Atherosclerosis 153 (2000) 255 – 256
Case study
Increased lipid peroxidation in a patient with CK-elevation and
muscle pain during statin therapy
Helmut Sinzinger
a,b,*, Graziana Lupattelli
c, Fahdi Chehne
baInstitute for Diagnosis and Treatment of Lipid Disorders and Atherosclerosis(ATHOS),Nadlergasse1,A-1090Vienna,Austria bDepartment of Nuclear Medicine,Uni6ersity of Vienna,Vienna,Austria
cInstitute of Internal Medicine,Angiology and Atherosclerosis,Uni6ersity of Perugia,Perugia,Italy
Received 29 November 1999; accepted 13 January 2000
www.elsevier.com/locate/atherosclerosis
Muscle pains, CK-elevation and, rarely, rhabdomyol-ysis may occur during HMG-Co-enzyme-A-reductase inhibitor therapy. The underlying pathogenetic mecha-nisms are not yet identified. Recently, we reported a patient who showed symptoms of muscle pains during statin therapy which improved when he received vita-min E [1]. After submitting that manuscript, Holt et al. described an increase in lipid peroxidation in patients with rhabdomyolysis [2] using 8-epi-prostaglandin (PG)F2a as a determinant for in-vivo oxidation injury [3,4].
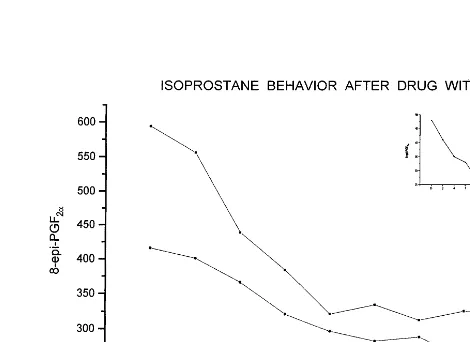
Recently, in our clinical practice we identified a patient suffering from severe familial hypercholes-terolemia (male; GH, 54 a; 184 cm/180 kg) without any other risk factor who experienced severe muscle pain on lovastatin 40 mg/day with CK-elevation (329 U/l). We proceeded to measure the isoprostane 8-epi-PGF2a in plasma, serum and urine as a measure of in-vivo oxida-tion injury at the time of onset of pain, after with-drawal of the drug (Fig. 1), and throughout the following 3 months. 8-epi-PGF2ain plasma, serum and urine was increased strikingly. Withdrawing the drug resulted in a stepwise decrease in the respective values, almost normalizing within 2, and completely normaliz-ing within 4 weeks. CK rapidly normalized as well. Changing to atorvastatin had no adverse effect on 8-epi-PGF2a, which has continued to remain normal until now (\6 months).
Our findings show for the first time that during the symptomatic period of muscle pains with CK-elevation during statin therapy, 8-epi-PGF2ais severely increased
indicating a significant in-vivo oxidation injury. As lipid lowering drugs are known to improve 8-epi-PGF2a either directly or indirectly via lipid lowering [5], the effect described cannot be due to the drug itself. The extent of the increase was clearly associated with the extent of symptoms seen in the patient. There is no information available yet as to whether the individual antioxidant status is relevant for the development of muscular side effects [6]. These findings, however, ex-plain the benefit of vitamin E-therapy seen in one patient with similar side effects [1]. The role of antioxi-dant status and antioxiantioxi-dants thus needs to be assessed in detail in patients suffering from various side effects under statin treatment.
Fig. 1. 8-Epi-PGF2adrops immediately after stopping statin therapy
in urine, plasma and serum. * Corresponding author. Tel.: +43-1-4058440; fax: +
43-1-4081366.
H.Sinzinger et al./Atherosclerosis153 (2000) 255 – 256 256
References
[1] Sinzinger H. Does vitamin E beneficially affect muscle pains during HMG-Co-enzyme-A-reductase inhibitors without CK-ele-vation? Atherosclerosis 1999 (in press).
[2] Holt S, Reeder B, Wilson M, Harvey S, Morrow JD, Roberts LJ II, Moore K. Increased lipid peroxidation in patients with rhab-domyolysis. Lancet 1999;353:358 – 9.
[3] Morrow JD, Minton TA, Badr KF, et al. Evidence that the 172-isoprostane, 8-epi-prostaglandin F2a is formed in-vivo.
Biochim Biophys Acta 1994;1210:244 – 8.
[4] Morrow JD, Robert U II. The isoprostanes: current knowledge and direction of future research. Biochem Pharmacol 1996, 51: 1 – 9.
[5] Oguogho A, Mehrabi M, Sinzinger H. Increased plasma, serum and urinary 8-epi-prostaglandin F2( in heterozygous hypercholes-terolemia. Wr klin Wschr 1999;111:1133 – 8.
[6] Sinzinger H. Two different types of exercise-induced muscle pain without myopathy and CK-elevation during HMG-Co-enzyme-A-reductase inhibitor treatment. Atherosclerosis 1999;143:459 – 60.