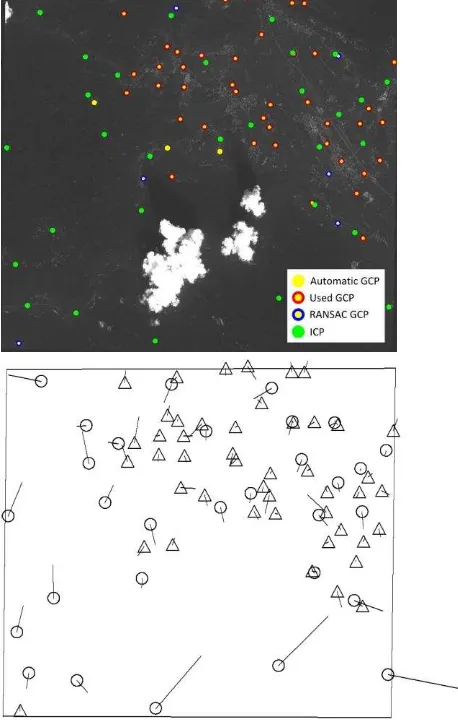
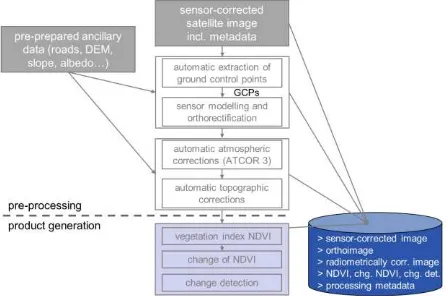
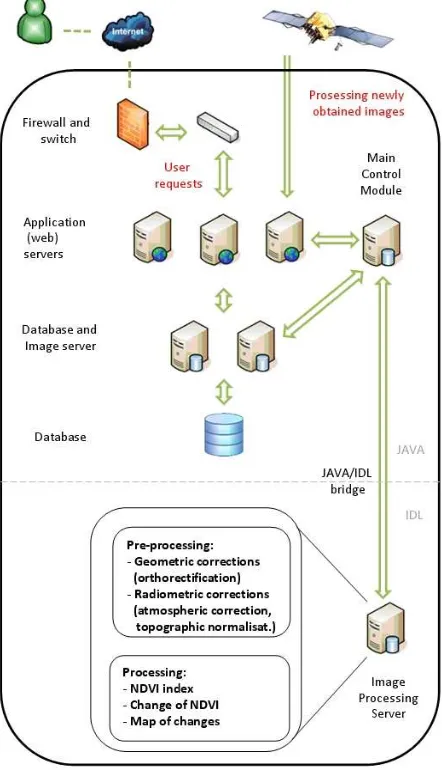
isprsarchives XL 7 W3 669 2015
Teks penuh
Gambar
Garis besar
Dokumen terkait
As shown in Table 2, the fractal dimensions for colors values of natural landscape images is also obviously smaller than that of urbanscape images.. Fractal dimensions for colors
It is already necessary to make a compromise between spatial and temporal resolution – if the data are available in high temporal resolution (from geostationary
Remote sensing data of four different spatial resolutions; broad- scale (250 m resolution Terra/MODIS); medium scale (10 m resolution SPOT/HRG-2); fine scale (0.5m
Study on shadow detection method on high resolution remote sensing image based on HIS space transformation and NDVI index. Shadow analysis in high-resolution
This paper examines whether improved temporal sampling at high spatial resolution (20m) with satellite data actually improves our knowledge of deforestation and
In this study, the feasibility of RapidEye data to derive leaf area index (LAI) time series and to relate them to grassland management practices is assessed.. The LAI is a
The comparison of the LAI retrieval based on RapidEye and OLI shows that the SLC model and the data assimilation concept in PROMET is very suitable for
In this work, we jointly process high spectral and high geometric resolution images and exploit their synergies to (a) generate a fused image of high spectral and geometric