ABSTRACT
Mubarrak, Akbar. 2012. Online Moodle as E-Learning Media in Teaching English for Industrial Internship Students. Yogyakarta. The Graduate Program in Language Studies.Sanata Dharma University. activities begin in July. As a result they will do not get any teaching learning material for 2months. So it will be difficult for the English teacher to teach their students especially to prepare for the national final examination.
Meanwhile the growth of information and communication technology has brought big impact in all aspects of our lives including in education. In language learning, information and communication technology brings many advantages that are very useful in teaching and learning process. One of the advantages that can be seen clearly today is that teacher and students are familiar with internet. They use internet to search teaching learning material, answer difficult question in their homework, and communicate by sending e-mail or chatting with friends.
Considering those things, this study attempts to address research questions. How is online Moodle as e-learning media in teaching English for industrial internship student designed?
The question was answered through incorporating the five phases of instructional design model named ADDIE (Analysis, Design, Development, Implementation and Evaluation) into Educational Research and Development (R & D) cycles(Research and Information Collecting, Planning, Developing Preliminary Form of Product, Preliminary Field Testing, Main Product Revision, Main Field Testing and Operational Product Revision) as the framework. The Research and Development cycles are used to ease the description of the material designing process. The data were obtained through questionnaires and interview, which were distributed to the grade three Technique of Light Vehicle students of SMK Negeri 1 Purworejo, an English teacher of SMK Negeri 1 Purworejo and also an expert from SEAMOLEC (Southeast Asian Ministers of Education Organization Regional Open Learning Center)
media in teaching English for the industrial students could be accessed on www.cc.pakakbar.com.
ABSTRAK
Mubarrak, Akbar. 2012. .Online Moodle as E-Learning Media in Teaching English for Industrial Internship Students.Yogyakarta. Program Pasca Sarjana Kajian Bahasa Inggris, Universitas Sanata Dharma.
Sebagai sekolah kejuruan, SMK Negeri 1 Purworejo memiliki program magang industri sebagai bagian integral dari proses pendidikan kejuruan dan pelatihan untuk mempersiapkan pesertadidik guna bekerja dalam bidang tertentu. Pelaksanaan magang industri di SMK Negeri 1 Purworejo dilakukan oleh siswa kelas tiga selama 3 bulan dari bulan Juni sampai bulan September, sedangkan kegiatan belajar mengajar dimulai pada bulan Juli. Akibatnya siswa tidak akan mendapatkan materi pembelajaran selama 2 bulan. Jadi akan sulit bagi guru bahasa Inggris untuk mengajar siswa mereka terutama untuk mempersiapkan ujian akhir nasional.
Sementara itu pertumbuhan teknologi informasi dan komunikasi telah membawa dampak besar dalam semua aspek kehidupan kita, termasuk dalam pendidikan. Dalam pembelajaran bahasa, teknologi informasi dan komunikasi membawa banyak keuntungan dalam proses belajar mengajar. Salah satu keuntungan yang dapat dilihat dengan jelas saat ini adalah bahwa guru dan siswa yang terbiasa menggunakan internet. Mereka menggunakan internet untuk mencari materi mengajar dan pembelajaran, menjawab pertanyaan yang sulit dalam tugas mereka, dan untuk komunikasi dengan mengirim surat elektronik atau bercakap-cakap dengan teman.
Menyadari hal-hal tersebut, maka penelitian ini bertujuan untuk menjawab pertanyaan tentang bagaimana merancang Moodle dalam jaringan sebagai media pembelajaran elektronik dalam pengajaran bahasa Inggris untuk siswa yang magang di industri.
Pertanyaan itu dijawab dengan memasukkan lima fase model desain pembelajaran bernama ADDIE (Analisis, Design, Pengembangan, Implementasi dan Evaluasi) ke siklus Penelitian dan Pengembangan Pendidikan (R & D) yang meliputi penelitian dan pengumpulan informasi, perencanaan, pengembangan bentuk awal produk, pengujian awal, revisi, pengujian dan revisi setelah pengujian. Siklus Penelitian dan Pengembangan digunakan untuk memudahkan dalam proses perancangan material. Data diperoleh melalui wawancara dan kuesioner yang dibagikan kepada siswa kelas tiga Teknik Kendaraan Ringan SMK Negeri 1 Purworejo, seorang guru bahasa Inggris SMK Negeri 1 Purworejo dan juga seorang ahli dari SEAMOLEC (Organisasi menteri pendidikan di Asia tenggara yang menangani pendidikan terbukadan pendidikan jarak jauh)
Moodle dalam jaringan sebagai media pembelajaran elektronik dalam pengajaran bahasa Inggris untuk siswa yang magang di industri dapat diakses pada www.cc.pakakbar.com.
i
ONLINE MOODLE AS E-LEARNING MEDIA IN TEACHING
ENGLISH FOR INDUSTRIAL INTERNSHIP STUDENTS
A THESIS
Presented as a Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements to Obtain the Magister Humaniora (M.Hum.) Degree
in English Language Studies
by
Akbar Mubarrak Student Number: 106332038
THE GRADUATE PROGRAM OF ENGLISH LANGUAGE STUDIES SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY
ii A THESIS
ONLINE MOODLE AS E-LEARNING MEDIA IN TEACHING ENGLISH FOR INDUSTRIAL INTERNSHIP STUDENTS
by
Akbar Mubarrak Student Number: 106332038
Approved by
F.X Mukarto, Ph.D.
iii A THESIS
ONLINE MOODLE AS E-LEARNING MEDIA IN TEACHING ENGLISH FOR INDUSTRIAL INTERNSHIP STUDENTS
Presented by Akbar Mubarrak Student Number: 106332038 Defended before the Thesis Committee
and Declared Acceptable.
THESIS COMMITTEE
Chairperson : F.X Mukarto, PhD. __________________ Secretary : Dr.B.B.Dwijatmoko, M.A. __________________ Member : Paulus Kuswandono, M.Ed., Ph.D. __________________ Member : JaslinIkhsan, Ph.D. __________________
Yogyakarta, March 3rd, 2014 The Graduate Program Director Sanata Dharma University
iv
DEDICATION PAGE
I dedicate my thesis to
my beloved parents and family, my beloved wife and my children,
v
STATEMENT OF WORK‘S ORIGINALITY
This is to certify that all ideas, phrases, sentences, unless otherwise stated, are the ideas, phrases, and sentences of the thesis writer. The writer understands the full consequences including degree cancellation if he took somebody else’s ideas, phrases, sentences without proper references.
Yogyakarta, March 3rd, 2014
vi
LEMBAR PERNYATAAN PERSETUJUAN
PUBLIKASI KARYA ILMIAH UNTUK KEPENTINGAN AKADEMIS
Yang bertanda tangan dibawah ini, saya mahasiswa Universitas Sanata Dharma:
Nama : Akbar Mubarrak NIM : 106332 038
Demi pengembangan ilmu pengetahuan, saya memberikan kepada Perpustakaan Universitas Sanata Dharma karya ilmiah saya yang berjudul:
ONLINE MOODLE AS E-LEARNING MEDIA IN TEACHING ENGLISH FOR INDUSTRIAL INTERNSHIP STUDENTS
beserta perangkat yang diperlukan (bila ada). Dengan demikian, saya memberikan kepada Perpustakaan Universitas Sanata Dharma hak untuk menyimpan, mengalihkan dalam bentuk media lain, mengelolanya dalam bentuk pangkalan data, mendistribusikannya di Internet atau media lain untuk kepentingan akademis tanpa perlu meminta ijin maupun memberikan royalty kepada saya selama tetap mencantumkan nama saya sebagai penulis.
