AN ANALYSIS OF COHESION ARE USED BY JOHN
COLLIER’S
IN
THE CASHER
THESIS
By Arlina
Reg. Number: A03211008
ENGLISH DEPARTMENT
FACULTY OF LETTERS AND HUMANITIES
STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY SUNAN AMPEL SURABAYA
AN ANALYSIS OF COHESION ARE USED BY JOHN
COLLIER’S
IN
THE CASHER
A THESIS
Submitted as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Sarjana Degree of English Department Faculty of Humanities UIN Sunan Ampel Surabaya
By: Arlina
Reg. Number: A03211008
ENGLISH DEPARTMENT
FACULTY OF LETTERS AND HUMANITIES
ABSTRACT
Arlina. 2015.An Analysis of Cohesion are used by John Collier’s in The Casher. Thesis. English Department. Faculty of Letters and Humanities. State Islamic University Sunan Ampel Surabaya.
The Advisor : Endratno Pilih Swasono, M.Pd.
Language has an important role for human to do daily activities. It means to communicate to do certain things in personal life or group. Hereby, language will be applied to analyze conversations by people in group which relates to the short story entitled The Casher.
The approach of this study is done as content analysis which the writer focuses to the content analysis which the writer focuses to the content of the dialogue from the Alan and old man.
The writer makes herself as the instrument in taking all data. The data is taken from all the certain events of the short story where all the cohesion occurs when the Alan and old man are in tiny room at Peel Street. The dialogue is classified to make the reader easy to understand before going to the analysis chapter.
The writer found some results of cohesive devices in this short story. The result shows that there are cohesive item such as reference, substitution, conjunction, reiteration and collocation found in the casher.
Cohesion is the way one element relates with another in a certain order. Cohesion relates element said with the element stated before in a discourse by using cohesive device. In other words, cohesion is such a semantic relation which refers to relation of meaning that exist within the text and that define it as text. Cohesion is divided into two sections, grammatical cohesion and lexical cohesion.
2.2.2 Grammatical Cohesion………. 11
2.2.2.1 Reference ... 11
4.2 Discussion ... 50 CHAPTER V CONCLUSSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
1.1Background of the Study
Language is very important in our lives. People at least use one
language to convey and express their ideas, desire and feelings through
communication process with others. Language is used by people to
express their ideas and thoughts. There are two forms of language which
are used to communicate with other people. They are spoken and written
language. In spoken language, speakers express their ideas and thoughts
then the listeners can directly interpret what speakers say. If the listeners
cannot interpret what the speakers actually mean, they can directly ask to
the speakers about their spoken utterance. However, this condition differs
from that of written language. In written language the writer can also
directly express their ideas and thoughts otherwise in written language
definitely the readers have different interpretation but they cannot ask or
clarify the written utterances directly. Therefore, in this situation the
writers are required to arrange the words in grammatical order to make a
complete thought so that the readers can get the message clearly without
doing misunderstanding.
Language and literature are inseparable. By using language, a
literary work can be created. For instance, novel, drama and poetry are built
up from a written language in the form of words or text. In Cook and
2
literature. First, literature is made from language that sensitivity to language
use is a strong basis for the development of an understanding of literary
texts. Second, suitably selected literary texts can provide a motivating and
stimulating source of content which is serving as a basis for discussion and
interpretation in which the response of the individual learner is encouraged.
Thirdly, the skill of decoding literary texts are transferable to most
language learning contexts in which meanings because they are not always
immediately transparent, have to be experienced, negotiated, or read
between lines. Such principles stress the mutual reinforcement and support
of literary and linguistics skills and underlie an essentially integrated view
of language and literature.
Language is also inseparable from what is called discourse.
Discourse is seen as language as a form of social practice determined by
social structures (Fairclough, 1989: 18, 22). This implies that language is a
part of society, a social process, and socially conditioned process which
means conditioned by other non-linguistics parts of society. Bex (1996: 56)
states that discourse refers beyond individual or groups of texts to the kinds
of social behaviors which recognize and confer meaning on such texts.
Several levels of discourse which are not directly encoded in the text, but
they are also a part of the society in which the text occurs and is therefore a
part of the meaning of the text. It is in this way that meaning can be said to
3
A short story is the one of part of literature that has fictional work
of prose that is shorter in length than a novel. Edgar Allan Poe in his
essay’’ The Philosophy of Composition’’ said that a short story should be
read in one sitting, anywhere from a half hour or two hours. In
contemporary fiction, a short story can range from 1,000 to 20,000 words.
A short story usually focuses on one plot, one main character (with a few
additional minor character), and one central theme. Since the writer thinks
that short story is essential in this current era, she wants to know deeper
about the Cohesion Devices in the Chaser by John Collier. She find that
this short story has a special language, meaning and the languages used in
this story easy to understand.
There have been many study and researches in literary discourse
about short story but most of the research focused on the general issues of
literary discourse like the relation between short story and literature,
figurative woman in short story, speech act in short story, politeness
strategies and etc. There are researcher do research about cohesion and
coherence but only focus to analyze a paragraph, article, banner, mass
media, newspaper. So that the writer wants analyze something that never
do researcher before. The purpose of this research to find the Cohesion
that exist in short story entitle the Casher based on the founding of
cohesive ties. Haliday and Hasan (1997:10) state that the concept of
cohesion is set up to account for relation in discourse, but in rather
4
is above the sentence. Cohesion refers to the range of possibilities that
exist for linking something with was has gone before. Based on this idea it
is said that in order to get the meaningful understanding of utterances
found in this short story ‘’The Chaser‘’ by John Collier , the readers must
be equipped with the knowledge grammatical points mainly cohesive
devices such as conjunction, reference, ellipsis and other transitional
words. According to Brian Paltridge (2006: 2) states that:
Discourse analysis focuses on knowledge about language beyond the world, clause, phrase and sentence that is needed for succesful communication. It looks at patterns of language accross texts and considers the relationship between language and the social and cultural context in which it is used. Discourse analysis also considers the ways that the use of language presents different views of the world and different understandings. It examines how the use of language is influence by relationship between participants as well as the effects the use of language has upon social identities and relations.
According to Brown & Yule (1983:191), cohesive relationship
within a text is set up where the interpretation or some elements in the
discourse is dependent on that of another.
The writer choice one of famous short story from John Collier, he
is a writer of various genre. John was born in London on May 3, 1901. He
obtained a private education, and began writing poetry at age nineteen, and
was published in 1920. During the early 1930s he concentrated on writing
novels and short stories. Coller’s other published works include Gemini
(poetry collection, 1931), Tom’s A cold (novel, 1933), Defy the foul fiend
(novel, 1934). There are still many creation of his work, the one is ‘’The
5
happened when Alan Austen as a main character meet with an old man
who sale love potion, and this story will be analyzed by writer use
cohesive ties. The result of this study is hopefully to be useful to
contribute the research on literary discourse, especially about short story.
