STUDENTS’ ENGAGEMENT LEVEL: VERBAL PARTICIPATION IN PARTICIPATION POINT SYSTEM AT
MTs. ROUDLOTUL BANAT TAMAN SIDOARJO
THESIS
Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirement for the degree of Sarjana Pendidikan (S.Pd) in Teaching English
By Eka Oktaviana NIM D05213007
ENGLISH TEACHER EDUCATION DEPARTMENT
FACULTY OF TARBIYAH AND TEACHERS TRAINING
SUNAN AMPEL STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY
SURABAYA
ABSTRACT
Oktaviana, Eka. 2017. Students’ Engagement Level: Verbal Participation in Participation Point System at MTs. Roudlotul Banat Taman Sidoarjo. A thesis. English Teacher Education Department, Faculty of Education and Teacher Training, Sunan Ampel State Islamic University. Surabaya. Advisors: Rizka Safriyani, M.Pd and Sigit Pramono Jati, M.Pd.
Key words: Students’ Engagement, Verbal Participation, Participation Point System
they always ask to play game while it cannot be fulfilled by the teacher, the last challenge is about the teacher’s anxiety if she couldn’t fair with her students.
ABSTRAK
Ketertarikan siswa juga dikenal sebagai keterlibatan siswa dalam proses pembelajaran. siswa yang bisa melibatkan dirinya dalam proses pembelajaran dikenal sebagai siswa yang aktif, sementara siswa yang tidak bisa melibatkan dirinya dikenal sebagai siswa yang pasif. kepasifan siswa dan keaktifan siswa dipengaruhi dari metode yang mungkin diterapkan guru dikelas. untuk membuat siswa aktif, guru harus memikirkan metode yang sesuai yang dapat diterapkan di kelasnya untuk dapat membuat siswa-siswa nya berpartisipasi secara baik selama proses pembelajaran. Participation Point System atau PPS adalah salah satu metode yang dapat meningkatankan keaktifan siswa khusunya pada partisipasi verbal mereka. oleh karena itu, tujuan dari penelitian ini adalah untuk mengetahui level dari partisipasi verbal siswa yang diukur melalui PPS dan juga untuk mengetahui tantangan yang dihadapi guru selama menerapkan PPS dikelasnya. penelitian ini dilaksanakan di MTs. Roudlotul Banat dan mengambil sampel siswa kelas 7. kemudian, dengan menggunakan penelitian qualitative deskriptif, penelitian ini menggunakan observation checklist dan interview. observation checklist digunakan untuk mengetahui level partisipasi verbal siswa dan interbiew digunakan untuk mengetahui tantangan yang dihadapi guru dalam menerapkan PPS. Berdasarkan hasil penelitian ini, ada 3 siswa dari 41 siswa tang termasuk kedalam very high level, 12 siswa termasuk kedalam high level, 8 siswa termasuk kedalam medium and low level,dan 9 siswa termasuk kedalam low level. Secara keseluruhan, siswa dikelas 7 termasuk kedalam high level yang mana mengindikasikan bahwa mereka siswa yang sangat aktif, dan untuk tantangan yang dihadapi guru yang pertama adalah siswa tidak mempunyai kepercayaan diri dikelas untuk mengangkat tangat kereka karena mereka takut jika salah menjawab, kedua adalah siswa mempunya ekspektasi yang tinggi sepertimereka selelu meminta bermain game sementara itu tidakbisa dipenuhi oleh guru, dan tantangan terakhit adalah kekhawatiran guru jika tidak bisa adil dengan siswanya.
TABLE OF CONTENT
TITLE SHEET ... i
APPROVAL SHEET ... ii
EXAMINER APPROVAL SHEET ... iii
MOTTO ... iv
DEDICATION SHEET ... v
ABSTRACT ... vii
ACKNOWLEDGMENT ... ix
PERNYATAAN KEASLIAN TULISAN ... xi
TABLE OF CONTENT ... xii
LIST OF TABLE ... xiv
LIST OF FIGURES ... xv
LIST OF APPENDICES ... xvi
CHAPTER I: INTRODUCTION ... 1
A. Background of Study ... 1
B. Research Question ... 5
C. Objective of Study ... 5
D. Scope and Significance of Study ... 6
E. Definition of Key terms ... 7
CHAPETR II: REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE . 9 A. Theoretical Background ... 9
1. Students’ Engagement ... 9
2. Measuring Students’ engagement Level ... 10
3. Teacher’s Challenges ... 15
4. Verbal Participation ... 18
5. Participation Point System ... 20
CHAPTER III: RESEARCH METHOD ... 28
A. Approach and Research Design ... 28
B. Research Presence ... 28
C. Research Location ... 29
D. Source of Data ... 29
E. Research Stages ... 29
F. Data Collection Technique ... 31
G. Data Collection Instrument ... 32
H. Data Analysis Techniques ... 33
I. Checking Validity ... 34
CHAPTER IV: FINDING AND DISCUSSION ... 35
A. Research Finding ... 35
1. Students’ Verbal Participation Level ... 35
2. Teacher’s Challenges in Implementing PPS ... 52
B. Discussion ... 53
1. Students’ Verbal Participation Level ... 54
2. Teacher’s Challenges in Implementing PPS ... 57
CHAPTER V: CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION ... 61
A. Conclusion ... 61
B. Suggestion ... 62
REFENRENCES ... 64
1
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTIONA. Background of Study
In teaching English, students’ engagement is one of influential aspects in improving students achievement. According to Leah and Jim student engagement is the most important aspect and historically focused upon increasing achievement, positive behaviors, and a sense of belonging in students so they might remain in school.1Indeed, students’ engagement is important for increasing the students’ achievement because if the students engage the learning process they will enjoy the lesson and have spirit for studying. Beside that, if the students engage the learning process they will be motivated and committed to learn.2As Skinner and Belmont describe in their research:3
“Students who are engaged show sustained behavioral
involvement in learning activities accompanied by a positive emotional tone. They select task at the border of their competencies, initiate action when given the opportunity, and exert intense effort and concentration in the implementation of learning task; they show generally positive emotion during ongoing action, including enthusiasm, optimism, curiosity, and interest.”
