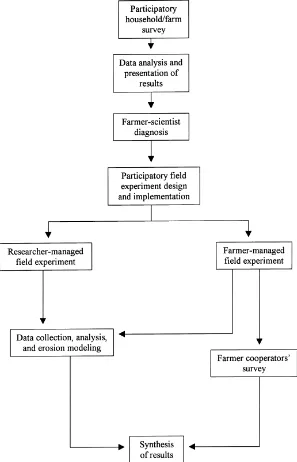
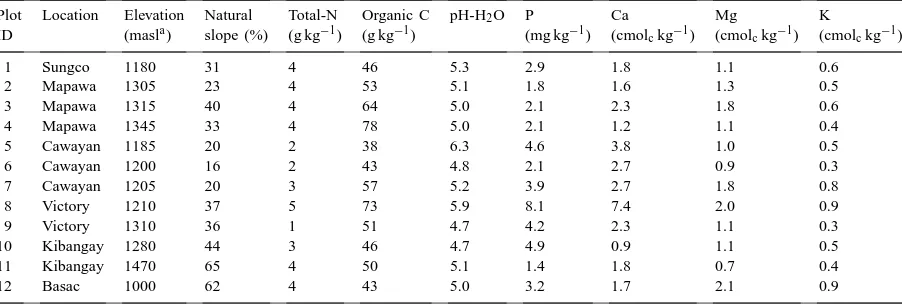
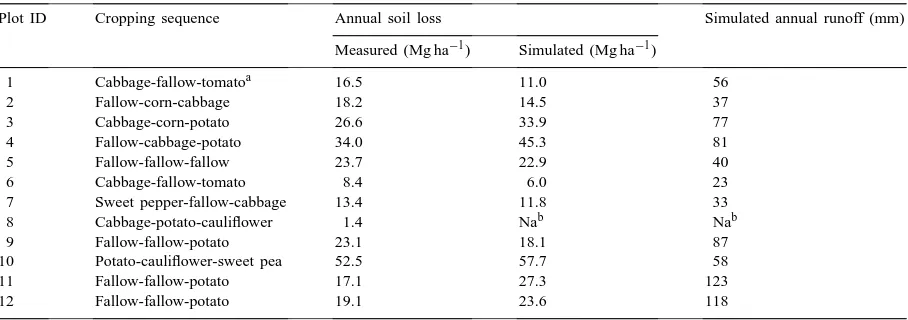
Directory UMM :Data Elmu:jurnal:A:Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment:Vol79.Issue2-3.July2000:
Teks penuh
Gambar
Dokumen terkait
Allelopathic effects of sorghum stalk incorporation into soil and sorgaab foliar spray along with chemical and cultural weed control methods were studied on the growth of different
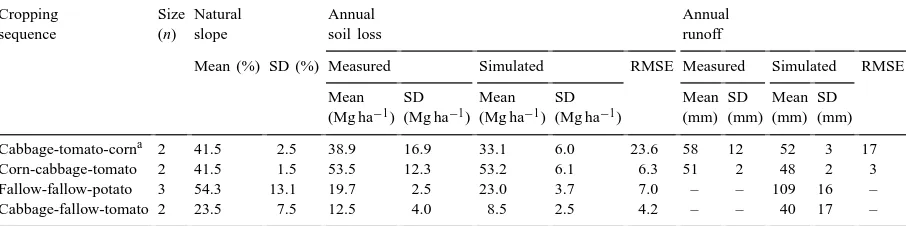
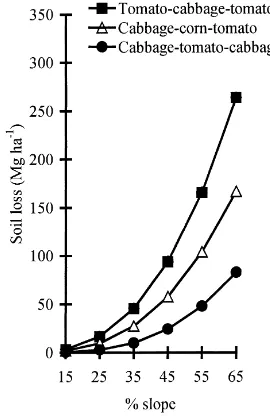
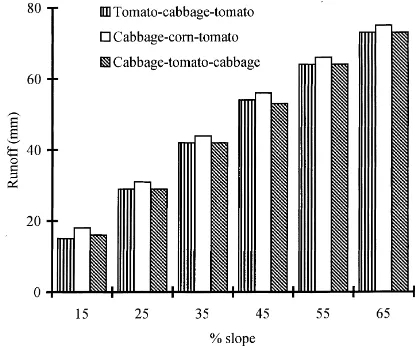
The objectives of this study were to: (1) determine the grain and above- ground biomass production and water-use efficiency of individual crops grown in the rotation; (2) analyze
Sites established by natural regeneration had greater cover and relative frequency of annuals and leafy species, lower cover of peren- nials, and greater relative frequency
On the other hand, for those who wish to work with others to support their action and their learning, the book provides a very nice account of a particular experience in the
Although similar patterns of drift were recorded at both sites, higher levels of fallout were recovered at Site 1 beyond approximately 25 m, attributed to greater wind speeds
Using the Fenland as a case study, this paper examines the hydrological requirements and likely financial and economic effects of a change in land use associated with the restoration
The effects of inorganic N fertilizers on upland taro (Colocasia esculenta (L.) Schott) and sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas (L.) Lam.) were quantified with the aim to
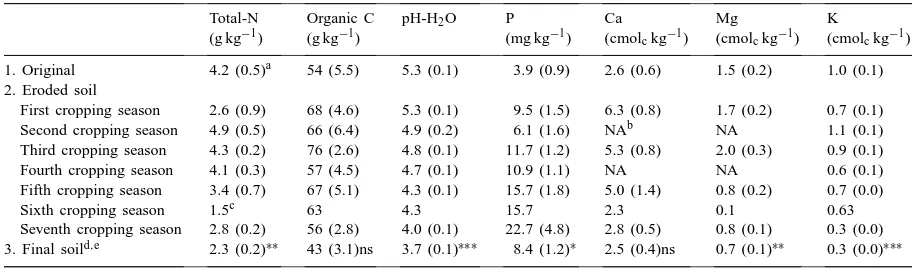
Significant changes in soil chemical properties included a decrease in pH and base saturation (Hobu) and a decrease in CEC and exchangeable K (Unitech). No significant changes in