Temperature Control Personal Computer Using
Liquid Cooling System Based PID Control
Nur Hidayat
Engineering Physics, School of Electrical Engineering
Telkom University Bandung, Indonesia
Reza Fauzi Iskandar*
Engineering Physics, School of Electrical Engineering
Telkom University Bandung, Indonesia [email protected]
Mamat Rokhmat
Engineering Physics, School of Electrical Engineering
Telkom University Bandung, Indonesia [email protected]
Abstract— Central Processing Unit (CPU) is an important
part of a system, where most of the data processing is done there. Therefore, CPU temperature tends to be higher than other components. High CPU temperature can result in degraded performance due to malfunction or damage the CPU permanently. In this study, the control proportional-integral-derivative (PID) is selected to control the CPU temperature. This study aimed to obtain information on the effect of using a liquid cooling system fans to the CPU temperature. There are two stages, testing the effect of the use of liquid cooling system fans and the effect on the temperature control system. The first test results obtained the highest CPU temperature is at 336 K before experiencing shutdown during the test without a fan, while the highest CPU temperature was 316 K when using the fan. The second test results obtained by the average error between the CPU and the setpoint temperature is 2 degree with rise time (Tr)
96 s and settling time (Ts) 424 s.
Keywords—pid; personal computer; temperature; control;
liquid cooling system; thermistor;
I. INTRODUCTION
CPU development is rapidly increasing, evidenced by the manufacturers who created the microprocessor CPU with manufacturing small as possible. The smaller size of the microprocessor, the more the number of transistors on a chip [8]. This will result in the CPU generates high temperatures. Currently there are two types of CPU cooling systems, liquid cooling systems and air. Liquid cooling system consists of a water block, water pump, radiator, reservoir, coolant, and fans [1-3]. The liquid cooling system is still the best innovation for the cooling system of a computer processor in terms of performance [4]. For the measurement of CPU temperature in real-time, use NTC thermistor sensor. Thermistor is a temperature indicator that has a resistance value depends on the height and the low temperature is detected [7]. The output of the thermistor should be changed to be the value of the temperature.
CPU produces undesirable high temperature in the computer system, so that the temperature of the CPU must be controlled to avoid overheating which can lead to defective function or permanent damage [4]. CPU used in this research is the AMD FX-8350. FX-8350 is one of the products of the largest microprocessor manufacturers are AMD. This CPU has eight cores with a frequency of 4.0GHz (default) and 4.2GHz
(Turbo Boost). This CPU was created in 2012 with 32 nm manufacturing technology [5].
In order to optimize the performance of the liquid cooling system, in this study will be conducted by the PID control method of Ziegler Nichols [6].
II. METODOLOGY
In the liquid cooling system, there are several heat transfer processes, such as conduction and convection. heat transfer process that occurs in the heat distribution system of equations based on Eq. 1.
)
(
hAc T T
dx dT kA dt dT mC
Q p cond conv
(1) where Q, m, Acond, Aconv, and T∞ is the flow of heat from the CPU, the mass of Ni blocks, the surface area of the fin normal to the heat flow, the temperature of fin surface, and the temperature of the environment, respectively. The process of heat absorption, conduction, and convection is shown in Eq. 1.
In industrial, PID control is also often used for controlling [6]. In this study, using PID control to regulate the radiator fan rotation in order for the forced convection occurs between the radiator fin with the environment. Regulation of fan rotation is set using the equation of Eq. 2.
) ( )
( ) ( ) (
0
set d
t set i
set
p T T
dt d K dt T T K T T K t
k
(2) Parameter input is proportional control (Kp), integral (Ki), derivative (Kd), and the temperature setpoint (Tset).
III. EXPERIMENTAL RESULT
A. Experimental Design
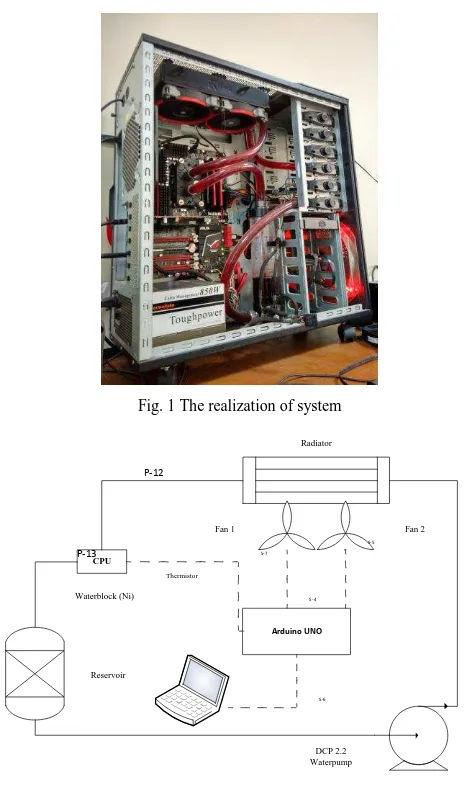
The general process and setup of this study is shown in Fig. 1 and 2. CPU temperature is measured using a NTC thermistor sensor that is connected to the Arduino UNO during testing. Before the system is turned on, the temperature of the system should be equal to 298 K. The system tested during 2200 second for each set point by using the Intel Burning Test (IBT) software. The test is performed 4 times by using a set point different. In this study, Arduino UNO is used as data acquisition system.