It means that the behavior of the students will show their interesting in learning if they are engage with. They will enthusiasm in receiving the lesson from the teacher and also they will receive the lesson well. Students’ engagement can be created from the teacher by providing fun activity and the activity involves the students’ participation. It is line with Indonesia Curriculum 2013 on the Learning Concept and Strategy:4
1 Taylor, L. & Parsons, J., “Improving Students’ Engagement”. Current Issues in
Education. Vol. 14 No. 1, (2011) p. 4 2
Richard D.J., Student Engagement Level: Teacher Handbook (New York: International Center for Leadership in Education, 2009), 24
3 Skinner, E.A., & Belmont, M.J., “Motivation in the classroom: Reciprocal effect of the teacher behavior and student engagement across the school year. Journal of Educational Psychology. 85 (4). P.572
4
2
“Untuk mencapai kualitas yang telah dirancang dalam dokumen kurikulum, kegiatan pembelajaran perlu menggunakan prinsip yang: (1) berpusat pada peserta didik, (2) mengembangkan kreativitas peserta didik, (3) menciptakan kondisi menyenangkan dan menantang, (4) bermuatan nilai, etika, estetika, logika, dan kinestetika, dan (5) menyediakan pengalaman belajar yang beragam melalui penerapan berbagai strategi dan metode pembelajaran yang menyenangkan, kontekstual, efektif, efisien, dan bermakna.”
This statement stated that for achieving the quality of Indonesia Curriculum, the learning process has to use principle such (1) Students’ Centered (2) Developing students’ creativity (3) creating enjoyable and challenging learning environment (4) containing ethic, esthetic, logic, and kinesthetic value, and (5) providing various learning experiences through implementing kind of enjoyable, contextual, effective, efficient, and meaningful teaching strategy and method.
Basically, students’ engagement is influenced by the classroom environment that is created by the teacher. If the teacher can make the students participate well in the classroom, it means that the teacher success in making the students engage with the lesson. However, sometimes some teachers feel difficult to make the students engaged with the lesson. According on an article it is because students today live digitally every day. They used the internet, text messaging, social network, and multimedia frequently in their lives outside of school, and they expect a parallel level of technology opportunity in their academic lives. There is a disconnection between the way students live and the way they learn, and student engagement ultimately suffers. Closing this gap is a challenge for our current school systems.5 This might be one of the teachers’ challenging in engaging the students.
A key for increasing students’ engagement in the classroom is finding appropriate ways to measure it.6 According
5
Teaching in the 21st Century: A review of The Issues and Changing Models in The
Teaching Profession, (eduviews: Washington DC, 2008) retrieved from
www.blackboard.com 6
3
to Richard there are three dimensions of students’ engagement, there are intensity, breadth, and consistency.7 He further also said that from these three kinds of dimension the teacher can use different engagement scenario to engage the students. They are low engagement intensity, moderate engagement intensity but low consistency and the last is moderate engagement intensity but low breadth. From these three dimensions, there is one of the ways to measure the students’ engagement and that is by using active learning. Active learning method is included in the moderate engagement intensity but low consistency dimension.
One of active learning methods that the teacher might be used is Participation Point System or it usually called as PPS. This method is discovered by Hadley in 1997, it has been created to measure a participation mark of the students to see the students’ progress. This method also is adopted by Jeffrey; he stated that by adapting this method in the classroom, it can overcome the students’ passivity because the students can see directly their mark. Meanwhile, he further also stated that the aim of PPS is to overcome this obstacle by letting them know directly their progress of their work. The intention of this method is by giving the students tangible reward so that they can see and touch, and making these participation point as an important of grading score8. The focus of this method is to make the students active in the class by giving them tangible reward. Hence, this method not focus in the skill but in the students’ participation in the classroom. If the participation of students good it means that the students engage with the learning process.
According to Richard, there are 10 students’ engagements characteristic they are positive body language, consistent focus, verbal participation, student confidence, fun and excitement, meaningfulness of work, rigorous thinking, and performance orientation.9 As what have been written in the previous paragraph, PPS is focus in the students’ participation so that the characteristics of students’ engagement that can be measured in PPS is verbal participation. Verbal Participation is
7
Ibid 34
8 Jefferey, D.M, “A Motivational Participation Point”. Proceeding Conference. Tokyo:JALT 2004
4
about the students’ participation verbally, such give their idea when there is discussion in the classroom and also they are active in answering and asking question to/for the teacher. Richard further said that verbal participation is students express thoughtful idea and answer, they ask question that relevant or appropriate with learning. Students participation is not passive, it can involve the students in the discussion and they can share their opinion and reflecting on complex problem.10
Some previous studies state that in measuring students’ engagement level have predominantly focused on quantitative data such as attendance, standardized test scores, and truancy or graduation rates. The majority of these measures track levels of achievement (outcomes such as high scores, full attendance for the year) but not levels of student engagement in learning (interest, time on task, enjoyment in learning).11 Another previous study stated by Jessica and Linda, they stated that in measuring students’ engagement level they used Classical Test Theory (CTT). CTT is relatively simple to employ and has served measurement researchers well for many years, but since CTT was first popularized a more powerful measurement theory has been developed—Item Response Theory (IRT). IRT is theoretically and mathematically more sophisticated than CTT and can be used to obtain estimates of constructs and latent traits that have many desirable attributes (such as interval scale properties), yet it has largely been ignored by higher education researchers interested in measuring student involvement.12
In addition, in this research students’ engagement level will be measured through Participation Point System. This method is related with verbal participation in order to overcome the students’ passivity, because by using this method in the classroom the teacher can measure the students’ engagement level especially in their verbal participation. This research will be different from the previous research because in this research the
10
Ibid 29 11
Taylor, L. & Parsons, J., “Improving Students’ Engagement”. Current Issues in Education. Vol. 14 No. 1, (2011), p. 5
5
tool that is used in measuring the students’ verbal participation is PPS, and PPS itself is a strategy that can overcome students’ passivity. As what have been stated in the previous paragraph, verbal participation has correlation with the students’ activeness so that is why PPS is a strategy that can be used to measure this characteristic of students’ engagement. Beside that, most of previous researches in PPS used this strategy for increasing the students’ activeness generally, but in this research the focus of students’ activeness is measured only in their verbal participation and this is characteristic of students’ engagement.
This research will be conducted at Mts. Roudlotul Banat because in this school the teacher has already implemented PPS in her class. It can be seen from the lesson plan of the teacher, there is a method that use tangible reward for improving the students’ activeness.
B. Research Question
There are two research questions in this research, they are: 1. How is the students’ verbal participation level in PPS? 2. What are the challenges faced by the teacher in
implementing PPS regarding her students’ verbal participation?