1.2 Statement of the Problems
Dealing with the background of the study described previously, the writer
formulates the statement of the problem as the following:
1. What Cohesive devices are used by John Collier’s in The Chaser?
2. What Cohesive devices are mostly used by John Collier’s in The Chaser?
1.3 Objectives of the Study
In accordance with the statement of the problem, the writer takes the objective of
the study as the following:
1. To identify the Cohesive devices are used by John Collier’s in The Chaser.
2. To explain the Cohesive devices which are mostly used by John Collier’s
in The Chaser.
1.4 Significance of the study
By conducting this study, the writer hopes that this study can give a clear
idea to the readers about Halliday and Hassan’s theory of cohesion ties which is
applied in the John Coller’s in The Chaser. This research is also hoped to be
6
about cohesion that exists. Besides that, the writer also hoped that this study can
give the contribution of study discourse analysis especially about cohesion which
is used in short stories by John Coller’s in The Chaser.
1.5 Scope of Limitation
The scope of this study is concerning with the discourse analysis mainly
about written discourse. In this study, the writer analyzes cohesive ties as her main
discussion. The writer focuses on the idea of Haliday and Hasan’s cohesive ties:
they are reference, ellipsis, conjunction, substitution, reiteration and collocation.
The scopes of this a short stories by John Collier’s, because the writer has interest
in this story and wants to focuses. Then, found the cohesion that exist.
1.6 Definition of Key term
1. Cohesion: Brown and Yule (1983: 191) Cohesive relationship within a
text are set up where the interpretation of some element in the
discourse is dependent on that of another.
2. Cohesive Devices are defined as a text is enabling to function as a
single meaningful unit. The cohesive devices cover reference,
conjunction, substitutions, ellipsis, and lexical cohesion (Halliday and
Hassan (1976: 6).
3. A short story is fictional work of prose that is shorter in length than a
novel Edgar Allan Poe, in his essay ‘’The Philosophy of
Composition’’ said that a short story should be read in one sitting,
7
4. John Collier, a contemporary English author, was born in London in
1901, and lived his last years in Palisades. Collier was a writer of the
1920’s era, There are some of his works such as: ‘’Tom’s A-cold
(1933), ‘’Bottle Party, Thus I Refute Beelzy, His Monkey Wife’’ and so
on. Collier writing is full surprises. ‘’The Casher’’ is a one famous
short story by him that deals with a man’s dream of gaining a
8
CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
In this chapter, the writer presents theories which underline this study. Some
theories of discourse will be described as a background in viewing and
understanding the research. Those are the theories about text, discourse, cohesion,
the other theories are not excluded because all of the theories supporting each
other.
2.1Discourse
Cook (1994;25) state that discourse as opposed to text, is a language in use,
taking on meaning in context for its users, and perceived by them as purposeful,
meaningful, and connected. This quality of perceived purpose, meaning, and
connection is known as coherence. According to Mc Carthy (1991: 5) maintains
that discourse analysis is concerned with the study of the relationship between
language and the context in which it is used. Bhatia (2004: 3), a leading writer on
genre analysis distinguishes four frameworks that represent different concerns
about discourse, He identifies: (i) discourse as text, (ii) discourse as genre, (iii)
discourse as professional practice, and (iv) discourse as social practice. On the
other hand, the first phase can be seen as focusing on the textualization of
lexico-grammatical resources and the second one on the regularities of organization, with
9
2.2Text
A text is a string of words where a writer has to encode the ideational meaning
into words and the reader has to decode that meaning from those words
(Coulthard, 1994: 9). Text may have been said to have three meanings (Bex,
1996: 74). First, meaning as in the original utterances or sentence. For example, a
simple sentence such as ‘’Maya goes to school’’, which implied a real activity
where someone name Maya is making activity going to the school. Second,
meaning as in new text. For example, the sentence is repeated by using indirect
sentence such as ‘’The school is visited by Maya’’, which spoken or written by
the third person who knows the activity. Third, the set meanings it has
independently of either text, but which allows it to mediate between the two
longer texts in which occur. For example, the sentence ‘’ Maya goes to school’’ is
written in a novel which has its own theme, which makes the meaning becomes
different because of the current context or novel’s theme.
According to Halliday and Hassan (1976:1), A text may be spoken or written,
prose or verse, dialogue or monologue. It may be anything form a single proverb
to a whole play, from a momentary cry for help to an all-day discussion and
committee text is also unit of language in use; it is not grammatical unit, like a
clause or a sentence. (Brown and Yule, 1984:6) state that a text may be differently
presented in different editions, with different size of paper, in one or two column
10
2.2.1 Cohesion
Halliday and Hassan (1976:4) state that the concept of cohesion is
semantic one: it refers to relation of meaning that exist within the text, and that
define it as text. Cohesion occurs when the interpretation of some element in the
discourse is dependent on that of another. The one presupposed the order, in the
sense that it cannot be effectively decoded except by recourse to it. When this
happens, a relation of cohesion is set up, and two elements the presupposing and
the presupposed, are there by at least potentially integrated into a text.
An Example, consider the old piece of schoolboy humour: [I :5] Time flies
You can’t; they fly too quickly.
The first sentence gives no indication of not being a complete text; in fact it
usually is, and the humour lies in the misinterpretation that is required if the
presupposition from the second sentence is to be satisfied. Here, incidentally, the
cohesion is expressed in no less than three ties : the elliptical from you can’t
(Chapter 4), the reference item they (Chapter 2), and the lexical repetition fly
(Chapter 6).
11
According to Brown and Yule (1983: 191) Cohesive relationship within a text
are set up where the interpretation of some element in the discourse is dependent
on that of another.
In other words, cohesion is such a semantic relation which refers to relation of
meaning that exist within the text and that define it as text. Cohesion is divided
into two sections, grammatical cohesion sand lexical cohesion (Haliday & Hasan,
1976: 6).
2.2.2 Grammatical Cohesive Devices
Grammatical cohesion is the surface making of semantic links between clauses
and sentence in written discourse. Grammatical cohesion consists of reference,
ellipsis, substitution and conjunction (Halliday and Hassan 1976:6).
2.2.2.1Reference (Halliday & Hassan 1976: 31-87)
Reference is an item which instead of being interpreted semantically on its
own, it ferers to something else for its interpretation. The reference is divided
in two types, exophora and endophora, they are:
1. Exophora reference: the interpretation lies outside of the text. It is found in
the context situation
The Government are to blame for unemployment.
She was using one of those tools
2. Endhopora reference: the interpretation lies within a text. There are two
12
a) Anaphora reference, words referring to the other words
preceeding the text,
Madona won the academy awards in 1985.
She plays in a movie ‘’Evita’’
b) Cataphora reference, words referring to the other words
following the text.
He swims in the swimming pool.
Ray becomes an athlete as a swimmer
There are three types of reference: Personal, Demonstrative, and Comparative
(Halliday &Hassan, 1976:37). Personal is reference by means of function in the
speech situation, personal pronoun, possessive determiners/adjectives and
possessive pronouns. Personal indicated by the first person (I, me, we, us).
