isprs archives XLI B4 71 2016
Teks penuh
Gambar
Garis besar
Dokumen terkait
There are four key steps: Partitioning point clouds into cross sections according to the GPS time of points and vehicle trajectory; Pre-processing point clouds to denoise
The performance of this method is dependent on the positioning results. Floor changes will fail to be detected if there is a large deviation in positioning. Moreover, this method
Hence we would like to suggest a model where an ontology of indoor space is defined and using this understanding (which is based on geo- metric as well as functional properties of
New obstacle point is detected on the path and it is added with the corresponding buffer to the network (see Figure 4.b). New path avoiding the excluded area is calculated
Another is the medium method (Med), which is selected a medium height value i.e. If it shows a masked value, same value is kept in AW3D30. This is likely keeping the terrain
The negative elevation bias (negative mean error) exhibited by GDEM v3 in open land cover areas is important because it is indicative of the overall performance of
NASADEM is a near-global elevation model that is being produced primarily by completely reprocessing the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) radar data and
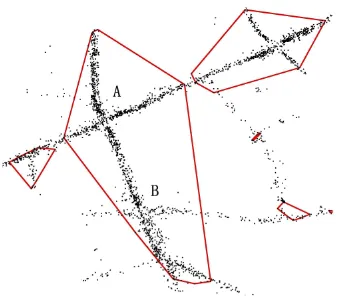
In this study, we analyze urban traffic flow using taxi trajectory data to understand the characteristics of traffic flow from the network centrality perspective