C. Objective of the Study
The objective of this study is to measure the students’ verbal participation through teaching method called PPS. The students are at MTs. Roudhlotul Banat Taman in the 7th grade. How the level of the student’s verbal in this class is. In specific, the researcher objectives are;
1. Describe the students’ verbal participation level that is measured through participation point system.
2. Describe the teacher’s challenges in implementing PPS regarding her students’ verbal participation
D. Significance of the Study The significance of this study is:
6
they can apply these results to their classroom. They can use PPS as the tool to enhance the students’ verbal participation.
2. For the students, they will know how their level of verbal participation and their progress in class. It can motivate the students’ learning and lead to development of their achievement.
3. For the researcher, this research will give many benefits for the researcher as the teacher will be, because in this research there is a teaching method that can be used to measure the students’ verbal participation by giving the students tangible reward, which this strategy also can enhance the students’ activeness. However, as the teacher it is important to be known.
E. Scope and Limitation of the Study The scope and limitation for this study is:
1. The scope of the study is to describe the students’ verbal participation level through PPS. Verbal participation here will measure through reward or in this case “star” that the students get. From this research the teacher can enhance the students’ activeness and they can engage the students in their verbal participation. PPS here only as the tool for measuring this level because PPS has correlation with this kind of students’ engagement characteristics.
2. This research will be conducted at MTs. Roudhlotul Banat Taman Sidoarjo and take students in the 7th A grade as the subject. There are 41 students in this class, and all of them will be the subject of this research.
F. Definition of Key term
The researcher wants to avoid misunderstanding by defining the key terms of this study as follows:
7
take visible delight in accomplishing their work.13 It means that students’ engagment is students’ behavior in the class, how they engage during learning process. Then, in this research students’ engagement means the students’ involvement during learning English.
2. Students’ engagement level: Trowler indicates three dimension to students’ engagement that can measure the students’ engagement level, they are behavior, emotion and cognition.14 Then, the definition of students’ engagement level in this research is the level of students’ engagement that can be measured through learning method called PPS.
3. Verbal participation: Richard said that verbal participation is students express thoughtful idea and answer, they ask question that relevant or appropriate with learning. Students participation is not passive, it can involve the students in the discussion and they can share their opinion and reflecting on complex problem.15 Then in this research verbal participation is students’ activeness in giving their opinion and frequently asks question to their teacher during learning process. 4. Teacher Challenge: According to Luciano teacher
challenge includes union ideas such as putting oneself to a test, dealing with interesting things, and facing the unexpected and the unpredictable.16 While in this research, teacher’s challenges is the obstacle that is faced during implementing PPS to know the students’ verbal participation
4. Participation Point System: According to Hadley the participation point system is a method of motivating classroom participation, especially communicative participation, by giving students something tangible
13
Adam, F. Defining Student Engagment: A Literature Review. (Retrieved from
http://soundout.org/defining-student-engagment-a-literature-review/, accessed on March 11, 2017)
14
Vicki Trowler, Students’ Engagement Literature Review (Department of Educational Research: Lancaster University, 2010)
15 Ibid 29
8
(such as discs, marbles, poker chips, etc).17 Participation Point System (PPS) in this research as the tool to measure the students’ verbal participation and performance orientation. This method uses points to score down the involvement of students in the learning activity.
17
Hadley. G, “Encouraging Oral Communication in the EFL Classroom”. (Paper presented at Niigata University General Education and Language Research Group. Niigata City. Japan. Retrieved from
CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
A. Literature Review
This chapter discusses some issues related to the students’ engagment in PPS which become the focus of this research. It contains the theoritical background and review of related study or calls the previous study. Some previous studies related to this research are also discussed. Another, it consists of some theories strengthening the problem discussed here.
1. Theoretical Background
There are some theoretical backgrounds that relate with this research. There are five theoretical backgrounds that will be discussed. Those theories will be stated as below:
a. Students’ Engagement Definition
According to David’s research, students’ engagement was
divided into three terms; they are engagement, attendance and participation. It has a high profile in discussions of improving educational outcomes for Indigenous students.1 They
sometimes have indistinct boundaries with attendance being used as a synonym for participation for example, and engagement ranging in people’s minds from meaning concentrated effort in the classroom to a description of very broad types of involvement. At ground level, participation probably means things like joining in a sports carnival or providing an item at a concert, whereas from a technical perspective it is often related to grade retention and suspension statistics. Belonging brings a different flavour to the discussion and is included here for reasons explained overleaf. But taken together they provide a description of how we want our students to be, immersed constructively and enthusiastically in the developmental experiences and products that schooling provides.
Based on Trowler’s opinion, student’s engagement is involved with the interaction between the time, effort and other relevant resources invested by both students and their
2
institutions that intend to optimize the students’ experience enhance the learning outcomes and development of students and the performance, and reputation of the institution.2 So, students’ engagement is a part of learning process which is intended to enhance the students’ achievement.
b. Measuring the Students’ Engagement Level
Jessica and Linda said that in measuirng students’ engagment there are two ways. They are CTT (Classical Test Theory) and IRT (Item Response Theory).3 CTT is relatively simple to employ and has served measurement researchers well for many years, but since CTT was first popularized a more powerful measurement theory has been developed. IRT is theoretically and mathematically more sophisticated than CTT and can be used to obtain estimates of constructs and latent traits that have many desirable attributes (such as interval scale properties), yet it has largely been ignored by higher education researchers interested in measuring student involvement. So, in Jessica and Linda opinion, they compared between CTT and
IRT to measure the students’ engagement level, and the result
of this research is not only argue for unidimensionality but also, provide evidence of „„local independence,’’ which is a critical assumption of IRT.