Demonstrative is reference by means of location (this, these, those, here/now,
there, then). Comparative is indirect reference by means of identity and similarity
(better, more, less, equal, so, such, other, different, else, otherwise, same, similar,
likewise).
2.2.2.2Substitution (Halliday & Hassan 1976: 88-141)
Brown and Yule said substitution is the replacement of an expressions that is
obvious from the context by another element in a text (Brown and Yule 1983,
p.201)
(Haliday and Hassan 1976: 88-141) Substitution is the replacement on an item
13
substitution (one, ones, the same), verbal substitution (do, does, did, done, doing)
and clausal substitution (so, not). Below are the examples:
a. ‘’My axe is to blunt. I must get a sharper one.’’
b. ‘’These biscuits are stale. Get some fresh ones.’’
c. ‘’John thought it was impossible.-Yes, it thought the same.’’
(Nominal)
a. ‘’The word did not come the same as they used to do.’’
(Verbal)
a. ‘’Is there going to be an earthquake?-it say so.’’
b. ‘’Has everyone gone home?-I hope not.’’
(Clausal)
In example of nominal substitution, one is substituting the noun axe, ones is
substituting the noun biscuits and the noun phrase the same is substituting it was
impossible. In example of verbal substitution, do is substituting come. In example
of clausal substitution, so is substituting there going to be an earthquake and not
is substituting gone home but in the negative expression or in other words it has
the same meaning as (everyone) are not going home.
2.2.2.3Ellipsis (Halliday & Hassan 1976: 142-225)
Ellipsis is the omission of elements normally required by the grammar which
the speaker or writer assumes are obvious from the context and therefore need to
be raised. Ellipsis deal with ‘something left unsaid but understood ‘where
14
mentioned as’ substitution by zero’’. There are three types of ellipsis: nominal
ellipsis, verbal ellipsis and clausal ellipsis.
Nominal ellipsis means ellipsis within the nominal group. Nominal ellipsis
consist of specific deictic (the, possessive and demonstrative), non-specific deictic
(each, every, all, both, any, either, no, neither and some), pre-deictic (all, both),
post-deictic (other, same, different, identical, usual, regular, certain, odd, famous,
well-known, typical, obvious), numeratives (first, next, last, second, third, fourth)
and epithets (adjectives). Verbal ellipsis means ellipsis within the verbal group.
Verbal ellipsis consists of lexical ellipsis (by inspecting its form) and operator
ellipsis (ellipsis from the left). Clausal ellipsis means ellipsis within the clause.
Clausal ellipsis consists of ellipsis in modal and prepositional elements, ellipsis in
questions-answer and other rejoinder sequences, and ellipsis in
‘reporting-reported’ sequences. Below are the examples:
a. ‘’He has read a few novels. He says that the best is that of Hemingway’’
(Nominal)
b. ‘’Have you been swimming?-yes, I have.’’ (Verbal lexical ellipsis)
c. ‘’In the park the Duke was going to plant a row.’’ (Clausal-prepositional
element)
2.2.2.4Conjunction (Halliday & Hassan 1976: 226-273)
Conjunctions are the word on the borderline of grammatical and lexical cohesion.
They are mainly grammatical but also have a lexical component in them.
15
the text, but they express certain meanings which presuppose the presence of other
component in discourse. Conjunction which commonly used are such as: and, but,
or, and because. There are four kinds of conjunctive expressions: additive,
adversative, causal and temporal conjunctions.
Additive conjunction relation is a sentence equals a clause complex that is
any set of clauses that are hypotactically and/or paratactically related with the
simple clause as the limiting case. For example, and, or and nor. Adversative
conjunctions has a basic meaning of ‘’contrary to expectation’’. The expectation
may be come from the content of what is being said, or from the communication
process. For example, but. Causal conjunction is the conjunction which shows the
relation cause and effect. For example, because, so, and therefore. Temporal
conjunction is the relation in external terms that may be simply one of sequence in
time; the one is subsequent to the other. For example, first, next, then, and finally,
16
Emphatic : however,
nevertheless, despite this Contrastive external : Simple : but, and Emphatic : however, on
oral Temporal, (external only): simple
Sequential : then , next, after that
Simultaneous : just then , at the same time
sentence boundaries in written texts. Halliday and Hassan (1976:318) states that
lexical cohesion consists of reiteration and collocation.
17
Reiteration is the repetition of a lexical item at one end of the scale, the use of
a general word refer back to a lexical item at the other end of the scale, and a
number of things in between such as the use of synonym, near-synonym,
superordinate, or general word. Synonym or near synonym occurs when two
lexical items are used to mean the same thing. Superordinate is the item which
meaning includes the part of the items that dominates in the lexical taxonomy.
General word corresponds to the major noun classes such as human noun, place
noun, fact noun and the like. Below are the examples of reiteration:
a. ‘’There was a large mushroom growing near her, about the
Same height as herself; and, when she had looked under it,
It occurred to her that she might as well look and she what
Was on top of it. She stretched herself up on tiptoe, and
Peeped over the edge of the mushroom…’’
(Repetition)
b. ‘’Accordingly... I took leave, and turned to ascent of the
Peak. The climb is perfectly easy…’’
(Synonym)
c. ‘’Then quickly rose Sir Bedivere, and ran,
And leaping down the ridges lightly, plung’d
Among the bulrush beds and clutch’d the sword
And lightly wheel’d and threw it. The great brand
Made light’nings in the splendor of the moon…’’
18
d. ‘’Henry bought himself a new Jaguar. He practically lives in the
Car.’’(Superordinate)
In repetition, ‘mushroom’ refers back to ‘mushroom’. In synonym, ‘climb’ refers
back to ‘ascent’ because they are synonym to each other. In near synonym,
‘brand’ refers back to ’sword’ because it is a near synonym. In superordinate,
‘car’ refers back to ‘Jaguar’ because ‘car’ is the superordinate of ‘jaguar’.
2.2.3.2Collocation (Halliday & Hassan 1976: 284-292)
Collocation is the similarity of lexical environment of words. Collocation
includes a word that is in some way associated with another word in the preceding
text because it is a direct repetition of it, or is in some sense synonymous with it,
or tends to occur in the lexical environment, coheres with that word and contribute
to the texture. Collocation includes some environments of words. The
environments are:
a. Complementaries, such as boy-girls, stand up-sit down;
b. Antonyms, the item opposed in meaning with other such as like-hate,
Wet-dry, crowded-deserted;
c. Converses, such as order-obey;
d. Pair of series or pair of words drawn from the same ordered series such as
Tuesday-Thursday, dollar-cent, north-south, colonel-brigadier,
Basement-roof, road-rail and red-green;
e. Part to whole , such as car-brake, box-lid ;
19
g. Proximity is the nearness relationship of one lexical item with others ;
h. Co-hyponyms, members of the same general class such as chair-table
(both hyponyms of ‘furniture’) and walk-drive (both hyponyms of ‘go’).