Demikian pernyataan ini saya buat dengan sebenarnya. Dibuat di Yogyakarta
Pada tanggal : 3 Maret 2014
Yang menyatakan
vii
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Foremost, Alhamdulillahirabbil’alamin, I praise to Allah SWT, the Most Gracious and the Most Merciful who has given me the greatest love, grace, and blessing that I have finished this thesis.
My deepest gratitude and appreciation goes to F.X. Mukarto, Ph.D. as my advisor, who gave me advice and guidance during the writing of this thesis especially in GRP class. I would also like to extend my gratefulness to all lectures, Dr. J. Bismoko, and Dr. B.B. Dwijatmoko who have taught, guided, and helped me during the study.
Iwant to express my gratitude to Dr. Ir. Gatot Hari Priowirjanto, Pak JaslinIkhsan, Ph.D., Pak Zubeir, Bu Cahya, Pak Taufik, Bu Dewi, Pak Jarwo, Pak Aritonang and Pak Rizal for the scholarship they have given, the knowledge and the valuable experience they have shared to the students of SEAMOLEC class.
My greatest appreciation also goes to Budiono, M.Pd. the head of State Vocational 1 Purworejo, for permitting me to conduct this study. I would like to thank the English teachers of State Vocational 1 Purworejo as well for their cooperation and suggestions to improve this thesis. I also would like to than the grade three Technique of Light Vehicle for spending their time practicing the designed materials and filling in the questionnaire.
Many thanks are addressed to all of my SEAMOLEC friends, Puri, Patricia, Mega, TanteSiska, Ary, Edward, Pram and Muji for willingly sharing the joy and spirit during my study in this university. I also thank Mbak Lely and Pak Mul for their countless service and help during my study.
My endless love and appreciation are presented to my beloved parents and my parents in law for their never ending support and prayer, my sisters and my brother who have supported me to accomplish my study.
viii
Mubarrak and Fatimah Az Zahra Mubarrak. You have been there for me and helped me to get through every happy and sad moment in my life.
Finally, my gratitude also goes to those whom I cannot mention by names. May all of them be blessed with health and happiness in life.
Akbar Mubarrak
ix
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page
TITLE PAGE ... i
APPROVAL PAGES ... ii
PAGE OF DEDICATION ... iv
STATEMENT OF WORK’S ORIGINALITY ... v
LEMBAR PERNYATAAN PERSETUJUAN PUBLIKASI ... vi
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS ... vii
TABLE OF CONTENTS ... ix
LIST OF TABLES ... xii
LIST OF FIGURES ... xiii
LIST OF APPENDICES ... xiv
ABSTRACT ... xv
ABSTRAK ... xvii
CHAPTER I. INTRODUCTION ... 1
1.1.Background ... 1
1.2.Problem Identification ... 4
1.3.Problem Limitation ... 5
1.4.Statement of Research Questions ... 5
1.5.Goal of Research and Development ... 5
1.6.Product Specification ... 5
1.7.Benefit Research and Development ... 6
CHAPTER II. LITERATURE REVIEW ... 7
2.1.Theoretical Review ... 7
2.1.1. Moodle ... 7
2.1.2. General Aspect on E-Learning ... 9
x
2.1.2.2. Teaching, Instructing and Evaluating in
online Learning ... 14
2.1.3. Industrial Internship ... 15
2.1.4. English Language in Vocational School ... 16
2.1.5. Instructional Design Model ... 17
2.2.Theoretical Framework ... 20
CHAPTER III. METHODOLOGY ... 24
3.1.Research Method ... 24
3.2.Research Participants ... 27
3.3.Research Instrument ... 28
3.3.1. Questionnaire ... 28
3.3.2. Interview ... 29
3.4.Data Gathering Technique ... 30
3.5.Data Analysis Technique ... 31
CHAPTER IV. RESEARCH AND DISCUSSION ... 35
4.1. The Process of Designing Online Moodle ... 35
4.1.1. Analysis ... 35
4.1.1.1. Students’ Needs ... 36
4.1.1.2. Teacher’s Needs ... 40
4.1.2. Design ... 41
xi
4.1.4. Implementation ... 55
4.1.5. Evaluation ... 60
4.2. The Designed Online Moodle ... 60
CHAPTER V. CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS ... 65
5.1.Conclusions ... 65
5.2.Suggestions ... 66
REFERENCES ... 68
xii
LIST OF TABLES
Page
Table 3.1. The Data Needed by the Researcher ... 30
Table 3.2. The Template of the Needs Analysis Questionnaire ... 32
Table 3.3. Template of Descriptive Statistics of Experts’ Opinion on Online Moodle ... 33
Table 3.4. The Interpretation of the Degree of Agreement ... 33
Table 4.1 The Need of English and English in the Classroom ... 36
Table 4.2 English in National Final Examination ... 37
Table 4.3 Students and Technology ... 38
Table 4.4 Task and Topic Needed ... 40
Table 4.5 Rough Estimate of Connection Speeds Required by Various E-Learning Formats ... 43
Table 4.6 The Description of Competency Standard, Basic Competency, Indicator, Instructional Strategy and Delivery Strategy ... 44
Table 4.7 Web Pages Functions and Content Description ... 47
Table 4.8 Meaning of Point Agreement ... 48
Table 4.9 The Interpretation of the Degree of Agreement ... 48
Table 4.10 The Descriptive Statistics of Expert’s Opinions ... 49
Table 4.11 The Point of Agreement of Main Field Testing Questionnaire ... 56
Table 4.12 The Meaning of Score Criteria ... 57
xiii
LIST OF FIGURES
Page
Figure 2.1 ADDIE Instructional Design ... 20
Figure 2.2 The Flowchart of the Theoretical Framework ... 21
Figure 3.1 ADDIE Combined With R and D Cycle ... 25
Figure 4.1 C Panel ... 46
Figure 4.2 Front Page ... 46
Figure 4.3 Error ... 52
Figure 4.4 Revision in Learning Material ... 52
Figure 4.5 Disabled Email Based Self Registration ... 54
Figure 4.6 Added Plugin Moodbile (Mobile Learning for Moodle) ... 54
Figure 4.7 Hacked Online Moodle ... 60
Figure 4.8 Login Menu ... 61
Figure 4.9 Available Course ... 61
Figure 4.10 The Course ... 62
Figure 4.11 Download Material ... 63
Figure 4.12 The Movie ... 63
Figure 4.13 The Quiz ... 64
xiv
LIST OF APPENDICES
APPENDIX 1 Syllabus ... 71
APPENDIX 2 Questionnaire for Students’ Need ... 73
APPENDIX 3 TheResult of Students’ Need ... 82
APPENDIX 4 Interview Result With English Teacher (teacher’s need) ... 84
APPENDIX 5 Result of Expert Validation Questionnaire ... 86
APPENDIX 6 Result of User Validation Questionnaire ... 88
xv ABSTRACT
Mubarrak, Akbar. 2012. Online Moodle as E-Learning Media in Teaching English for Industrial Internship Students. Yogyakarta. The Graduate Program in Language Studies.Sanata Dharma University. activities begin in July. As a result they will do not get any teaching learning material for 2months. So it will be difficult for the English teacher to teach their students especially to prepare for the national final examination.