In the other hand, Trowler indicates three dimension to students’ engagement.4
They are: 1) Behavioral engagement
Students who are behaviorally engaged would typically comply with behavioral norms, such as attendance and involvement, and would demonstrate the absence of disruptive or negative behavior. So, behavioral engagement can be seen from the behavioral norms of the students. In addition, Mintz states that survey questions that are grouped within this dimension of engagement
2 Vicki Trowler, Students’ Engagement Literature Review (Department of Educational Research: Lancaster University, 2010)
3 Jessica, S., Linda, DA., Measuring Student Involvement: A Comparisonof Classical Test Theory and Item Response Theory in the Construction of Scales from Student Surveys: Cooperative Institutional Research Program at the Higher Education Research Institute. (2011) , p. 481
3
include questions about homework, preparation for class, classroom discussions and assignments, and the level of academic challenge that students report.5 It means that the behavioral engagement of the students includes their behavior in class activity, such as: the students’ contribution in class, the students’ performance, etc. Moreover, based on Lester opinion, the involvement in learning and academic tasks includes student behaviors related to concentration, attention, persistence, effort, asking questions, and contributing to class discussions.6 It means that the students’ involvement in learning can be seen from their behavior includes their concentration, attention, asking question, etc. So, behavioral engagement includes the participation of the students to the activities of the institution in order to achieve positive outcomes. According to those theories and the purpose of this research which focus on students’ verbal participation, it can be concluded that behavior engagement is students’ behavior in class that shows their involvement in class including their positive behavior toward the teacher and class activities.
2) Emotional engagement
Students who engage emotionally would experience affective reactions such as interest, enjoyment, or a sense of belonging. So, emotional engagement can be seen from the affective reactions of the students. Moreover, Finlay states that emotional engagement includes interest, values, emotion.7 For example, affective reactions in the classroom, attitudes towards school and teachers, identification with school, feelings of belonging, appreciation of success in school, antithesis of positive feelings is also emotional engagement items. So, emotional engagement here means the students’ reaction
5 Ethan Yazzie Mintz. Charting the Path from Engagement to Achievement: A Report
on the 2009 High School Survey of Student Engagement. (Indiana: Indiana University, 2009).
6Derek K. Lester: “Environmental engagement demand differences within and among
Holland academic environments” (Las Vegas: University of Nevada, 2011), 24.
4
includes interest, enjoyment, values toward the class activity and the teacher.
According to those theories and the purpose of this research which focuses on classroom observation especially on the students’ verbal participation, it can be concluded that emotion engagement is the students’ reaction, feeling and emotion to the class activities that can be positive or negative emotion.
3) Cognitive engagement
Cognitive engagement reflects a student’s investment in learning. Students who are cognitively engaged set learning goals, self-regulate their own behavior, and desire to go beyond the minimum requirements.8 She further also said that It isdifference between surface level rotelearning and deep level discoveries ofmeaning and connections. It is effortfocused on mastering the material. Teachers can
increase this type of engagement by developing students’
higher level thinking skills (analysis,making connections) and encouraging active responding (writing, responding) as opposed to passive participation (listening, taking turns). Teachers can also generate this engagement by
making learning fun, like the comic-book scenario
mentioned earlier. It means that this form of engagement is also linked to achievement, deep understanding, and flexible thinking skills.
Then based on Fredricks thought, cognitive engagement is defined as the student’s level of investment in learning; it includes being thoughtful and purposeful in the approach to school tasks and being willing to exert the effort necessary to comprehend complex ideas or master difficult skills.9 It means cognitive engagement can be defined as students’ will, purpose and effort to master the skill.
8 Karen, V. Badell, “From Research to Practice: Students’ Engagment”( retrieved from www.punyamishra.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/02.Bedell-Student-Engagement.com)
9 J Fredricks, W McColskey, et al. Measuring student engagement in upper
5
According to those theories and the purpose of this research which focus on classroom observation especially in students’ verbal participation, it can be concluded that cognitive engagement is the students’ thought and comprehension about the lesson that have been explained by the teacher during the class activities.
Based on Jones the students’ engagement level can be measured from the characteristics of students’ engagement. They are positive body language, consistent focus, fun and excitement, individual attention, clarity of learning, meaningfulness of work, rigorous thinking, and performance orientation.10
1) Positive body language
Students show body postures that indicate listening and paying attention to the teacher or other students. It includes their eye contact, head position, leaning forward or backward, and positions of arms. All of them show the student’s level of interest and attention. 2) Consistent focus
Students are focused on the learning activity with minimum disruptions including their attention that shows they interest with the activities.
3) Verbal participation
Students show thoughtful ideas and answers which indicate they are active students. For example, they ask questions that appropriate to learning, share their opinion about the lesson, and reflect problem that they get in the class.
4) Student confidence
Students show confidence in doing their task with limited coaching or approval-seeking and active in participation of team-based work.
5) Fun and excitement
6
Students show interest, enthusiasm and use positive humor.
6) Individual attention
Students feel comfortable in asking help or questions.
7) Clarity of learning
Students can describe the purpose of the lesson or unit rather than describing the activity based on the lesson of the day.
8) Meaningfulness of work
Students discover that the work interesting, challenging, and connected to learning.
9) Rigorous thinking
Students can work on complex problems, create solutions by them selves, and reflect on the quality of their work.
10) Performance orientation
Students know what quality of work is and how it will be assessed. They can evaluate the quality of their work.
Considering those theories, the researcher concludes that in measuring students’ engagement level we have to consider the characteristic of students’ engagement, it includes students’ behavior, emotion, and cognitive in class.