2.2.4 Previous Study
Siti Nur Hasanah (2000) ‘’Universitas Wijaya Kusuma Surabaya’’did
another related study, with the title ‘’A study on the cohesive devices used in the
newspaper Jakarta Post’’ taken from the Jakarta Post’’. She has a purpose to find
out whether the ‘’National News’’ in Jakarta Post was cohesive or not. She uses
theory by H.A.K Halliday and Ruqaiya Hasan as the main theory to analyze the
data. She uses some steps: divided and analyze data into fulfillment of cohesive
devices and violation of cohesive devices, identify the data, analyze the
fulfillment of the data, comparing the fulfillment and violation of the cohesive as
the result, fulfillment (93.08%) and violation (6.92%). She conclude that
‘’National News’’ in Jakarta Post was cohesive.
The previous study on cohesive devices, is written by Prasetia
(2002)‘’Universitas Kristen Petra Surabaya’’ entitled’’ Cohesive Devices used in
nine advertorial articles takes from website in the internet’’. He looked for nine
advertorial articles in internet, then analyzed them using Cohesion Devices theory
by H.A.K Halliday and Ruqaiya Hasan as the main theory. The result of his
20
conjunction (63.51%). While for lexical Cohesive Devices, the most occurrences
are collocation particularly part to part (50%).
The last previous research is ‘’ Toyo Haryono (2005)’’Universitas Kristen
Petra’’ with title ‘’ Grammatical cohesion devices used in Website Banners’’
taken from Yahoo. He uses theory by H.A.K Halliday and Ruqaiya Hasan and
Brown and Yule (1983) as the supporting theory. He uses some steps: collect 50
banners randomly as the data, uses table to categorize the data, and then analyze
the data. The result of his thesis is the most frequent Grammatical Cohesive
21
CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHOD
In this chapter, the writer presents the research method consisting of approach,
the source of the data, data collections procedure and data analysis.
4.1Approach
This study uses descriptive qualitative approach in doing the research. The
writer applies the descriptive quantitative approach to carry out her study since
she wants to determine the cohesive devices of text of short story. She used
descriptive quantitative approach because this study starts with analyzing and
calculation.
According to Bodgan (1982: 30) state‘’ in collecting descriptive data,
qualitative researchers approach the worlds in nitpicking way’’. He also states that
qualitative research is a descriptive study for the reason that the data collected in
form of words or pictures rather than numbers. This research is not emphasized on
questioner form but by observing, collection and describing the sentences of
‘’’The Casher’’ by John Collier’s by using Halliday and Hassan theory of
cohesion or cohesive devices to gain descriptive data of the kinds of cohesive
22
4.2Research Instrument
The instrument of this result is the writer. Since the research design belongs
to descriptive qualitative method that emphasizes on observation.
4.3Data and Data Source
The source of data was taken from a short story with title ‘’The Casher’’ by
John Collier’s. The writer concentrated more on sentences and tries to identify the
short stories by applying the Hassan and Halliday’s theory and other theory of
cohesion that consist of grammatical (reference, substitution, ellipsis and
conjunction) and lexical cohesion (reiteration and collocation).
4.4Technique of Collecting Data
After collecting data from John Collier’s, the writer analyzed them by
applying the steps ; first the writer analyzed the data by reading all short story to
know the situation that happened in this story, in this step the writer tries to
understand the sentence. After that, the writer classifying the data in two
categorizes grammatical cohesion and lexical cohesion to find out all the cohesion
aspects. Next, the writer explains all the cohesion that exists in short story.
After that, the writer counted each aspects of grammatical and lexical
cohesion was the next thing that she would do. She would know which one of
those aspects of grammatical and lexical cohesion mostly occur in the Casher by
23
4.5Analyzing the Data
In analyzing the obtained data, firsly the writer reads and
checks the data again then understanding the meaning of each sentence.
After that, the writer analyzes the data then classifies them into the
appropriate kinds of grammatical and lexical cohesion. After analyzing
and classifying, the writer calculate the frequency of grammatical and
lexical cohesion’s occurrences. After calculating the percenteage, the
writer make the conclusion of cohesion devices.
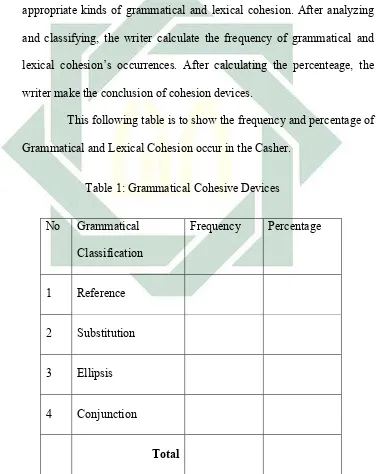
This following table is to show the frequency and percentage of
Grammatical and Lexical Cohesion occur in the Casher.
Table 1: Grammatical Cohesive Devices
No Grammatical
Classification
Frequency Percentage
1 Reference
2 Substitution
3 Ellipsis
4 Conjunction
24
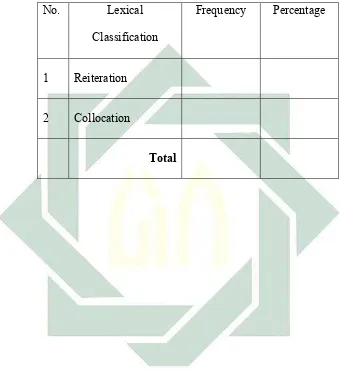
Table 2: Lexical Cohesive Devices
No. Lexical
Classification
Frequency Percentage
1 Reiteration
2 Collocation
54
CHAPTER V
CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION
5.1. Conclusion
In this chapter, the writer presents the general conclusion of her study on
‘’Cohesion used by John Collier’s in the Casher’’. The writer wants to find out
the kind of Grammatical and Lexical Cohesion devices occur in the short story by
John Collier’s and how often they occur in percentage, thus makes this research.
In order to complete the research, the writer use theory of Cohesion by Halliday &
Hassan (1980) as the main theory. She also uses the theory by Brown and Yule
(1983), and also McCarthy (1985) as the supporting theory. The writer also uses
the table to categorize the data easily and systematically, based on the
Grammatical and Lexical Cohesion theories. The writer collect the data from one
of the short story by John Collier’s randomly as the data. In the writer data, she
finds three Grammatical Cohesion Devices are occurred such as Reference,
Substitution, and Conjunction. She also finds two Lexical Cohesion Devices are
occurred such as Reiteration and Collocation. Finally, the writer finds that the
most frequent used in Reference.
Personal Reference is mostly occurred from the data. As an example, it can
be seen in appendix. For the second occurrence of the most is Collocation. The
other Grammatical Cohesion Devices found in this research is Conjunction.
55
found the least of Cohesion in Grammatical cohesion in the Casher is Ellipsis. The
other Lexical Cohesion Devices found in this research is Collocation. Reiteration
places as the second devices which are mostly occurred in Lexical Cohesion.
5.2 Suggestion
Cohesion that consists of Grammatical and Lexical cohesion is a topic that
has been researched by many researchers before. The benefit and the difference of
this study that many studies before analyzed only used one theory, H.A.K.