Meanwhile the growth of information and communication technology has brought big impact in all aspects of our lives including in education. In language learning, information and communication technology brings many advantages that are very useful in teaching and learning process. One of the advantages that can be seen clearly today is that teacher and students are familiar with internet. They use internet to search teaching learning material, answer difficult question in their homework, and communicate by sending e-mail or chatting with friends.
Considering those things, this study attempts to address research questions. How is online Moodle as e-learning media in teaching English for industrial internship student designed?
The question was answered through incorporating the five phases of instructional design model named ADDIE (Analysis, Design, Development, Implementation and Evaluation) into Educational Research and Development (R & D) cycles(Research and Information Collecting, Planning, Developing Preliminary Form of Product, Preliminary Field Testing, Main Product Revision, Main Field Testing and Operational Product Revision) as the framework. The Research and Development cycles are used to ease the description of the material designing process. The data were obtained through questionnaires and interview, which were distributed to the grade three Technique of Light Vehicle students of SMK Negeri 1 Purworejo, an English teacher of SMK Negeri 1 Purworejo and also an expert from SEAMOLEC (Southeast Asian Ministers of Education Organization Regional Open Learning Center)
xvi
media in teaching English for the industrial students could be accessed on www.cc.pakakbar.com.
xvii ABSTRAK
Mubarrak, Akbar. 2012. .Online Moodle as E-Learning Media in Teaching English for Industrial Internship Students.Yogyakarta. Program Pasca Sarjana Kajian Bahasa Inggris, Universitas Sanata Dharma.
Sebagai sekolah kejuruan, SMK Negeri 1 Purworejo memiliki program magang industri sebagai bagian integral dari proses pendidikan kejuruan dan pelatihan untuk mempersiapkan pesertadidik guna bekerja dalam bidang tertentu. Pelaksanaan magang industri di SMK Negeri 1 Purworejo dilakukan oleh siswa kelas tiga selama 3 bulan dari bulan Juni sampai bulan September, sedangkan kegiatan belajar mengajar dimulai pada bulan Juli. Akibatnya siswa tidak akan mendapatkan materi pembelajaran selama 2 bulan. Jadi akan sulit bagi guru bahasa Inggris untuk mengajar siswa mereka terutama untuk mempersiapkan ujian akhir nasional.
Sementara itu pertumbuhan teknologi informasi dan komunikasi telah membawa dampak besar dalam semua aspek kehidupan kita, termasuk dalam pendidikan. Dalam pembelajaran bahasa, teknologi informasi dan komunikasi membawa banyak keuntungan dalam proses belajar mengajar. Salah satu keuntungan yang dapat dilihat dengan jelas saat ini adalah bahwa guru dan siswa yang terbiasa menggunakan internet. Mereka menggunakan internet untuk mencari materi mengajar dan pembelajaran, menjawab pertanyaan yang sulit dalam tugas mereka, dan untuk komunikasi dengan mengirim surat elektronik atau bercakap-cakap dengan teman.
Menyadari hal-hal tersebut, maka penelitian ini bertujuan untuk menjawab pertanyaan tentang bagaimana merancang Moodle dalam jaringan sebagai media pembelajaran elektronik dalam pengajaran bahasa Inggris untuk siswa yang magang di industri.
Pertanyaan itu dijawab dengan memasukkan lima fase model desain pembelajaran bernama ADDIE (Analisis, Design, Pengembangan, Implementasi dan Evaluasi) ke siklus Penelitian dan Pengembangan Pendidikan (R & D) yang meliputi penelitian dan pengumpulan informasi, perencanaan, pengembangan bentuk awal produk, pengujian awal, revisi, pengujian dan revisi setelah pengujian. Siklus Penelitian dan Pengembangan digunakan untuk memudahkan dalam proses perancangan material. Data diperoleh melalui wawancara dan kuesioner yang dibagikan kepada siswa kelas tiga Teknik Kendaraan Ringan SMK Negeri 1 Purworejo, seorang guru bahasa Inggris SMK Negeri 1 Purworejo dan juga seorang ahli dari SEAMOLEC (Organisasi menteri pendidikan di Asia tenggara yang menangani pendidikan terbukadan pendidikan jarak jauh)
xviii
kemajuan belajar mereka seperti partisipasi siswa dalam belajar dan mengerjakan kuis. Moodle dalam jaringan sebagai media pembelajaran elektronik dalam pengajaran bahasa Inggris untuk siswa yang magang di industri dapat diakses pada www.cc.pakakbar.com.
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION
This research is concerned to design and implement online Moodle as e-learning media in teaching English for students who undergo industrial internship out of town. This chapter discusses the general explanation of this research. There are seven sections to be discussed in this chapter i.e. background, problem identification, problem limitation, statement of research question, goal of research and development, product specifications, and benefit of research and development.
1.1. Background
English in vocational school was divided into three competency standards. The competency standard of third-grade is to communicate using English in Intermediate Level. This competency standard is divided into seven basic competences which are not clearly separated for the first semester and the second semester. The time allotment is 146 lesson hours. It is because there are two factors which influence the application of the syllabus. The first factor is that the third year students or level twelve have a period for doing industrial internship for about three months. They leave school and go to industrial places to have industrial internship. The second factor is that the second semester does not fully have effective lesson hours because the program will end in late of March by having National Examination.
English teacher used to give students handbook to be learned while they conducted industrial internship but he had difficulty to control the students in order to learn autonomously as well as to give assignment and scores. As a result, the English teacher had to work hard to achieve the target material when the students came back from industrial internship because the students had left behind two basic competences and unfortunately the teacher could not achieve all the materials in the syllabus due to the time limit.
Moreover, Beatty (2003) also states that ICT-based learning can also motivate students to study diligently and willingly; and to develop study skills as independent learners. The learning materials and activities can be designed so that it can meet with the students’ needs. Meanwhile the ministry of national education in strategic plan for Year 2010-2014 also has scheduled the usage of ICT in teaching and learning beginning from Basic Education level to Higher Education, and extended to non-formal or informal education.
1.2. Problem Identification
Based on the Law on National Education System article 3 about The National Education Goals and an explanation of Article 15 which states that vocational school is secondary education that prepares learners to work in a particular field. As a result, vocational school has industrial internship program where the students can practice their skill in industry or workshop. The implementation of industrial internship in State Vocational School 1 Purworejo was performed by the third-grade students for three months from June to September, whereas teaching and learning activities began in July. As a result, they missed the material for two months so it is difficult for the English teacher to achieve all the materials in syllabus due to the time limit. The teacher also has limited time to prepare the students for the national examination because English lesson at the vocational school is one of the lessons which are ended by National Examination in March. The teacher cannot monitor and control their students to study autonomously when they undergo industrial work practice out of town.
