www.elsevier.com / locate / bres
Short communication
1 21
Na –Ca
exchanger isoforms in rat neuronal preparations: different
changes in their expression during postnatal development
a a b b
Masaki Sakaue , Hiroaki Nakamura , Ikuyo Kaneko , Yasushi Kawasaki ,
a a a a
Naohisa Arakawa , Hitoshi Hashimoto , Yutaka Koyama , Akemichi Baba ,
b ,
*
Toshio Matsuda
a
Laboratory of Molecular Neuropharmacology, Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Osaka University, 1-6 Yamada-oka, Suita,
Osaka565-0871, Japan
b
Laboratory of Medicinal Pharmacology, Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Osaka University, 1-6 Yamada-oka, Suita, Osaka 565-0871,
Japan
Accepted 8 August 2000
Abstract
1 21
We examined the relative amounts of Na –Ca exchanger (NCX) isoform mRNAs in cultured neurons, astrocytes and developmental rat brain. NCX1 transcript was predominant in neurons and astrocytes, but NCX2 transcript was about four-fold higher than NCX1 or NCX3 transcript in adult rat cortex. NCX2 transcript in the cortex increased markedly during postnatal development, whereas NCX1 and
1 45 21
NCX3 transcripts decreased. Na -dependent Ca uptake in the cortical homogenate increased significantly during postnatal development. 2000 Elsevier Science B.V. All rights reserved.
Theme: Neurotransmitters, modulators, transporters and receptors
Topic: Uptake and transporters
1 21
Keywords: Na –Ca exchanger; Isoform; Postnatal development
1 21
The Na –Ca exchanger (NCX) has a role in regulat- highest in newborn rats and declines gradually during
21 21
ing intracellular Ca concentration ([Ca ] ) [8,14,19].i postnatal development [1–3]. The present study examined There are three NCX isoforms (NCX1–3) and several the predominant isoforms in cultured cells and brain tissue, splicing variants in brain, cultured rat cortical neurons, and postnatal changes in brain NCX isoforms.
astrocytes and oligodendrocytes [6,11,12,16,17,21]. North- Relatively pure cultures of astrocytes were prepared ern blot analysis showed that NCX2 expression was an from cerebral cortices of 1-day-old rats as previously order of magnitude higher than NCX1 or NCX3 expression reported [15,23,24]. The dissociated cortical neurons were in rat brain regions, except in the brainstem / spinal cord prepared from 17 to 19-day rat fetuses and seeded onto [25]. These observations suggest that each NCX isoform is culture plates [5]. After 48 h, the cells were treated with 10 expressed in cell-type- and brain-region-specific manner. mM Ara-C for 48 h, and cultured for 6–10 days. The cell However, there is little information on the distribution cultures consisted of more than 90% neurons, as de-ratio of the three NCX isoforms in brain or in specific cells termined by positive immunostaining with anti-microtu-such as neurons and astrocytes. Furthermore, it is not bule-associated protein-2 antibody. In developmental ex-known if brain NCX changes during postnatal develop- periments, male and female Wistar rats were decapitated at ment, although previous studies show that expression and 0, 3, 14, 21, 28 and 56 days of age. Procedures involving function of cardiac NCX, which consists of NCX1, is animals and their care were conducted according to Guiding Principles for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals approved by the Japanese Pharmacological
Socie-*Corresponding author. Tel.: 181-6-6879-8161; fax: 1
81-6-6879-ty. Total RNA was extracted from the cultured cells and
8159.