Halliday and Hasan. While, this study elaborates many theories of lexical
cohesion. Furthermore, this study does not only focus in Lexical Cohesion but
also in Grammatical Cohesion.
After doing this research, the writer hopes that by understanding
Grammatical Cohesion and Lexical Cohesion and the usage of its devices, readers
can really understand or catch the implicit aim that it created in the Casher.
Hence, by understanding Grammatical and Lexical Cohesion devices avoids the
readers to misinterpret the Casher words and goal. The writer suggests, further
studies will be more focused on movie or novel so the result will be more accurate
25
CHAPTER IV
FINDINGS AND DISCUSSION
As mentioned in the previous chapter, the aims of the study are to
show the kinds of Cohesion that consist of Grammatical and Lexical in the
Casher.
This chapter presented the findings, the analysis, and the result of the
study. The researcher analyzes the data after the data were collected. The
researcher tried to find out what Cohesion Devices are most frequently used
by John Collier in the Casher.
The researcher employed Halliday and Hassan theory to describe the
kinds of Cohesion and other theory that support each other that exist. Then, in
order to describe the factors influencing in the Casher, the researcher
analyzed it by considering factors that influence the use of Cohesion also
based on Halliday and Hassan’s.
4.1 Findings
Data 1.
Grammatical Cohesion (Reference)
26
Alan Austen, as nervous as a kitten, went up certain dark and creaky stairs in the neighborhood of Pell Street, and peered about for a long time on the dime landing before he found the name he wanted written obscurely on one of the doors.
Context of situation:
In dark night Alan was visit an old man in the Peel Street, he came to buy
something; he came in a small room. When his arrived in small room, an old man
sees him and feels good.
Data interpretation
The story shows that ‘’He’’ as a first person or Personal Reference which
appear in sentence above, Means he referring to Alan it is also continued by
Anaphoric Reference. According to Brown and Yule (1983: 191) state that
Anaphoric reference is two sentences together constitute a text. In data above, it is
clear that he in the next sentence refers back to (is Anaphoric) Alan.
Data 2.
Grammatical and lexical Cohesion
Second Paragraph
He pushed open this door, as he had been told to do, and found himself in a tiny room, which contained no furniture but a plain kitchen table, a rocking-chair, and an ordinary chair. On one of the dirty buff-colored walls were a couple of shelves, containing in all perhaps a dozen bottles and jars.
27
After arrive in tiny room, Alan became confuse because he looked around the
scenery of that room with bad situation. There are old chair, table, and other old
furniture. He see some of bottles and jars. He find shadow of person who sits in
the rocking chair. He starts to close the shadow.
Data interpretation
Personal Reference: ‘’He’’ is the personal reference that refers first
person as Alan Austen. The data above also shows that, Alan use Verbal
substitution of ‘’Do’’. In Alan action, he tries to open the door to enter in tiny
room. The verbal substitution of do happened when the word of pushed occur.
So, do as a head and pushed as a modifier. There are two additive conjunction of
word ‘’and’’ in data above, additive conjunction of (and) happened to link one
sentence or word to another, in sentence above ‘’and’’ is link condition of Alan
when he outside of room and inside in tiny room. The adversative Conjunction
of ‘’but’’ occur when expresses a relation which is not additive but adversative.
The Collocation occur when the word of kitchen table, a rocking-chair, and an
ordinary chair’’ appear. The categorize of these things is represent about furniture
or general class of things or both hyponyms are furniture.
Data 3
Grammatical and Lexical Cohesion
28
The conversation took place in the one of room in Peel Street. An old man
asked Mr. Austin and give the appreciate when his customer came, as a buyer Mr.
Austen asked him that it is true he sell the many potion. Austen feels anxious to
find the potion. The old man reply him question and explain to him that he sells
something that never do another seller.
Old Man : “Sit down, Mr. Austen, “I am glad to make your acquaintance.”
Alan Austin : “Is it true,“that you have a certain mixture that has-er-quite extraordinary effects?”
Old Man : “My dear sir,, “my stock in trade is not very large-I don’t deal in laxatives and teething mixtures-but such as it is, it is varied. I think nothing I sell has effects which could be precisely described as ordinary.”
Data Interpretation
The excerpt containing by Alan and old man above show that the Personal
Reference of’’ I’’ most occur happened between Alan and old man in this
situation. The personal reference of I as speaker only with/without other person.
In old man the Comparative Reference occur when he say such. The word of
Such is refers to compare or identify between potion and another potion in this
story. The comparative references happen when the class of adjective or adverb
represents identity or similarity. So, ‘’ such’ ’is the part of adverb. There is
additive conjunction of word ‘’and’’ in data above, additive conjunction of (and)
happened to link one sentence or word to another, in sentence above, the old man
use ‘’and’’ to link the kinds of potion that he sells to Alan. According to Halliday
29
expresses a relation which is not additive but adversative. The old man use word
of ‘But’ because, is a complex one including components of emphasis which are
absent from the elementary ‘and’.
Data 4.
Grammatical and Lexical Cohesion
Context of Situation
The conversation took place in the room in Peel Street, In conversation
above Alan wants to know what the kinds of love potion that him sell are.
Finally, the old men give the example of bottles on the shelf and show it to Alan.
He explains that his thing is unique because, the potion has no taste.
Alan Austin : “Well, the fact is. . …”.
Old Man : “Here, for example, “, reaching for a bottle from the shelf. “Here is a liquid as colorless as water, almost tasteless, quite imperceptible in coffee, wine, or any other beverage. It is also quite imperceptible to any known method of autopsy.”
Data Interpretation
In Alan’s utterance “Well is show that he use Continuatives
Conjunction, the function of well in Alan’s utterance is to response the previous
dialogue that happened in this story. Well serves to indicate that what follow is in
fact a response to what has preceded. The old man replied Alan’s questions with
use ‘’Here’’. As a writer explain before that Demonstrative Reference happened
when the word of ‘’Here’’ exist, the function of here in this sentence as an adverb
30
happened before the old man take the bottle from the shelf, here indicate that the
bottles are long from him hands. The Collocation occur when the word of
’Coffee-wine’ appear. These subjects are representing about pair of series. Coffee
and wine are has a semantic relation to one another (both are class of drinking).
Data 5.
Grammatical and Lexical Cohesion
Description of context situation
This story happened in a tiny room in Peel Street, when Alan feels
horrified while he interprets that the old man sells the danger potion. He scary
with his life and also imagine that is bad situation to buy that. But, the old man
replied that this potion is no danger and if he wants to clean his life, he must be
bought it. The old man thinks that Alan was trouble with his life so, he must be
repairs his mind, his act and so on.
Alan Austin : “Do you mean it is a poison?
The Old Man : “Call it a glove-cleaner if you like,”. “Maybe it will clean gloves. I have never tried. One might call it a life-cleaner. Lives need cleaning sometimes.”
Data Interpretation
The conversations containing by old man that show the Personal
Reference of’’ I’’ occur in this situation. The personal reference of I as speaker
31
Verbal Substitution, the function of Do in Alan’s utterance is refers to
interrogative action. Do serves to indicate that Alan give the question to old man.