1.3. Problem Limitation
To limit the research in order to be specific to conduct and to find particular problems easier, this research was conducted for third-grade students of Automotive department in State Vocational School 1 Purworejo which consists of 36 students who undergo industrial internship out of town. The researcher only focuses on designing online Moodle as e-learning media in teaching English for the industrial students.
1.4. Statement of Research Question
This study is aimed to answer the research questions: How is online Moodle as e-learning media in teaching English for the industrial students
designed?
1.5. Goal of Research and Development
The goal of this research is to design online Moodle as e-learning media in teaching English for the industrial students.
1.6. Product Specifications
The researcher designs e-learning by using Moodle and makes it online in webhosting so students can access by using computer or mobile phone. They just visit www.cc.pakakbar.com and then register themselves to get username and password to login.
e-learning media in teaching English when the students undergo industrial internship. Both teacher and students will be asked by the researcher to give evaluation about the features or materials in the online Moodle to be revised.
1.7. Benefit of Research and Development
The result of this research is expected to give contribution to people who concern the teaching and learning activity in vocational school in solving their problems which occur when the student undergo industrial internship. Hence, the teacher can still control, monitor, and give teaching materials as well as scores.
CHAPTER II LITERATURE REVIEW
This chapter presents the review of some supporting theories related to the studies. It consists of two sections: theoretical review and theoretical framework. The first section discusses Moodle as e-learning, general aspects on e-learning, industrial internship, English language in vocational school, and instructional design model. Meanwhile, the second section elaborates the framework synthesized from the discussed theories.
2.1. Theoretical Review
The theoretical review discusses the theories used in this research. Those theories are: Moodle as e-learning, general aspects on e-learning, industrial internship, English language in vocational school, and instructional design model.
2.1.1. Moodle
collaborate, and experience online learning in exciting multiple ways. It can be used as additional offline courses or can be used to host completely online courses.
Moreover, Moodle is an open-source; the programming code that runs Moodle can be changed to meet the specific needs of users and institutions. Moodle is also free to download and use; there is no licensing fee.
Moodle has many useful features to support students’ learning. The first is
Resource. These features can be in the form of: files that are uploaded to the course server, pages that are created directly in Moodle, or links that are connected to external web pages. The second feature is Assignment. It specifies a task that requires students to upload their work to a server. Typical assignments include essays, projects, reports, and so on. The third feature is Chat. It will be useful for the students because this feature facilitates them to chat directly with the teachers online. The chat feature allows participants to have a real-time discussion on the web. This is a useful way to understand the topic being discussed. The fourth feature is Forum. This facility enables students to discuss the learning materials with the teachers and their classmates online. The general forum is an open forum where anyone can start a new topic at anytime. The learning forum is where students might post a discussion response to a question posed by the teacher or peers’ postings. Students in the class are then required to
2.1.2. General Aspects on E-Learning
Online learning is learning which takes place in a network; it could be the Internet or just a school’s internal/closed net. Ally (2004) wrote that there are at least the following synonyms used for online learning: online learning, Internet learning, distributed learning, networked learning, tele-learning, virtual learning, computer-assisted learning, web-based learning, and distance learning. So it can be said that in online learning the learner is at a distance from the tutor or instructor and the learner uses some form of technology to access the learning materials. According to Ally (2004), online learning can be divided into three classes: contact learning supported by the internet, multiform learning in the internet, and self studying in the internet.
In the first class, some parts of a course can be in the net for example the delivery of learning material and the teachers are given as contact learning. The second class is multiform learning which means using multiple options in learning for example: forum discussions, help from tutors and learning objects (e-books, videos). The third class means that the learner studies alone in the net or in a virtual learning environment without outside help. With online learning, the traditional close learning lessons do not exist but the course material is available in the internet for the students. E-learning is a form of distance learning where the teacher has more or less a tutor’s role and student’s contribution to his learning is
exercise material are in the internet. Using the virtual learning environment as a part of teaching poses an extra duty for the teacher. Less time is left for updating the material than when the whole course is in the internet. This lowers the quality of the course.
Ally (2004) also states that there are five points of view when considering the suitability of online learning and web courses with constructive learning theory. When the matters to be learned are connected with earlier knowledge and experiences, the things to learn should be bonded to the student’s own empirical world. Students’ capacity for information is limited and therefore new information
has to be in proportion to the receiver’s capacity. Different interpretations of
information bring challenges to learning if the student’s interpretations differ largely from other students’ points of view. Learning is bound by culture which
should be taken into account when organizing the learning environment. A dynamic view of learning leads to the fact that information is changing and recurrent. There are various different available versions of the same learning concept in the learning process and the learners should have good skills to be able to select and direct their learning behavior.
Environment) in studying should be taught to obtain the best possible learning level. There are several studies about the Web-based learning but most of them are done in the humanities. The studying process is basically the same in the technology field but the learned matters are completely different.
Studying in the internet does not mean just sitting next to a computer “doing nothing”. It gives the student the independency of time and place for
studying but also the responsibility to gather the needed information instead of the teacher bringing the material into one’s lap. Although academy level students are used to academic freedom, studying in the internet brings an extra step towards freedom and hence challenge students to a new learning method. This freedom also means the responsibility for students about their own studies. The students’ own motivation and awareness on their learning style must be in order to achieve good learning results in e-learning. It is hard to affect student’s motivation but for example a handy learning environment and bringing the course content interestingly up have a raising status in student’s motivation. The learning
responds to students’ questions. It could be presupposed that teaching in the
internet brings more time for the teacher to do other activities and relieve the workload since there is no more lectures or exercises to be given. However, putting up a virtual course itself is a time consuming process when all the course material has to be created to the internet. On the other hand, once the course has been created it does not vanish and it is easier in the following years. However, the updating of the material and keeping it up to date takes a lot of time. The course has to be updated all the time and the teacher has to participate in the forum discussions. Besides, revising and evaluating the exercises and other assignments that students have returned also takes time.
2.1.2.1. Strengths and Weaknesses on Online Learning
There are some strengths and weaknesses of implementing online learning. The strengths of using online learning are:
using asynchronous discussion structures (for example forums) because participants have more time to consider their responses than in the face-to-face conversation. Interactivity is often self-evidently connected to working on the internet.
According to Illinois Online Network (2006) to bring about target-oriented collaborative learning is a major issue in online learning. It is a problematic issue and hard to realize and therefore an essential problem in online learning. The way the students see learning should change so that other students are seen also as a source of information and comprehension.
2. Online learning can be easily adapted to Indonesian society. Online learning is based on technology. Nowadays, technology plays an enormous part in many countries, including Indonesia. Computers and internet connections are easy to find. Students can easily access the internet in the internet café (Warnet), broadband connection through modem, and mobile phone. Moreover there are many free hotspot as public services so that students have possibility to participate in online course.