c. Teacher’s Challenges
Engaging students is not easy thing to do in the classroom since there are many different characteristic of students in the class. Based on the Julie said that as the teacher we need to provide our learning with activities that are innovative and challenging as well as purposeful if we want them to be engaged in learning.11 As the teacher, challenging in engaging students is common problem and need solution. The challenging that sometime occurs are:
a. Students’ Anxiety
7
According to Steven and Lynn, Reticent behavior poses particular problems when it comes to language learning. They also defined as a person for whom anxiety about participation in oral communication outweighs his projection of gain from that situation.12 b. Students High Expectation
Students across the achievement and socioeconomic spectrum need and deserve motivating, supportive instructional environments, engaging content, and the opportunity to learn in settings that support collaboration with peers, teachers, and the larger world community. Students today live digitally every day. They use the Internet, text messaging, social networking, and multimedia fluidly in their lives outside of school and they expect a parallel level of technology opportunity in their academic lives. There is a disconnect between the way students live and the way they learn, and student engagement ultimately suffers. Closing this gap is a challenge for our current school systems.13 Based on Peter and Julie, it is importance of teachers being clear, setting high expectations for student achievement, and working hard to develop good relationships between students.14 Not only that need the students are wanted, students also need the enjoyment learning in the class, if the students didn’t enjoy the lesson they will bored all the time. Peter and Julie further also said that boredom, as well as teacher-student misunderstandings and students’ negative attitudes towards school, they could be consequences of students being uninterested in the curriculum, students being unhappy at home or in the schoolyard, or poor quality teaching.15
12 Steven J. C. & Lynn E. H., “Addressing Reticence: The Challenge of Engaging Reluctant Adult ESL Students”. Journal of Adult Education. Vol 44 No.4, 2015 13Teaching in the 21st Century: A review of The Issues and Changing Models in The
Teaching Profession, (eduviews: Washington DC, 2008) retrieved from
www.blackboard.com
14Peter G. & Julie T., “Engaging Students: Creating Classroom That Improve Learning”. (Gratan Institute, 2017) 6
8
Respectful relationships and interaction, both virtual and personal are shown to improve student engagement. Students today are intensely social and interactive learners. The results from Imagine a School, Design For Learning, and What did you do in school today? repeatedly show that: (1) Students want stronger relationships with teachers, with each other, and with their communities locally, provincially, nationally and globally. They want their teachers to know them as people. (2) Students want their teachers to know how they learn. They want their teachers to take into account what they understand and what they misunderstand, and to use this knowledge as a starting place to guide their continued learning. (3)Students want their teachers to establish learning environments that build interdependent relationships and that promote and create a strong culture of learning.16
In addition, according to Prayong and Rapeepon, teacher’s anxiety is also become one of the challenges of the teacher, they are teacher’s expectation, students’ attitude towards studying English, and teacher’s language proficiency.17
a. Teacher’s Expectation
They may perceive disorganized behavior of the low ability students and have a large number of the students in their classroom. Moreover, the teachers have doubts in using bilingual teaching resulting from their concerns about their pronunciation and fluency in speaking English. In addition, teachers would like to collect information about the students related to their motivation in learning the language, proficiency in learning the language both using the native language and English, and their reluctance to use English while studying in the classroom. b. Student Attitudes Towards Studying English
16Leah T. & Jim P., “Improving Students Engagment”. Currents Issues in Education. Vol 14 No.1, 2011
17Prayong K. & Rapeepon S., “ EFL Teacher’s Anxiety in Using English in Teaching
9
This component was ranked as the second most important. Overall there were medium level concerns about the students’ attitudes towards studying English. This study found that a language learner is always anxious about error correction in the classroom. As a teacher instructing in a non-native language, teaching causes anxiety. There is also stress since they have difficulty using the language. However, they need to speak to the whole class. If the instructor makes some, it can be quite embarrassing. This causes a loss of confidence. This can be equivalent to public scolding.
c. Teacher’s Language Proficiency
The students not only learn the language, but also learn through using classroom English and common expressions in daily life. Finally, using the target language in teaching benefits the students in gaining proper language and good attitudes towards learning languages. A language teacher can provide a good example in using a second language effectively. He or she can impart linguistic and cultural knowledge. This can solve other learning problems for students as well.
These challenges are sometime faced by the teacher during teaching English. However, not all from the challenges above will be faced by teacher.
d. Verbal Participation
According to Richard verbal participation is students show thoughtful ideas and answers which indicate they are active students. For example, they ask questions that appropriate to learning, share their opinion about the lesson, and reflect problem that they get in the class.18 Beside that, according to Meghan Condon, students’ verbal participation is influenced also by verbal learning. In her opinion, verbal learning here created engaged
10
citizens such young people who acquire greater verbal skill in school participate more in political and community affairs later in life.19 Means that if the teacher can engage the student in their verbal participation it will create future young people who are active in community and they can survive in citizen area. For each level there are the characteristics, to know each characterictics in each level, see table below:
19 Meghan. A., “Improving verbal learning in schools can increase political
11
Table 2.1 Criteria of Verbal Participation Level
Criteria Very High
High Medium Low Very
12
The table above clearly defined the characteristics of students in each level. This level can be used to identify the level of students’ verbal participation in the class.
e. Participation Point System
Participation Point System is one of methods that the teacher might use in improving students’ motivation in learning English. This method was created by Hadley in 1997 and developed by Jeffery in 2003. Both of them did those researches in Japan. The purpose of this method is to have effective method to measure a participation mark of the student to see the students’ progress (English speaking skill) and to make students get accustomed to speaking.20 According to Hadley the participation point system is a method of motivating classroom participation, especially communicative participation, by giving students something tangible (such as discs, marbles, poker chips, etc.)21 while activities are underway to represent their participation scores. At its foundation, the PPS is very simple, and operates as follows:22
1) Desirable behaviors (answering or asking questions, giving opinions, volunteering for activities, etc.) are assigned a point value
2) Students who engage in desirable behaviors are rewarded with a physical representation of the point value (coins or tokens)
3) At the end of each lesson, the number of points received by each student is calculated
20A. Sri Asrina, “Imoroving The Students’ Speaking Ability Through Participation
Point System (PPS) Method (A Class Action Research on the Tenth Grade Students of
SMA PGRI Sungguminasa)” (Makasar: University of Muhammadiyah) 122 retrieved from http://unismuhwriters.com/2015/11/28/improving-the-students-speaking-ability/
21 Hadley, G . Encouraging Oral Communication in the EFL Classroom. (Paper Presented at Niigata University General Education and Language Research Group. Niigata City. Japan). Retrieved from
www.nuis.ac.jp/~hadley/publications/partpoints/participation.htm on October 09, 2016
13
4) Special prizes are awarded at the end of each semester for the students with the most point 5) The value of points may also count toward students’
final grades.
It means active participation is a must for every student; clearly communicating daily expectations is a must for every teacher. This participation points system combines these in a measurable, visual way. Each class activity is assigned a number of points that students can earn as they complete tasks. As students engage in the activities, they write on their grids the points they earn by participating. Just before the class ends, the students write their total for that day. These can be then used for giving daily, weekly or semester long participation grades.
The intention of the participation point system is to reward students in a simple yet tangible way. The best form of praise is rewarding them immediately with participation point that they can actually see and touch, and making these participation points an important part of the grading process.23 Participation point system is a simple method devoleped by Hadley. The idea of the method is how to make students participation become tangible so that students can evaluate their progress. Participation Point Systems can be highly effective in helping students overcome their anxieties and become more proactive language learners.24 In addition, the PPS aims to overcome the students’ passivity by giving students something on the spot that lets them know immediately of their progress. Students then feel an immediate sense of achievement, which is needed to
23 Hadley, G . Encouraging Oral Communication in the EFL Classroom. (Paper Presented at Niigata University General Education and Language Research Group. Niigata City. Japan). Retrieved from
www.nuis.ac.jp/~hadley/publications/partpoints/participation.htm on October 09, 2016
14
encourage them to speak more, and to use their imagination.25
According to those theories and the purpose of this research which focus on classroom observation especially in students’ verbal participation and perfomance orientation, it can be concluded that PPS is a method that can make students’ active in the class by giving them something tangible in order to make them know their progress in learning process.