While the old man replied him, he use Reiteration with category repetition in
words ‘’Glove-gloves, life-lives, cleaner-clean, cleaner-cleaning. The old man use
3 repetition words to indicate that all these instances have in common that one
lexical item refer back to another.
Data 6.
Grammatical and Lexical Cohesion
Context of Situation
This story still in tiny room and the conversation happen between Alan
and old man. In conversation above Alan did not want to but the love potion
however, the old man was explained that the potion has many function especially
for life. Although Alan did not want to buy it, the old man gives the price of one
teaspoonful to Alan.
Alan Austin : “I want nothing of that sort,”.
The Old Man : “Probably it is just as well,”. “Do you know the price of this? For one teaspoonful, which is sufficient, I ask five thousand dollars. Never less. Not a penny less.”
Data Interpretation
In Alan’s utterance he use Personal Reference of ‘’I’’. The word
32
man utterance’s ‘’ for one teaspoonful’’ it indicated the usage of Nominal
Substitution. The word of One is the type of nominal substitution that refers to
cardinal number. This function of word one in sentence above as a numeratives, in
other hand it maybe singular or plural but, in sentence above one is singular. The
Collocation occur when the word of ’Thousand-dollars’ appear. These subjects
are representing about pair of series. Thousand and dollars are has a semantic
relation to one another (both are class of money).
Data 7.
Grammatical and Lexical Cohesion
Description of context situation
This story happen still in tiny room at the dark night at Peel Street, while
the old man said the price of teaspoonful, Alan was shock and try to offer a price
of potion. However the old man did not approve it. The old man said that this
price is suitable. He explains to Alan that the price is not considerable if compared
with quality. Every people did not aware about the best quality of potion and
some of people willing to buy or leaving it.
Alan Austin : “I hope all your mixtures are not as expensive,”.
33
Data Interpretation
In Alan’s utterance he use Personal Reference of ‘’I’’. The word of I is
use to emphasize Alan as speaker only with/without other person. From the data
above, the writer found Anaphora Reference that refers to speech roles between
(first and second person) and the other roles or third person ‘’they’’, in this
sentences only third person form typically refers to ‘’young people’’ anaphorically
to a preceding item in the text. T he use word of them as third person is indicating
to the reader that Alan and old man speak about other people that not in situation
while the discussion happened. Next, in old man utterance’s he shows about the
repetition. Reiteration is typically of repetition in sentence above, the old man
repeat ’’Love-potion, love potion. The old man use 2 repetition words to indicate
that all these instances have in common that one lexical item refer back to another.
Data 8.
Grammatical and Lexical Cohesion
Context of Situation
When Alan hear the explanation from old man, he was great to hear that,
he interested potion that him sell. The old man as a seller tries to persuade his
customer again through many tricks. The old man use something like analogy that
34
Alan Austin : “I am glad to hear that,”.
The Old Man : “I look at it like. “Please a customer with one article, and he will come back when he needs another. Even if it is more costly. He will save up for it, if necessary.”
Data Interpretation
The excerpt containing by Alan and old man above show that the Personal
Reference of’’ I’’ most occur happened between Alan and old man in this
situation. The personal reference of I as speaker only with/without other person.
In old man utterance’s ‘’ one article’’ is indicated the usage of Nominal
Substitution. The word of One is the type of nominal substitution that refers to
person. Here the old man explain that he have to give the best for his customer
with one articles. So, one appear as a head without modifier. There is additive
conjunction of word ‘’and’’ in data above, According to Halliday and Hassan
(1986: 244) additive conjunction of (and) happened to link one sentence or word
to another, in sentence above, the old man use ‘’and’’ to link the word customer
and back .
Data 9.
Grammatical and Lexical Cohesion
35
This story happened in the tiny room at Peel Street. Based on conversation
above, Alan asked to old man the quality of his potion then old man explains that
his potion has many function and permanent.
Alan Austin : “And these potions,”. “They are not just-just-er-”
The Old Man : “Oh, no,”. “Their effects are permanent, and extend far beyond the mere casual impulse. But they include it. Oh, yes they include it. Bountifully, insistently. Everlastingly.
Data Interpretation
From the data above, the writer found Demonstrative Reference: that
occur in word ‘’these’’, this word happened to indicate the distance of subject that
was called by speaker. The word of these uses to describe a thing that closes with
us. According to Halliday and Hassan (1986: 250) the adversative Conjunction
of ‘’but’’ occur when expresses a relation which is not additive but adversative.
The old man use word of ‘But’ because, is a complex one including components
of emphasis which are absent from the elementary ‘and’. Means that the use word
of but is to link one phrase with another phrase. The Collocation occur when the
word of Bountifully, insistently. Everlastingly appear. These categorize of things
is represent about pair of word.
Data 10.
Grammatical and Lexical Cohesion
36
When the old man explain more about the function of potion in his room’s,
Alan was aware and want to buy it. The old man give the step how do mix the
love potion with some of drinking. He said that this potion has no taste in kinds of
drinking. So, he can do it itself without help by other people, Even his girlfriend
will be loving him forever.
Alan Austin : “I do,.
The old man : “For indifference,”, they substitute devotion. For scorn, adoration. Give one tiny measure of this to the young lady-its flavour is imperceptible in orange juice, soup, or cocktails-and however gay and giddy she is, she will change altogether. She will want nothing but solitude and you.”
Data Interpretation
In Old Man’s utterance he use additive conjunction of word ‘’and’’ in
data above, additive conjunction of (and) happened to link one sentence or word
to another, in sentence above ‘’and’’ is link condition of Old Man when he
compare the function of his potion and Diana’s attitude. Reiteration that appear
in above is typically of synonyms, the old man uses Synonym appear in words
‘’Scorn-adoration’’. The Collocation occur when the word of ‘’Juice-cocktail’’
happened. These categorize of things is represent about general class of things
(both hyponyms of ‘’Drink).
Data 11.
Grammatical and Lexical Cohesion
37
The story happened in old man rooms, Alan start to talks about Diana to
old man. Alan shows the character of his girlfriend to old man. She is beauty, like
party and so on. He is not believed that love potion can make her changes but, the
old man convince him. The old man said that she can change faster. She will be
loved you and she be a scary while the other pretty woman meet you. She can give
you all everything that you want.
Alan Austin : “I can hardly believe it,”. “She is so fond of parties.”
The Old Man : “She will not like them any more,”. “She will be afraid of the pretty girls you may meet.”
Data Interpretation
In Alan’s utterance he use Personal Reference of ‘’She’’. The word of
she is use to emphasize the third person. From the data above, the writer found
Exophora Reference that refersto speech roles between (first and second person)
and the other roles or third person ‘’she’’, in this refers to ‘’pretty girls’’ the
exophoric happened when the interpretation lies outside of the text. The use word
of her as third person is indicating to the reader that Alan and old man speak about
other people that not in situation while the discussion happened. Next, in Alan
utterance’s he uses Comparative Reference of so that indicate her girlfriend like
much party than other. The function of comparative reference is to adverb to get
the meaning of speaker.