Some strengths of e-learning have been presented above. However, there are some weaknesses of this learning method such as the online environment itself can limit the levels of synergy. With large groups (more than 20 people), the dialog becomes somewhat limited. The virtual environment is not suitable to all kinds of education, for example public speaking, surgery, or sports. Putting up an online curriculum and learning environment cannot directly transfer the old courses into virtual ones to obtain a high quality e-course. The need of qualified professionals to develop distance education programs is often overlooked.
2.1.2.2. Teaching, Instructing and Evaluation in Online Learning
According to Fahy (2004), online learning teaching and instructing can be used as synonyms because the interaction is often delayed and happens through an interface. Routines related to teaching are made mainly beforehand in an online environment and many traditional teacher’s tasks and roles are replaced by hypermedia objects and communication tools. Ally (2004) proposes five important roles for the teacher in an online learning environment as presented below.
1) The teacher’s role as a motivator is emphasized because the online environment lacks the typical motivation aspects of the traditional learning. To maintain the motivation, the teacher should provide: enough challenging tasks, current and quality learning material, versatile interactions, and social contacts.
3) The teacher is an organizer. S/he organizes the didactic challenges according to learning such as the used tools and applications.
4) A communicator is one of teacher’s roles in the online environment. Communication in online learning is done via e-mails, chat groups, forums, and the Internet pages.
5) The teacher should actively follow and guide the students and act as a tutor because there is no chance of face-to-face communication. Guiding is very important in the online learning and it is based on discussion.
Online learning demands strong self-steering, motivation, and empirical atmosphere. Therefore new ways of acting are needed in evaluation. How can learning be evaluated comprehensively when the teacher and the student may never meet? Practices on evaluation should be in the same line with other actions in an online course. In the online learning, it is possible to use various evaluation methods by using information from forum discussions, exercises, quizzes, feedback questionnaires, learning diaries, and portfolios. One form of evaluation is a web-examination. It is an evaluation that is done by the students by completing or doing the tasks in the website. Self-evaluation is a practical tool and also peer evaluation can be used where students evaluate each other.
2.1.3. Industrial Internship
professional expertise, which combines a systematic and synchronized between education programs in schools and exploitation program obtained through direct work activities in the workplace to achieve a level of professional expertise. Where the professional expertise can only be established through the three main elements: knowledge, technique and experience. Knowledge and technique can be learned and mastered at school but experience only can be got directly by practice in the workshop.
Wena (1996) stated that the objective of implementation of education and training at vocational school with industrial internship are created professional employments that have the expertise, the manpower that have the knowledge, skills, and work ethic accordance with the demands of employment. Improve and strengthen linkages and conformity (link and match) between educational institutions and the world of work. Improving the efficiency of education and training the process to create qualified and professional employments. Give recognition and appreciation of work experience as a process of education.
2.1.4. English Language in Vocational School
that can be applied in their daily lives or that become basis of working competencies. The third group is productive lessons which are given to students according their skill programs. The skill programs are based on the National Standard of working competencies.
The objectives of English language for vocational education are to make students understand the basic skills of English to help them reach the vocational competence and to make the students able to apply their abilities and skills in English to communicate spoken and written.
2.1.5. Instructional Design Model
In this part, the researcher uses ADDIE as Instructional Design Model in creating e-learning. Instructional Design is the strategic planning of a course. It is a blueprint that is designed and followed. Rogers (2002) develops ADDIE model into five phases. They are Analysis (process of defining what is to be learned), Design (process of specifying how it is to be learned), Development (process of authoring and producing the materials), Implementation (process of installing the project in the real world context), and Evaluation (process of determining the adequacy of the instruction). Each step has an outcome that feeds into the next step in the sequence. One of its benefits is that this model allows the idea of receiving continual or formative feedback while instructional materials are being created.
Need analysis should be conducted in the first phase to identify the learning problems, learners’ needs, learning environment, learners’ background knowledge, and any other characteristics. Richards (2007) states that different types of students have different language needs and what they are taught should be restricted to what they need. Analysis also is needed to determine the course content and this phase is the foundation for all other phases of instructional design process. The outputs of this phase often include the instructional goals and a list of tasks to be instructed.
and delivery strategies. The outcome of the design stage is a blueprint that will be used as a reference to develop the course. The blueprint illustrates the curriculum structure, the learning objectives associated with each unit and the delivery methods and formats (interactive self-paced materials, synchronous and/or asynchronous collaborative activities) to deliver each unit.
The Development phase builds on the Analysis and Design phases. In this stage, the e-learning content is actually produced. All contents in the e-learning such as instruction, all supporting media, and assessment test are developed in this phase.
The Implementation phase refers to the actual delivery of the course materials. At this stage, the course is delivered to learners. The Moodle is installed on a server and made accessible for learners. In facilitated and instructor-led courses, this stage also includes managing and facilitating learners’ activities.
The five steps of ADDIE’s design model can be seen in the following
figure:
Figure 2.1. ADDIE Instructional Design (Rogers, 2002)
2.2. Theoretical Framework
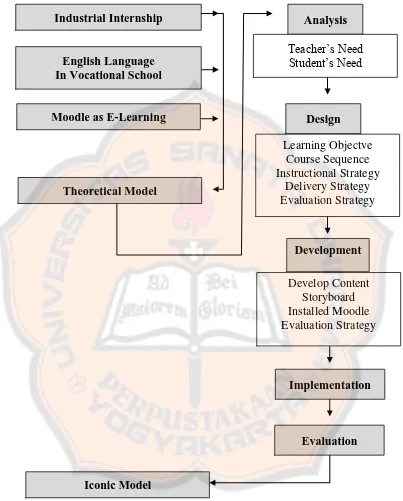
Figure 2.2. The flowchart of the theoretical framework
To begin with, as what had been discussed earlier, vocational high school is a sub-system of the Indonesian national educational system whose main goal is to prepare the students so that they become competent to fulfill the need for
Implementation
Evaluation Industrial Internship
English Language In Vocational School
Moodle as E-Learning
Analysis Teacher’s Need
Student’s Need
Design Learning Objectve
Course Sequence Instructional Strategy
Delivery Strategy Evaluation Strategy
Development Develop Content
Storyboard Installed Moodle Evaluation Strategy Theoretical Model
middle level of labors (Sutrisno, 2005: 1). In addition, based on the Law on National Education System article 3 about The National Education Goals and an explanation of Article 15 which states that vocational school is secondary education that prepares learners to work in a particular field. As a result, vocational school has industrial internship program where the students can practice their skill in industry or workshop.
The theory of English language in vocational school defines the competency standard and basic competency. The competency standard of third-grade was to communicate using English in Intermediate Level. This competency standard was divided into seven basic competences which are not clearly separated for the first semester and the second semester. The time allotment is 146 lesson hours. It is so because there are two factors which influence the application of the syllabus. The first factor is that the third year students or level twelve have a period for doing industrial internship for about three months. They leave school and go to industrial places to have industrial internship. The second factor is that the second semester does not fully have effective lesson hours because the program will end in late of March by having National Examination. The problem emerges due to the limit of the time for English teacher to achieve all the materials in syllabus and prepare the students to face National Examination.
online so that students do not have to gather in one place. They can do the test from their houses, internet cafes, even at road using mobile phones and laptops.