*Corresponding author
2015 International Conference on Automation, Cognitive Science, Optics, Micro Electro-Mechanical System, and Information Technology (ICACOMIT), Bandung, Indonesia, October 29–30, 2015
Fig. 1 The realization of system
Waterblock (Ni)
DCP 2.2 Waterpump Reservoir
Radiator
Fan 2 Fan 1
Arduino UNO Thermistor
S-4 S-5
S-6 CPU
P-12
P-13 S-7
Fig. 2 Schematic configuration of system
Based on Fig. 2, the flow of the liquid cooling system is a closed-loop, so that the heat generated by the CPU is delivered by waterblock connected with NTC Thermistor to be absorbed by the coolant. The cooling fluid is moved toward the reservoir using water pump, after it goes into the radiator where there is forced convection caused by the use of a fan. coolant flowing into the CPU has a lower temperature.
Temperature sensors are used for this study is NTC Thermistor temperature sensor (Negative temperature Coefficient) that temperature value is inversely proportional to the resistance. The results of the characteristic test can be seen in Fig. 3. This test is used to ensure that the sensor is not defective.
23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31
6,5 7,0 7,5 8,0 8,5
R
e
s
is
ta
n
s
i
(O
h
m
)
Temperatur (Celcius)
Resistansi
Fig. 3 Thermistor NTC 10K characteristic
In this study, the effect of the use of liquid cooling system fans. Results of the testing system can be seen in Fig. 4 which shows that the system still requires a fan to exhaust heat generated CPU. The CPU is shut down when testing the system without using a fan
0 500 1000 1500 2000
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70
T
e
mp
e
ra
tu
r
(C
e
lc
iu
s
)
Waktu (detik)
Fan OFF Fan ON
Fig. 4 System test characteristic
Based on the reaction curve of Fig. 4, the variable L (dead time) and T (delay time) can be obtained. These variables are useful to get the PID constants with Ziegler-Nichols method. The use of these variables can be seen in Table 1.
Table 1. Ziegler-Nichols Recipe - first method [6]
Tipe Kp Ti Td
P T/L ~ 0
PI 0,9 * T/L L / 0,3 0
PID 1,2 * T/L 2L 0,5L
B. Result and Discussion
0 500 1000 1500 2000
0 500 1000 1500 2000
-14
0 500 1000 1500 2000
600
0 500 1000 1500 2000
-600
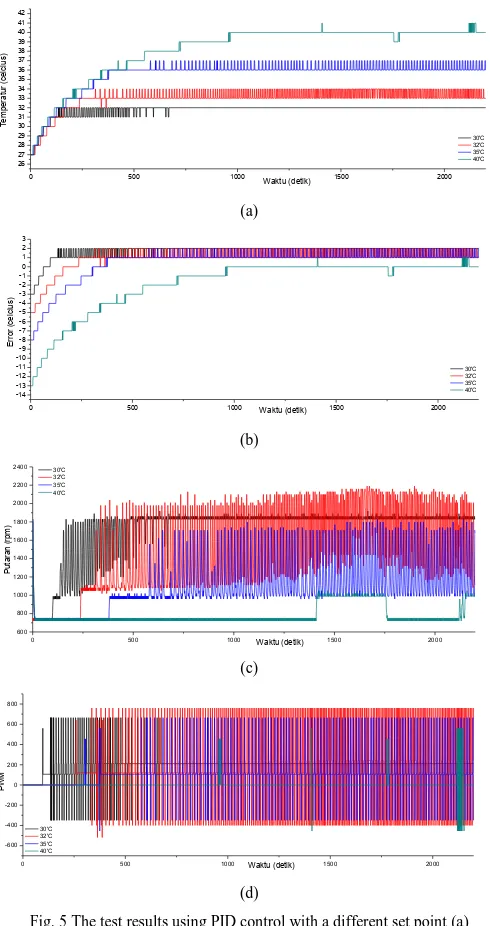
Fig. 5 The test results using PID control with a different set point (a) temperature (b) error (c) rotary fan (d) PWM signal
Based on Fig. 5, the average error between the CPU and the setpoint temperature is 2 degree with rise time (Tr) 96 s and settling time (Ts) 424 s.
When the control system is tested with setpoint 313 K, there is no system error. It is because the forced convection processes running optimally. However, the control system generates an error of 2 degrees when testing using other setpoint.
IV. CONCLUSION
Characterization and implementation of NTC thermistor sensor has been done on CPU to convert CPU temperature into resistance and then converted into temperature value by Arduino UNO. Based on Fig. 4, the system still requires a fan to exhaust heat generated CPU. Based on Fig. 5, with the implementation of PID control on the system, the temperature of the CPU can be reduced, with the average error between the CPU and the setpoint temperature is 2 degree with rise time (Tr) 96 s and settling time (Ts) 424 s. Therefore, the CPU life time can be extended with the implementation of PID control on the system.
Acknowledgment
This project is financially and hardware support by D.Comp Technology.
References
[1] Kang, S., Miller, D., & Cennamo, J., “Closed Loop Liquid Cooling For
High Performance Computer Systems” , Canada , ASME , (2007).
[2] Sharma, R.P., “Experimental Analysis Of Liquid Cooling System For
Desktop Computer”, India, IJMET, (2013).
[3] Ogawara, T. & Ikeda, T., “High Cooling Performance / Low Noise
Measures : High Performance Liquid Cooling System”, SANYO
DENKI Technical Report, No.18 (2004-11).
[4] Carr, J.D & Sundin, W.D., “Minimizing CPU Overheating with Liquid
Immersion Cooling”, www.dsiventures.com
[5] Hagedoorn, H. “AMD FX 8350 Processor Review”, (2012). http://www.guru3d.com/articles-pages/amd-fx-8350-processor-review,1.html
[6] Copeland, B.R., “The Design of PID Controller using Ziegler Nichols
Tuning”, (2008).
[7] Recktenwald, G., “Temperature Measurement with a Thermistor and a
Arduino”, (2013).
[8]