B. Previous Study
There are eight previous studies that relate with this study. These previous studies are useful for this research because it can make different between current study with the previous study. Below are the previous studies:
The first research was written by Armbruster entitled “Student Engagement and Motivation: Research Analysis of Influences and Effects on Student Achievement”, the researcher found that teacher practices and student-teacher relationships, student motivation and self-efficacy, classroom environment/ students’ perceptions of school influenced the students’ engagement and motivation.26
The second thesis was written by Delialioğlu entitled
“Student Engagement in Blended Learning Environments with
Lecture-Based and Problem-Based Instructional Approaches”. This research was about how blending of a different instructional approach with technology affected students’ engagement.27
The third research was conducted by Santi Dwi Rahayu in 2014 entitle “An Analysis of Students’ Engagement Level in Outdoor and Indoor Class at English Intensive Grammar Class of Madrasah Aliyah Bilingual Krian”. The finding of this research talks about the level of students’ engagement in
25 Jefferey, D.M. Participation Point System to Encourage Classroom
Communication. The Internet TESL Journals vol. IX. No 8, August 2003.Retrieved at
http://iteslj.org/techniques/Jeffrey-PointSystem.html onOctober 9, 2016 26Ashley Armbruster: “Student Engagement and Motivation: Research Analysis of
Influences and Effects on Student Achievement”. (USA: Webster University, 2007).
27Ömer Delialioðlu: “Student Engagement in Blended Learning Environments with
Lecture-Based and Problem-Based Instructional Approaches”. (Turkey: University of
15
outdoor and indoor class. From the result of observation in indoor class, the highest level of students’ engagement can be found in group work activity. The average level of students’ engagement can be found in watching movie activity. While the lowest level of students’ engagement can be found in lecturing activity. It happens because the students are more enjoyable in watching movie and group work discussion than they just listen to the teachers’ explanation. While From the result of the observation in outdoor class. The highest level of students’ engagement can be found in group work discussion activity and individual work activity. While the lowest level of students engagement can be found in lecturing activity. It happens because they feel very enjoyable when they do group work activity in outdoor class. Each of groups discusses in different places in outdoor that makes them do not feel boring. While, in individual work activity they have to do a task by themselves and the teacher will give them mark for the process of doing the task. So they engage more in this activity because they have high motivation to get a good mark. 28
The fourth is research by Eva Zuliati from University of Muria Kudus. Her title of the research is “The Use of Participation Point System in Teaching Speaking For the Eighth Grade Students of SMPN 2 Jati Kudus in Academic Year 2013/2014”.29 The findings of this research show that PPS
was useful method that might be used for the teacher to increase the students’ speaking skill. The students will have more self-confidence than before. This research used experimental method which was there were two variables (Independent and dependent variable). The researcher used pre and post test, and the result of those test showed a significance result of the students. In the pre-test which was haven’t taught by using PPS, the students’ score was 65.73 (it indicates enough score), while in the post-test which was have been
28Rahayu Santi, D., Undergraduate Thesis “An Analysis of Students’ Engagement Level in Outdoor and Indoor Class at English Intensive Grammar Class of Madrasah
Aliyah Bilingual Krian”. Retrieved from http://digilib.uinsby.ac.id
29 Zuliati Eva, Postgraduate Thesis: “The Use of Participation Point System in
Teaching Speaking For the Eighth Grade Students of SMPN 2 Jati Kudus in Academic
Year 2013/2014” (Kudus: University of Muria Kudus, 2014) retrieved from
16
taught by using PPS the students’ score were increase become 77(it indicates good score). Hence, the researcher can conclude that the use of participation point system can improve students’ speaking ability.
Fifth research was conducted by Nurul Hidayah from University of Pancasakti Tegal. The title of her research is “The Effectiveness of Using Participation Point System (PPS) Method in the Teaching of Reading for The Second Grade Students of Vocational High School (An Experimental Study in SMK Muhammadiyah Belik in The Academic Year of 2013/2014).30 The result of this research shows that there is a significant difference between students who are taught using PPS and students who are taught using Grammar Tranlation Method. It can be concluded that using PPS in teaching reading for Vocational High School is effective method. The participant of this research is 30 students which were include as experimental and control group, the students was given 30 item of multiple choice in order to know the reliability and validity of the test.
The sixth research was done by A. Sri Asrina from Univeristy of Muhammadiyah Makasar. The title of her
research is “Imoroving The Students’ Speaking Ability Through
Participation Point System (PPS) Method (A Class Action Research on the Tenth Grade Students of SMA PGRI
Sungguminasa)”.31
The result of this research showed that the mean score of the students’ speaking diagnostic test was 3.7 as categorized poor (low ability) while the mean score of the students’ speaking test in cycle 1 was 5.2. It had a significance progress but still the result did not reach the determined standard score 6.5, so the researcher conducted the cycle II. In the cycle II the researcher got the mean score 70 which was it was good. Therefore, in the cycle II there was a significance
30H. Nurul, Undergraduate Theis: “The Effectiveness of Using Participation Point
System (PPS) Method in the Teaching of Reading for The Second Grade Students of Vocational High School (An Experimental Study in SMK Muhammadiyah Belik in The
Academic Year of 2013/2014)” (Tegal: University of Pancasakti) retrieved from
http://perpus.upstegal.ac.id
31A. Sri Asrina, “Imoroving The Students’ Speaking Ability Through Participation
Point System (PPS) Method (A Class Action Research on the Tenth Grade Students of
SMA PGRI Sungguminasa)” (Makasar: University of Muhammadiyah) retrieved from
17
improvement from the students’ ability both in the accuracy (vocabulary and grammar) and fluency (smoothness). This research took 26 students as the subject and used Classroom Action Research containing 4 stages (planning, action, observation, and reflection). The data were collecting after did diagnostic test for the students.
