Integration
• The Indefinite Integral
• The Definite Integral
• The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
• Application of Integration : Area between two
curves
• Definition : A function F(x) is called an antiderivative
of a function f(x) if the derivative of F(x) is f(X) or F
‘(x) = f(x)
• Examples :
1. F(x) = x
2+ 3 f(x) = 2x
2. F(x) = x
2– 10 f(x) = 2x
3. F(x) = x
2+ 15 f(x) = 2x
• If F ‘(x) = f(x) then the functions of the form F(x) + C
are antiderivative of f(x)
• The process for finding antiderivative is called
antidifferentiation
or
integration
.
• Notation :
The Indefinite Integral
Integration Formula
etc
....
....
C
x
sin
dx
x
cos
x
cos
x
sin
dx
d
.
3
2
1
...
r
x
dx
d
.
b
C
x
dx
x
dx
d
.
a
r
1
1
1
1
1
1
r
C
r
x
dx
x
r
r
Problems
dx
x
)
dx
x
)
dx
x
)
dx
x
sin
x
cos
)
dx
x
cos
x
sin
)
3
3 2
2
2
1
5
4
3
2
1
dx
x
x
)
dx
x
x
)
dx
)
dx
x
cos
x
sin
)
dx
x
cos
x
tan
x
sec
)
3
2
3 2
3
10
2
9
8
2
7
6
The Properties of Indefinite Integral
cf
(
x
)
dx
c
f
(
x
)
dx
)
1
f
(
x
)
g
(
x
)
dx
f
(
x
)
dx
g
(
x
)
dx
)
2
dx
x
x
x
sin
x
.
dx
x
x
.
dx
x
x
.
:
Examples
2
2
2
2
3
1
2
1
1
• Let y = (fog)(x). The derivative of y with respect
to x is y ‘ = (fog)’(x) = f ‘(g(x)) g’(x) [ The Chain
rule]
• If u = g(x) then the formula of integration is
Integration by Substitution
g
(
x
)
C
F
C
)
u
(
F
du
)
u
(
f
dx
dx
du
)
u
(
f
dx
'
u
)
u
(
f
Problems
dx
x
sin
x
cos
)
dx
x
cos
x
sin
)
dx
x
x
x
)
dx
x
x
cos
)
dx
x
x
)
2
2
2
2
2
5
4
1
2
1
3
1
2
1
2
1
dx
x
sec
x
)
dx
x
sin
)
dx
x
x
)
dx
x
cos
x
sin
)
dx
x
)
x
3
2
2
2
1
3
2
3
5
10
9
1
8
2
5
2
7
2
1
6
• How to find the area of a region D bounded
below by the x-axis, on the sides by the lines x = a
and x = b , and above by a curve y = f(x), where
f(x) is continuous on [a,b] and f(x) ≥ 0 for all x in
(a,b)
• D = { (x,y) | a ≤ x ≤ b, 0 ≤ y ≤ f(x) }
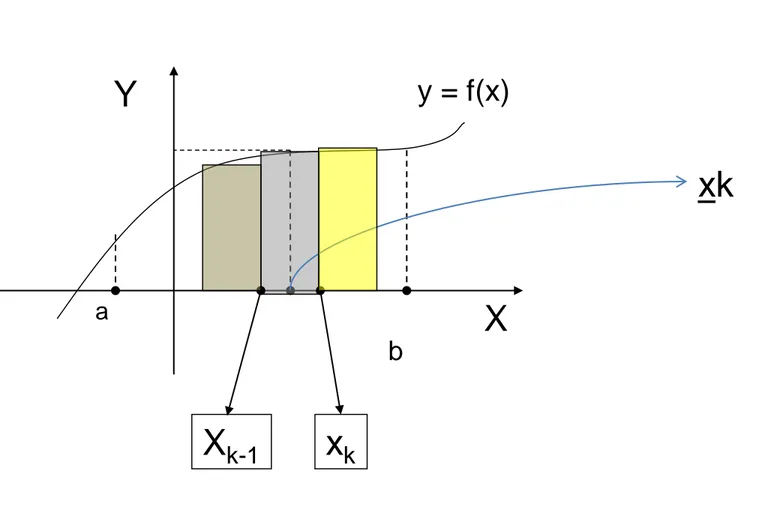
1. Divide [a,b] into n subintervals by choosing points x1,
x2, …,xn such that a < x1 < x2 < …< xn < b. These
points are said to form a partition of [a,b]. Let
x1,
x2, …,
xn are the length of the partition.