Finally, in Alan and old man utterance’s he shows about the Reiteration
38
instances have in common that one lexical item refer back to another. The
repetition of she means to make the topic more significant or clear because, this
story happened when Alan want to buy a love potion to get her love. So, they use
repetition of ‘she’ to make the reader focuses on his problems.
Data 12.
Grammatical and Lexical Cohesion
Context of Situation
This story containing by the old man explain about the condition while
Alan arrive at home. Diana will be the best for him and she will be sad when
know that Alan leaving her. Alan was excited when he hear that.
Alan Austin : “Wonderful!” cried Alan.
The Old Man : “She will want to know all you do,” said the old man. “All that has happened to you during the day. Every word of it. She will want to know what you are thinking about, why you smile suddenly, why your are looking sad.”
Data Interpretation
In the Old Man utterance he use Personal Reference of ‘’She’’. The word
of she is use to emphasize the third person in this data. In old man’s utterance he
use Personal Reference of ‘’She’’. He also use Exophora Reference that refers
to speech roles between (first and second person) and the other roles or third
person she. In she refers to ‘’Diana’’ the exophoric happened when the
39
indicating to the reader that Alan and old man speak about other people that not in
situation while the discussion happened. The old man’s also use antonyms in his
excerpt. Antonyms is the typically of Collocation, the use of collocation occur in
word smile-sad in data above.
Data 13.
Grammatical and Lexical Cohesion
Context of Situation
This story represent about the old man who give an advice to Alan so that
he must be carefully if there are many problems happened in his life. There are
many woman want to be his wife or his girlfriends but, Alan must be known that
anything his act or situation, Dianna still love him and will forgive him. Then,
Alan emphasize that he will never do it.
The Old Man : “You will not have to use your imagination,” said the old man. “And, by the way, since there are always sirens, if by any chance you should, later on, slip a little, you need not worry. She will forgive you, in the end. She will be terribly hurt, of course, but she will forgive you-in the end.”
Alan Austen : “That will not happen,”.
Data Interpretation
Based on data above, In the Old Man utterance he use Personal Reference
of ‘’She’’. The word of she is use to emphasize the third person in this data. The
40
According to Halliday and Hassan (1981: 48) Anaphora Reference occur when the
speech roles (first and second person) and the other roles or third person. But,
only third person or ‘’She’’, in this sentences typically refers anaphorically to a
preceding item in the text. In sentence above she if refers to Dianna. In Old Man’s
utterance he also uses additive conjunction of word ‘’and’’ in data above,
additive conjunction of (and) happened to link one sentence or word to another, in
sentence above ‘’and’’ is link condition of Old Man when he asked and advice
Alan about Dianna. According to Halliday and Hassan (1986: 250) the
adversative Conjunction of ‘’but’’ occur when expresses a relation which is not
additive but adversative. The old man use word of ‘But’ because, is a complex
one including components of emphasis which are absent from the elementary
‘and’. Means that the use word of but is to link one phrase with another phrase. In
data above ‘but’ uses to explain about cause and result. The last is Of course that
typically of Continuatives Conjunction, the old man use this word to likely or
reject something.
Data 14.
Grammatical and Lexical Cohesion
Context of Situation
The story still happened in Old Man rooms at Peel Street, the conversation
continuing by the old man who said to Alan that he does not worry if Dianna
41
old man and ask how the price it, but the old man said that if some of people must
be save up for it.
The Old Man : “Of course not,” said the old man. “But, if it did, you need not worry. She would never divorce you. Oh, no! And, of course, she will never give you the least, the very least, grounds for-uneasiness.”
Alan Austin : “And how much,” said Alan, “is this wonderful mixture?”
The Old Man ; “It is not as dear,” said the old man, “as the glove-cleaner, or life-cleaner, as I sometimes call it. No. That is five thousand dollars, never a penny less. One has to be older than you are, to indulge in that sort of thing. One has to save up for it.”
Data Interpretation
In the Old Man utterance he use Personal Reference of ‘’She’’. The word
of she is use to emphasize the third person in this data. The adversative
Conjunction of ‘’but’’ occur to explain about cause and result. ‘’Of course’’
typically of Continuatives Conjunction that happened in this data, the old man
use this word to likely or reject something. Next, in old man utterance’s he shows
about the Reiteration typically repetition of She-she, least-least, cleaner-cleaner.
The usages of 3 words of repetition are to indicate that all these instances have in
common that one lexical item refer back to another. The Collocation occur when
the word of ’Thousand-dollars’ appear. These subjects are representing about
pair of series. Thousand and dollars are has a semantic relation to one another
42
Data 15.
Grammatical and Lexical Cohesion
Context of Situation
The situation of this story still in tiny rooms, Alan wants to know where
the love potion is now. He wants to get this and go home. Then the old men taking
out from his kitchen table and give to him.
Alan Austin : “But the love potion?”.
The Old Man : “Oh, that,” opening the drawer in the kitchen table, and taking out a tiny, rather dirty-looking phial. “That is just a dollar.”
Data Interpretation
According to McCarthy (1990: 46) Adversative Conjunction used just
not to link used not just to link individual utterances within turns, but often at the
beginning of turns, linking one speaker's turn with another speaker's, or linking
back to an earlier turn of the current speaker, or else marking a shift in topic or
sub-topic. The adversative conjunction find in Alan’s utterance of first word of
but. These conversations continue by Alan’s utterance, he uses But which is
43
that the old man still have a love potion. Then, the old man taking out his potion
and give to Alan.
Data 16.
Grammatical and Lexical Cohesion
Context of Situation
The last of story represent that Alan gives so many thanks to the Old Man,
because he was tell him many function of his things that was he sell to Alan. Alan
feels so great and happy when he out from the old man room’s. Before that, the
old man said to Alan that he was really happy to help him and he hopes that Alan
will come back to his shop or his room. Alan promise that he will came back
again.
Alan Austin : “I can’t tell you how grateful I am,” said Alan, watching him fill it.
The Old Man : “I like to oblige,” said the old man. “Then customers come back, later in life, when they are better off, and want more expensive things. Here you are. You will find it very effective.”
Data Interpretation
In Alan’s and the Old Man utterance they use Personal Reference of ‘’I’’.
The word of I is use to emphasize Alan and the Old Man as speaker only
44
word ‘’and’’ in data above, additive conjunction of (and) happened to link one
sentence or word to another. The last section Demonstrative Reference: ‘’Here’’
appear in data above, here means is adverb or indicates of distance. Here in
sentence above represent about the fast function of love potion by old man.
4.2 Discussion
Based on the findings, the most occurrences of Cohesion devices is
Grammatical Cohesion, and the least occurrence is Lexical Cohesion. Reference
as the most common occurrence of Grammatical Cohesive Devices has hold
important role in making the short and incomplete sentences become attractive
and clear to be understood. For instance, the occurrence of Personal Reference
can also make the short story in the Casher understandable the text though the
item referred is not in the text.
Cohesion is a topic that has been researched by many researchers before.