E-mail address: [email protected] (T. Matsuda). cerebral cortex [7]. Rat cerebral cortex was homogenized
in ten volumes of 0.32 M sucrose (adjusted to pH 7.4 with were as follows: NCX1 and NCX2, 948C for 1 min, 588C Tris–HCl), and the homogenate was used as crude mem- for 1 min, and 728C for 2 min for 28 cycles; NCX3, 948C branes. In some experiments, the microsomes were purified for 1 min, 588C for 1 min, and 728C for 2 min for 30 by a sucrose-density gradient procedure [22]. The crude cycles;b-actin, 948C for 1 min, 608C for 1 min, and 728C membranes and purified microsomes were resuspended in for 2 min for 23 cycles. The PCR products were separated 160 mM NaCl–20 mM Tris–HCl (pH 7.4) and stored at on 2% agarose gels containing Vistra Green (Amersham
45 21
2808C. Ca (5–50 mCi / mg, Amersham, Tokyo, Japan) Pharmacia Biotech) and the signal intensities were calcu-uptake was determined as previously reported [13,18]. The lated with Image Quant software (Molecular Probes). The protein concentration was determined using BCA assay ratio of native PCR product and standard PCR product was reagents (Pierce, Rockford, IL, USA). For construction of calculated as described previously [4].
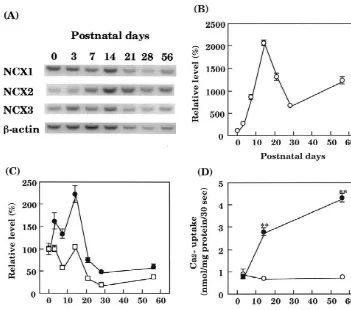
RNA competitors, rat cDNA fragments of NCX1 [11], Fig. 1 shows that the mRNAs of three NCX isoforms NCX2 [12] and NCX3 [17] were amplified by PCR from can be quantitatively determined by competitive RT-PCR. rat whole brain cDNA using primers, and cloned into Each RNA competitors inhibited RT-PCR of endogenous pT7Blue Vector (Novagen). The amplification primers are mRNA in a dose-dependent manner. Quantities of NCX as follows: NCX1 sense 2570–2593, 59-TTCATTGAAG- isoform mRNAs are summarized in Table 1. NCX1 CGATCACCGTCAGC-39; NCX1 antisense 3223–3246, mRNA was predominant in cultured neurons and as-59-AAGCCTTTTATGTGGCAGTAGGCC-39; NCX2 trocytes (neurons, 60% of total NCX; astrocytes, 74%). sense 2038–2061, 59-ACAAACCTGGCCTTGGTGATT- The distribution ratio of NCX3 transcript was similar GGG-39, NCX2 antisense 2741–2764, 59-AGA- between neurons and astrocytes (about 20% of total NCX), AGCCCCGAATGTGGCAATAAG-39; NCX3 sense but that of NCX2 transcript was much higher in neurons 2792–2815, 59-AGAGATGGGAAAGCCAGTATTG- than in astrocytes (neurons, 15% of total NCX; astrocytes, GG-39, NCX3 antisense 3614–3637, 59-GGAGGT- 6%). In contrast to cultured cells, NCX2 mRNA was CTTGTTCTGGTGGTTCAG-39. The BamHI / XbaI frag- predominant in adult brain tissue (65% of total NCX). To ments were then subcloned into pBluescript II KS(1) examine the relative change in mRNA abundance of NCX (Stratagene). The NCX1, NCX2 and NCX3 cDNA clones isoforms, we used a non-competitive RT-PCR method that contained one restriction site of NheI, MluI and NcoI, was simpler than the competitive RT-PCR method (Fig. respectively. The plasmids were digested with the en- 2A–C). NCX2 mRNA markedly increased from postnatal zymes, both ends were deleted using a Kilo-Sequence day 7, peaked at postnatal day 14 and, thereafter, decreased deletion kit (Takara Shuzo Co., Shiga, Japan), and the to some degree. In contrast, NCX1 and NCX3 mRNAs plasmids were religated. To synthesize cRNA competitors, decreased after postnatal day 21, although NCX3 mRNA the plasmids were digested with XbaI and transcribed increased a little at postnatal day 14. Although house-using T3 RNA polymerase (Stratagene). Then, 300 U of keeping genes such asb-actin and glyceraldehyde-3-phos-DNase I were added and the reaction was allowed to phate dehydrogenase were reported to change during proceed for 60 min at 378C. The RNA competitors were postnatal development [10,20], we determined b-actin extracted with phenol / chloroform, precipitated with etha- mRNA. b-Actin mRNA decreased during postnatal de-nol and dissolved in water. The concentrations of the velopment, in agreement with a previous report [10]. We competitors were calculated from the absorbance at 260 also determined brain NCX activity of postnatal rats. In nm. RT-PCR was carried out as previously reported [8], this experiment, the homogenate was used as a membrane except that the reaction time of the reverse transcription vesicle preparation to eliminate the possibility that the was 90 min and Taq RNA polymerase (GIBCO BRL) was difference in the activity between pups and adults might be used for PCR. The primers are as follows [11,12,17]: due to that in the degree of purification of the preparations.