2. Choose the any point x1,x2,…,xn in subinterval and
we have a
Riemann sum
:
f(x1)
x1 + f(x2)
x2 + … + f(xn)
xn =
3. Increase n ( n
) in such a way the length of the
partition approaches zero (
xk 0 ) and form the
limit
Steps : The Definite Integral
n
k
xk
k
x
f
1
n
k
n
n
k
xk
lim
0
1
f
x
k
xk
lim
1
f
x
k
xk
Illustration : The Definite Integral
y = f(x)
X
Y
b ax
kX
k-1xk
• If a function f(x) is defined on [a,b], then the
Definite
Integral
of f(x) from a to b is defined to be (provided the
limit exits)
• If the limit exits then the function f(x) is said
integrable
on [a,b]
• The values a and b are called respectively
lower
and
upper limits of integration
and f(x) is called the
Integrand
.
Definition : The Definite Integral
n
k
n
n
k
xk
b
a
xk
k
x
f
lim
xk
k
x
f
lim
dx
)
x
(
f
1
1
0
• If f(x) is continuous on [a,b] and F(x) is
antiderivative of f(x) on [a,b] then
The First Fundamental Theorem
)
a
(
F
)
b
(
F
a
b
)
x
(
F
dx
)
x
(
f
b
a
20
2
1
2
1
dx
x
cos
)
(
dx
x
)
(
:
Examples
The Properties of Definite Integral
) b ( g ) a ( g b a b c c a b a a b b a a a b a b a b adu
)
u
(
f
dx
)
x
(
'
g
)
x
(
fog
)
(
dx
)
x
(
f
dx
)
x
(
f
dx
)
x
(
f
)
(
dx
)
x
(
f
dx
)
x
(
f
)
(
dx
)
x
(
f
)
(
dx
)
x
(
g
q
dx
)
x
(
f
p
dx
)
x
(
qg
)
x
(
f
p
)
(
5
4
3
0
2
1
Problems
2 0 2 4 1 9 4 3 1 23
2
5
2
4
5
3
3
2
2
1
1
2 6 2 3dx
x
)
(
dt
t
t
sin
)
(
dx
x
x
x
)
(
dx
x
x
)
(
dx
x
)
(
4 4 0 0 2 3 1 2 2 1 2 2 12
3
7
2
10
9
7
4
2
8
8
7
2
6
dt
t
sin
t
cos
)
(
dt
t
sec
t
tan
)
(
dx
x
x
x
)
(
dx
x
x
)
(
dx
x
)
(
• Let f(x) is continuous on open interval I and a
I.