The benefit and the difference of this study does not only focus in Lexical
Cohesion but also in Grammatical Cohesion.
The writer found seventy six (69) grammatical cohesive devices, which are
classified into four main cohesive devices (table 1): Reference with percentage
(49%), (table 2) Substitutions (4%), (table 3) Ellipsis (0%), and (table 4)
Conjunction (16%). The writer also found (38) lexical cohesion devices, which
are classified into two main cohesive devices (table 5) Reiteration with (13%),
then the last in (table 6) Collocation (25%). Each of these six main cohesive
45
shows in this chapter. All kinds of percentage and frequency of sub devices of
Grammatical and Lexical will be describe also in (table 1.1 and 1.2).
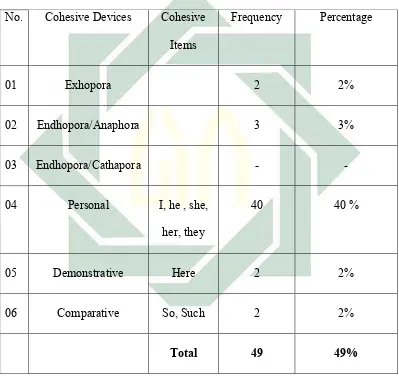
Table 1: Grammatical Cohesive Devices of Reference
No. Cohesive Devices Cohesive
Items
Frequency Percentage
01 Exhopora 2 2%
02 Endhopora/Anaphora 3 3%
03 Endhopora/Cathapora - -
04 Personal I, he , she,
her, they
40 40 %
05 Demonstrative Here 2 2%
06 Comparative So, Such 2 2%
Total 49 49%
In the short story entitle ‘The Casher’, the writer found 2 Exhopora
Reference, 3 Anaphora Reference, 40 personal references, 2 demonstrative
reference and 2 comparative reference used. There are 5 items of personal
46
they. The personal reference I is focused on the first person that describe to Alan
himself. The personal reference also used to an old man while discussion.
The personal reference He focuses on the third person or male continue for
She and Her refers to the reader of the woman in this story. Next is personal
reference They refers to love potion (things).
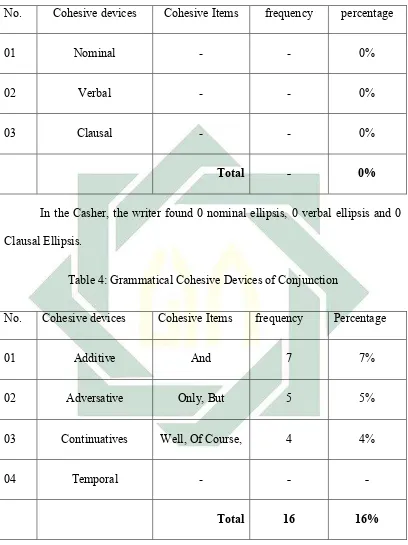
Table 2: Grammatical Cohesive Devices of Substitution
No. Cohesive devices Cohesive Items frequency percentage
01 Nominal One 2 2%
02 Verbal Do 2 2%
03 Clausal - - -%
Total 4 4%
The writer found 2 nominal substitution, 2 Verbal substitution and
0 Clausal substitution used in the casher.
The nominal substitution ‘’One’’ refers to the reader about thing, person and
cardinal number. The verbal substitutions ‘’Do’’ refers to interrogative verbal
such as‘’ “Do you mean it is a poison? ‘’ the word Do is interrogative verbal
because, the form of do is the finite verbal operator.
47
No. Cohesive devices Cohesive Items frequency percentage
01 Nominal - - 0%
02 Verbal - - 0%
03 Clausal - - 0%
Total - 0%
In the Casher, the writer found 0 nominal ellipsis, 0 verbal ellipsis and 0
Clausal Ellipsis.
Table 4: Grammatical Cohesive Devices of Conjunction
No. Cohesive devices Cohesive Items frequency Percentage
01 Additive And 7 7%
02 Adversative Only, But 5 5%
03 Continuatives Well, Of Course, 4 4%
04 Temporal - - -
Total 16 16%
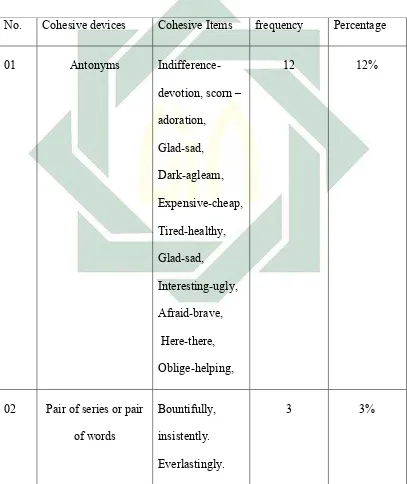
In the Casher, the writer found 7 additive conjunctions, 5 adversative
conjunctions and 4 continuatives conjunction used. The additive conjunction and
48
conjunction only is found in 28 paragraphs continued by but in 5, 19, 21 and 37
paragraphs.
Table 5: Lexical Cohesive Devices of Reiteration
No. Cohesive devices Cohesive Items Frequency Percentage
01 Repetition Chair-chair,
Sat-sit, Love
potion-love potion,
Cleaner-cleaner,
Forgive-forgive,
Least-least
6 6%
02 Synonyms Sort-appearance,
Fervently-abroad
2 2%
03 Near Synonyms 3 3%
04 Superordinate 2 2%
Total 13 13%
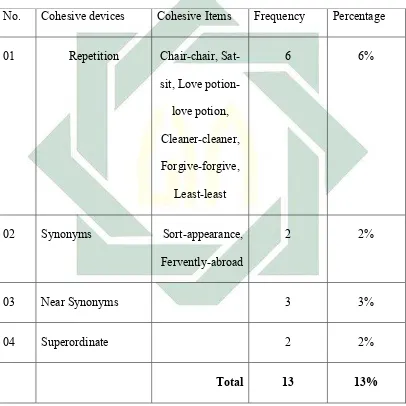
The writer found 6 word of Repetition, 2 Synonyms, 3 Near Synonyms, and 2 Superordinate.
49
A racking chair and an ordinary chair.
An old man sat in the rocking-chair, reading a newspaper. Alan,
without a word, handed him the card he had been given. “sit down,
Mr. Austen,”
How carefully she will look after you! She will never allow you to
be tired.
She will forgive you, in the end. She will be terribly hurt, of
course, but she will forgive you.
She would never divorce you. Oh, no! And, of course, she herself
will never give you the least, the very least.
1. Synonym
I want nothing of that sort. Probably it is appearance just as well
I am glad to hear that, he is sad because didn’t loss his pistols.
That will not happen, said Alan fervently. He is lazy to abroad it.
2. Near-synonym
Young people who need a love potion very seldom have five
thousand dollars. Otherwise they would need a love potion.
You need not worry. She would be patient with you.
As the glove-cleaner, or life-cleaner.
3. Super ordinate.
She will forgive you, in the end. She will be terribly hurt, of
course, but she will forgive you in the end.