CHAPTER III METHODOLOGY
This chapter gives detailed information about how the research was conducted. It gives information of how the data were gathered and analyzed to answer the research question. This chapter consists of research method, research participants, research instrument, data gathering technique, data analysis technique, and research procedure.
3.1. Research Method
In order to answer the problem stated in the problem formulation, the researcher employed Research and Development (R & D). According to Borg and Gall(1983),the goal of R & D is to develop the research knowledge and to incorporate it into a product that combines educational research and educational practice rather than to discover new knowledge or to answer specific questions about practical problems. Borg and Gall (1983) also stated that Research and Development is used to design new products and procedures, which then are systematically field tested, evaluated, and refined until they meet certain criteria.
instructional design into research and development can be seen in the following figure:
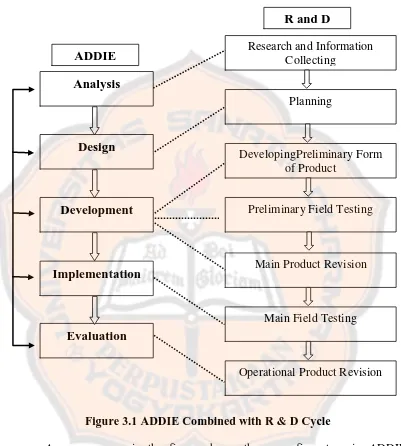
Figure 3.1 ADDIE Combined with R & D Cycle
As we can see in the figure above, there are five steps in ADDIE instructional design that the researcher used in creating online Moodle as electronic learning.
The first step of ADDIE instructional design is Analysis which is the same as the first step in R & D cycle that is Research and Information Collecting. In this step, the researcher conducted need analysis, target audience analysis, and
Analysis
Design
Development
Implementation
Evaluation
Research and Information Collecting
Planning
DevelopingPreliminary Form of Product
Preliminary Field Testing
Main Product Revision
Main Field Testing
Operational Product Revision ADDIE
task and topic analysis, by conducting interviewsand distributing questionnaires to the students.
The second step of ADDIE phases is Design, which is known as Planning in R & D cycles.The Planning step includes defining learning objective, course sequence, media, instructional strategy, delivery strategy, and evaluation strategy. In this step, the researcher also selected webhosting, domain name, template, and designed the user interface for e-learning. The outcome of the design stage was a blueprint that would be used as a reference to develop the course.
The third step of ADDIE phases is Development. Meanwhile the next step in R&D cycle areDeveloping Preliminary Form of Product, Preliminary Field Testing andMain Product Revision.In these stages, the researcher installed Moodle in the web hosting, developed its contents, and uploaded it.
The fourth step of ADDIE phases is Implementation, while in R & D cycle is Main Field Testing. At this stage, the researcher asked the students and the expert to try the online Moodle.Then, the researcher interviewed them and gave them questionnaires to get thefeedback.
The last step of ADDIE phrases is Evaluation or Operational Product Revision in R & D cycle. In this step, the results from the interviews and the questionnaires were used by the researcher to evaluate the achievement of the learning objectives and to revise the online Moodle.
By following the steps which were combined from R & D cycles and ADDIE phases, the final product i.e. online Moodle is expected to meet the
3.2. Research Participants
In conducting the research, the researcher divided the participants into three categories: research and information collecting participants, preliminary field testing participants, and implementation participants.
The research participants in the research and information collecting were the English teachers of SMK Negeri 1 Purworejo, thirty six students of grade threeof Technique of Light Vehicle SMKN 1 Purworejo and an expert from SEAMOLEC. The English teacher was chosen since he had experiences in teaching learning process and developing learning content and curriculum. The students of grade three Technique of Light Vehicle SMKN 1 Purworejo were chosen since they were the targeted users of online Moodle. They were expected to describe theirneeds, lacks, and wants, through the distributed questionnaires and interviews. An expert from SEAMOLEC was chosen since he had experiences in designing and developing online distance learning.
The participants in the preliminary field testing were the English teachers of SMKN 1 Purworejo and an expert from SEAMOLEC. They were involved in this research because the researcher considered them the experts in the application of the theories that are related to this research. Those theories were Moodle as e-learning, industrial internship, English language in vocational school, and instructional design model.They were expected to give comments, feedback, and evaluations on the pedagogic aspect and IT aspect which were significantly beneficial to revise and improve the designed online Moodle.
involved in this step due to their participation on the implementation of the designed online Moodle. The students gave feedback after the designed learning model was implemented.
3.3. Research Instrument
This study required data from the research participants to be collected and then to be analyzed. In conducting the study, therefore, the researcher used research instrument to collect valid and reliable datafrom the research participants. The research instruments were questionnaire and interview.
3.3.1. Questionnaire
The questionnaire was designed in Indonesian to ease the students in answering each item in the questionnaire. Besides allowing respondents to tick the answer based on their condition, the respondents were also allowed to state their opinion by writing their opinion in the provided space.
In this study, the researcher employed the structured questionnaire in needs analysis. Meanwhile in evaluation the researcher use both structured and unstructured questionnaire.The needs analysis questionnaire was distributed to the third grade students of Technique of Light Vehicle SMKN 1 Purworejo during the Analysis phase. The expert validation questionnaire was distributed to the English teacher who taught the third grade of technique of light vehicle in SMKN 1 Purworejo and the expert from SEAMOLEC during the Evaluation phase. The needs analysis questionnaire served as the way to give contribution for the content and features of the online Moodle, while the expert validation served as the evaluation sheets for the respondents to assess the designed online Moodle. 3.3.2. Interview
3.4. Data Gathering Technique
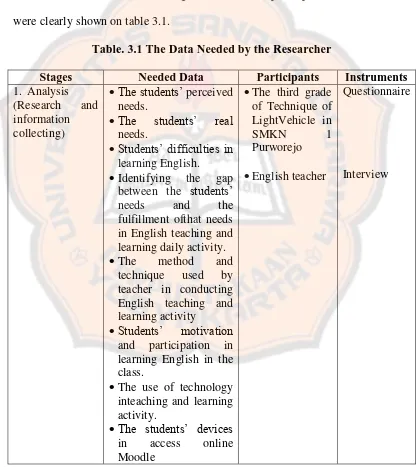
The data were gathered from the two instruments used in the research as elaborated in the previous part. The research was conducted to the third grade of technique of light vehicle in SMKN 1 Purworejo on 20 Mei 2012 to 30 September 2012. The needed data classified into the stages based on the combination of R&D and ADDIE model. The stages, needed data, participants and instruments were clearly shown on table 3.1.
Table. 3.1 The Data Needed by the Researcher
Stages Needed Data Participants Instruments
1. Analysis (Research and information collecting)
The students’ perceived needs. between the students’ needs and the fulfillment ofthat needs in English teaching and learning daily activity. The method and
technique used by teacher in conducting English teaching and learning activity
Students’ motivation
and participation in learning English in the class.