If G(x) is defined by
Then G’(x) = f(x) at each point x in interval I
The Second Fundamental Theorem
x
a
dt
)
t
(
f
)
x
(
G
v
(
x
)
v
'
(
x
)
f
u
(
x
)
u
'
(
x
)
f
)
x
(
'
G
dt
)
t
(
f
)
x
(
G
)
x
(
v
)
x
(
u
Problems
)
x
(
"
F
and
)
x
(
'
F
dt
t
sin
)
x
(
F
)
(
g
sin
increa
only
is
)
x
(
F
which
erval
int
open
find
)
b
(
value
imum
min
its
attains
)
x
(
F
where
x
find
)
a
(
x
dt
t
t
)
x
(
F
)
(
)
(
"
H
and
)
(
'
H
dt
t
t
cos
)
x
(
H
)
(
)
(
"
G
and
)
(
'
G
dt
t
)
x
(
G
)
(
x x x x x
3 2 2 0 2 0 2 2 24
7
3
3
0
0
3
2
2
2
1
3
1
• Let D is region that bounded below by the x-axis,
on the sides by the lines x = a and x = b , and
above by a curve y = f(x), where f(x) is continuous
on [a,b] and f(x) ≥ 0 for all x in (a,b) or D = { (x,y) |
a ≤ x ≤ b, 0 ≤ y ≤ f(x) }
• Then the area of D is
Area of Region (1)
b
a
dx
)
x
(
f
A
• Let D is region that bounded below by the x-axis,
on the sides by the lines x = a and x = b , and
above by a curve y = f(x), where f(x) is continuous
on [a,b] and f(x) ≤ 0 for all x in (a,b) or D = { (x,y) |
a ≤ x ≤ b, f(x) ≤ y ≤ 0 }
• Then the area of D is
Area of Region (2)
b
a
dx
)
x
(
f
A
• Find the area of region that bounded by the
curve y = sin x, x-axis, and on the sides by the
lines x = 0 and x = 3π/2
• Let D is region that bounded below by the line y
= c , on the sides by the y-axis and a curve x =
g(y), and above by the line y = d, where g(y) is
continuous on [c,d] and g(y) ≥ 0 for all y in (c,d) or
D = { (x,y) | 0 ≤ x ≤ g(y), c ≤ y ≤ d }
• Then the area of D is
Area of Region (3)
d
c
dy
)
y
(
g
A
• Let D is region that bounded below by the line y
= c , on the sides by the y-axis and a curve x =
g(y), and above by the line y = d, where g(y) is
continuous on [c,d] and g(y) ≤ 0 for all y in (c,d) or
D = { (x,y) | g(y) ≤ x ≤ 0, c ≤ y ≤ d }
• Then the area of D is
Area of Region (4)
d
c
dy
)
y
(
g
A
• Find the area of region that bounded by g(y) =
y
3
– 2y
2
– 3y , y-axis and on the sides by the
lines y = -1 and y = 4.
Example # 2
- 1/3 3 4
• Let D is region that bounded below by a curve y =
g(x), on the sides by the lines x = a and x = b , and
above by a curve y = f(x), where g(x) and f(x) are
continuous on [a,b] or D = { (x,y) | a ≤ x ≤ b, g(x) ≤
y ≤ f(x) }
• Then the area of D is
Area between two curves (1)
b
a
dx
)
x
(
g
)
x
(
f
A
• Let D is region that bounded below by the line y
= c , on the sides by a curve x = g(y) and a curve x
= f(y), and above by the line y = d, where g(y) and
f(y) are continuous on [c,d] and f(y) ≥ g(y) for all y
in (c,d) or D = { (x,y) | g(y) ≤ x ≤ f(y), c ≤ y ≤ d }
• Then the area of D is
Area between two curves (2)
d
c
dy
)
y
(
g
)
y
(
f
A
1. Find the area of the region enclosed by the
curves y = x
2
and y = 4x by integrating
a) With respect to x
b) With respect to y
2. Sketch the region enclosed by the curves and
find its area by any method
a) y = x
2+ 4 and x + y = 6
b) y = x
3, y = - x and y = 8
Sketch the region and find its area by any methods
1. y = x
3
– 4x, y = 0, x = 0, x = 2
2. x = y
2
– 4y, x = 0, y = 0, y = 4
3. x
2
= y, x = y – 2
4. y
2
= - x, y = x – 6, y = - 1, y = 4
5. y = x
3
– 2x
2
, y = 2x
2
– 3x, x = 0, x = 3
Problems
Menghitung volume benda putar
Metoda Cakram
(
x
,
y
)
|
a
x
b
,
0
y
f
(
x
)
D
a. Daerah diputar terhadap sumbu x
a b
f(x)
D
Benda putar
a b f(x)
D
x
Untuk menghitung volume benda putar gunakan pendekatan Iris , hampiri, jumlahkan dan ambil limitnya.