The seventh research was done by Stephanie Almagno entitled “Participation Point: Making Students Engagement Visible”.32 In this research, the researcher did some method in giving point to the students’ participation such as use a new moniker, lead with preparation, share and review the student’ engagement rubric from day one, students must score themselves against the Engagement Rubric, recognize quiet learners (during and after class), and re-direct talkative students who don’t full engage with contents. By using this method, the researcher found that the students’ involvement or engagement was increase during implementing these kinds of teaching strategies that she had been planned.
Eighth research was conducted by Kelly S Rocca entitled “Participation in the College Classroom: The Impact of Instructor Immediacy and Verbal Aggression”.33 This study exemined the students’ behaviour of classroom participation at undergradute students. This research talked about the teacher’s intruction that used immediacy and verbal aggression. The finding of this research is that participation in the classroom increase if the teacher used immediacy instruction rather than verbal aggression. Based on this research, the researcher conclude that teacher’s instruction influenced the students’ participation. It did’t mean that students’ not engage with the learning process, but they more percieved if the teacher used immediacy instruction because immediacy intruction clearer than verbally aggression.
This curent study will be different with the previous studies above. The first difference is that in this study the researcher will focus only in the students’ verbal participation which is it includes in the students’ engagement level. In one to three
32Stephanie, A., “Participation Ponit: Making Student Engagment Visible” Effective
18
previous studies above the writer talked about the students’ engagement generally not in the specific characteristics of it. As what have been stated before that there are ten characteristic of students’ engagement, and the previous studies measure all of those characteristics while here in this research only one characteristic and that is verbal participation.
The second difference is that in this current study the way how to measure students’ verbal participation will use PPS method. In this study PPS will be used as the tool to measure the student’s verbal participation by counting the reward that the students get. While in the fourth to sixth previous studies above disscuss about the implementing PPS in order to enhance the students’ motivation in learning English. The researchers in the previous studies implement the PPS to know the effectiveness on PPS in improving students activeness in the class but, in this current study the researcher only analyze the implementing of PPS that has been implement by the teacher at Mts. Roudhlotul Banat and also analyze the students’ verbal participation through reward that they get.
1
CHAPTER III RESEARCH METHODA. Approach and Research Design
The research method that is used in this research is qualitative. Qualitative research is a process which tries to understand more about the complexity on the interaction of human.1 This study was a qualitative research which consists of interpretations and descriptions rather than numbers. In line with Kothari, Qualitative research is specially important in the behavioural sciences where the aim is to discover the underlying motives of human behavior.2 Through such research we can analyze the various factors which motivate people to behave in a particular manner or which make people like or dislike a particular thing. This research included open-ended results from the data collection procedures. It include a mixture of transcript of interview and the result of the checklist observation.
This research focused on describing the level of students’ verbal participation which is measured through implementation of Participation Point System. The design of this qualitative research was a case study design.
B. Research Presence
In this research, the role of the researcher is as the key instrument. The researcher as the key instrument means the researcher observes or interviews the participants directly.3 The researcher collected the data by themselves by observation and interview. The researcher used Obtrusive or Undisguised Observation. Obtrusive or undisguised observation means the respondents are aware that they are under observation by the
1 Sarwono, Jonathan, 2006 “Metode Penelitian Quantitative dan Qualitative” Yogyakarta
2
C.R. Kothari, Research Methodology: Methods and Techniques (Jaipur: New Age International, 2004), 3
3 John W. Creswell,
2
observer.4 Before the observer observes the class, the teacher introduced the observer to the students, so her presence as an observer in the class is obvious to the students.
C. Research Location
This research was conducted at Mts. Roudlotul Banat Taman Sidoarjo and took students in the 7th A grade. This class consists of 41 students was selected because according to the teacher, some of the students in this class are smart, having high motivation in learning English, and they can be handled well rather than the other classes.
D. Data and Source of Data
In this study, the researcher gained the data from the observation by filling observation list which is adapted from “students’ engagement walkthrough checklist” to observe the students’ characteristic in class that shows their verbal participation in class and to support or enrich the data, questionnaire also was spread. Then, the interview session was done to get information about the teacher challenges when implementing PPS to know the students’ engagment level especially verbal partcipation.
The researcher took VIIII A for analyzing the students’ engagement level in verbal participation. The class consists of 51 students. The researcher took all of the students for observation class.
E. Research Stages
Doing research, the researcher used research stages as follow:
a. Preliminary Research
The preliminary research was done on 10 March 2017 to get the information about the situation and condition of the class and the school in MTs. Roudhlotul Banat. The researcher also did litle interview to the English teacher in the VII grade about the condition of the
3
students there when learning English and also asking about PPS method.
b. Designing research
In designing research, the researcher design the ways of identifying and analyzing the students’ engagement level especially in verbal participation. It was designed by adapting the instrument from the previous study, they are observation checklist and interview guide. For ensuring the good instrument validity and to be applied for the test of reliability, the expert advisor checked this instrument.
c. Implementing the research 1) Observation
The researcher did the observation using checklist which is adapted from “students’ engagement walkthrough checklist” to observe the characteristic of engagement only in their verbal participation. In this session, the researcher need co-observer who helped the researcher in doing observation in class which consists of 41 students. In this case, the researcher will train the co-observer on how to do the observation a day before doing the observation.There are two observers in class to record the learning process and to observe the students.
2) Interview
After observation, the researcher did interview the teacher in order to know her challenging in implementing PPS regarding the students’ verbal participation.
d. Analyzing data
After obtaining the data from some instruments used in this research, the researcher directly collected and analyzed the data to get the answer of the research questions. The data were analyzed from the results of teacher’s interview and observation checklist.
e. Concluding data
4
observation checklist, interview, questionnaire, the literature review also was used in this research. Moreover, the teachers’ opinion about the finding was needed in this research. Finally, the researcher was able to conclude the research findings of this study.
F. Data Collection Techniques
In collecting the data, the researcher used several techniques:
a.
ObservationIn this case, the researcher observed the class directly using checklist which is adapted from “students’ engagement walkthrough checklist”. The researcher and the co-observer observed during the class activity. Moreover, a camera was used to record the situation and condition of the class.
b.
InterviewInterview took important role in this research. In this interview technique, the researcher asked some questions to the teacher of VII A class. The researcher used a question list to ask the teacher.
[image:39.420.36.386.140.525.2]For making the data collection techniques clearer, the researcher provided the table to specify the data collection as below:
Table 3.1 Data collection Technique
Research Question
Source of Data
Instrument Aspect How to measure
RQ 1 Students Observation checklist
The level of students’ verbal participation
- Counting the “star”
- Input the level into
observation checklist
RQ 2 Teacher Interview
Guideline
The teacher challenging
5
G. Data Collection Instrument
The research instruments applied in this research are observation checklist, interview guideline, and questionnaire in order to collect the valid data from the field. Those instruments was described as the following:
a. Observation Checklist.