1 45 21
NCX1 sense 2802–2825, 59-TTGGCTGCAC- Na -dependent Ca uptake, i.e., NCX activity,
in-1
CATTGGTCTGAAAG-39; NCX1 antisense 3166–3189, creased during postnatal development, whereas Na
-in-45 21
59-AGGAGCACAAACAGGGAAGATGTG-39; NCX2 dependent Ca uptake did not change (Fig. 2D). A sense 2261–2284, 59-TCTGCATCCTGGTCATT- similar result was obtained in the microsomes purified
1 45 21
GGTCTGC-39; NCX2 antisense 2575–2598, 59- from the cerebral cortex: Na -dependent Ca uptake GGCGAAGACGGTGAACAGTGTGAC-39; NCX3 sense (nmol / mg protein / 30 s, mean6S.E.M. of 12–19 determi-2916–2936, 59-ACCCATTCCTGGAGGGACCAATTC- nations) at postnatal days 3 and 14 was 6.0560.59 and 39; NCX3 antisense 3207–3230, 59-GGTGC- 9.2060.53, respectively (P,0.001 by Student’s t-test), and
1 45 21
CGAATGCCACAAAAACAAC-39. For competitive RT- Na -independent Ca uptake at postnatal days 3 and 14 PCR, known concentrations of RNA competitors were was 0.8560.05 and 1.0460.06, respectively.
Fig. 1. Quantification of three NCX isoforms using competitive RT-PCR in cultured rat astrocytes. (A) The signal intensities of NCX isoform fragments were increased as the competitors decreased. (B) A typical measurement of NCX isoforms in cultured rat astrocytes with competitive RT-PCR.
isoforms were much higher in neurons than in astrocytes, astrocytes, whereas NCX2 is predominant in adult brain. in agreement with the results of a previous immuno- The preferential distribution of NCX2 in brain tissue is in cytochemical study using anti-NCX antibody [9], and the agreement with the results found in a recent study [25]. distribution ratio of NCX2 transcript was much higher in The difference in the predominant NCX isoform between neurons than in astrocytes. This observation suggests that cultured cells and brain may be due to postnatal changes in NCX isoforms have cell-specific functions in the regula- NCX isoforms, since cultured cells are prepared from
21
tion of [Ca ] . It should be noted that cultured cells andi embryonic or neonatal brains. The present study, using adult brain tissue differed in the distribution ratio of NCX non-competitive RT-PCR, shows that NCX2, but not isoforms. NCX1 is predominant in cultured neurons and NCX1 and NCX3, transcript in the brain increases
marked-1
ly during postnatal development. We also found that Na
-45 21
dependent Ca uptake in the homogenate and purified
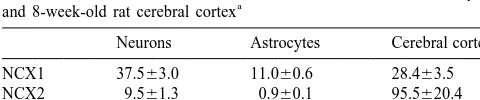
Table 1
microsomes increased during postnatal development.