Jika irisan berbentuk persegi panjang dengan tinggi f(x) dan alas diputar terhadap sumbu x akan diperoleh suatu cakram lingkaran dengan tebal dan jari-jari f(x).
x
x
x
x
f
V
2(
)
b adx
x
f
V
2(
)
sehinggax
f(x)Contoh: Tentukan volume benda putar yang terjadi jika daerah D yang dibatasi oleh , sumbu x, dan garis x=2 diputar terhadap sumbu x
2
x
y
2 x y 2 x 2x
Jika irisan diputar terhadap sumbu x akan diperoleh cakram dengan jari-jari
dan tebal 2
x
x
Sehinggax
x
x
x
V
2 2 4)
(
Volume benda putar
2 0 2 0 5 45
32
|
5
x
dx
x
V
2 x
(
x
,
y
)
|
c
y
d
,
0
x
g
(
y
)
D
b. Daerah
diputar terhadap sumbu y
c d
x=g(y) D
Daerah D Benda putar
c d
Untuk menghitung volume benda putar gunakan pendekatan Iris , hampiri, jumlahkan dan ambil limitnya.
c d x=g(y) D y
Jika irisan berbentuk persegi panjang dengan tinggi g(y) dan alas diputar terhadap sumbu y akan diperoleh suatu cakram lingkaran dengan tebal dan Jari-jari g(y). y
y
y ) ( y g sehinggay
y
g
V
2(
)
d cdy
y
g
V
2(
)
Contoh : Tentukan volume benda putar yang terjadi jika daerah yang dibatasi oleh garis y = 4, dan sumbu y diputar terhadap sumbu y
2 x y 2 x y 4 y
Jika irisan dengan tinggi dan tebal diputar terhadap sumbu y akan diperoleh cakram dengan jari-jari dan tebal
y y y y y y y Sehingga
y
y
y
y
V
2
)
(
Volume benda putar
4 0 4 0 28
|
2
ydy
y
V
y x 7.2.2 Metoda Cincin
(
x
,
y
)
|
a
x
b
,
g
(
x
)
y
h
(
x
)
D
a. Daerah
diputar terhadap sumbu x
h(x) g(x) a b D Daerah D Benda putar
h(x)
g(x)
a x b D
Untuk menghitung volume benda putar gunakan pendekatan Iris , hampiri, jumlahkan dan ambil limitnya.
Jika irisan berbentuk persegi panjang
dengan tinggi h(x)-g(x) dan alas diputar terhadap sumbu x akan diperoleh suatu
cincin dengan tebal dan jari –jari luar h(x) dan jari-jari dalam g(x).
x
x
x
sehinggax
x
g
x
h
V
(
2(
)
2(
))
b adx
x
g
x
h
V
(
2(
)
2(
))
h(x) g(x)Contoh: Tentukan volume benda putar yang terjadi jika daerah D yang dibatasi oleh , sumbu x, dan garis x=2 diputar terhadap garis y=-1
2 x y 2 x y x 2 y=-1 1 2 1 x D
Jika irisan diputar terhadap garis y=1 Akan diperoleh suatu cincin dengan Jari-jari dalam 1 dan jari-jari luar 2
1 x Sehingga
x
x
V
((
21
)
21
2)
x
x
x
(
42
21
1
)
x
x
x
(
42
2)
2 18615 3 16 5 32 2 0 3 3 2 5 5 1 2 4)
(
)
|
(
2
x
x
dx
x
x
V
(
x
,
y
)
|
a
x
b
,
0
y
f
(
x
)
D
Metoda Kulit Tabung
Diketahui
f(x)
a b
D
Jika D diputar terhadap sumbu y diperoleh benda putar
Daerah D Benda putar
Untuk menghitung volume benda putar gunakan pendekatan Iris , hampiri, jumlahkan dan ambil limitnya.
