Directory UMM :Data Elmu:jurnal:A:Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment:Vol80.Issue1-2.Aug2000:
Teks penuh
Gambar
Dokumen terkait
The model results are provided in digital raster format (100 m × 100 m) within a geographic information system (GIS). The calculated pesticide loads in surface waters were compared
Three main explanations for this were (1) large areas of bare fallow typical for the farming practice at the time; (2) enhanced mineralisation from newly cultivated land; and (3)
Integration of the normalized soil property values into the soil quality index resulted in the integrated plots receiving a significantly higher score than the conventional plots
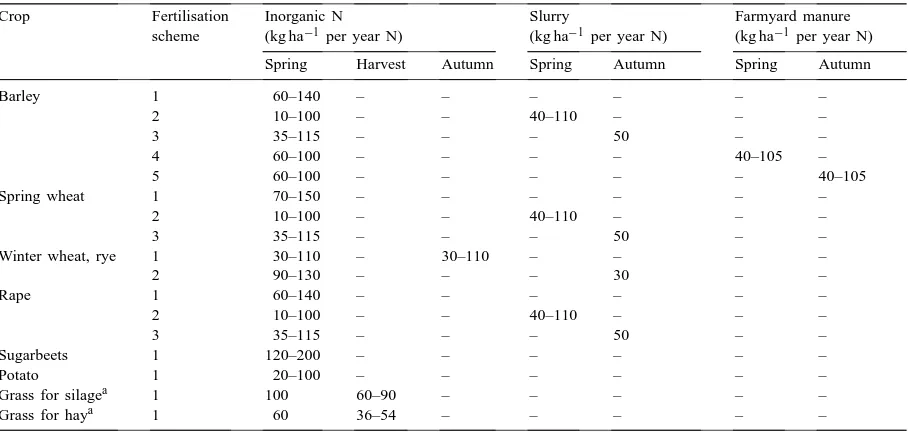
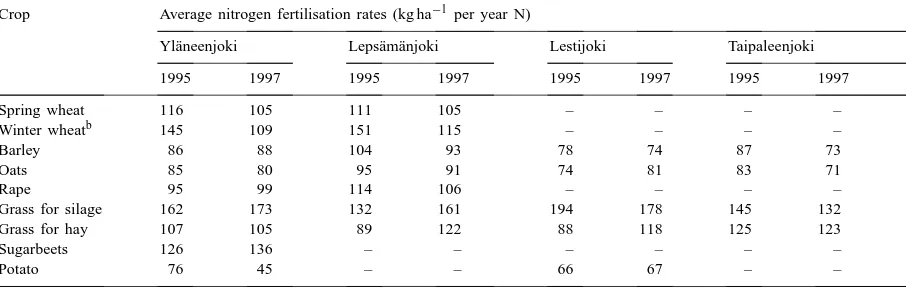
The objective of this study was to analyze the long-term consequences of rainfall expressed as a standardized precipitation index (SPI) and fertilizer nitrogen (N) on yields and
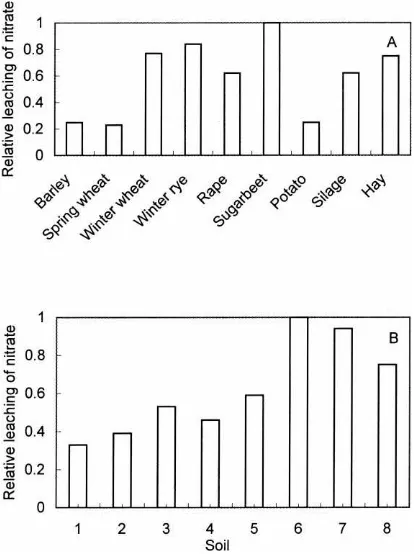
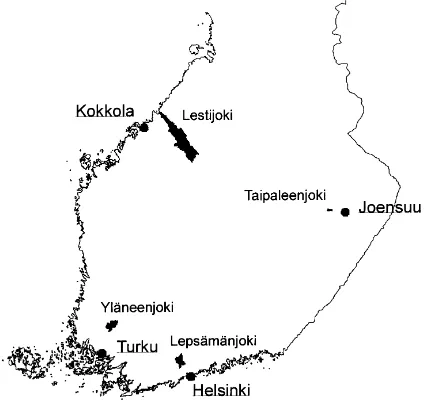
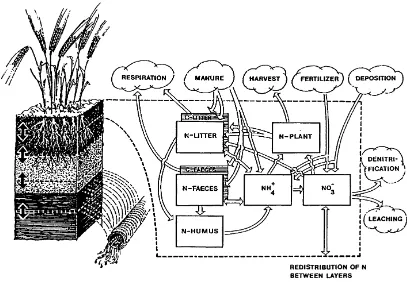
Based on the results of these studies it was concluded that the local and regional specialization of farms is one important reason for the high losses of plant nutrients: one type
Rsur as proposed by Van der Werf and Zimmer (1998) depends on five input variables: (1) the runoff risk of the field site; (2) the drift percentage (depends on application tech-
Although the plant species number in grass strips decreased clearly during succession, changes in species richness of leafhoppers were not so great.. Factors affecting the
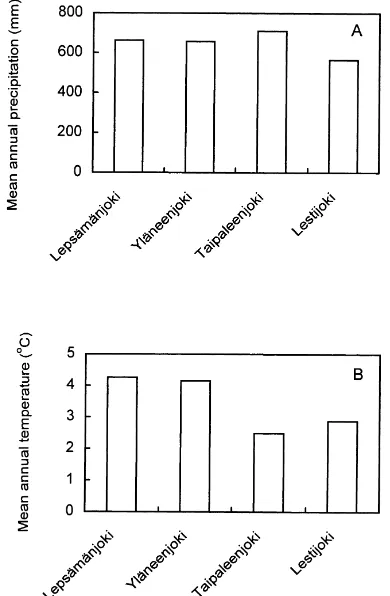
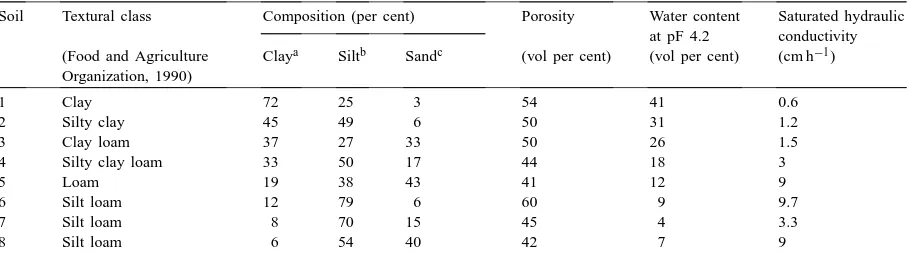
Detailed hydrological studies examined effects on the soil water balance and its components (precipitation, interception, runoff and soil moisture status); equivalent measurements