How-Relative amounts of NCX isoform mRNAs in cultured neurons, astrocytes 45 21
a ever, the Ca uptake activity did not always reflect
and 8-week-old rat cerebral cortex
mRNA abundance of NCX isoforms: NCX2 transcript in
Neurons Astrocytes Cerebral cortex 45 21
the cerebral cortex peaked at day 14, whereas the Ca
NCX1 37.563.0 11.060.6 28.463.5 uptake reached a plateau. The exact reason for the apparent
NCX2 9.561.3 0.960.1 95.5620.4 45 21
discrepancy is not known, although Ca uptake is
NCX3 15.161.1 2.960.4 23.162.1
driven by three NCX isoforms. The finding that NCX1
a 5
Data (310 copies /mg total RNA) are expressed as the mean6S.E.M. transcript decreased after postnatal development is similar for three to five experiments. Total RNA was extracted from cultured
to the previous observation in cardiac NCX [1]. Although
neurons, cultured astrocytes and cerebral cortex of male rats
(8-weeks-the postnatal change in cardiac NCX may be regulated by
old), and each transcript of NCX isoforms was determined by a
post-45 21
Fig. 2. Postnatal changes in NCX isoform mRNAs and Ca uptake of rat cerebral cortex. (A) A typical demonstration of agarose gel electrophoresis of mRNAs of postnatal NCX isoforms andb-actin. (B) Densitometric analysis of mRNA levels of NCX2 of postnatal rats. Results are expressed as the mean6S.E.M. of five determinations. (C) Densitometric analysis of mRNA levels of NCX1 (h) and NCX3 (d) of postnatal rats. Results are expressed as
45 21 1 45 21
the mean6S.E.M. of five determinations. (D) Ca uptake in the cortical homogenate of postnatal rats. Na -dependent Ca uptake (d) and
1 45 21 1
Na -independent Ca uptake (s) were determined by incubating the Na -loaded crude membranes in choline chloride and NaCl buffer, respectively. Results are expressed as the mean6S.E.M. of 12–19 determinations.
21
Ca –ATPase in developing rat heart, Am. J. Physiol. 275 (1998)
natal development of brain NCX isoforms is not known.
H264–H273.
Further studies are required to clarify the regulation
[4] G. Gilliland, S. Perrin, K. Blanchard, H.F. Bunn, Analysis of
mechanism of postnatal development of NCX isoforms in cytokine mRNA and DNA: detection and quantitation by competi-the brain. tive polymerase chain reaction, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87
(1990) 2725–2729.
[5] H. Hatanaka, H. Tsukii, I. Nihonmatsu, Developmental change in the nerve growth factor action from induction of choline acetyl-Acknowledgements
transferase to promotion of cell survival in cultured basal forebrain cholinergic neurons from postnatal rats, Dev. Brain Res. 39 (1984)
This work was supported by grants form the Ministry of 85–95.
Education, Science, Sports, and Culture of Japan and [6] S. He, A. Ruknudin, L.L. Bambrick, W.J. Lederer, D.H. Schulze,
1 21
Isoform-specific regulation of the Na / Ca exchanger in rat
Taisho Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.
astrocytes and neurons by PKA, J. Neurosci. 18 (1998) 4833–4841. [7] R. Hosoi, T. Matsuda, S. Asano, H. Nakamura, H. Hashimoto, K. Takuma, A. Baba, Isoform-specific up-regulation by ouabain of
1 1
References Na , K –ATPase in cultured rat astrocytes, J. Neurochem. 69
(1997) 2189–2196.
1 21 [8] L.V. Hryshko, K.D. Philipson, Sodium–calcium exchange: recent
[1] M. Artman, H. Ichikawa, M. Avkiran, W.A. Coetzee, Na / Ca
advances, Basic Res. Cardiol. 92 (suppl. 1) (1997) 45–51. exchange current density in cardiac myocytes from rabbits and
[9] M. Juhaszova, H. Shimizu, M.L. Borin, R.K. Yip, E.M. Santiago, guinea pigs during postnatal development, Am. J. Physiol. 268
1 21
G.E. Lindenmayer, M.P. Blaustein, Localization of the Na –Ca (1995) H1714–H1722.