f(x) a b D x
x
x Jika irisan berbentuk persegi panjang
dengan tinggi f(x) dan alas serta berjarak x dari sumbu y diputar terhadap sumbu y akan diperoleh suatu kulit tabung dengan tinggi f(x), jari-jari x, dan tebal
x f(x) x
x
sehinggax
x
f
x
V
2
(
)
b adx
x
xf
V
2
(
)
Contoh: Tentukan volume benda putar yang terjadi jika daerah D yang dibatasi oleh , sumbu x, dan garis x=2 diputar terhadap sumbu y
2 x y 2 x y x 2 2 x D x
x
Jika irisan dengan tinggi ,tebal
dan berjarak x dari sumbu y diputar terhadap sumbu y akan diperoleh kulit tabung
dengan tinggi , tebal dan jari jari x 2
x
2x
x
Sehinggax
x
x
x
x
V
2 32
2
Volume benda putar
2 0 2 0 4 38
|
2
2
x
dx
x
V
Catatan :
-Metoda cakram/cincin
Irisan dibuat tegak lurus terhadap sumbu putar
- Metoda kulit tabung
Irisan dibuat sejajar dengan sumbu putar
Jika daerah dan sumbu putarnya sama maka perhitungan dengan menggunakan metoda cakram/cincin dan metoda kulit tabung akan menghasilkan hasil yang sama
Contoh Tentukan benda putar yang terjadi jika daerah D yang dibatasi Oleh parabola ,garis x = 2, dan sumbu x diputar terhadap
a. Garis y = 4 b. Garis x = 3
2 x y
a. Sumbu putar y = 4 (i) Metoda cincin
2 x y 2 D y=4 x
Jika irisan diputar terhadap garis y=4 akan diperoleh cincin dengan
Jari-jari dalam = rd (4 x2) ) 4 ( x2 Jari-jari luar = 4
r
l
4
Sehinggax
x
V
((
4
)
2(
4
2)
2)
x
x
x
(
8
2 4)
Volume benda putar
2 22415 5 32 3 64 2 0 5 5 1 3 3 8 4 2)
(
|
)
(
)
8
(
x
x
dx
x
x
V
(ii) Metoda kulit tabung 2 x y 2 D y=4 y y
Jika irisan diputar terhadap garis y=4 akan diperoleh kulit tabung dengan
Jari-jari = r = y 4 y 4 y 2 Tinggi = h = 2 y Tebal =
y
Sehinggay
y
y
V
2
(
4
)(
2
)
y
y
y
y
y
2
(
8
4
2
)
Volume benda putar
4 0 ) 2 4 8 ( 2 y y y y dy V
4 0 2 / 5 5 2 2 2 / 3 3 8)
|
8
(
2
y
y
y
y
22415
b. Sumbu putar x=3 (i) Metoda cincin
2 x y 2 D y
x=3 Jika irisan diputar terhadap garis x=3 diperoleh cincin dengan
Jari-jari dalam = 1 1 d r Jari-jari luar = 3 y 3 y y rl 3 Sehingga
y
y
V
((
3
)
2(
1
)
2)
y
y
y
(
8
6
)
Volume benda putar
dy
y
y
V
4 0)
6
8
(
(
8
y
4
y
3/2
8
|
04)
8
(ii) Metoda kulit tabung 2 x y 2 D x x=3 x
Jika irisan diputar terhadap garis x=3 diperoleh kulit tabung dengan
Tinggi = h = 2
x
2 x Jari-jari = r = 3 3-x 3-x Tebal =
x
Sehinggax
x
x
V
2)
3
(
2
x
x
x
2
(
3
2 3)
Volume benda putar