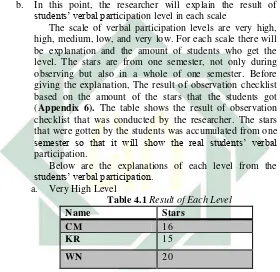
The researcher used an observation checklist adapted from “Students’ Engagement Walkthrough Checklist” which is developed by Jones as a guide to observe the students’ engagement level.5 The observation checklist consists of positive body language, consistent focus, verbal participation, student confidence, fun and excitement of the students. Those are the characteristic of students’ engagement which will be used to measure the level of students’ engagement. But in this research, the researcher took only one characteristic of students’ engagement level and that is verbal participation. Each level there are the scale of the stars as follows:
- Very high : >15 stars
- High : 14-11 stars
- Medium : 10-7 stars
- Low : 6-3 stars
- Very low : <2 stars
b. Interview Guideline.
The researcher used a question list which was made by the researcher herself by adapting the theory from Lynn and Prayong. The questions was asked to the teacher related her challenging in implementing PPS regarding verbal participation.
The observation checklist and interview guide will be validated by one expert. He is an expert lecturer of English Education Department of the State Islamic University Sunan Ampel Surabaya.
5
6
H. Data Analysis Technique
In this study, the researcher obtained the data through observation and interview. The data will be analyzed trough the following procedures:
a. Observation
As stated before, the researcher used observation checklist which was adapted from “Students’ Engagement Walkthrough Checklist”. This observation checklist shows the level of students’ engagement in accordance with the characteristics of the students’ engagement in class activity. But in this current research, the researcher took one parts only of the students’ engagement walkthrough checklist, that is students’ verbal participation. Here were the steps to analyze the observation checklist:
1) Observation checklist from “Students’ Engagement Walkthrough Checklist”
a) Collected the observation checklist
b) Analyzed the data that is provided in this checklist c) Before input the data into observation checklist,
“star” was counted to decide the students’ verbal participation level
d) After counting the star, the data was input into the observation checklist
b. Interview
The data also was collected through interview. It was analyzed deeply and thoroughly. The techniques conducted as below:
1) Analyzed the data of the interview; the transcribed data was identified
2) The data of the interview was analyzed by reading and reflecting the transcript
3) The data was interpreted and discussed before drawing conclusions based on the research questions 2) Combining the data collected from observation and
interview.
The data was collected from the observation and interview was analyzed through the following steps:
7
b) Given further explanation and interpretation for the result of the analysis.
The researcher combined those data to find out the answers of the research problems.
c) The last step made a conclusion based on the findings and discussion of this research. The researcher related the result to the data from preliminary research and theory used in this study to strengthen the result. The researcher combined them to make a cohesive and coherence conclusion.
8. Checking Validity of Finding
CHAPTER IV
FINDINGS AND DISCUSSION
This chapter presents the result of the observation checklist and also the interview. There are findings and the explanation of the result its discussion. The result of this research answered the research problem, they are the students’ verbal participation level and the teacher’s challenge in implemeting PPS regarding her students’ verbal participation.
A.
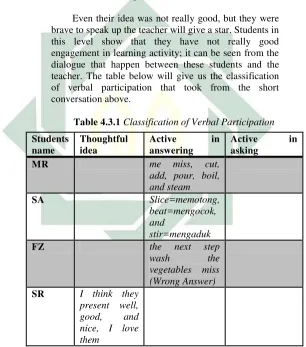
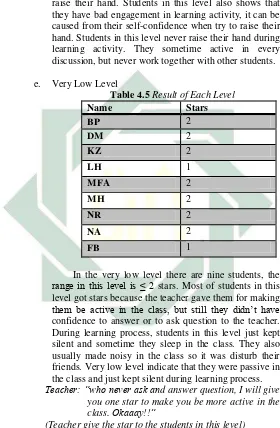
Research FindingsObservation has been done four times by the researcher and the co observer. We did the observation in one class and that was VII A. The co observer recorded the learning process while the researcher gave the star to the students. The researcher did observation by using obeservation checklist when all the record of learning process are collected. Because the students’ verbal participation level measured thorugh how many the stars they got during four meeting with the researcher and co observer, some part of the dialogue was transcribed into English. In this findings there will be a description of each students’ verbal participation level and also there will be the explanation of each scale of each students. The researcher analyzes the gathered data and they are presented as the detail below:
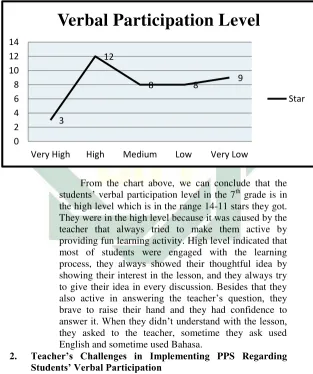
1. Students’ verbal participation level
a. In this point, the researcher explains the result of students’ verbal participation level in the learning activity
1) First meeting
In this meeting the teacher taught about procedure text (see appendix 2). At the beginning she explained about what is procedure text and the generic structure of procedure text. After that she gave questions to the students:
Teacher: “ok students now answer my question, what is the generic structure of procedure text? Who can answer correctly I will give you two stars, but if your answer incorrectly you will get one stars”.
2
Teacher: “Good, and next question is what is the aim of procedure text?”
Student HD: “Miss I Miss, the aim of procedure text is to tell the reader how to make something” Teacher: “yes that’s right, and the last question is what
is procedure text?”
Student: “Miss me, procedure text is a text that gives us instructions for doing something”
Teacher: “Good then! All of you are smart students!”
She gave three questions and also she asked the students to ask question related to the lesson that day.
Teacher: “Now, if you have any question related to our matery today, just raise your hand”
Student CM: “Miss I, does procedure text only for making food?”
Teacher: “ok good question, procedure text not only for making food, but also for making something like how to make pencil case, how to make picture frame etc. any other question?” Students KR: “Miss I miss, if I make kite, it’s also
procedure text?”
Teacher: “Yes of course, everything that uses any materials and also step it include in procedure text. Question again?”
Students WN: “I miss, does procedure text always use Present Tense?