1 21
exchanger in vascular smooth muscle, and in neurons and astrocytes, [2] S.R. Boerth, M. Artman, Thyroid hormone regulates Na –Ca
Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 779 (1996) 318–335. exchanger expression during postnatal maturation, Cardiovasc. Res.
[10] F. Lazarini, J. Deslys, D. Dormont, Regulation of the glial fibrillary 31 (1996) E145–E152.
acid protein, b actin and prion protein mRNAs during brain [3] J. Cernohorsky, F. Kolar, V. Pelouch, B. Korecky, R. Vetter, Thyroid
1 21
[11] S.L. Lee, A.S. Yu, J. Lytton, Tissue specific expression of Na–Ca [19] K.D. Philipson, D.A. Nicoll, Sodium–calcium exchange, Curr. Opin. exchanger isoforms, J. Biol. Chem. 269 (1994) 14849–14852. Cell Biol 4 (1992) 678–683.
[12] Z. Li, S. Matsuoka, L.V. Hryshko, D.A. Nicoll, M.M. Bersohn, E.P. [20] G. Prime, G. Horn, B. Sutor, Time-related changes in connexin Burke, R.P. Lifton, K.D. Philipson, Cloning of the NCX2 isoform of mRNA abundance in the rat neocortex during postnatal
develop-1 21
the plasma membrane Na –Ca exchanger, J. Biol. Chem. 269 ment, Dev. Brain Res. 119 (2000) 111–125.
(1994) 17434–17439. [21] B.D. Quednau, D.A. Nicoll, K.D. Philipson, Tissue specificity and
1 21 1 21
[13] T. Matsuda, T. Gemba, A. Baba, H. Iwata, Decrease of Na –Ca alternative splicing of the Na / Ca exchanger isoforms NCX1, exchange activity by ascorbate in rat brain membrane vesicles, Brain NCX2, and NCX3 in rat, Am. J. Physiol. 272 (1997) C1250–C1261. Res. 532 (1990) 13–18. [22] G.D. Schellenberg, P.D. Swanson, Sodium-dependent and
calcium-1 21
[14] T. Matsuda, K. Takuma, A. Baba, Na –Ca exchanger: physiology dependent calcium transport by rat brain microsomes, Biochim. and pharmacology, Jpn. J. Pharmacol. 74 (1997) 1–20. Biophys. Acta 648 (1981) 13–27.
[15] T. Matsuda, K. Takuma, S. Asano, Y. Kishida, H. Nakamura, K. [23] K. Takuma, T. Matsuda, H. Hashimoto, S. Asano, A. Baba, Cultured
21 1 21
Mori, S. Maeda, A. Baba, Involvement of calcineurin in Ca rat astrocytes possess Na –Ca exchanger, Glia 12 (1994) 336– paradox-like injury of cultured rat astrocytes, J. Neurochem. 70 342.
(1998) 2004–2011. [24] K. Takuma, T. Matsuda, H. Hashimoto, J. Kitanaka, S. Asano, Y.
1 21
[16] D.A. Nicoll, S. Longoni, K.D. Philipson, Molecular cloning and Kishida, A. Baba, Role of Na –Ca exchanger in agonist-induced
1 21 21
functional expression of the cardiac sarcolemmal Na –Ca ex- Ca signaling in cultured rat astrocytes, J. Neurochem. 67 (1996) changer, Science 250 (1990) 562–565. 1840–1845.
[17] D.A. Nicoll, B.D. Quednau, Z. Qui, Y.R. Xia, A.J. Lusis, K.D. [25] L. Yu, R.A. Colvin, Regional differences in expression of transcripts
1 21 1 21
Philipson, Cloning of a third mammalian Na –Ca exchanger: for Na / Ca exchanger isoforms in rat brain, Mol. Brain Res. 50 NCX3, J. Biol. Chem. 271 (1996) 24914–24921. (1997) 285–292.
[18] V. Panagia, N. Makino, P.K. Ganguly, N.S. Dhalla, Inhibition of
1 21