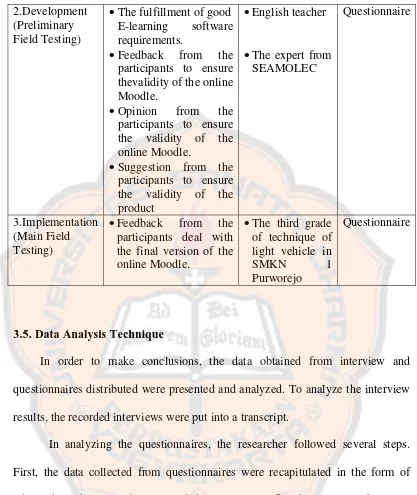
2.Development participants to ensure thevalidity of the online Moodle.
Opinion from the participants to ensure the validity of the online Moodle.
Suggestion from the participants to ensure the validity of the participants deal with the final version of the questionnaires distributed were presented and analyzed. To analyze the interview results, the recorded interviews were put into a transcript.
Note:
n = the total number of the students who chose certain answer N = the total number of the students
A table presented the data in the form of computation of the collected answers from the questionnaires which had been distributed to the research participants. Then, the researcher made the interpretation of the result in the form of written paragraphs.
Table 3.2: The Template of the Needs Analysis Questionnaire
No Questions and statements Answer Number Percentage
The data from materials evaluation were obtained through questionnaires that are in the form of scores. The classification was adapted from Likert Scaleproposed by Best (1970). There are five agreements are applied as follows: Strongly disagree = 1
Disagree = 2 Not sure = 3 Agree = 4 Strongly agree = 5
The score of the questionnaire was calculated using descriptive statistics to the source of variance. The source of variance here was number of cases and
mean. The central tendency of the respondents’ opinion on the designed set of
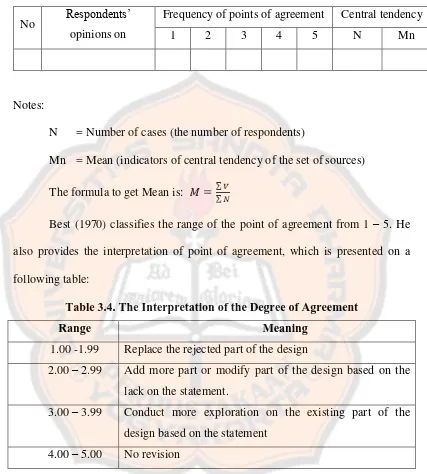
Table 3.3 Template of Descriptive Statistics of Experts’ Opinions on Online Moodle
No Respondents’
opinions on
Frequency of points of agreement Central tendency
1 2 3 4 5 N Mn
Notes:
N = Number of cases (the number of respondents)
Mn = Mean (indicators of central tendency of the set of sources) The formula to get Mean is:
Best (1970) classifies the range of the point of agreement from 1 – 5. He also provides the interpretation of point of agreement, which is presented on a following table:
Table 3.4. The Interpretation of the Degree of Agreement
Range Meaning
1.00 -1.99 Replace the rejected part of the design
2.00 – 2.99 Add more part or modify part of the design based on the lack on the statement.
3.00 – 3.99 Conduct more exploration on the existing part of the design based on the statement
4.00 – 5.00 No revision
CHAPTER IV
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
This chapter is essentially the realization of what has been planned in Chapter III. This chapter is divided into two major parts. The first part presents the process of designing online Moodle as e-learning media in teaching English for the industrial internship students. The second part presents the designed online Moodle.
4.1. The Process of Designing Online Moodle
The researcher adapted the steps of Research and Development cycles and also employed ADDIE model in the process of designing the learning model. To answer the research question of how is online Moodle as e-learning media in teaching English for the industrial students designed, the steps of how to create final version of the learning model were elaborated in this section. By elaborating each step clearly, it would describe the answer of the research question. There were five steps, namely analysis, design, development, implementation, evaluation.
4.1.1. Analysis
Purworejo. The researcher collected the necessary information for developing the designed learning model.
4.1.1.1. Students’ Needs
The students who participated in answering the questionnaire were thirty five students of grade three Technique of Light Vehicle SMKN 1 Purworejo. This questionnaire was distributed in the analysis step in order to find out the students’ needs. The explanation of the questionnaire result was presented below.
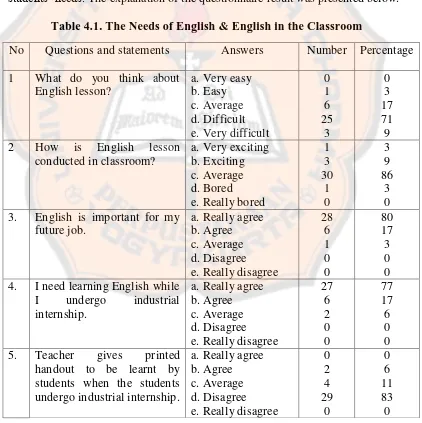
Table 4.1. The Needs of English & English in the Classroom
No Questions and statements Answers Number Percentage 1 What do you think about 4. I need learning English while
The researcher concerned on the students’ experience of English in the
beginning part of the questionnaire. Based on the result of the need analysis questionnaire, 25 students stated that English was difficult (71%). Therefore the researcher interviewed some students and they said that the most difficult part of learning English was when they did not know the meaning of the word and they also had to memorize the grammatical function and pattern. Then, 30 students stated that English teaching and learning activities were averagely attracted the students’ motivation (86%). Based on the interview result with the English teacher, it was because English teaching and learning activities began after the students finished practice in the school workshop due to the English teaching and learning activities concern on the grammar mastery (75%). Most of the students (80%) really agreed that English was important for their future job because almost every year there were many big factory such as Astra and Daihatsu who came to school to conduct recruitment. There were 27 students (77%) who really agreed that they need learning English while they undergo industrial internship. Based on the indirect interview to the students, almost of the students wanted to prepare for the National Examination. Then, 29 students (83%) disagreed with printed handout to be learnt by students when they undergo industrial internship.
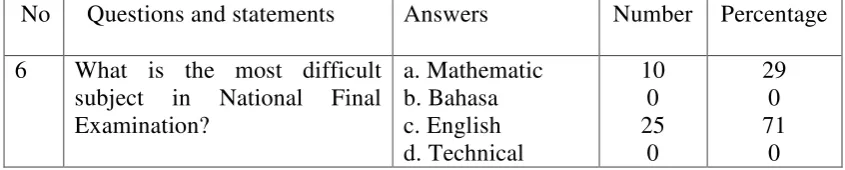
Table 4.2 English in National Final Examination
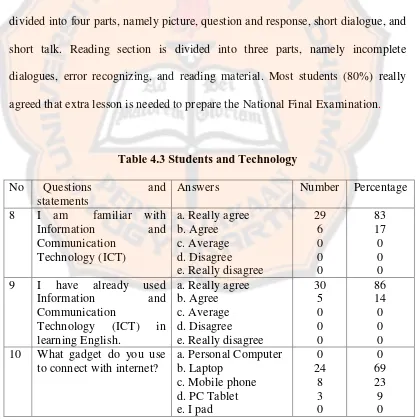
7 In order to face the National stated that English was the most difficult subject in National Final Examination. Based on the interview result with English teacher, it was because there were two sections in National Final Examination, listening and reading. Listening section is divided into four parts, namely picture, question and response, short dialogue, and short talk. Reading section is divided into three parts, namely incomplete dialogues, error recognizing, and reading material. Most students (80%) really agreed that extra lesson is needed to prepare the National Final Examination.
