Directory UMM :Data Elmu:jurnal:A:Agricultural & Forest Meterology:Vol106.Issue3.2001:
Teks penuh
Gambar
Dokumen terkait
When PE Estimates of variance components and heritability for daily milk effects are modeled by an RR function, covariances yields on selected test days with orthogonal
flavour Boggio et al., 1985. Sensory assessment showed no clear differences between groups except that smoked fillet of fish fed the low-fat diet has less fat and judged as more
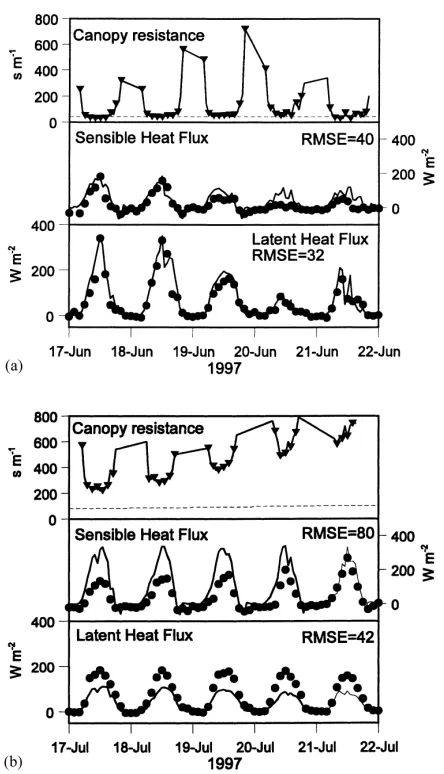
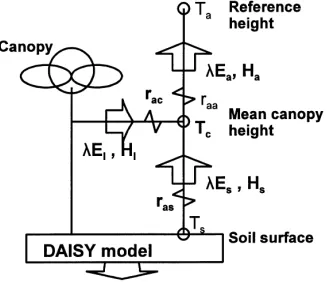
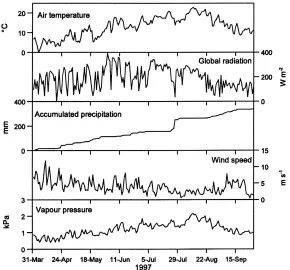
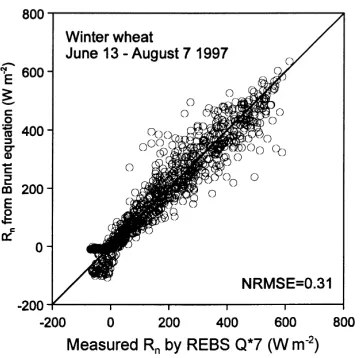
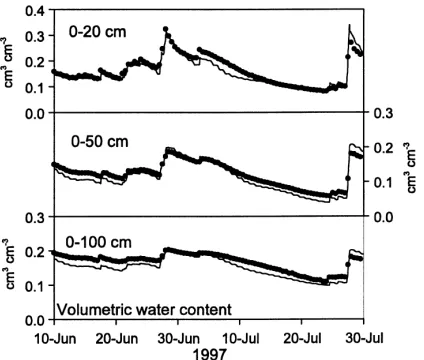
In this study, the hysteresis curves observed for tran- spiration rate and canopy conductance versus vapour pressure deficit and radiation were characterised under mist and
The agreement includes the following: (i) the upward-tilting “ramps” of higher water vapor content over the canopy identified in the LIDAR im- ages are captured by the model
Earlier experiments over dense, tall, and short canopies demonstrated that the surface renewal method works, but requires a correction for uneven heating (e.g. For sparse canopies,
Sources and sinks of heat in the canopy of a dense corn crop (LAI ∼ 5) were inferred through an inverse Lagrangian dispersion analysis. Input data were the profiles of air
A statistical interpolation method is proposed which allows calculation of the leaf area index LAI(t), the downward cumulative leaf area index L(z, t) and the canopy leaf area
Using a helicopter-mounted portable spectroradiometer and continuous eddy covariance data we were able to evaluate the photochemical reflectance index (PRI) as an indicator of