Table 4.3 Students and Technology No Questions and
statements
11 What do you usually do
Table 4.4 Task and Topic Needed
No Questions and statements Answers Number Percentage 13 I prefer work in group
part in listening section
a. Pictures
part in reading section
a. Incomplete
Based on the questionnaire result, it was found out that 29 students (83%) really agree to work in group. Based on the indirect interview with the students, they are in group of 4 or 6 students when undergo industrial internship. Then, 25 students (71%) answered that short talk is the most difficult part in listening section and 24 students (69%) answered that error recognizing is the most difficult part in reading section.
4.1.1.2. Teacher’s Needs
Intermediate. This competency standard was divided into seven basic competences which are not clearly separated for the first semester and the second semester. The time allotment is 146 lesson hours. It is so because there are two factors which influence the application of the syllabus. The first factor is that the third year students or level twelve have a period for doing industrial internship for about three months. They leave school and go to industrial places to have industrial internship. The second factor is that the second semester does not fully have effective lesson hours because the program will end in late of March by having National Exam.
English teacher used to give students handbook to be learned while they conducted industrial internship but he had difficulty to control the students in order to learn autonomously, give assignment and scores. As a result, the English teacher had to work hard to achieve the target material when the students came back from industrial internship because the students had left behind two basic competences and unfortunately the teacher couldn’t achieve all the materials in syllabus due to the limit of the time.
4.1.2. Design
In this stage, the researcher designed Moodle by defining learning objective, course sequence, instructional strategy, delivery strategy, and evaluation strategy based on the previous stage.
competency of the materials design was the goal of the designed materials. The basic competences were the general purposes of the designed material and then the researcher specified the indicators of each topic. The competence standard and basic competence describe the indicators which the students are expected to be able to do after learning English in certain time. Therefore, the online Moodle as e-learning media in teaching English for the industrial internship students would be designed in a way that helps the students master these competences. By stating the learning indicators, it was expected that the researcher know how to measure whether or not the competences have been mastered by the students.
Table 4.5 Rough Estimate of Connection Speeds Required by Various E-Learning Formats
E-Learning Format Speed of Internet Connection to Use
Video conferencing, live webcasting From 100 Kbps to 2 Mbps Audio conferencing From 54 Kbps to 128 Kbps Application sharing, animation From 256 Kbps to 1 Mbps Whiteboard, slides From 56 Kbps to 384 Kbps Chat, instant messaging 128 Kbps
E-mail, discussion forums, screens with text and images
From 56 Kbps to 128 Kbps
Based on the need analysis in the previous step and the information above, the researcher used collaborative methods as instructional method which emphasize the social dimension of learning and engage learners sharing knowledge and performing tasks in a collaborative way. They include online guided discussions, collaborative work and peer tutoring.
Guided discussions are designed to facilitate learning and improve knowledge and skills. The teacher asks learners questions to stimulate and guide reflection and critical thinking. These discussions complement other methods, such as a presentation, research or a case-based exercise. Guided discussions also facilitate communication and knowledge sharing among learners.
of an assignment or a project. This method requires students to collaborate, listen to each other, argue and negotiate; they develop interpersonal skills other than domain-specific and problem-solving skills.
Peer tutoring is designed to make students monitor and support each other. They have the opportunity to learn from each other’s work and to practice tutoring methods. This is a useful method for train-the-trainer projects.
The learning objective, course sequence, instructional strategy, delivery strategy, and evaluation strategy of the designed online Moodle for third-grade students of automotive department in state vocational school 1 Purworejo were presented in Table 4.6.
Table 4.6 The Description of competency standard, basic competency, indicator, instructional strategy and delivery strategy.
Unit Description
1
Competency Standard: communicate using English in Intermediate level Basic Competency: Understanding monologue which occur in certain work situation.
Indicator:
Students should be able to ask about general information dealing with monologue and answered correctly
Students should be able to ask about detailed information and answered correctly.
Students should be able to make summary from the monologue which occur in work situation
Instructional strategy:
Collaborative methods as instructional method which emphasize the social dimension of learning and engage learners sharing knowledge and performing tasks in a collaborative way
Delivery strategy:
E-mail, discussion forums, screens with text and images 2
Indicator:
Students should be able to make reservation. Students should be able to make complaint. Students should be able to make arrangement.
Students should be able to cancel arrangement ask about detailed information and answered correctly.
Students should be able to express their wish or unreal situation (conditional sentences and subjunctive wish)
Instructional strategy:
Collaborative methods as instructional method which emphasize the social dimension of learning and engage learners sharing knowledge and performing tasks in a collaborative way
Delivery strategy:
E-mail, discussion forums, screens with text and images
4.1.3. Development
In this stage, the researcher developed content, storyboard, and installed Moodle as courseware. This stage also employed the experts in order to validate the researcher’s online Moodle. The experts had an obligatory to give their opinions and suggestion by completing the provided questionnaires. The experts were the English teacher who taught the third grade of technique of light vehicle in SMKN 1 Purworejo and the expert from SEAMOLEC.
Figure 4.1: CPanel
The researcher develop the content of e-learning based on the previous stage then make storyboard to define each part of the e-learning. The users accessed the e-learning by accessing http://www.cc.pakakbar.com, they would then see the homepage contained navigation menus that allowed users to access the website contents. The screen shot of the front page could be seen in figure 4.2
The function and the description of content for each site page are stated in table 4.7.
Table. 4.7. Web Pages Functions and Content Description Online Moodle as E-Learning Media in Teaching English
for the Industrial Internship Students
Website Page and
Content
Home page
This page fast loading and contains welcome message,
This page provides 3 links to download, forum and FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions)
Course This page presents materials, video, sound and that are essential to build students’ knowledge about the topic in the course
This page also provides downloadable materials in form of PDF or PPT files which they can save for future recalling. Quiz This page contains exercises of the learned topic in several
kinds of exercises.
This page aims to measure students’ understanding on the discussed topic.
This page also provides obtained score and the lecturer’s feedback after students attempted the quiz.
Forum This page serves as a place for students to post and share their experience in.
This page offers collaborative learning activities allowing students to work together and share ideas.
Download This page provide video, sound and material to be downloaded by students.
FAQ This page contain frequently asked questions about how to use the electronic learning.
Widget Widgets can be accessed from home page. It contains useful additional applications embedded in the rght and left bar of the webiste to help students to:
o Chat with the teacher via Yahoo Messenger, o Look up confusing words via Online Dictionary
Navigation This page lists all links in the site enable students to go directly to their desired page.